A12 - Pediatric Cardiology 2025
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
22 days
Primitive heart tube is formed during which embryological age?
25 days
Septation of the ventricles happens during what embryological age?
30 days
Septation of the atria happens during what embryological age?
3 months
AV valve and semilunar valve formation is completed at what embryological age?
Increase in SVR
Closure of the ductus venosus
Important cardiac events following cord clamping
Functional closure of PFO
After the first breath, increase in LA pressure results in?
PDA
Increased arterial O2 saturation in the newborn period results in closure of?
10-15 hours after birth
Functional closure of PDA happens when?
2-3 weeks of age
Anatomic closure of PDA happens when?
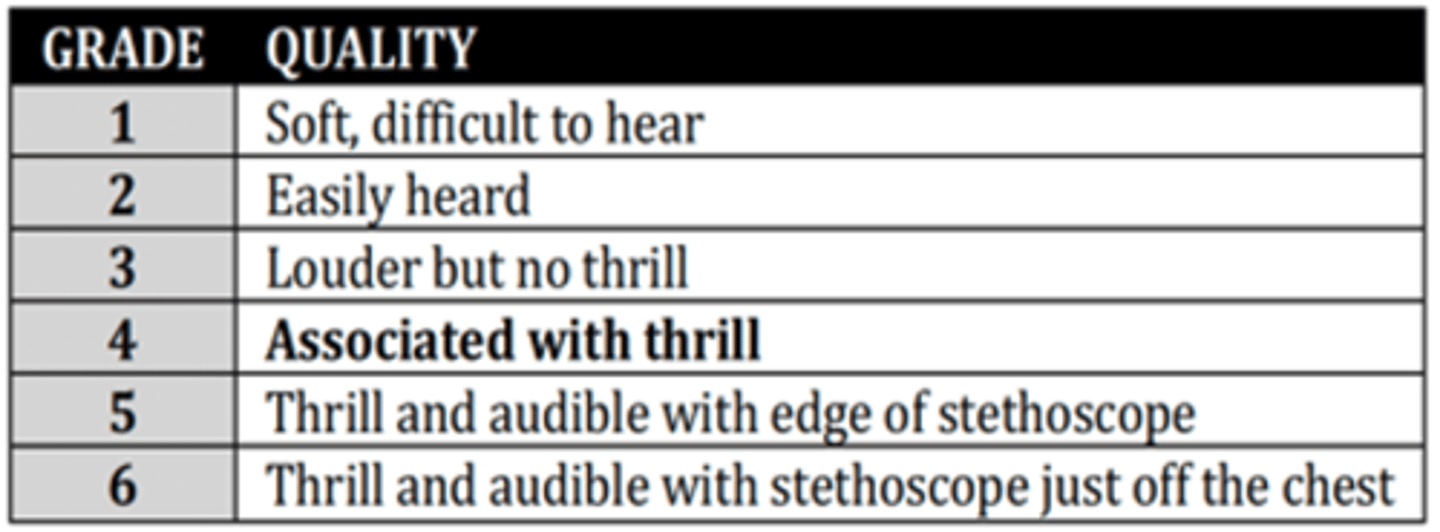
Grade 4
Murmur grade associated with Thrill
Systolic regurgitant murmur
Murmur that results from flow of blood from a chamber that is at a higher pressure throughout systole than the receiving chamber and usually occur while the semilunar valves are still closed. Associated with only VSD, MR, & TR
AS, PS
Associated disease with ejection murmur
TR, VSD
Associated condition with pansystolic murmur at the tricuspid area
TS, ASD
Associated condition with mid-to-late diastolic murmur at the tricuspid area
MR
Associated condition with pansystolic murmur at the apex
MS
Associated condition with mid-to-late diastolic murmur at the apex
Eisenmenger syndrome
Untreated VSD resulting in RVH and pulmonary hypertension → bidirectional shunting and cyanosis
RBBB
Cause of widely split S2 in ASD
PDA
Child with continuous "machinery-like" murmur at the 2nd left infraclavicular area, bounding pulses, wide pulse pressure, and left-sided enlargement. Impression?
VSD
Child with systolic regurgitant murmur at LLSB, loud and single S2, and L-sided enlargement. Impression?
ASD
Child with Systolic ejection murmur at 2nd LICS, widely split S2, and R-sided enlargement.
Marfan syndrome
Connective tissue disease associated with mitral valve prolapse and progressive enlargement of the aorta
Hunter syndrome (MPS II)
Genetic disorder wherein GAGs build up in body tissues, resulting in thickening of cardiac valves and improper valve closure
TOF
Cyanosis manifesting after the first year of life, usually in an infant or a toddler. (+) Systolic ejection murmur. Impression?
TGA
Cyanosis manifesting within few hours at birth or within few days of life. Impression?
• Tricuspid atresia
• Tetralogy of Fallot
• Single ventricle with PS
Cyanotic heart diseases with decreased pulmonary blood flow
• Boot-shaped heart
• Decreased pulmonary vascular markings
Chest x-ray finding in TOF
POSH
• Position (Knee-chest)
• Oxygen
• Sedation with Ketamine (increased SVR also)
• Hydration (IV boluses)
Other meds:
• NaHCO3- (1 mEq/kg) slow IV
• Morphine sulfate
• Phenylephrine
• Propranolol (may stabilize vascular reactivity of the systemic arteries)
Management of hypoxic spell
Blalock-Taussig Shunt (BTS)
Palliative systemic-to-pulmonary artery shunt performed to augment pulmonary artery blood flow in Tetralogy of Fallot
Modified BTS
Gore-Tex conduit anastomosed side to side from the subclavian artery to the homolateral branch of the pulmonary artery
Tricuspid atresia
Glenn shunt, Fontan procedure
Child with systolic regurgitant murmur at LLSB. On echo, hypoplastic RV and on ECG, LAD and LVH. Impression and surgical management?
TOF
BTS
Child with systolic ejection
murmur at 2nd LUSB; loud &
single S2, and boot-shaped heart on x-ray. Impression and surgical management?
• Transposition of the great vessels
• Total anomalous pulmonary venous return
• Truncus arteriosus
Cyanotic heart diseases with increased pulmonary blood flow
TGA
Most common cause of cyanotic CHD in the newborn and characterized by single & loud S2. On x-ray, with egg-shaped cardiac silhouette. Impression?
• Rashkind
• Senning
• Mustard
• Jatene
Surgical management of TGA?
Truncus arteriosis
Patient with single S2 and systolic ejection murmur at LSB. There is minimal cyanosis in neonates, but older children present with heart failure. Impression?
Rastelli procedure
Surgical treatment of Truncus arteriosus?
TAPVR
Patients with systolic murmur at LSB in mild cases and notable snowman sign on chest x-ray.
Coarctation of aorta
Turner syndrome
Child with weak femoral pulses and are delayed bilaterally. Noted with systolic murmur at 3rd-4th LICS with radiation to (L) infrascapular area. The disease described and associated syndrome?
Rib notching
Chest x-ray findings in older children with coarctation of aorta?
Primary re-anastomosis
or a patch aortoplasty
Surgical management for coarctation or aorta
Pulmonic stenosis
Child with systolic ejection
murmur at LUSB with
radiation to the upper
back. Impression?
MVP
Child with complaints of
exercise intolerance, easy fatigability. On PE, noted late systolic murmur with an opening click. Impression?
Norwood
Surgical procedure for hypoplastic L heart syndrome
Ebstein anomaly
Associated congenital heart defect in an infant born to a mother exposure to Lithium
Complete heart block
Associated congenital heart condition in an infant born to a mother with lupus
PDA
Most common CHD in a patient with congenital rubella?
• F – Fever
• R – Risk Factor (Previous RH or RHD)
• A – Arthralgia
• P – Prolonged PR interval on ECG
• E – Elevated acute phase reactants: ESR / CRP / leukocytosis
Minor criteria in RF?
Subclinical carditis
In RF, this refers to when classic auscultatory findings of valvar dysfunction either are not present or are not recognized by the clinician but 2Decho reveals mitral or aortic valvulitis.
Erythema marginatum
Nonpruritic serpiginous or annular erythematous evanescent rashes most prominent on the trunk and inner proximal portions of the extremities in RF.
CRP >3.0 mg/dL
• ESR >60 mm/hr (low risk popn)
• ESR >30 mm/hr (mod and high risk popn)
Elevated acute phase reactants in RF?
ASO titer
Well-standardized test to prove evidence of antecedent Group A strep infection
• > 2 major manifestations, or;
• > 1 major + 2 minor manifestations
• With evidence of previous streptococcal infection
Diagnosis of initial RF requires how many criteria fulfilled?
Past Hx of RF PLUS:
1. 2 major, or;
2. 1 major plus 2 minor, or;
3. 3 minor manifestations
Diagnosis of recurrent RF requires how many criteria fulfilled?
Oral Penicillin or Erythromycin x 10 days
OR
Benzathine Penicillin IM SD
To eradicate GAS in RF, what is the treatment regimen?
ASA 100 mkDay 4-6 doses x 3-5 days then 75 mkDay q6 hrs x 4 weeks
OR
Prednisone 2 mkDay q6 hrs x 2-3 wks & taper
To control inflammation in RF, what is the treatment regimen?
Pen VK 250 mg BID PO
OR
Benzathine PCN 0.6-1.2 MU IM q21 days
Recommended secondary prophylaxis for RF
5 years or until 21 years of
age, whichever is longer
How long do you give prophylaxis for patients with RF WITHOUT carditis?
10 years or until 21 years of
age, whichever is longer
How long do you give prophylaxis for patients with RF WITH carditis but NO valvular heart disease?
10 years or until 40 years of
age, whichever is longer
How long do you give prophylaxis for patients with RF WITH carditis and WITH valvular heart disease?
• Staphylococcus aureus
• viridans Streptococcus,
• Enterococcus
Most common organisms causing IE?
2 MAJOR criteria, or
1 MAJOR criterion and 3 MINOR criteria, or
5 MINOR criteria
Clinical criteria requirement for IE
Possible IE
A patient fulfilling 1 major criterion and 1 minor criterion, or 3 minor criteria of IE is tagged as?
-2 separate sites 12 hours apart
-3 or more 1 hour apart
Blood culture to be counted as 1 major criterion in IE must be taken?
Osler nodes
Tender, pea-sized intradermal nodules in the pads of fingers & toes that falls under immunologic criterion in IE?
Janeway lesions
Painless small erythematous hemorrhagic lesions on the palms and soles in IE?
CONSIDER for dental procedures requiring manipulation of the gingiva or periapical region, or perforation of oral mucosa
High-risk procedure for which IE prophylaxis is needed
Viridans Streptococci
IE in patients with underlying heart disease and underwent dental procedure. Organism involved?
Group D Streptococcus
IE in patients with GUT or lower bowel manipulation. Organism involved?
Staphylococcus/Pseudomonas
IE in patients with Hx of IV drug abuse. Organism involved?
CONS
IE in patients with CVP, prosthetic valves. Organism involved?
4-6 weeks
Recommended antibiotic duration of treatment for IE?
Vancomycin
DOC for IE patients without a prosthetic valve but with high risk for Staphylococcus aureus, viridans Streptococcus, enterococcus.
Aq Pen G
OR
Ceftriaxone (+/- Gentamicin)
DOC for native valve endocarditis due to viridans Streptococcus and Streptococcus bovis
Oxacillin
DOC for Endocarditis due to Staph without prosthetic materials