Amniotes and Angiosperms
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
for bio 005b
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Homeostasis
regulating internal, chemical,
and physical conditions within
living organism
Osmregulation
control solute
concentrations and
balance the loss and
gain of water
Osmlarity and how to describe osmolarity of soolutins relative to one another
hyperosmotic — plants like this
isoosmatic — animals like this
hypoosmotic
Why H2O is essential to plants and animals
water has special properties: cohesion (sticking tgether) and adhesion (sticking to walls)
plants and animals use the inherent features of water to move water throughout the body.
Difference between osmoregulators and osmoconformers (and environments they belong in)
Osmoregulators actively control their own internal water and solute concentrations — live in freshwater/terrestrial areas
osmoconformers match their internal concentration to their surroundings (isosomatic with surroundings) —live in marine areas
What is water potential?
water potential works like if water potential is higher outside it means that water flows in (water potential refers to the amnt of water concentration and water mves high to low)
equation:water potential = solute potential + pressure potential.
ex: H2O has water potential of 0
if water potential outside is positive then water is going to go inside
water movement in plants & associated terms
utilizes basic functions of H2O (adhesion and Cohesion)
^water in xylem is known as xylem sap
plants need turgidity
^turgid pressure is while plant cells have water in the vacuole (organelle which stores water food and waste) creating pressure on the walls of the plant — this is important for water flow!
xylem —> flow from root hairs and up the roots to leaves, this happens because the water potential is more negative at the top creating a water potential gradient making the water go up because water potential moves from high to low
transpiration (negative pressure) —> water is pulled up from the roots and outside the plant cells
cavitation - air bubbles which is bad for plants because it creates air bubbles in the plants water transport system blocking flow of water from the roots to the leaves
3 strategies to dispose of nitrogenous waste in animals (and relationship to environment and why strategies are necessary)
Strateegiies are necessary becaues nitrogenous waste (byproducts from processing nutrients) produces ammonia in aquous solutions the body which is poisonous to organisms and also negatively impacts water balance
environment effects the strategy because of the water that needs to be saved
most aquatic animals including most bony fishes— excrete straight ammonia because they live in water which can easily be diluted by surrounding water
mammals, most amphibians,sharks, and some bony fishes—use urea and is low toxicity but needs a lot of water (costly)
birds, reptiles, insects, land snails — since they need to be light its uric acid and is a complete paste and is very costly
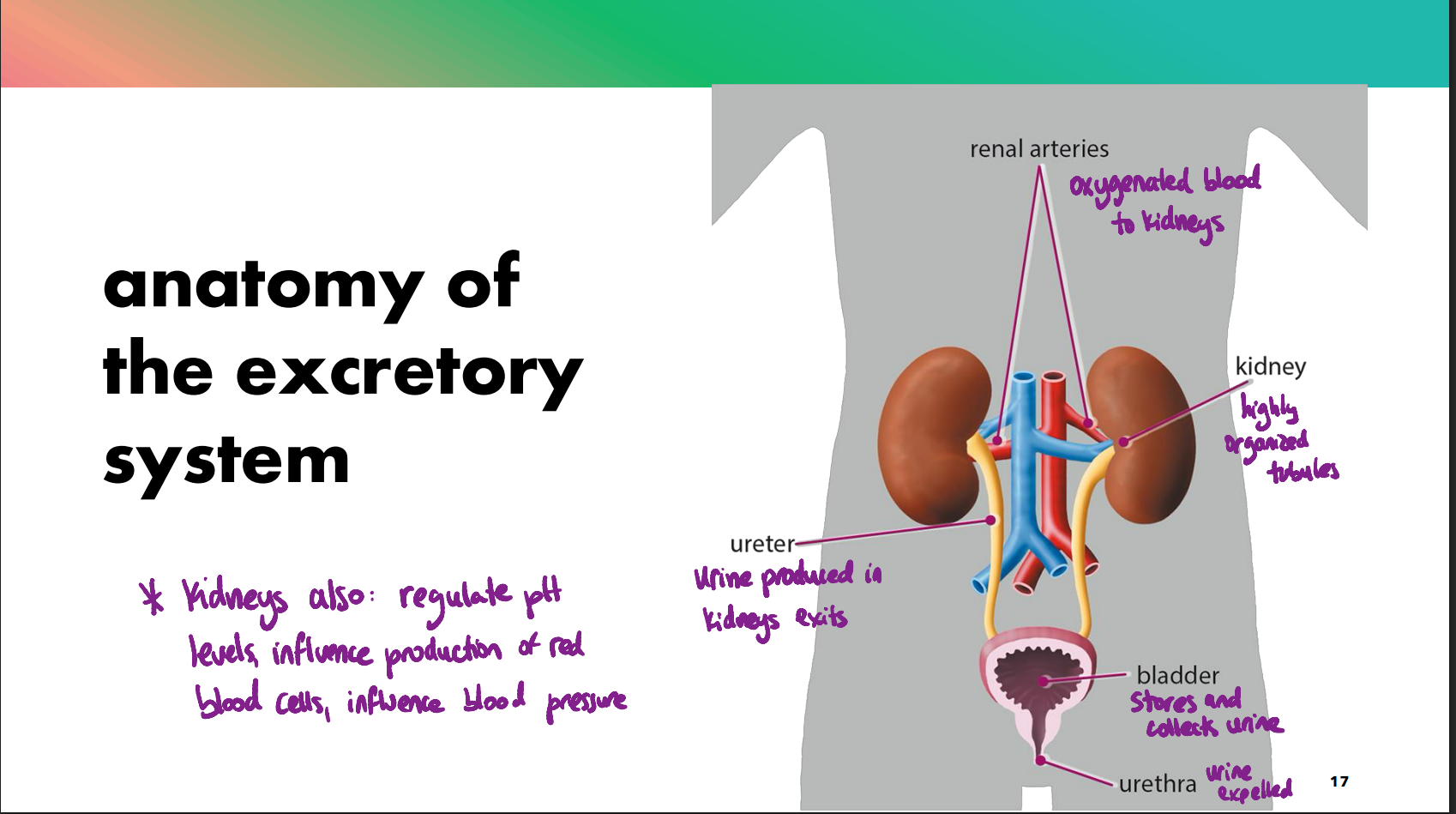
organs and functions of excretory system
parts of a kidney
renal arrtery— supplies blood
renal vein— drains blood
renal pelvis— collects urine
Nephrone types — do filtering (contain capillaries)
*kidneys filter 1600L of blood per day!
Nephron 3 steps
glomular filtration —H2O & small solutes filtered out of blood to produce filtrate
Tubular reabsorption—reabsorb sugars,amino acids,vitamins, other organic molecules
tubular secretion—adds last bits of wast
excretion happens after!
Nephron organization
bowman’s capsule fluid from bloodstream into lumen of Boman’s capsule
proximal tubule—reabsorption of ions,H2O and nutrients (permeable to H2O aquaporins)
loop of henle(descending limb and then the ascending limb)—creates concentration gradients which help absorb H2O+Salt (think in terms of osmolarity
distal tubule —Regulates K+ and NaCl concentration
collecting duct—processes filtrate into urine
What is nutrition and why is the acquisiition of it important?
nutrition is taking in and using food, to extract several aspects of it small enough to be enough for cellular uptake
Biological molecules and uses in living organisms
Proteins— do a bunch of stuff in thte body lol
lipids —make cellular membranes and store energy
nucleic acids—store information
carbohydrates—provide energy
Differences between and similarities between plant and animal nurient acquisition
animals are heterotrophic so they eat other organisms to
obtain energy for cellular (ATP)
acquire raw materials —building blocks + essential nutrients
Plants are autotrophic
use energy from sunlight and oxygen to make sugar
don’t eat other organisms and construct many nutrients
*still require essential nutrients/elements which they can get from the environment by uptaking the nutrients from root hairs into xylem
plants do digestion similar to animals animals have dedicated organs to do it while plants do it at a cellular level
Phyllotaxy?
how to calculate the the leaf area index which is uhhhh idk
Leaf area index and relation to nutrient acquisition?
uhhhh idk
direction of flow in xylem and phloem & what is carried in each
what is phloem sap and how is it transported
steps in animal food processing
ingestion—act of feeding
propulsion—food pushed to stomach
digestion—mechanical and chemical breakdown
absorption—cells uptake nutrients
elimination (defecation) —-remove undigested materrial
alimentarry canalfood moves in one direction
2 opening
the path of food from mouth to anus and organs of digestive system and know function and vocab
tongue - shapes bolus (food mashed together)
salivary glands - releases saliva
oral cavity - teeth mash
pharynx - leads to 2 passageways
esophagus - peristalsis pushes food to sphincter
liver - production and storage of bile
gallbladder (bile green-yellow fluid digests fats)
stomach - which do chemical and mechanical breakdown
pancreas - enzymes which which break down sugars, fats, and starches
small/large intestine - absorption, processing, and waste
rectum —> anus - dedication
digestion beginning at the mouth 2 steps
a. trachea open
epiglottis up (opens path to trachea on the left)
glottis down and open
esophageal sphincter contracted (prevents air from going into the esophagus
b. esophagus down
epiglottis down
glottis up and closed
esophageal sphincter relaxed ( allows food to go through the esophagus
stomach processes
stores food
processes food into liquid (chyme)
a bunch of stuff work together to produce and secrete gastric juice
inside the stomach the lining is epithelium
chief cells secrete pepsinogen, parietal cells secrete HCl which activates pepsinogen, pepsinogen -> pepsin (activated by acidic environment), pepsin-> digests protein in the stomach
small intestine and large intestine
small intestine has capillaries, and does absorption, digestion, and waste
Why gas exchange is essential for living organisms
the organisms exchange oxygen and CO2 with the environment because they have mitochondria which do cellular respiration
for large organisms simple diffusion isn’t enough and they need to use bulk flow which has partial pressures (high to low)
review
transpiration (plants release water vapor into the atmosphere)
passive transport cools plants, and results in a bulk flow of minerals
guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomata through changes in turgor pressure
transpiration is regulated by the stomata opening and closing which depends on light humidity and temperature
when turgor pressure is high, guard cells(kind of like the gate of stomata) open and the stomata(hole) is out in the open which releases water and vice versa is true
stomata can be different in plants depending on environment
capillaries
blood air
smallest blood vessels diffuse
tradeoffs for plants and animals for gas exchange
minimize water loss and maximize CO2
turgor pressure mechanism explanation
absorption of the K+ in the guard cells makes the stomata open and water potential becomes negative in the guard cells which makes water flow inside of the cells easier??
upper respiratory tract
nasal cavity
pharynx
larynx
trachea
lower respiratory tract
right lung
left lung
bronchus - large airway which leads from trachea to windpipe to lung
bronchiole - plural of bronchus
alveoli - balls
anatomy of the heart
four chambers
right atrium (left) -recieves deoxygenated blood which is low pressure
left atrium (right) - recieves oxygenated blood which is low pressure
right ventricle - pumps deoxygenated blood (high pressure or becomes when it recieves oxygen
left ventricle - pumps oxygenated blood
deoxygenated blood travel
superior vena cava and inferior vena cava (receives from body) —> right atrium —> right ventricle—> pulmonary artery
oxygenated blood travel
pulmonary vein —> left atrium —> left ventricle —> aorta
pericardium - heart lining
right atrium --(tricuspid valve)--> right ventricle--(pulmoonary valve)--> pulmonary artery
left atrium--(mitral valve)--> left ventricle--(aortic valve-->aorta
things that include capillaries and why are capillaries important
kidneys, intestine, liver
mammalian circulation
pulmonary circuit (O2 poor blood to lungs)
right ventricle
pulmonary artery
capillaries of lungs (blood becomes oxygenated)
pulmonary vein
left atrium
systemic circuit
left ventricle
aorta and travels to capillaries of the head & forelimbs capillaries of abdominal organs and hind limbs (blood becomes deoxygenated)
inferior vena cava & superior vena cava
right atrium
systemic circuit
right ventricle
veins vs arteries
walls of arteries have 2 layers of tissue and are thick to accomadate high pressure blood pumped fromo heart
veins bring blood back to heart to lower pressure and require vales to ensure unidirectional flow (gravity would make it go down because veins go upstream since theyre deoxygenated)
hormones, glands, and target cells ? processes they regulate ?
hormones are secreted signalling molecules that circulate throughout the body and stimulate target cells
metaloblism
growth and development
body defense
homeostatic processes
glands are any structure that makes & secretees hormones
target cells are activated by hormones and have a response which do something
two systems of regulation and control
nervous system (can overlap with endocrine because neurons can regulate release of hormones)
fast acting and short lived
neurons —> synapses
endocrine system
slower, broad areas, long-lived (secrete hormones in blood
three classes of hormones and response pathways
types & response pathways
hydrophillic —>receptors on plasma membrane trigger response
directly into blood stream; PM receptor initiates response via signal transduction, the receptor protein is right at the walls of the target cell which results in either cytoplamic response or gene regulation to cytoplasmic response
hydrophobic —> receptors in cytoplasm or nucleus
transport protein carried through blood which combined with the hormone from the secretory cell in blood, the horrmone w/ transport proteini meets receptor in cell triggers cellular response (usually gene expression) and then to cytoplasmic response
classes
polypeptides (hydrophillic)
sterroids (hydrophobic/lipid soluble
amines (both)
five types of signalling
a. endrocrine signalling
diffuse: bloodstream
target: anywhere
b. paracrine signalling
diffuse: locally
target: neighbor
c. autocrine signalling
diffuse: locally
target: self
d. synaptic signalling
diffuse: across synapses
target: specific tissues
e. neuroendocrine signalling
diffuse: bloodstream
target: anywhere
has a neurosecretory cell which releases horrmones
endocrine glands
pituitary gland (in brain)
thyroid gland(in throat)
adrenal gland (2 of them itts proximal to the kidneys (kidney bean)
pancreas ( they are the yellow hockey stick sponge looking thing)
ovary
testis
how do positive and negative feedback function
negative feedback
response reduces initial stimulus
positive feedback
response reinforces initial stimulus
response pathways in adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex
adrenal medulla (neuroendocrine)
physicaal threat/exercise/cold exposurer
stress in hypothalamus results in nerve impulses to spinal cold to neuron and then to the adrenal medulla leads to…
epinephrrine + noepinephrine
higher blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, metabolic late
adrenal cortex (endocrine)
hypothalamus
anterior pituitary releases horrmones
hormones circulate in blood stream
adrenal cortex leads to cortocosteroids
mineralocorticoids
higher blood volume and pressure
glucocorticoids
higher blood glucose
factors that plants must sense and respond to and what the classic five to refer to
plants senses
light
heat
graviity
wounding/infection
wind
internal chemical signalling (hormones)
drought or flooding
time
plants use hormones to coordinate growth, development, and environmental responses
however, plants have no circulatory system
signal transduction pathways alter functions of plants similar to animals
plant growth regulator (classic five)
auxins
cytokinins
gibberellins
abscisic acid
ethylene
phytochrome response pathway
reception of sunlight acts as a signal which is detected by the phytochrome receptor
activates 2 signal transduction pathways
pathway 1
phytochrome produces cGMP which increases the cytosolic level of Ca2+ which activates the specific protein kinase 1
cGMP acts as a second messenger which activates the specific protein kinases 1
pathway 2 (calcium)
activated phytochrome makes calcium channels in the cell membrane open increasing cytosolic calcium
cytosolic calcium results in the specific protein kinase 2 activating
3. response
protein kinases move into the nucleus leading to combining with transcription factors to perform expression
This creates proteins that function in De-etiolation response (leaves expanding, roots elongating, stem elongation slows)
variation in mechanisms of reproduction
sexual (fusion of two gametes)
isogamous (same size)
anisogamous (different sizes)
dioecous —seperate male and female organisms
hermaphroditic —same organisms makes male and female gametes
some other combination! — flowering plants can display all kinds of combinations
asexual (no fusion of gametes)
fission — separate male and female organisms
parthenogenesis — development of embryo from one gamete
budding — new individual buds off parent organism
angiosperms & animals similarities and differences
similarities
both primarily reprooduce via sexual reproduction
primarily possses anisogamous gametes
differences
animials segregate ssexes into seperate organisms (dioecy)
plants are mostly hermaphroditic
^(there are exceptions to the rules above)
two ways that fertilization can occur (and relationship to environment)
Internal fertilization
common across land animals
typically requires complex and compatible reproductive structures
external fertilization
most common in fish and some amphibians
tend to produce more ggametes
conception in humans? fertile window?
ovulationo is the release of a mature oocyte
oocyte when fertilized by sperm results in conception
fertiile window: 4 days before ovulation and ends 24 hours before
hormones & phases in menstrual cycle
follicular phase
stimulate ovarian follicles
OVULATION (transition)
luteal phase
progesterone increases and suppresses follicle stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone
hormones involved
hypothalamus (GnRH)
anterior pituitary
follicle-stimulating hormone
luteinizing hormone
estrogen —> antidepressant effect—>maybe decrease triggers plus
uterine cycle
menses — lining expels if no implantation of the zygote
proliferative —estrogen causes lining to thicken
secretory —progesterone makes lining receptive to blastocyst
how to check home pregnancy
home pregnancy checks the presence of a hormone in urine which is produced by the placenta once the fertilized egg implants in the uterus
anatomy of a plant
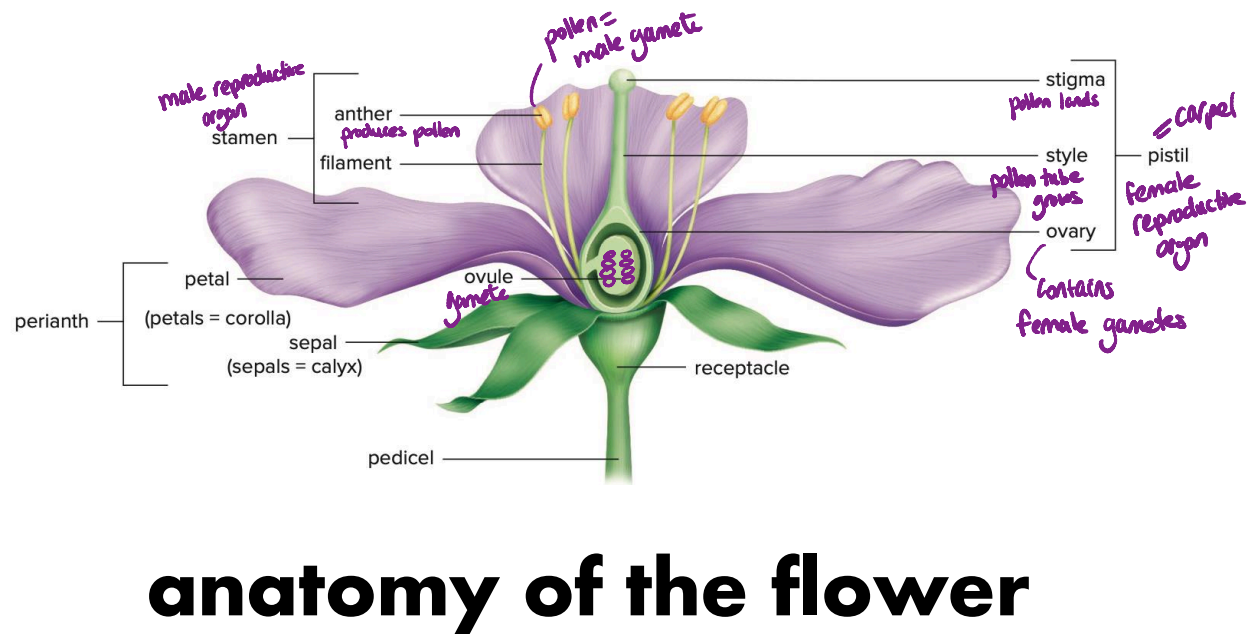
fertilization in flowering plants and adaptations that limit or prevent self fertilizaitono
self-fertilizaiton (autogamy: obligately pollinate themselves)
pollination by wind or water (abiotic)
pollination by insects or animals (biotic)
preventing self fertilization
dioecy (flowers or whole organisms):separation of sexes
herkogamy: anatomical adaptation that prevent anther and stigma from touching
dichogamy: male and female gametes arernt produced at the same time
heterostyly: different flower morphs in a population that can only mate with the opposite morph
self incompatibility: rejecting its own pollen
3 types of fruits and flowers that produce them
simple fruit
pea flower
aggregate fruit
raspberry flowerr
multiple fruit
pineapple inflorescence
accessory fruit
apple flower
differences between monocots and leudicots
monocots v eudicot
seed: 1 cotyledon 2 cotyledon
flower: petal in 3s 4/5 petals
leaf: narrow/parallel net like veins and oval shape