IB chemistry R3.1
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
what is a bronsted lowry acid
a proton donor
what is a bronsted lowrly base
a proton accepter
how do you represent a proton in an aqueous solution
H+ or H3O+
what is a conjugate acid-base pair
a pair of species differing by a single proton
in the conjugate acid and base pair, which one has one more proton
the acid
what is an alkali
a soluble base that can dissolve in water and release a hydroxide ion
what is an amphiprotic species
substances that can act as both an acid and a base
must possess both a lone pair of electrons and hydrogen
what is the pH used to describe
the H+ of a solution.
the pH number is ——- related to the [H+]
inversely
a change in one unit of pH is a —- change in
10 fold
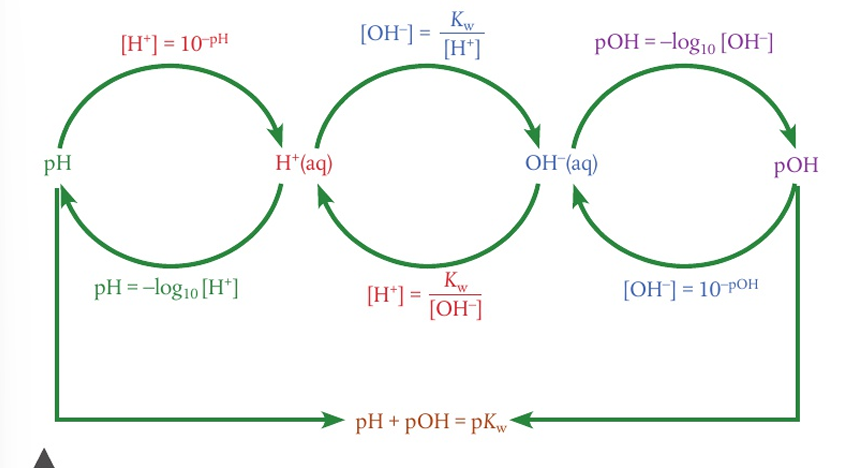
what is Kw
the ionic constant of water [H+][OH-]
in pure water, what is Kw
[H+]=[H+], so H+=Kw²
Kw depends on —— because ——
temperature, equilibrium constant
what is a strong acid
one that fully dissociates
a strong acid has a —- conjugate base, and vice versa
weak
what is a weak acid
one that partially dissociates
which conjugate do dissociation reactions favour
the weaker one
what is a strong base
one that is fully ionized (dissociates fully)
which acids are strong acids
HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4, group 17 exceot HF
which bases are strong
LiOH, NaOH, KOH, all of the bases made from alkali metals
what is the periodic trend of acid strength
as you go down a group, the acid strength increases because there is an increase in the H-halogen bond, which is weaker and needs less energy to break. so, the strength of the hydrogen halide decreases down the group
to distinguish between a strong and a weak acid and base, you need
the same concentration are compared at the same temperature. the one with a higher concentration of ions is stronger
how can you measure pH with electrical conductivity
it depends on the concentration of mobile ions. strong acids and bases will have a higher conductivity than weak acids and bases if they have the same concentration of acid/ base. this is measured using a conductivity meter or probe
how is rate of reaction affected by the strength
the stronger the acid, the faster the rate because it depends on the concentration of H+ ions
acids react with bases in ——— reactions
neutralization
a — base and a —- acid make a salt
parent
acid + base →
salt + water
acid + carbonate →
salt + water + carbon dioxide
what is the point of inflection
when there is a big jump in pH
what is the equivalence point
when the acid and base have exactly neutralized each other, so there is a big jump in pH
what are the characteristics of a strong base strong acid pH curve (5)
initial pH at 1
pH changes gradually until equivalence
very sharp jump at equivalence from pH 3 to 11
after equivalence the curve flattens out at a high value
pH at equivelance is 7
what is pOH
it describes the [OH-] of the solution
when you write pH or pOH, you write —- decimal places
2
look at this
what are Ka, Kb
acid/ base dissociation constants and can describe the strengths of weak acids and bases, fixed at specific temperatures
for a conjugate acid base pair, Kw=
Ka*Kb
what are the key points to know when doing calculations with Ka and Kb (ice)
the given concentration of an acid or base is it’s initial concentration
the pH or pOH refers to the concentration of those ions at equilibrium
the concentration values substituted into the expression for Ka and Kb must be the equilibrium values for all reactants and products
when Kb or Ka is small, the acid/ base is roughly equal to the acid/ base concentration at equilibrium
what are pKa and pKb
logarithmic expressions of Ka and Kb,
and they have an inverse relationship with them.
depend on temperature
for a conjugate acid base pair, pKw=14=
pKa+pKb
the pH of a salt solution depends on
the relative strength of the parent acid and the parent base because it depends on the extent to which they react with water and release OH- and H+ ions
weak acid + strong base
the conjugate base is enough to cause hydrolysis, so it releases OH-. which causes the pH to increase, and the solution becomes basic, with a pH > 7 at 298
salt of strong acid and weak base
the conjugate base of the acid is still able to cause hydrolysis and release H+, causing the concentration of the pH to decrease, so pH< 7 at 298 K
salt of weak acid and weak base
both the conjugates are strong enough to carry out hydrolysis, so it depends on the Ka and Kb values
pH curve of weak acid and strong base 5 characteristics
initial pH is relatively high
pH stays relatively constant till equivalence (buffer region)
jump in pH at equivalence from about pH 7-11
after equivalence, it flattens out at a high pH
pH at equivalence > 7
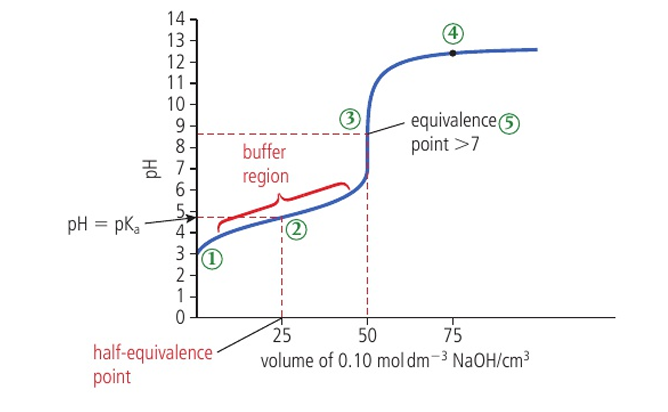
what is the half equivalence point
represents where half of the acid has been neutralized by the base and is converted into salt while the other is not reacted. so, it is known as a buffer
at the half equivalence point (buffer region), acid=
salt at equilibrium
at the half equivalence point, Ka = —- because
[H+], Ka=[H+][salt]/[acid], but [acid]=[salt], so they cancel out
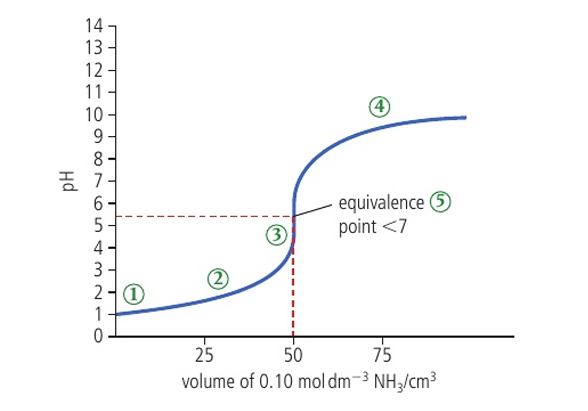
pH curve of strong acid and weak base characteristics (5)
initial pH is 1
pH stays relatively constant through the buffer region to equivalence
jump in pH from 3-7
after equivalence it flattens out at a low pH
pH at equivalence < 7
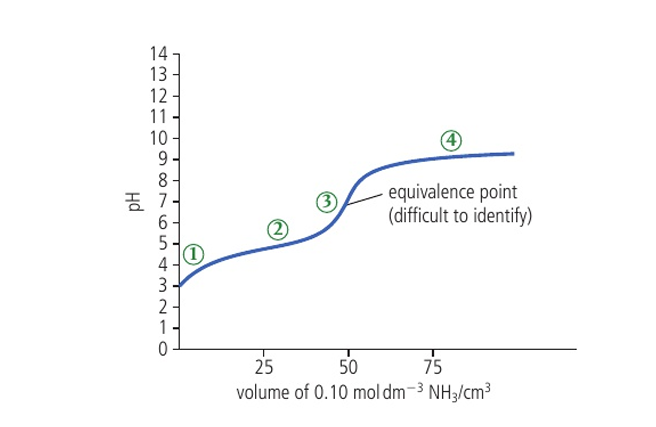
pH curve of a weak acid and a weak base at
initial pH is high
addition of base causes it to rise steadily
change in pH at the equivalence point is not sharp
after the equivalence point, it flattens out at a low pH
does not have a well defined equivalence point
the relationship between pH and the volume added is —-
non-linear
acid base indicators are
weak acids where the components of the conjugate acid base pair have different colors
an appropriate indicator for titration
has an endpoint range that coincides with the pH at the equivalence point
how would Hind respond to adding H+ or decreasing H+
according to Le Chatelier’s principle, adding H+ would shift it lefte in favour of Hind, color A dominates at low pH
decreasing H+ would shift it right in favor of ind-, color B at high pH
what is the endpoint of an indicator
the point where there is a color change
how can you use the endpoint to find the pH
becasue Hind=ind- because it is in the middle of it’s color change, they cancel out, so Ka=[H+], pKa=pH
what are indicators used for and how
to signal the equivalence point in titrations because they give a visible cue of when pH changes
how do you choose which indicator is best (3)
determine the combination of weak and strong acid and base reacting
deduce the pH of the salt solution
consult data tables to choose an indicator with an endpoint in the range of the equivalence point
what is a buffer solution
it is a solution that resists the change in pH on the addition of small amounts of acid or alkali
how are buffers made in detail (like how the chemistry works for weak acid)
a buffer solution is made by mixing an aqueous solution of a weak acid with a solution of its salt of a strong alkali
there is an equilibrium of the dissociation of the acid, which produces H+
the soluble salt fully dissociates in water, producing a A-
so there will be high concentration of the acid and the anion, which is the conjugate base
how do buffers work for weak acid
if H+ is added, it will combine with the conjugate base, taking it from A- to HA, removing most of the H+
if OH- is added, it will combine with the acid, HA, forming a conjugate base and water, removing OH-
how are buffers made in detail (like how the chemistry works for weak base)
a weak base is added to a solution with its strong conjugate acid
this means it will dissociate and make OH- in water
the salt fully dissociates in the solution
there is high concentrations of the base and the conjugate acid
how do buffers work for weak base
if H+ is added, it will combine with the base
if OH- is added, it will combine with the acid and produce water
what approximations can we make when doing calculations with buffers
the dissociation of the weak acid/ base is so small it is negligible, so [HA[=[HA],
the salt is fully dissociated so [MA]=[A-]
at equilibrium, for buffers, pH=,
pKa+log[salt]/[acid]
at equilibrium, for buffers, pOH=,
pKb+log[salt]/[base]
you can also create a buffer by….
mixing double the concentration of a weak acid/base with it’s strong conjugate
which factors influence buffers
the dilution, which does not affect Ka and Kb, but affects the buffering capacity
temperature, which affects Ka and Kb, so it needs to be constant