Fundamentals: The shape of molecules
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Why is molecular shape important?
Shape influences chemical and physical properties; e.g. reactivity, melting points
• In biochemistry, pharmacology and medicine - molecules and drugs have to fit precisely into the enzyme or protein
• Shape prediction allows improved drug design and development
Enzymes
Enzymes have binding sites which. Recognise very precise shapes of molecules
Lewis Dot structures vs Molecular Geometry
• Previously used Lewis Dot Structures (LDS) to understand bonding within molecules
• LDS does not give information about the 3-dimensional SHAPE of a molecule
• Information from LDS can be used to develop the GEOMETRY (3-d shape) of a molecule
• It is based on MINIMISING interactions between electron pairs
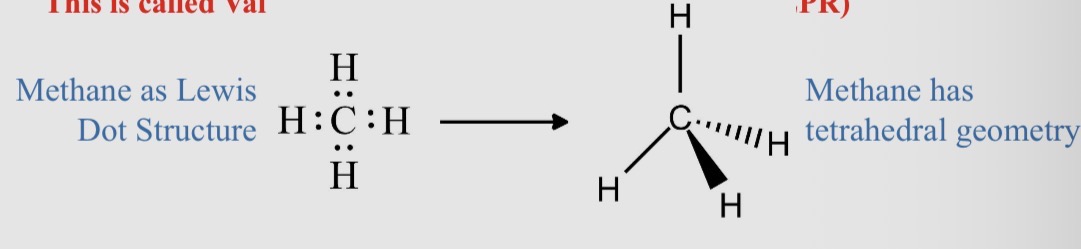
• This is called Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR)
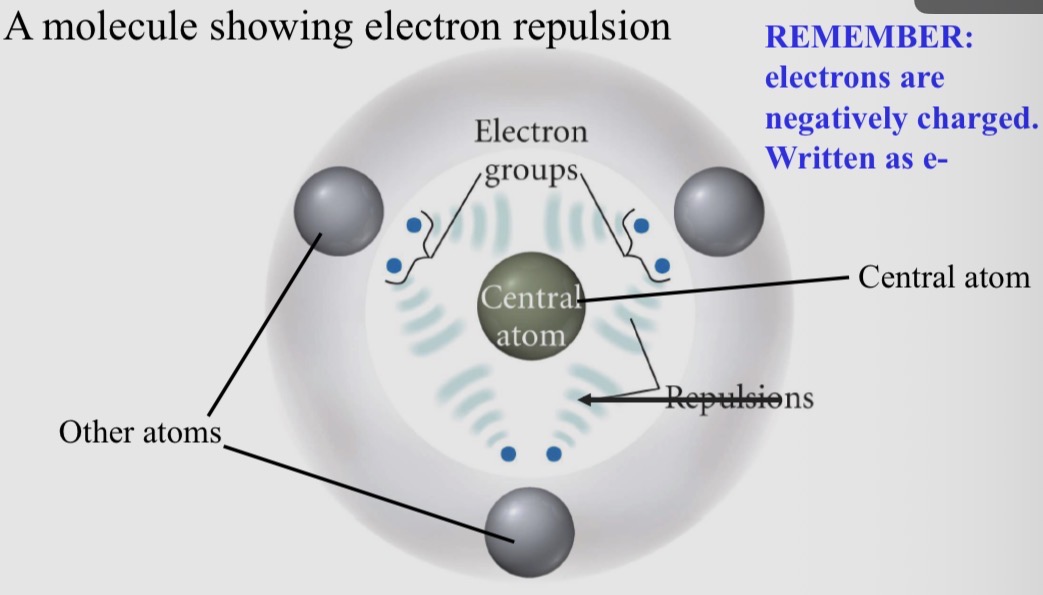
Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory
1) Atoms and molecules want the lowest energy state – most stable
2) Electron groups around the central atom of a molecule
3) Have bonding pairs of electrons and lone pairs of electrons (from LDS)
4) Electrons are negatively charged - Valence shell electrons want to be as far apart as possible
5) The constraints of needing to be bonded and trying to be distant allows geometry to be predicted
6) Knowing the geometry allows molecular shapes and bond angles of molecules to be predicted
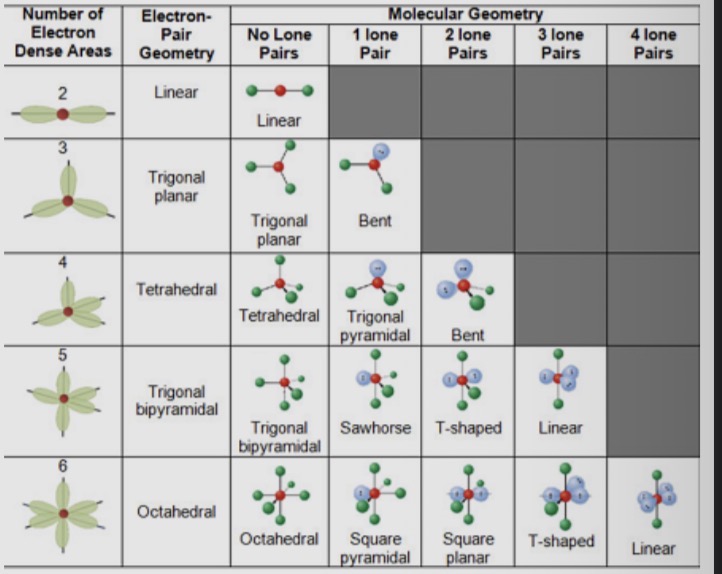
Define co-ordination number, steric number, molecular geometry, electron geometry and bond angle
Co-ordination Number: number of bonded atoms
Steric number (SN): (num of atoms bonded to central atom) + (num of lone pairs on central atom)
Molecular geometry (MG): 3-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule
Electron geometry (EG): 3-D arrangement of bonding electron pairs and lone electron pairs around central atom
Bond angle: the angle between the bonds
How to find the shape of a molecule?
•Draw the Lewis Structure
•Count the No. of electron groups and identify them as bond pairs or as lone pairs
•Decide the electron-pair geometry e.g. linear, trigonal-
planar, tetrahedral etc
•Put in positions of other atomic nuclei around the central atom
•Determine the molecular geometry.
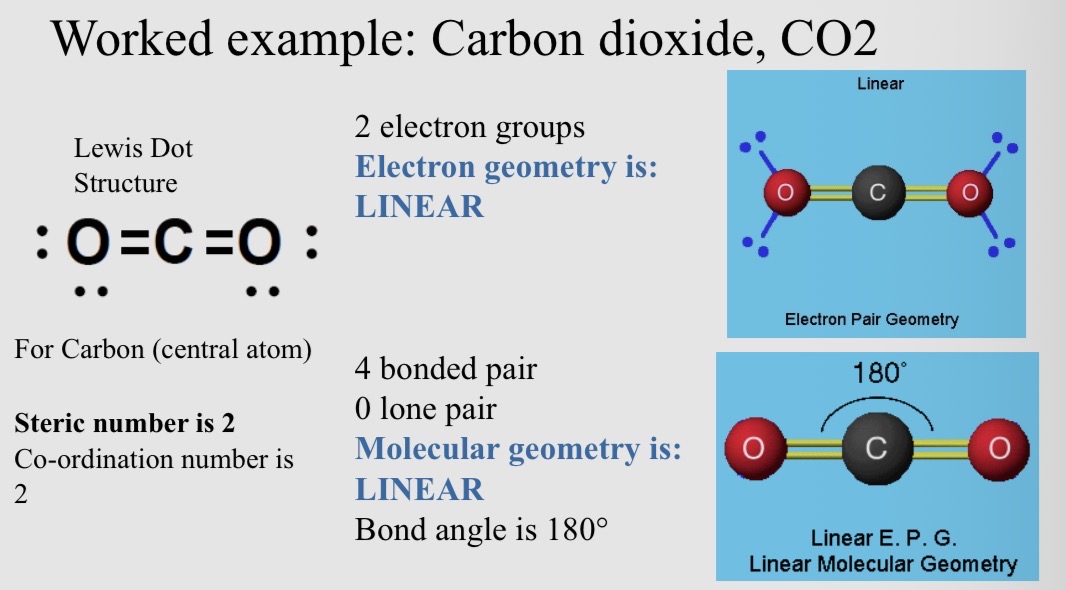
Example of carbon dioxide, CO2
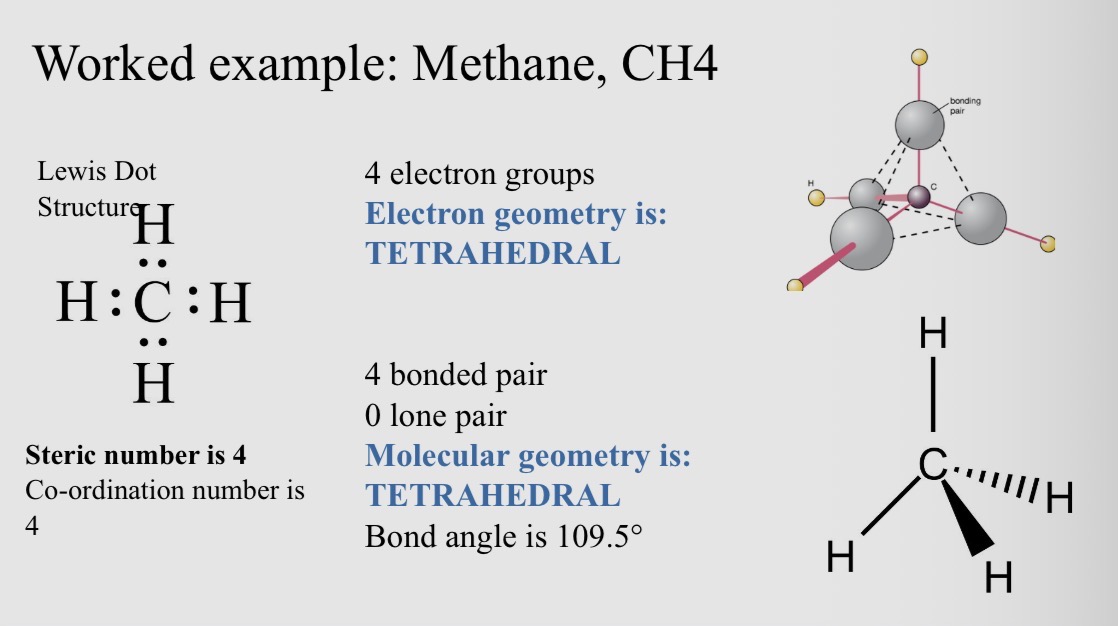
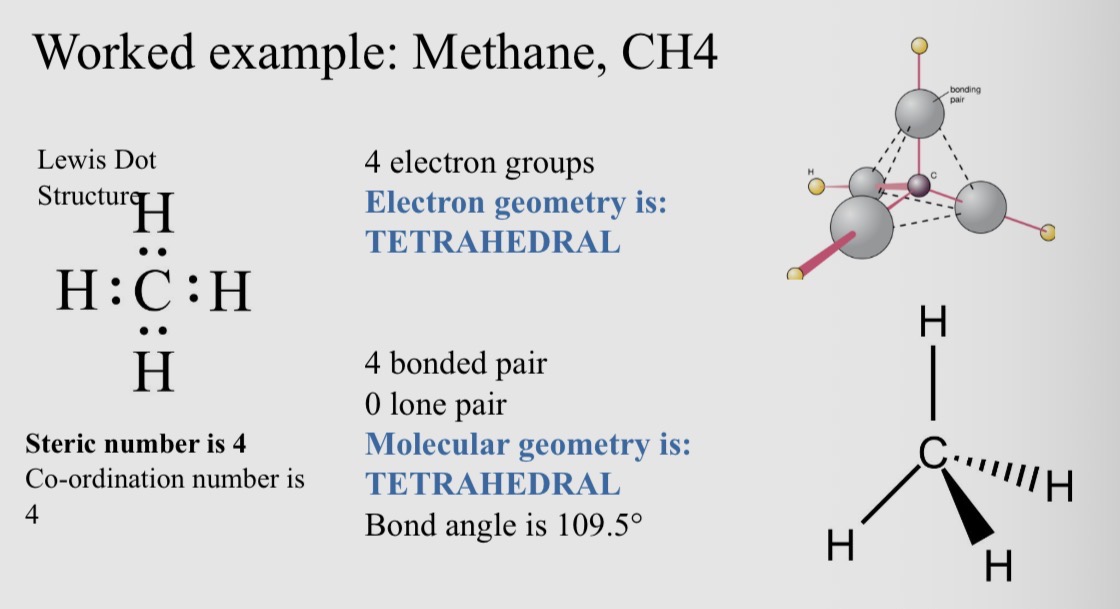
Worked example: Methane, CH4
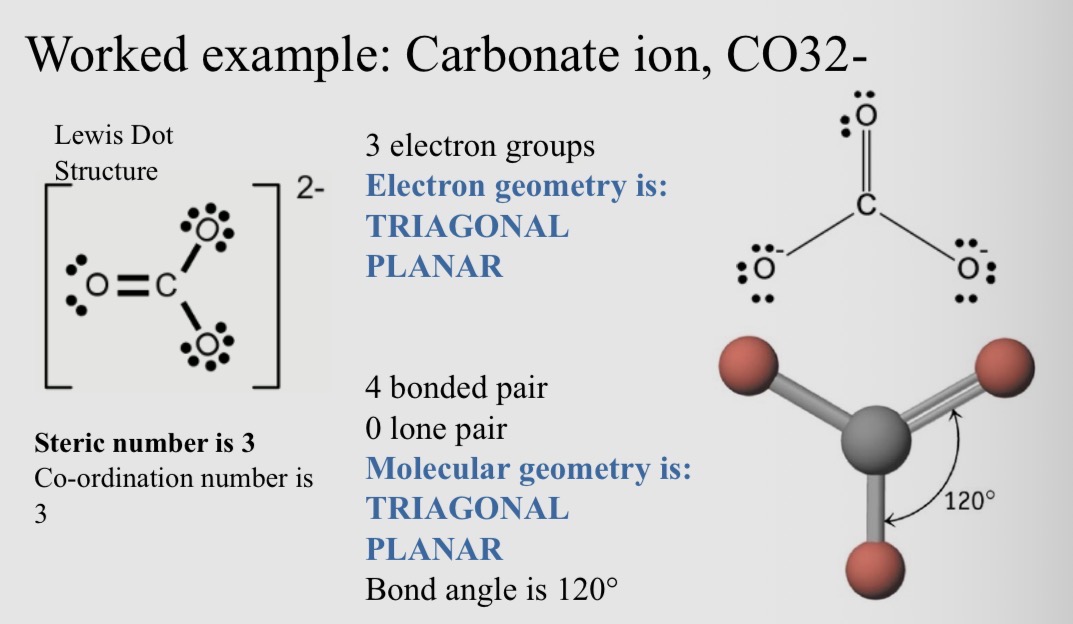
Worked example, Carbonate ion, CO32-
Worked example; Water, H2O

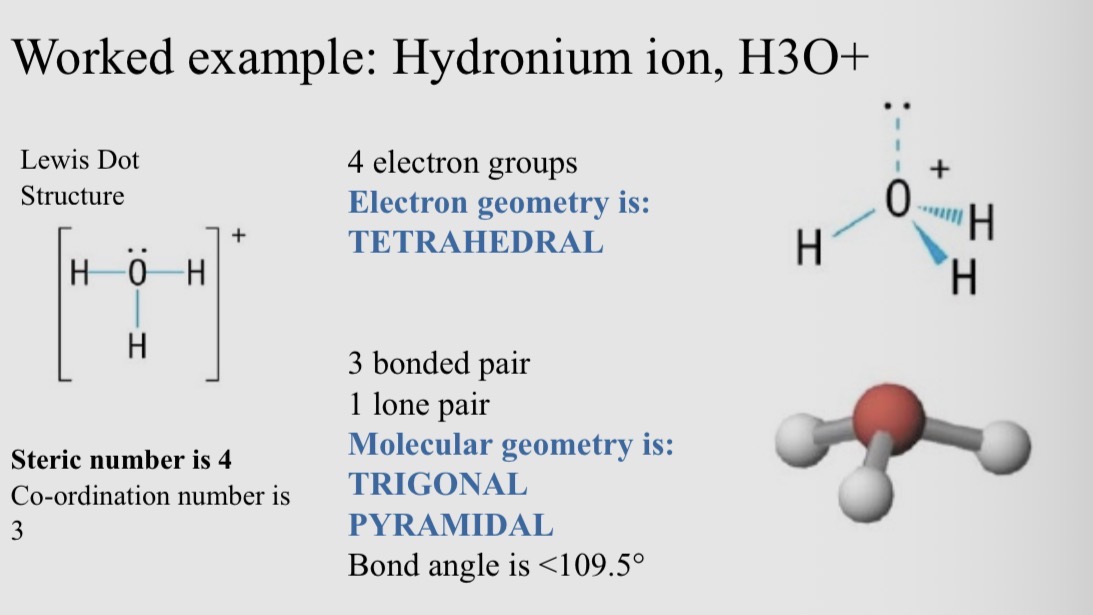
Worked example: Hydronium ion, H3O+
Worked example: Methane, CH4
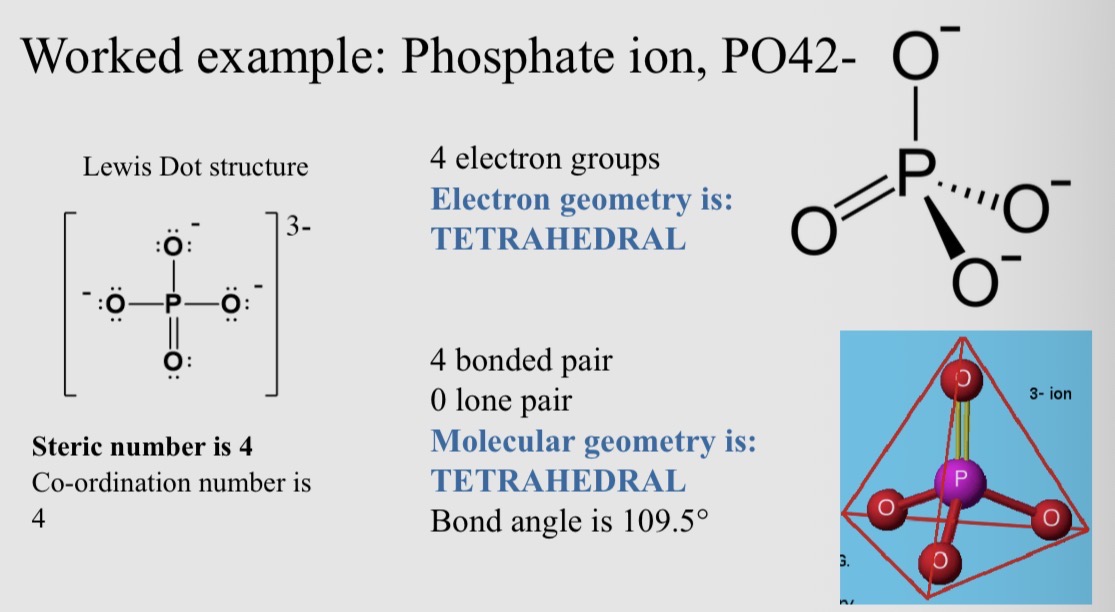
Worked example: Phosphate ion, PO42-