LESSON 3-4: SAMPLING TECHNIQUES (copy)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
SAMPLING
It is a procedure in which some members of a given population are selected as representatives of the entire population.
POPULATION
The larger group from which individuals are selected to participate in a study.
SAMPLE
The representatives selected for a study whose characteristics exemplify the larger group from which they were selected
SAMPLING FRAME
List of all people or units of the population from which the sample is drawn.
SAMPLE SIZE
Refers to the number of people or units selected to be a part of the sample.
POPULATION
N in the Slovins Formula stands for…
SAMPLE SIZE
n in the Slovins Formula stands for…
MARGIN OF ERROR
e in the Slovins Formula stands for…
PROBABILITY SAMPLING
It gives every member of the population equal chance to be selected as part of the study.
SIMPLE RANDOM SAMPLING
It gathers a random sample from the entire population, where each unit has an equal chance of selection. This is the most common way to select a random sample.
SYSTEMATIC RANDOM SAMPLING
It draws a random sample from the target population by selecting units at regular intervals starting from a random point.
STRATIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING
It collects a random sample from within certain strata, or subgroups within the population. All strata of a given population are adequately represented in your sample.
CLUSTER SAMPLING
It is the process of dividing the target population into groups, called clusters. Randomly selected clusters then forms your sample.
MULTISTAGE SAMPLING
It draws a random sample from a population using smaller and smaller groups (units) at each stage.
NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING
The researcher's judgment determines the choice of sample.
CONVENIENCE SAMPLING
Define what type of Non-Probability Sampling is being illustrated.
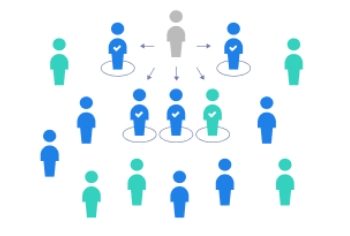
PURPOSIVE SAMPLING
Define what type of Non-Probability Sampling is being illustrated.
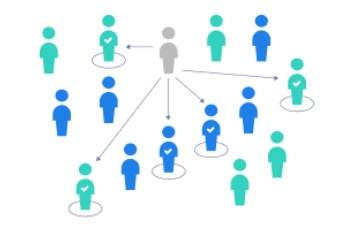
VOLUNTEER SAMPLING
Define what type of Non-Probability Sampling is being illustrated.
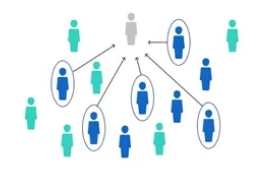
SNOWBALL SAMPLING
Define what type of Non-Probability Sampling is being illustrated.
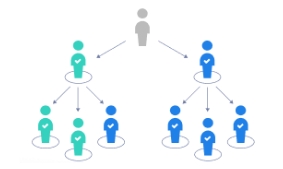
QUOTA SAMPLING
Define what type of Non-Probability Sampling is being illustrated.
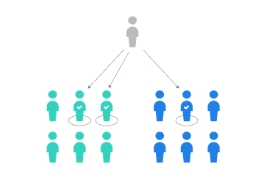
STRATIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING
Identify the sampling procedure used.
The One, a fashion company, has 800 female employees and 200 male employees. You want to ensure that the sample reflects the gender balance of the company, so you sort the population into two groups based on gender. Then you use random sampling on each group, selecting 80 women and 20 men, which gives you a representative sample of 100 people.
SYSTEMATIC RANDOM SAMPLING
Identify the sampling procedure used.
All employees of The One are listed in alphabetical order. From the first 10 numbers, you randomly select a starting point: number 6. From number 6 onwards, every 10th person on the list is selected (6, 16, 26, 36, and so on), and you end up with a sample of 100 people.
CLUSTER SAMPLING
Identify the sampling procedure used.
The One has offices in 10 cities across the country (all with roughly the same number of employees in similar roles). You don’t have the capacity to travel to every office to collect your data, so you use random sampling to select 3 offices and conduct a survey among its employees.