Organisms exchange substances with their environment
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Explain the advantage for larger animals of having a specialised system that facilitates oxygen uptake. (2 marks)
Larger organisms have a smaller surface area : volume ratio
Overcomes long diffusion pathway
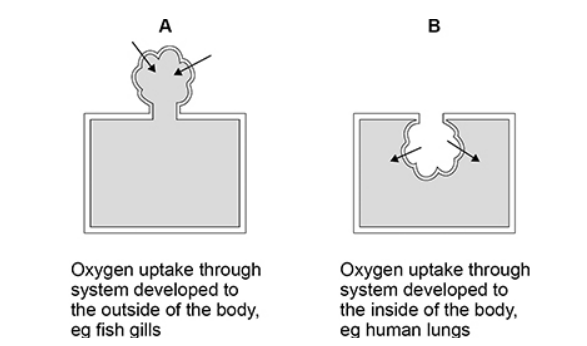
Suggest how the environmental conditions have resulted in adaptations of systems using Model A rather than Model B. (2 marks)
Water has lower oxygen concentration than air
So system on outside gives large surface area in contact with water
Mammals such as a mouse and a horse are able to maintain a constant body temperature. Use your knowledge of surface area to volume ratio to explain the higher metabolic rate of a mouse compared to a horse. (4 marks)
The mouse is smaller so larger surface area to volume ratio
More heat loss
Faster rate of respiration releases heat
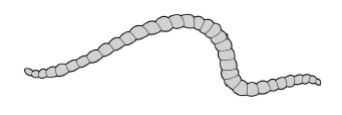
Tubifex worms are small, thin animals that live in water. They have no specialised gas exchange or circulatory system.
The figure shows a tubifex worm.
Using the information provided, explain how two features of the body of the tubifex worm allow efficient gas exchange. (2 marks)
Thin so short diffusion pathway
Small so large surface area to volume ratio
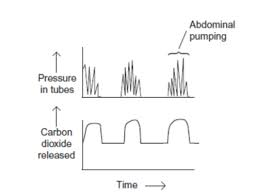
Abdominal pumping takes place during vigorous activity in insects. This causes regular squeezing of tubes of the gas exchange system, A scientist investigated the effect of abdominal pumping on the pressure in the tubes and the volume of carbon dioxide released by the insect. Her results are shown.
Describe and explain these results. (3 marks)
Abdominal pumping in tubes is linked to carbon dioxide release
Abdominal pumping raises the pressure in the body
Carbon dioxide is pushed out of the body
The ends of the tracheoles connect directly with the insect’s muscle tissue. When flying, water is absorbed into muscle tissue. Removal of water from the tracheoles increases the rate of diffusion of oxygen between the tracheoles and muscle tissue. Suggest one reason why. (1 mark)
Water is denser than air so when it is removed oxygen can diffuse faster through air than water
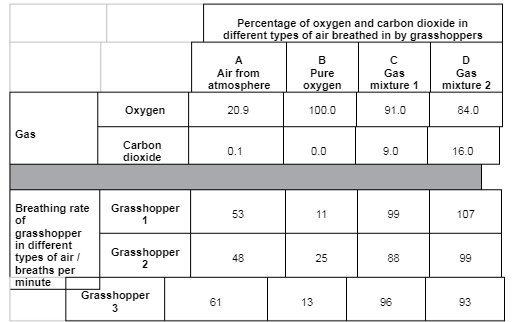
A scientist used grasshoppers to investigate the effect of composition of air on breathing rate in insects. He changed the composition of air they breathed in by varying the concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The scientist collected 20 mature grasshoppers from a meadow. He placed the grasshoppers in a small chamber where he could adjust and control the composition of air surrounding them. The small chamber restricted the movement of the grasshoppers. His results for three of the grasshoppers are shown in the table below in the form in which he presented them.
Use all the data to describe the effect of concentration of carbon dioxide on the breathing rate of grasshoppers
Breathing rate increases when carbon dioxide more than 0.1%
Breathing rate of grasshoppers increase as concentration of carbon dioxide increases
Breathing rate of grasshoppers actually lowest when there is no CO2
The estimate does not provide a reliable value for the mean breathing rate of all insect species in the meadow. Other than being an estimate, suggest and explain three reasons why this value would not be reliable. (3 marks)
Only 3 grasshoppers used, small sample size
Grasshoppers not the only species
Movement not restricted, rate of respiration increases
Explain how the counter current mechanism in fish gills ensures the maximum amount of the oxygen passes into the blood flowing through the gills. (3 marks)
Water and blood flow in opposite directions
Blood always passing water with a higher oxygen concentration
Diffusion gradient maintained throughout length of gill
Describe the processes involved in the absorption and transport of digested lipid molecules from the ileum into lymph vessels. (5 marks)
Micelles contain bile salts and fatty acids
making them more soluble in water
Bring fatty acids to the cells lining the epithelium
Fatty acids are absorbed by diffusion
Triglycerides reformed in cells
Vesicles move to cell membrane
Explain the advantages of lipid droplet and micelle formation. (3 marks)
Droplets increase surface areas for lipase
So faster digestion of lipids
Micelles carry fatty acids and glycerol through membrane to intestinal epithelial cell
Name structure Q in the diagram above and suggest how it is involved in the absorption of lipids.
Golgi apparatus
Modifies / processes triglycerides
Combines triglycerides with proteins
Packaged for exocytosis OR Forms vesicles
Cells lining the ileum of mammals absorb the monosaccharide glucose by co-transport with sodium ions. Explain how.
Sodium ions actively transported from ileum cell to blood
Maintains / forms diffusion gradient for sodium to enter cells from gut and with it, glucose
Glucose enters by facilitated diffusion with sodium ions
Describe the role of enzymes in the digestion of proteins in a mammal. (4 marks)
Hydrolysis of peptide bonds
Endopeptidase produces shorter polypeptides
Exopeptidase produces dipeptides
Dipeptidase produces single amino acids
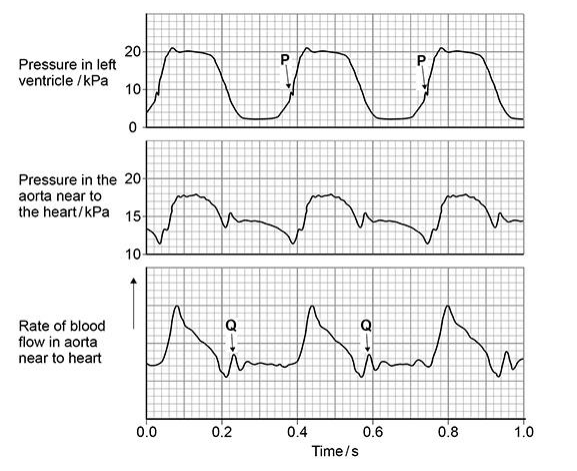
At Q on the diagram above there is a small increase in pressure and in rate of blood flow in the aorta. Explain how this happens and its importance. (2 marks)
Elastic recoil of the aorta tissue
Smooths blood flow
Suggest two ways the student could improve the quality of his scientific drawing of the blood vessels in this dissection. (2 marks)
Only use single lines/ do not use sketching lines
Add labels
Add magnification/scale bar
Draw all parts to same scale/relative size
Do not use shading/hatching
Tissue fluid is formed from blood at the arteriole end of a capillary bed. Explain how water from tissue fluid is returned to the circulatory system. (4 marks)
Plasma proteins remain
Creates water potential gradient OR Reduces water potential (of blood)
Water moves (to blood) by osmosis
Returns (to blood) by lymphatic system
Binding of one molecule of oxygen to haemoglobin makes it easier for a second oxygen molecule to bind. Explain why. (2 marks)
Binding of first oxygen changes tertiary structure of haemoglobin
Creates another binding site
Explain how blood in a vein in the leg is returned to the heart. (6 marks)
Muscles contract and press on vein wall squeezing blood along vein
Valves prevent backflow of blood
Systole pumps blood through arteries into veins
Recoil of heart muscle during diastole
Draws blood from veins into atria
Wide lumen ensure little friction
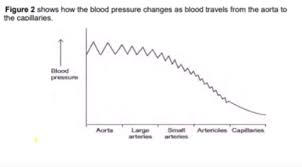
The rise and fall in blood pressure in the aorta is greater than in the small arteries. Suggest why. (3 marks)
Pressure is higher as it is linked directly to the heart
It has more elastic tissue
so greater stretch and recoil
The mass flow hypothesis is used to explain the movement of substances through phloem. Use your understanding of the mass flow hypothesis to explain how pressure is generated inside this phloem tube. (3 marks)
Sucrose actively transported into phloem
Lowering water potential
Water moves into phloem by osmosis from xylem)
Phloem pressure is reduced during the hottest part of the day. Use information in the graph above along with your understanding of transpiration and mass flow to explain why. (3 marks)
High rate of transpiration/evaporation
Water lost through stomata
Less water movement from xylem to phloem
Describe the cohesion-tension theory of water transport in the xylem. (5 marks)
Water lost from leaf because of transpiration / evaporation of water
Lowers water potential of mesophyll leaf cells
Water pulled up xylem creating tension
Water molecules cohere ‘stick’ together by hydrogen bonds;
forming continuous water column
Adhesion of water molecules to walls of xylem
Describe the mass flow hypothesis for the mechanism of translocation in plants. (4 marks)
In source sugars actively transported into phloem
By companion cells
Lowers water potential of sieve cell / tube and water enters by osmosis
Increase in pressure causes mass movement (towards sink / root)
Sugars used / converted in root for respiration for storage.