Vector Calculus Ch. 1 - Key Terms
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
component
a scalar that describes either the vertical or horizontal direction of a vector
coordinate plane
a plane containing two of the three coordinate axes in the three-dimensional coordinate system, named by the axes it contains: the xy-plane, xz-plane, or the yz-plane
cross product
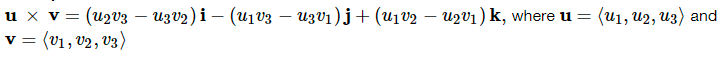
cylinder
a set of lines parallel to a given line passing through a given curve
cylindrical coordinate system
a way to describe a location in space with an ordered triple (r,θ,z), where (r,θ) represents the polar coordinates of the point’s projection in the xy-plane, and z� represents the point’s projection onto the z-axis
determinant
a real number associated with a square matrix
direction angles
the angles formed by a nonzero vector and the coordinate axes
direction cosines
the cosines of the angles formed by a nonzero vector and the coordinate axes
direction vector
a vector parallel to a line that is used to describe the direction, or orientation, of the line in space
dot product
u⋅v=u1v1+u2v2+u3v3
ellipsoid

elliptic cone

elliptic paraboloid

general form of the equation of a plane
an equation in the form ax+by+cz+d=0, where n=⟨a,b,c⟩ is a normal vector of the plane, P=(x0,y0,z0) is a point on the plane, and d=−ax0−by0−cz0
hyperboloid of one sheet

hyperboloid of two sheets

normal vector
a vector perpendicular to a plane
normalization
using scalar multiplication to find a unit vector with a given direction
orthogonal vectors
vectors that form a right angle when placed in standard position
parallelogram method
a method for finding the sum of two vectors; position the vectors so they share the same initial point; the vectors then form two adjacent sides of a parallelogram; the sum of the vectors is the diagonal of that parallelogram