Introduction to Science, the Scientific Method, and Research Studies
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
WHAT IS SCIENCE
“Science is the pursuit
and application of
knowledge and
understanding of the
natural and social world
following a systematic
methodology based on
evidence
CHARACTERISTICS OF SCIENCE
1) Based on empirical knowledge
2) Provides rational/natural explanations
3) Testable
4) Repeatable & reproducible (and reliable)
5) Involves observation and experimentation
6) Generality of principles
EMPIRICAL KNOWLEDGE
Based on evidence
data collection (qualitative or quantitative)
derived from observation or experimentation
TESTABLE
A scientific potential explanation
(HYPOTHESIS) to a question/problem
must be testable* (through observation
and/or experimentation)
→ it must generate specific expectations
(PREDICTIONS)
*may require the development of new
tools or techniques
HYPOTHESIS (H) VS. PREDICTION (P) - EXAMPLE
A good test for checking whether a prediction follows logically
from a hypothesis = ‘if…then’:
If (hypothesis), then (prediction) = DEDUCTIVE SYLLOGISM
For example:
“If competition among trees lowers reproductive output, then
fruit size should be smaller when tree density increases.
REPEATABLE/REPRODUCIBLE
Scientific results are subject to
confirmation by the same
(repeated) or other (reproduced)
investigators
• Confirmation is IMPORTANT!
- findings MORE reliable
- keeps science on track
OBSERVATION & EXPERIMENTATION
Experiment = a controlled setting where
there is an intervention/manipulation of a
natural process to observe the effects of such
intervention/manipulation
- BEST to study cause-effect
GENERALITY OF PRINCIPLES
Generality – the establishment of universal
principles that express how the natural
world works under certain conditions
- Common patterns
→ laws and theories
WHAT IS RESEARCH?
The systematic, planned,
and multiple-step process
that uses discoveries to
advance knowledge
- If purpose is contribution
towards science →
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH
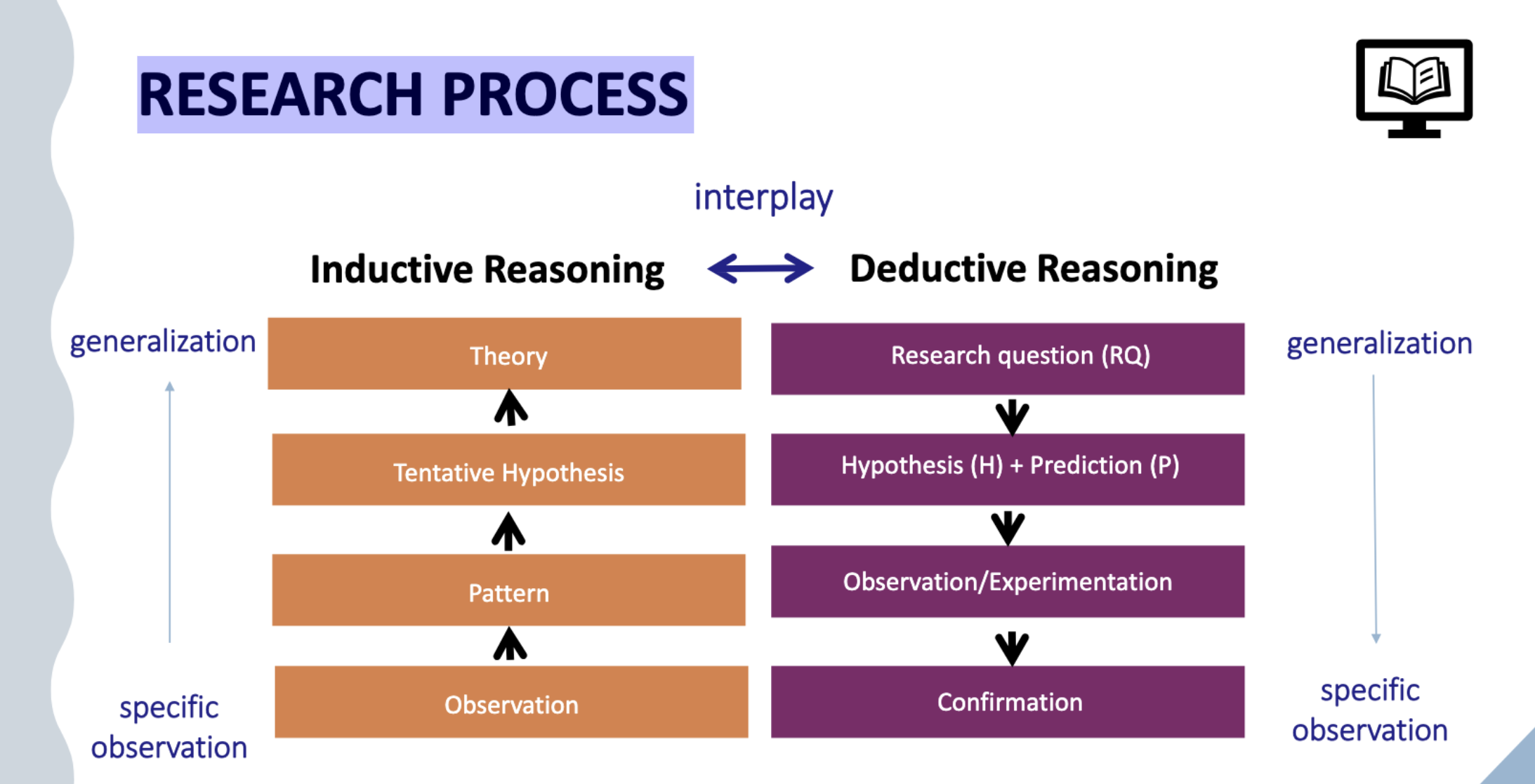
RESEARCH PROCESS
inductive vs deductive
SCIENTIFIC METHOD - STEPS
1. Define/Identify a Problem/Question
2. Formulate a hypothesis (‘potential explanation’)
3. Formulate predictions based on hypothesis
4. Test hypothesis by testing predictions
e.g. make observations or perform experiments and collect
data
5. Analyze data/results
6. Do data support hypothesis?
7. Draw conclusions
8. Communicate results
WHY SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH IS IMPORTANT
To provide solid knowledge by identifying and characterizing new phenomena, materials or organisms
• To solve a scientific problem for which solution is needed
• To develop scientific inventions (e.g. cloning, gene therapy)
• To provide basis for many government policies and industry productivity