8th Grade Social Studies STAAR Review 2024
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

218 Terms
Reasons for exploration
Religion (God); Wealth (Gold); Fame and International Recognition (Glory)

1607
Jamestown is founded; it is the first permanent English settlement
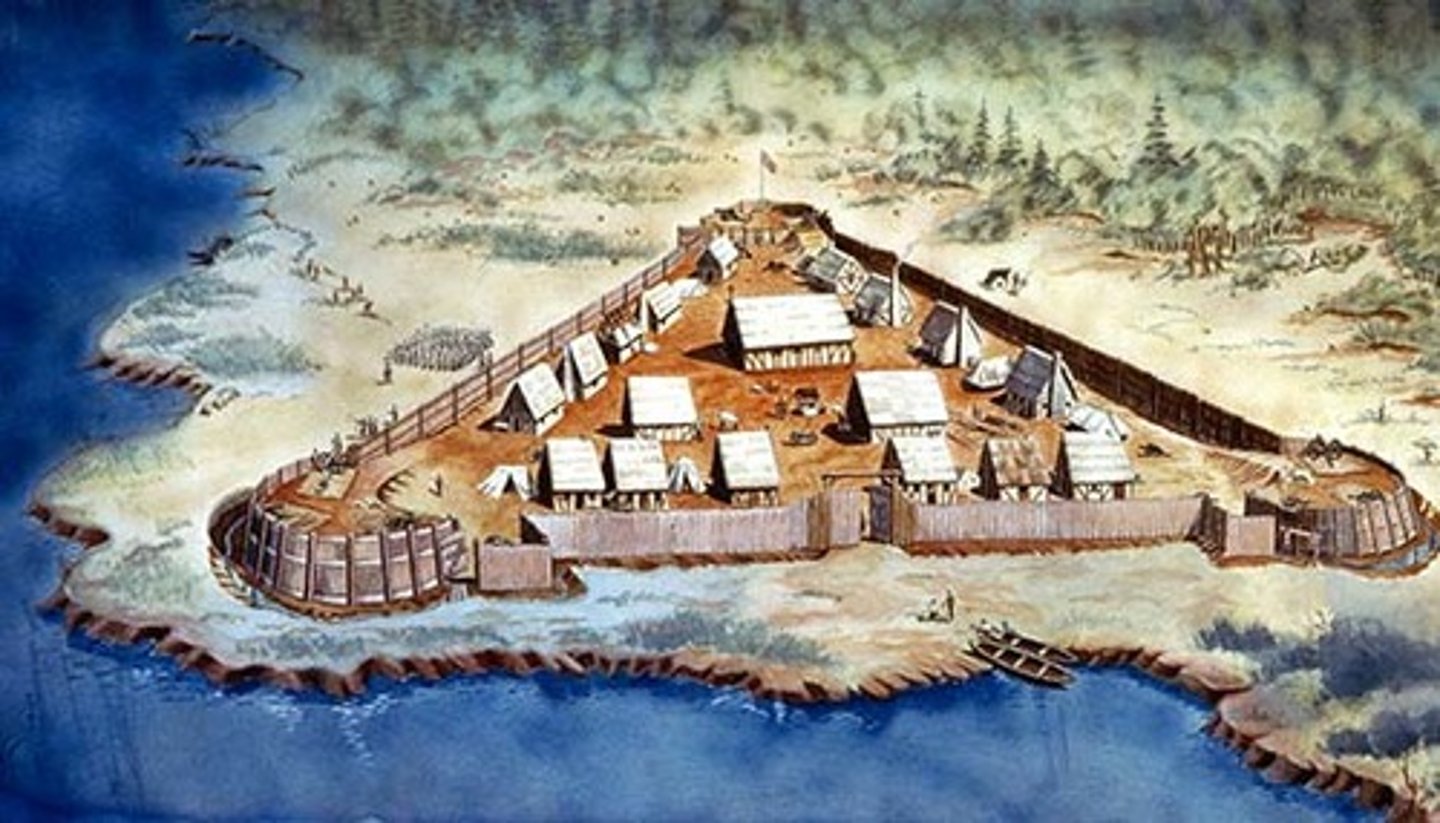
1620
Plymouth was founded; Pilgrims traveled to Plymouth and signed the Mayflower Compact to establish self-government
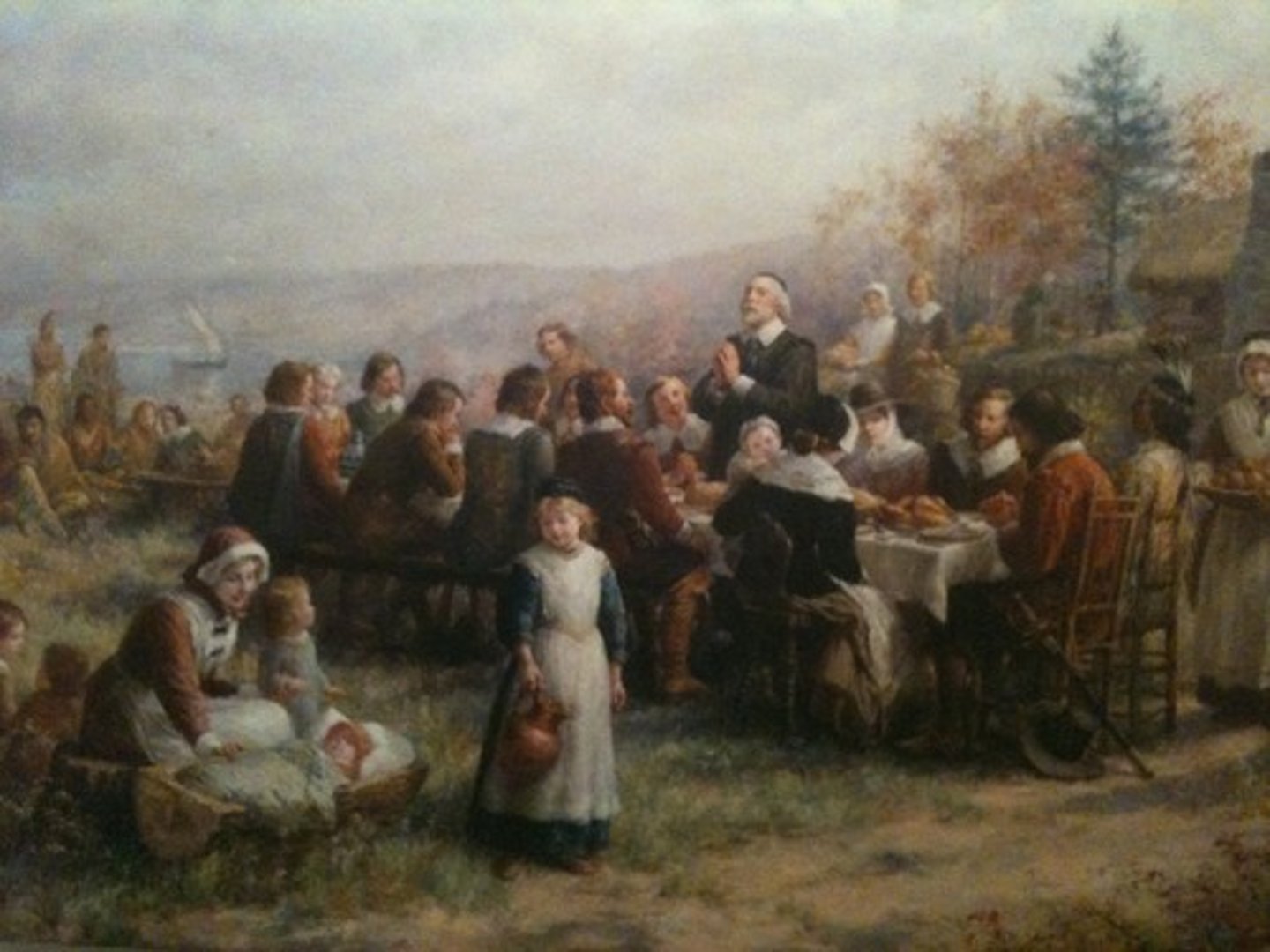
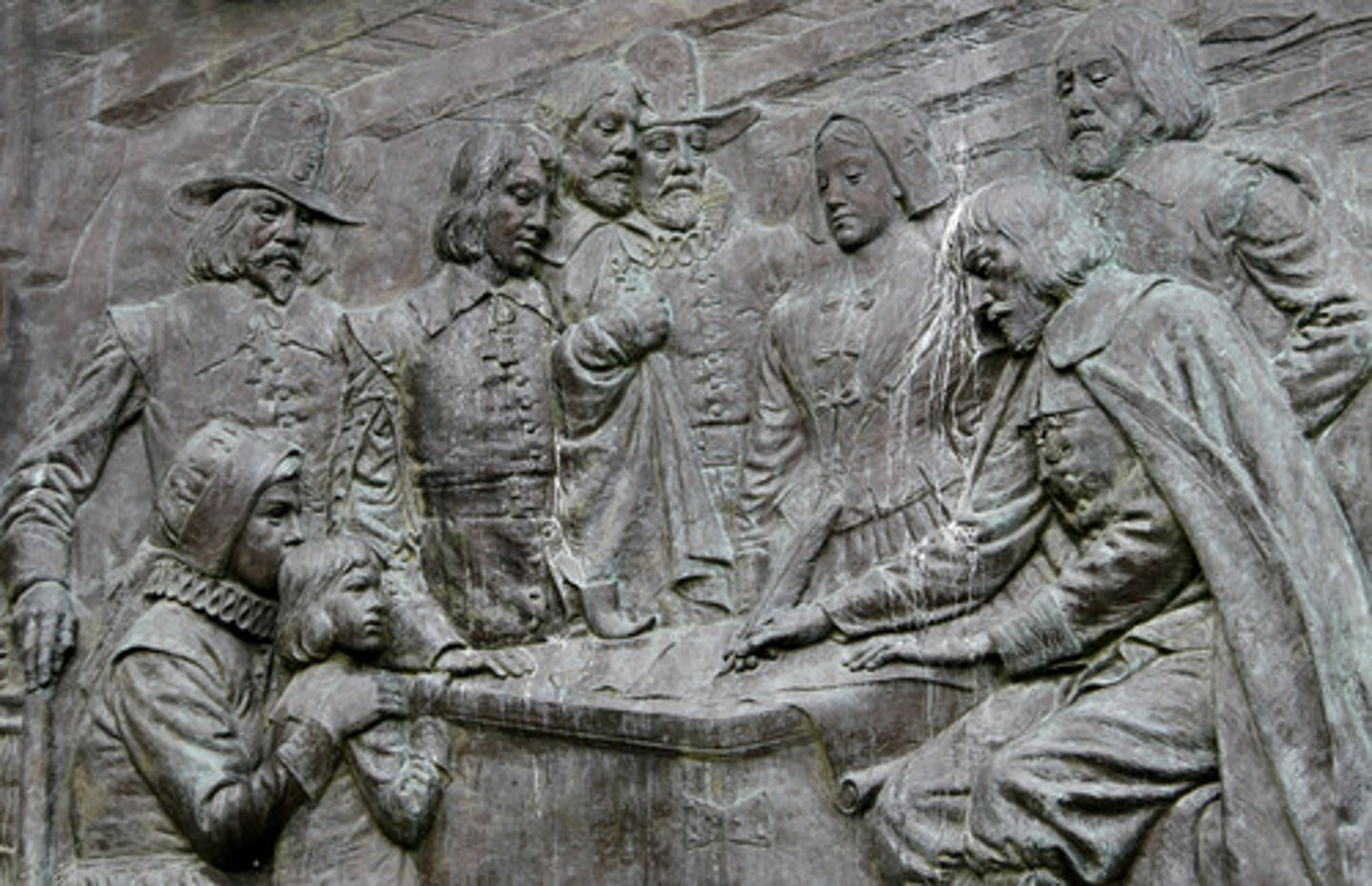
Mayflower Compact
signed by many pilgrims, helped establish the idea of self-government

Virginia House of Burgesses
1st representative assembly in North America

Reasons colonies were established
1) Religious and Political Freedom
2) Economic Opportunity
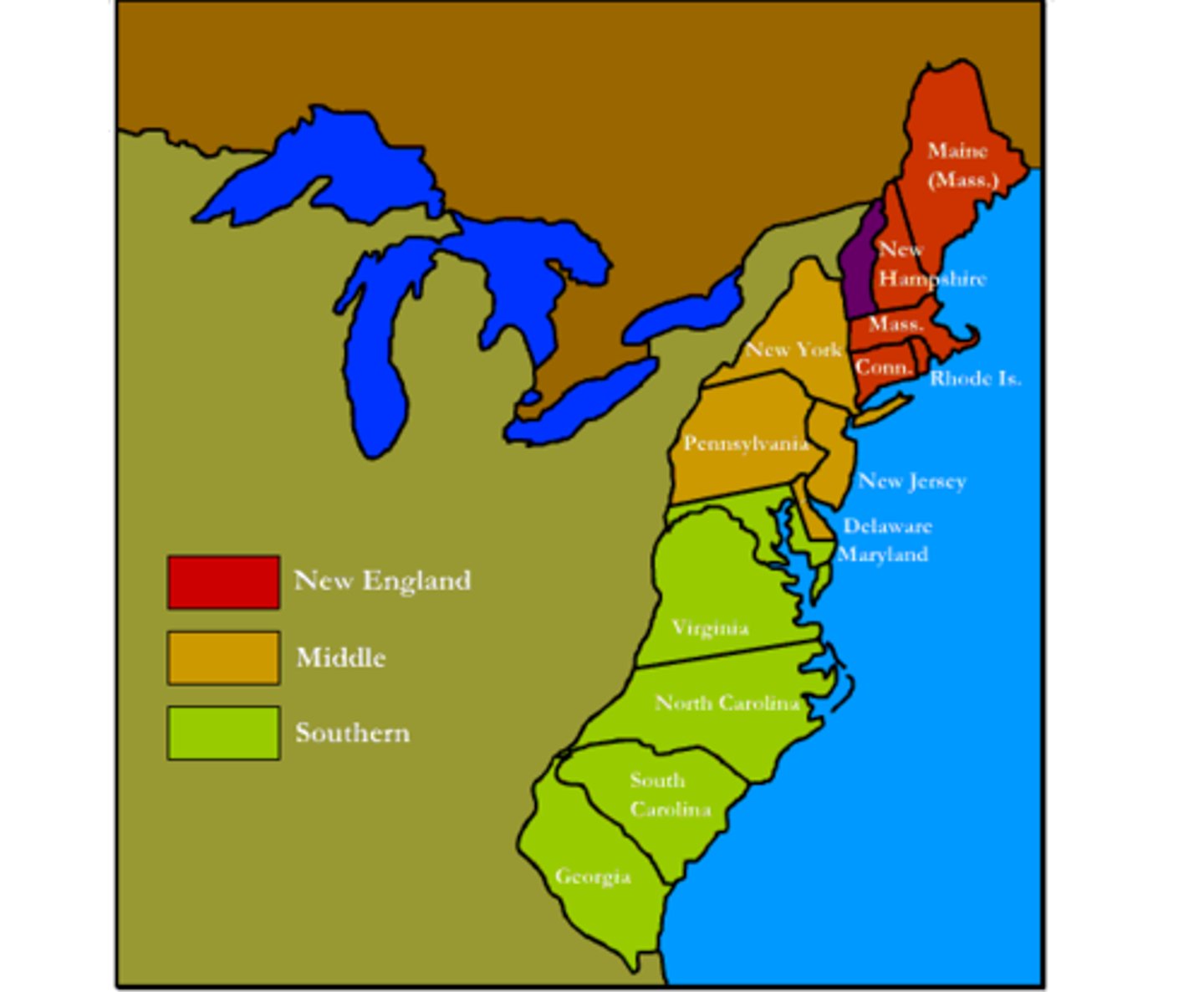
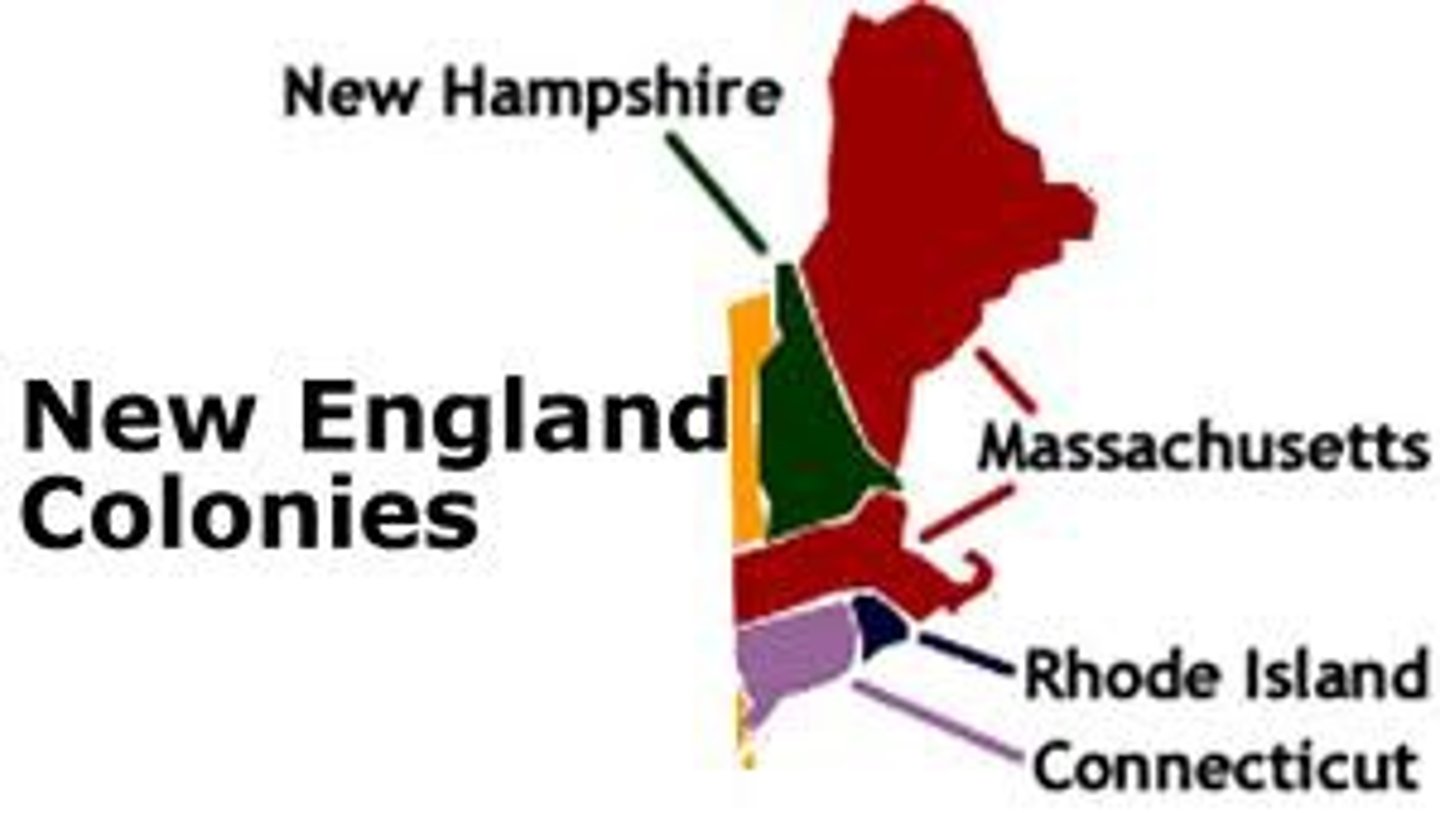
New England Colonies/Northern Colonies
Connecticut, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, and Rhode Island
Settled by Pilgrims in 1620 and Puritans in the 1630s to escape religious persecution in England.
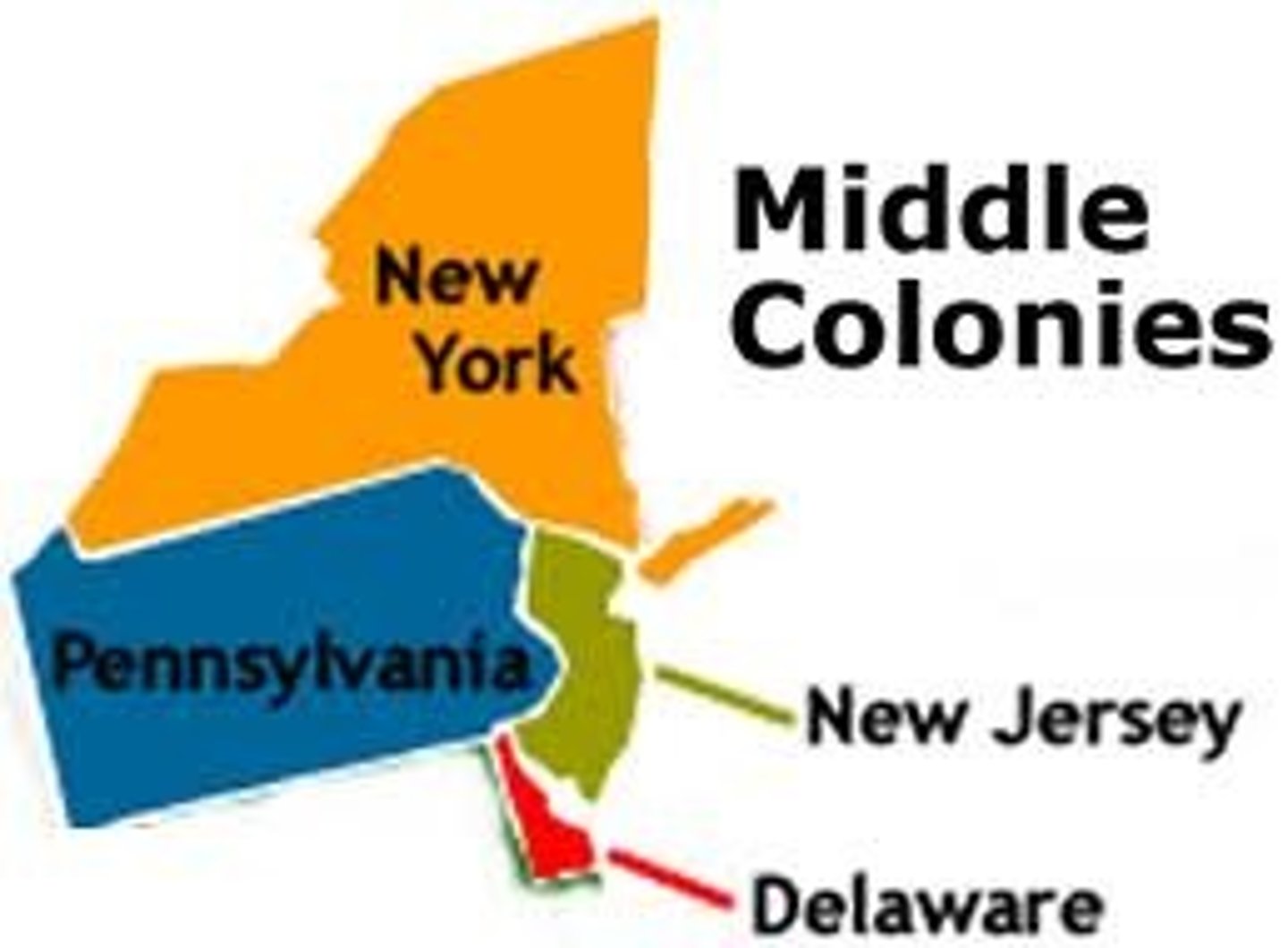
Middle Colonies
New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware
New York was important trading area, William Penn founded Pennsylvania for religious freedom
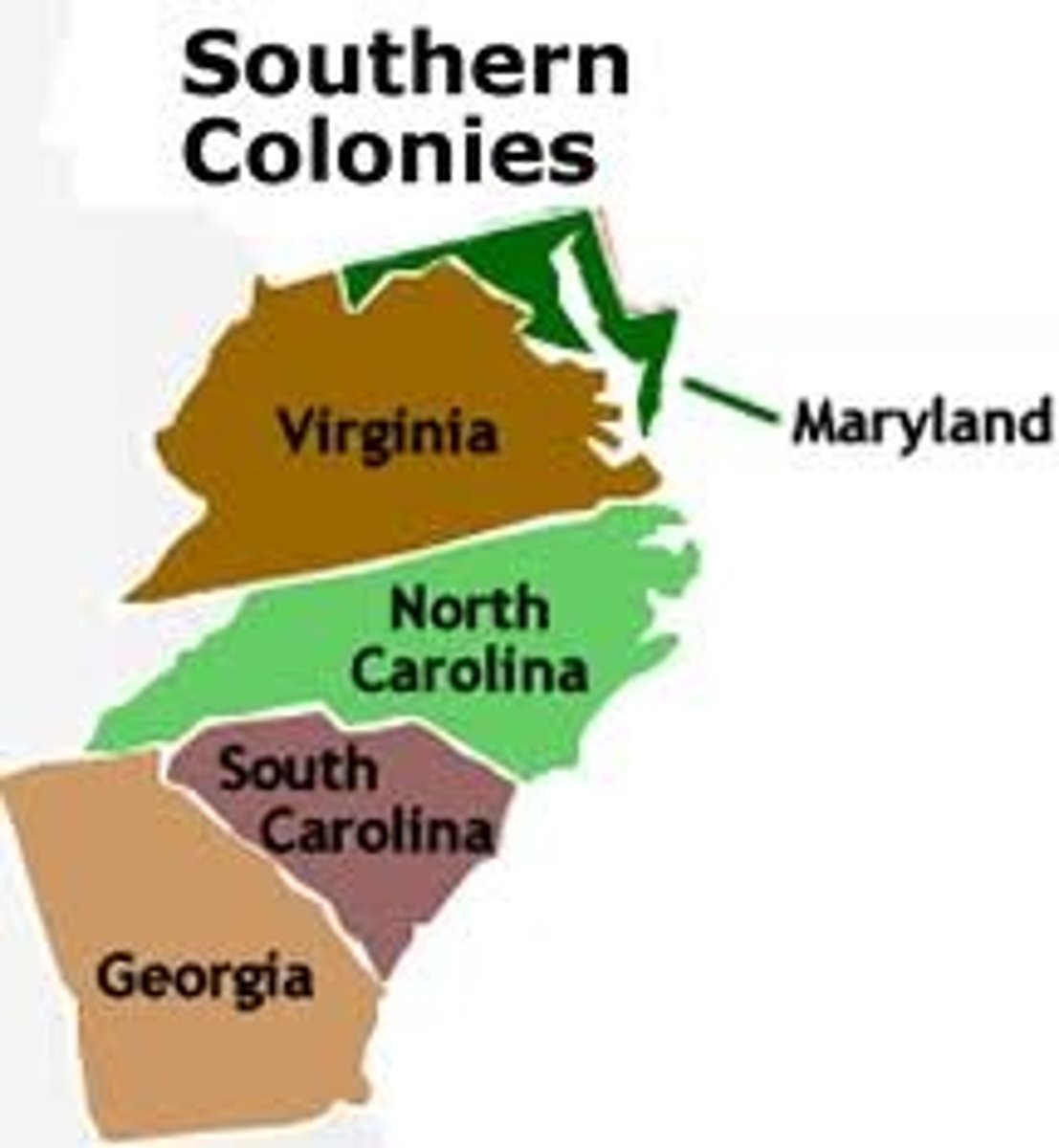
Southern Colonies
Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia
Maryland founded by Catholics fleeing religious persecution
Georgia was created for debtors (people who owed money)
Plantation
large farms used to produce cash crops (sugar, cotton, tobacco)

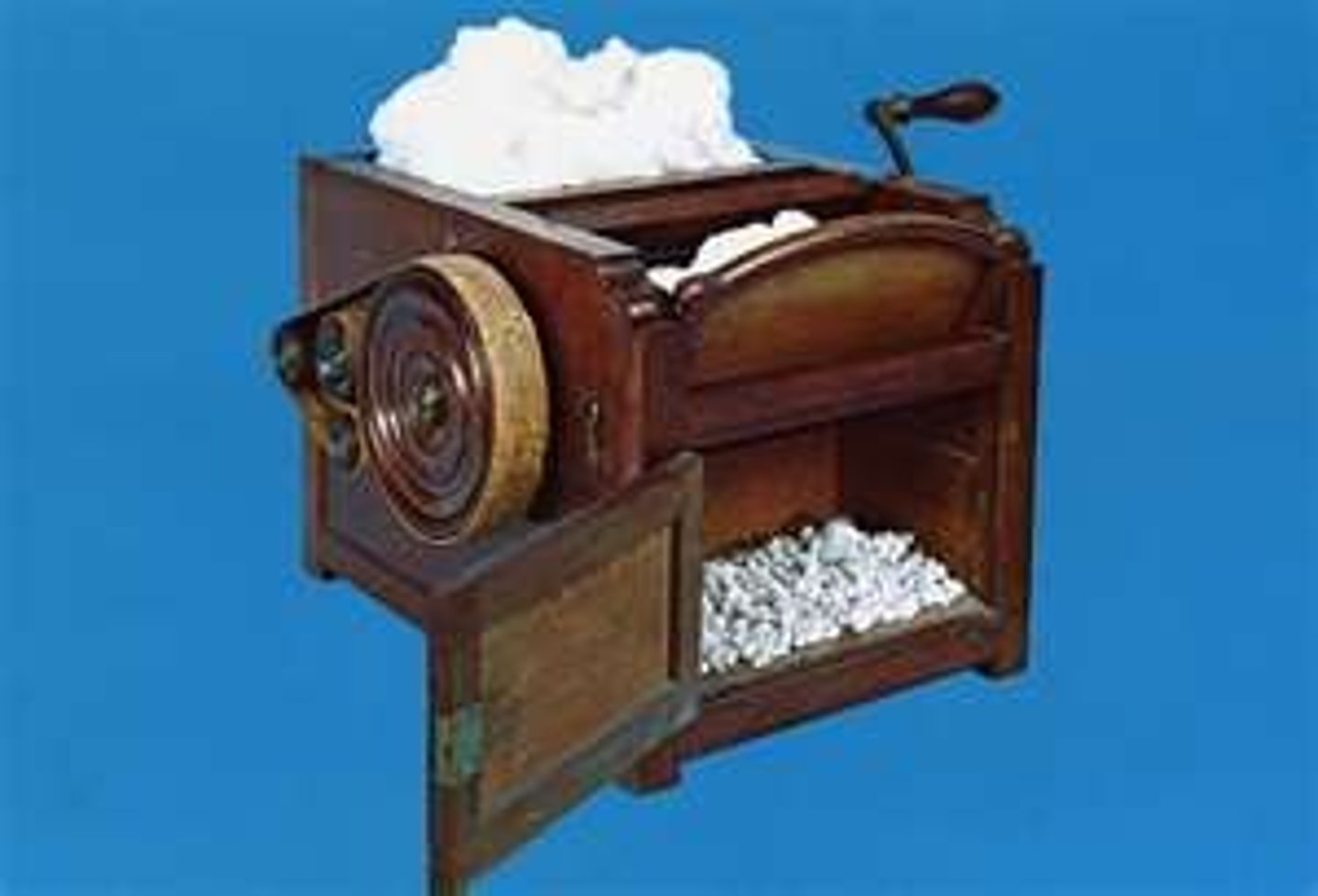
Cotton Gin
Invented in 1793 by Eli Whitney, made it easier and cheaper to grow cotton. This required more slaves to help the plantation owners grow it.

Thomas Hooker
founder of the state of Connecticut. Called the father of American Democracy. Connecticut adopted the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut which is sometimes called the first written constitution.

William Penn
established Pennsylvania as a refuge for Quakers. He supported freedom of worship, welcomed immigrants, and did not require residents to serve in a militia

Anne Hutchinson
Banished from Massachusetts colony, one of the founders of Rhode Island

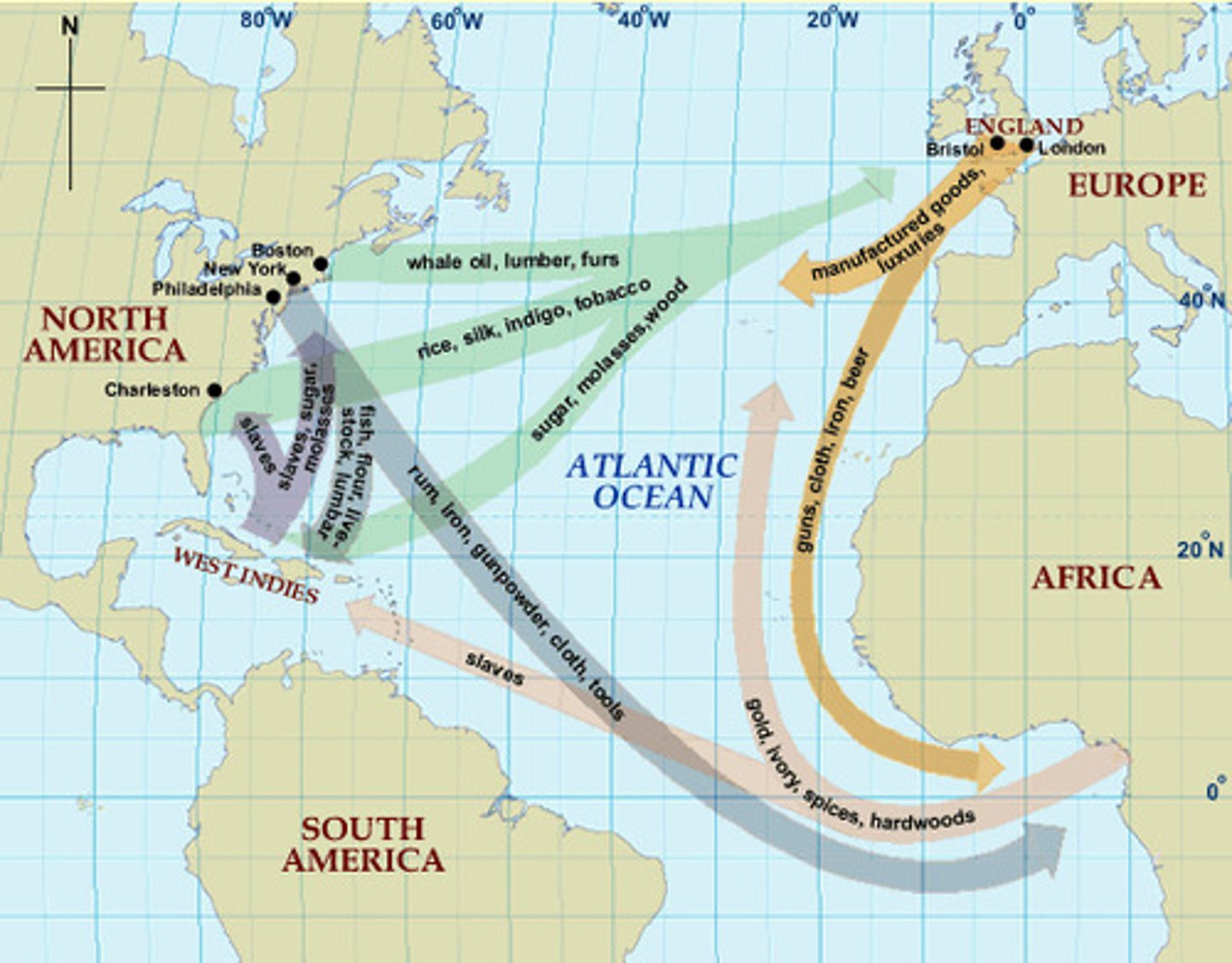
Triangular Trade
A three way system of trade during 1600-1800s Africa sent slaves to America, America sent Raw Materials to Europe, and Europe sent Guns and Rum to Africa
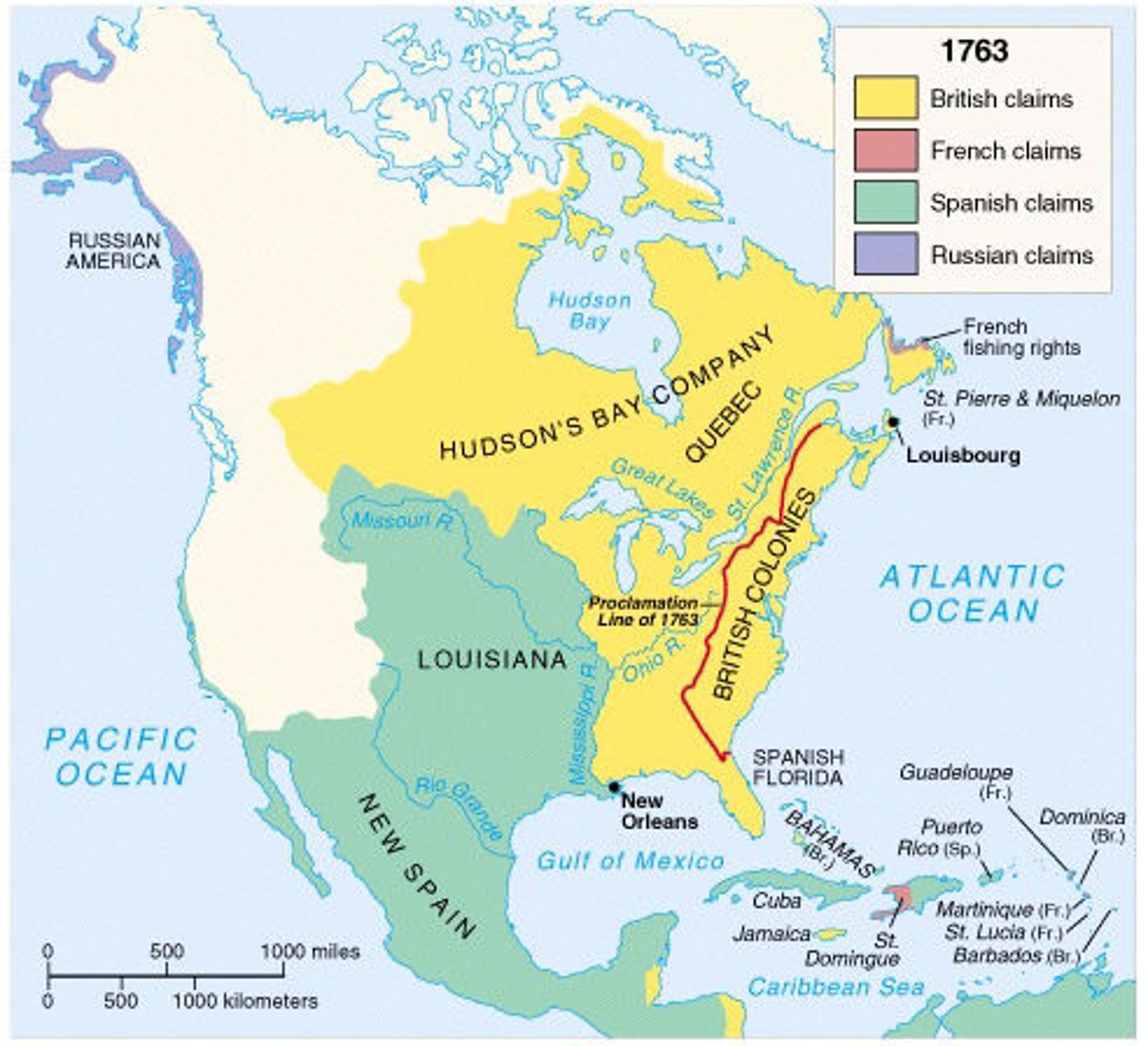
French and Indian War
(1754-1763) War fought in the colonies between the English and the French for possession of the Ohio Valley area. The English won.

Treaty of Paris 1763
Ended French and Indian War, France lost Canada, land east of the Mississippi, to British, New Orleans and west of Mississippi to Spain
Results of the French and Indian War
the British began taxing the colonists to pay for the war

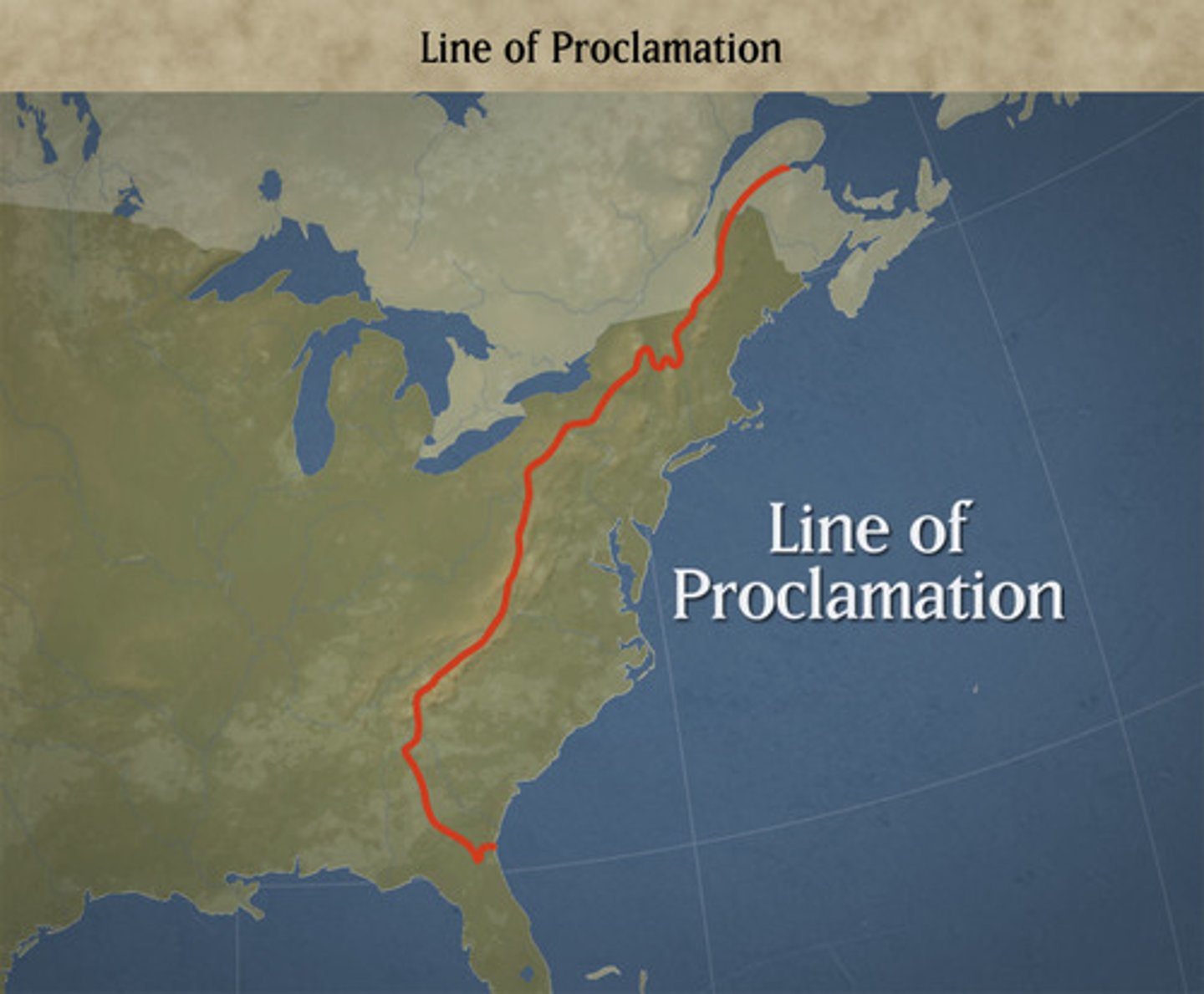
Proclamation Line of 1763
prohibited colonists from settling west of the Appalachian mountains
Sugar Act
(1764) British deeply in debt part to French & Indian War. English Parliament placed a tariff on sugar, coffee, wines, and molasses. colonists avoided the tax by smuggling and by bribing tax collectors.

Stamp Act
1765; law that taxed printed goods, including: playing cards, documents, newspapers, etc.

Townshend Acts
A tax that the British Parliament passed in 1767 that was placed on leads, glass, paint and tea

Tea Act
Law passed by parliament allowing the British East India Company to sell its low-cost tea directly to the colonies - undermining colonial tea merchants; led to the Boston Tea Party
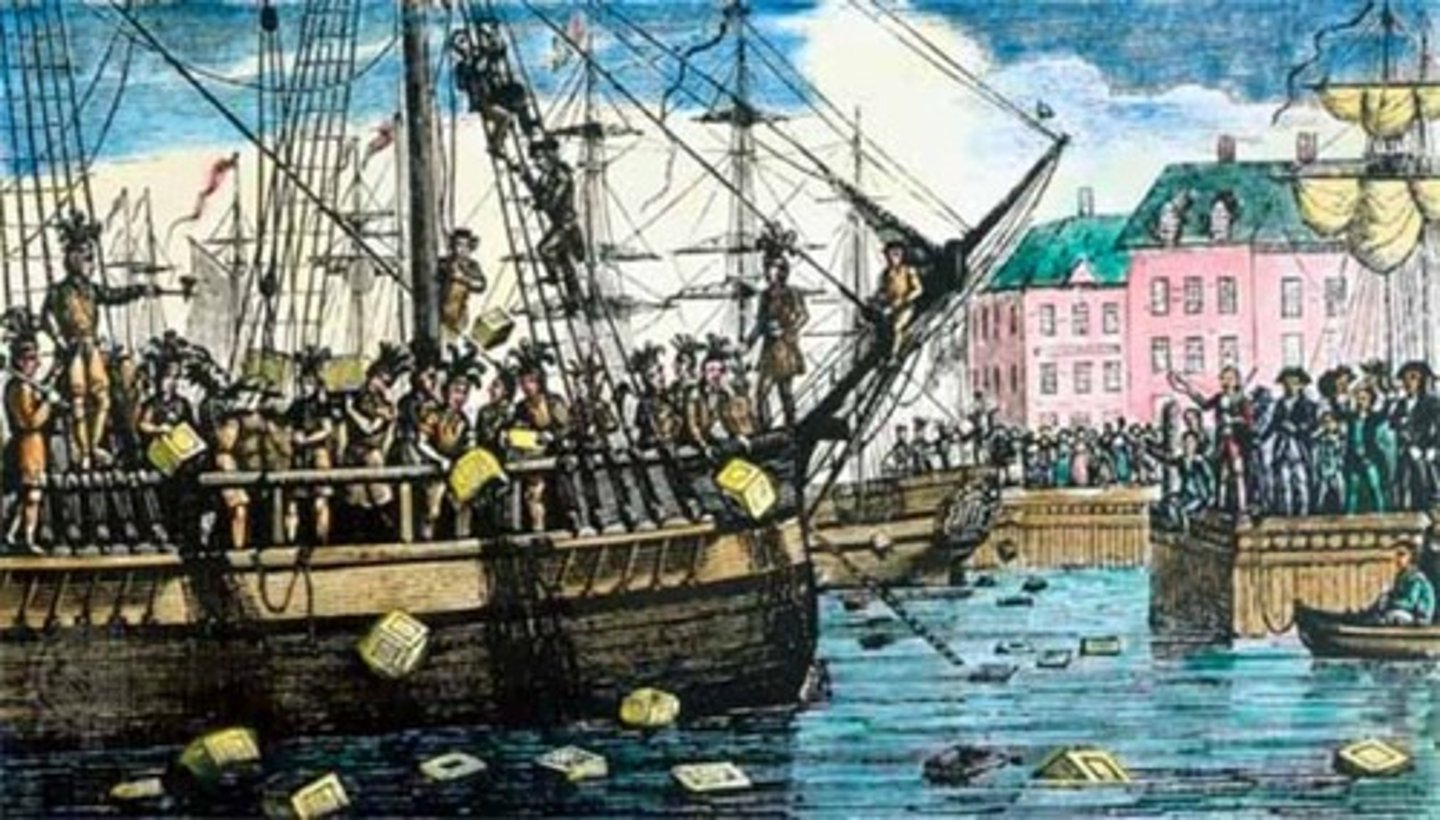

Intolerable Acts
in response to Boston Tea Party, 4 acts passed in 1774, Port of Boston closed, reduced power of assemblies in colonies, permitted royal officers to be tried elsewhere, provided for quartering of troop's in barns and empty houses

Declaration of Independence
1776 statement, written by Thomas Jefferson and issued by the Second Continental Congress, explaining why the colonies wanted independence from Britain.

Lexington and Concord
April 8, 1775: Gage leads 700 soldiers to confiscate colonial weapons and arrest Adam, and Hancock; April 19, 1775: 70 armed militia face British at Lexington (shot heard around the world); British retreat to Boston, suffer nearly 300 casualties along the way (concord)
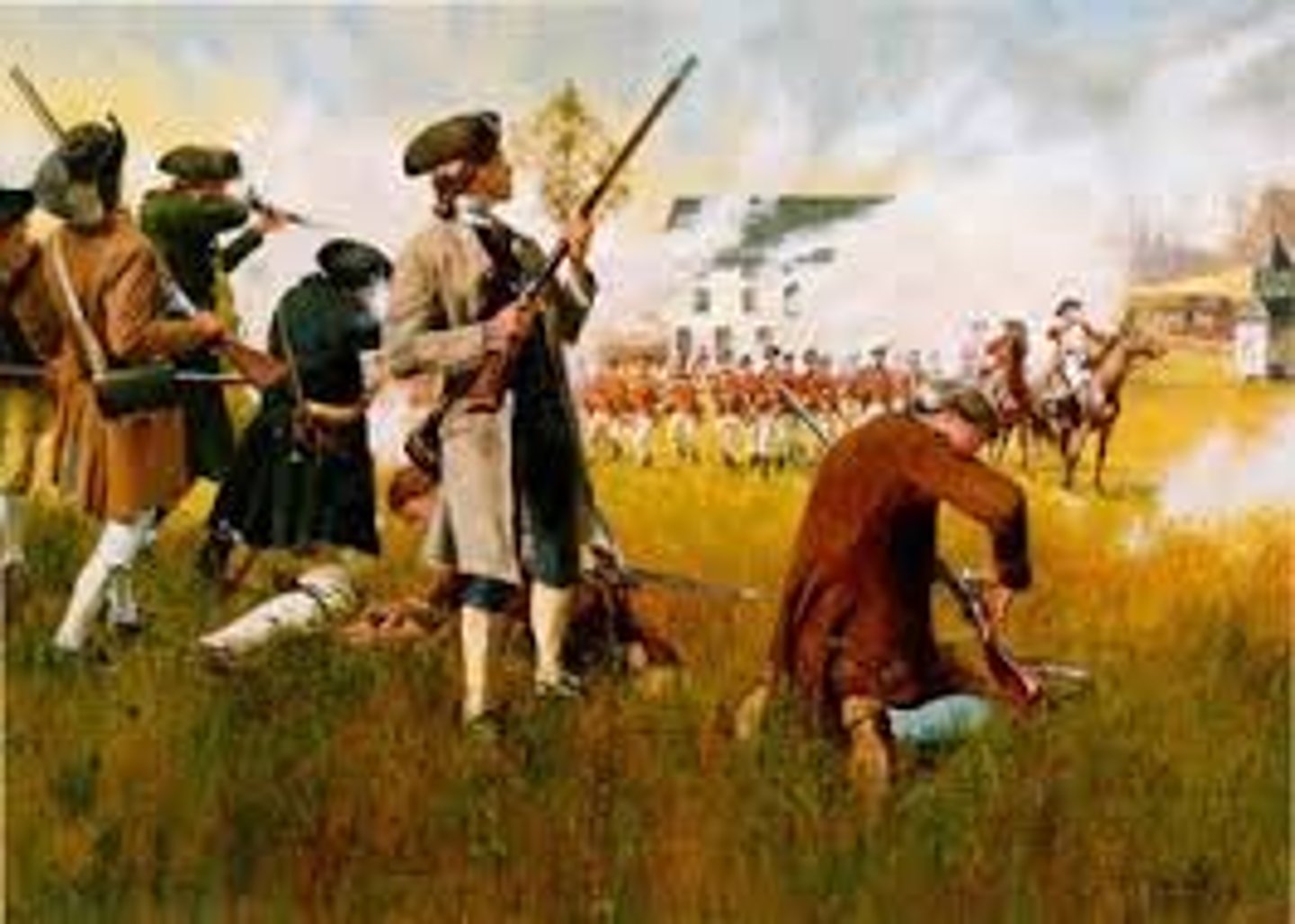

Saratoga
A battle that took place in New York where the Continental Army defeated the British. It proved to be the turning point of the war. This battle ultimately had France to openly support the colonies with military forces in addition to the supplies and money already being sent.

Yorktown
1781; last battle of the revolution; Benedict Arnold, Cornwallis and Washington; colonists won because British were surrounded and they surrended
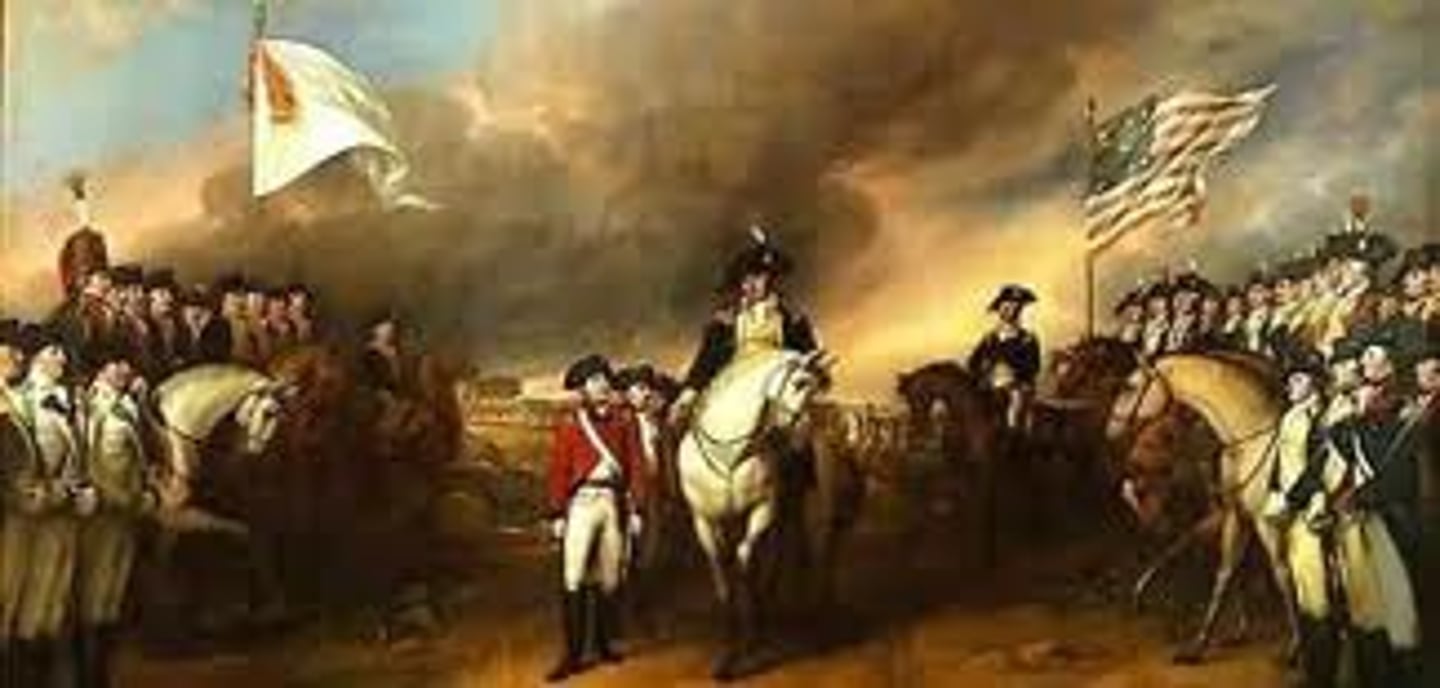

Treaty of Paris 1783
This treaty ended the Revolutionary War, recognized the independence of the American colonies, and granted the colonies the territory from the southern border of Canada to the northern border of Florida, and from the Atlantic coast to the Mississippi River

John Locke
17th century English philosopher who opposed the Divine Right of Kings and who asserted that people have a natural right to life, liberty, and property.

Charles de Montesquieu
famous for his articulation of the theory of separation of powers, which is implemented in many constitutions throughout the world.

George Mason
American Revolutionary leader from Virginia whose objections led to the drafting of the Bill of Rights (1725-1792)

Magna Carta
1215 document that limited the king's ability to tax English nobles and that guaranteed due process and a right to trial

English Bill of Rights
1689 laws protecting the rights of English subjects and Parliament

George Washington
1st President of the United States; commander-in-chief of the Continental Army during the American Revolution (1732-1799)

Samuel Adams
American Revolutionary leader and patriot, Founder of the Sons of Liberty and one of the most vocal patriots for independence; signed the Declaration of Independence

Benjamin Franklin
Printer, author, inventor, diplomat, statesman, and Founding Father. One of the few Americans who was highly respected in Europe, primarily due to his discoveries in the field of electricity. He helped to negotiate French support for the American Revolution.

Alexander Hamilton
1789-1795; First Secretary of the Treasury. He advocated creation of a national bank, assumption of state debts by the federal government, and a tariff system to pay off the national debt.
Hamilton emerged as a major political figure during the debate over the Constitution, as the outspoken leader of the Federalists and one of the authors of the Federalist Papers. Later, as secretary of treasury under Washington, Alexander Hamilton spearheaded the government's Federalist initiatives, most notably through the creation of the Bank of the United States.

Patrick Henry
A leader of the American Revolution and a famous orator who spoke out against British rule of the American colonies (1736-1799)
"Give me liberty or give me death"

James Madison
"Father of the Constitution," Federalist leader, and fourth President of the United States.

Thomas Paine
American Revolutionary leader and pamphleteer (born in England) who supported the American colonist's fight for independence and supported the French Revolution (1737-1809)

Abigail Adams
Wife of John Adams. During the Revolutionary War, she wrote letters to her husband describing life on the homefront. She urged her husband to remember America's women in the new government he was helping to create.

Wentworth Cheswell
Church leader, historian, and judge who fought at the Battle of Saratoga. 1st African American elected to public office in America.

Mercy Otis Warren
A 19th century American historian who wrote a 3-volume history of the American Revolution.

James Armistead
An African American slave who acted as a spy. He would pose as a runaway slave. He acted as an orderly and guide to the British. He would then get the information and pass it to General Lafayette.

Crispus Attucks
A free black man who was the first person killed in the Revolution at the Boston Massacre.

Marquis de Lafayette
French soldier who joined General Washington's staff and became a general in the Continental Army.

John Paul Jones
American naval commander in the American Revolution (1747-1792) said " I have not yet begun to fight."

King George III
was the King of England who disbanded the colonial legislatures, taxed the colonies, and refused the Olive Branch Petition leading to the final break with the colonies.

Articles of Confederation
1st Constitution of the U.S. 1781-1788 (weaknesses-no executive, no judicial, no power to tax, no power to regulate trade)

Philadelphia Convention - 1787
(Constitutional) The meeting of state delegates in 1787 in Philadelphia called to revise the Articles of Confederation. It instead designed a new plan of government, the US Constitution.

Anti-Federalist
Anti-Federalists rose up as the opponents of the Constitution during the period of ratification. They opposed the Constitution's powerful centralized government, arguing that the Constitution gave too much political, economic, and military control. They instead advocated a decentralized governmental structure that granted most power to the states

Federalist
Supporters of the Constitution that were led by Alexander Hamilton and John Adams. They firmly believed the national government should be strong. They didn't want the Bill of Rights because they felt citizens' rights were already well protected by the Constitution.

Date Constitution Written
1787

War of 1812 - Causes
British influence on Native Americans, violation of trading rights, British impressment, and U.S desired Canada

War of 1812
A war (1812-1814) between the United States and England who was trying to interfere with American trade with France.

War of 1812 - Effects
America proved it could protect itself
America manufacturing increased
Americans feel more patriotic
7 principles of the Constitution
Popular Sovereignty, Limited government, Separation of Powers, Checks and Balances, Federalism, Republicanism, and Individual Rights.

Popular Sovereignty
A government in which the people rule by their own consent.

Republicanism
A form of government in which people elect representatives to create and enforce laws

Federalism
A system in which power is divided between the national and state governments

Separation of Powers
Constitutional division of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, with the legislative branch making law, the executive applying and enforcing the law, and the judiciary interpreting the law

Checks and Balances
A system that allows each branch of government to limit the powers of the other branches in order to prevent abuse of power
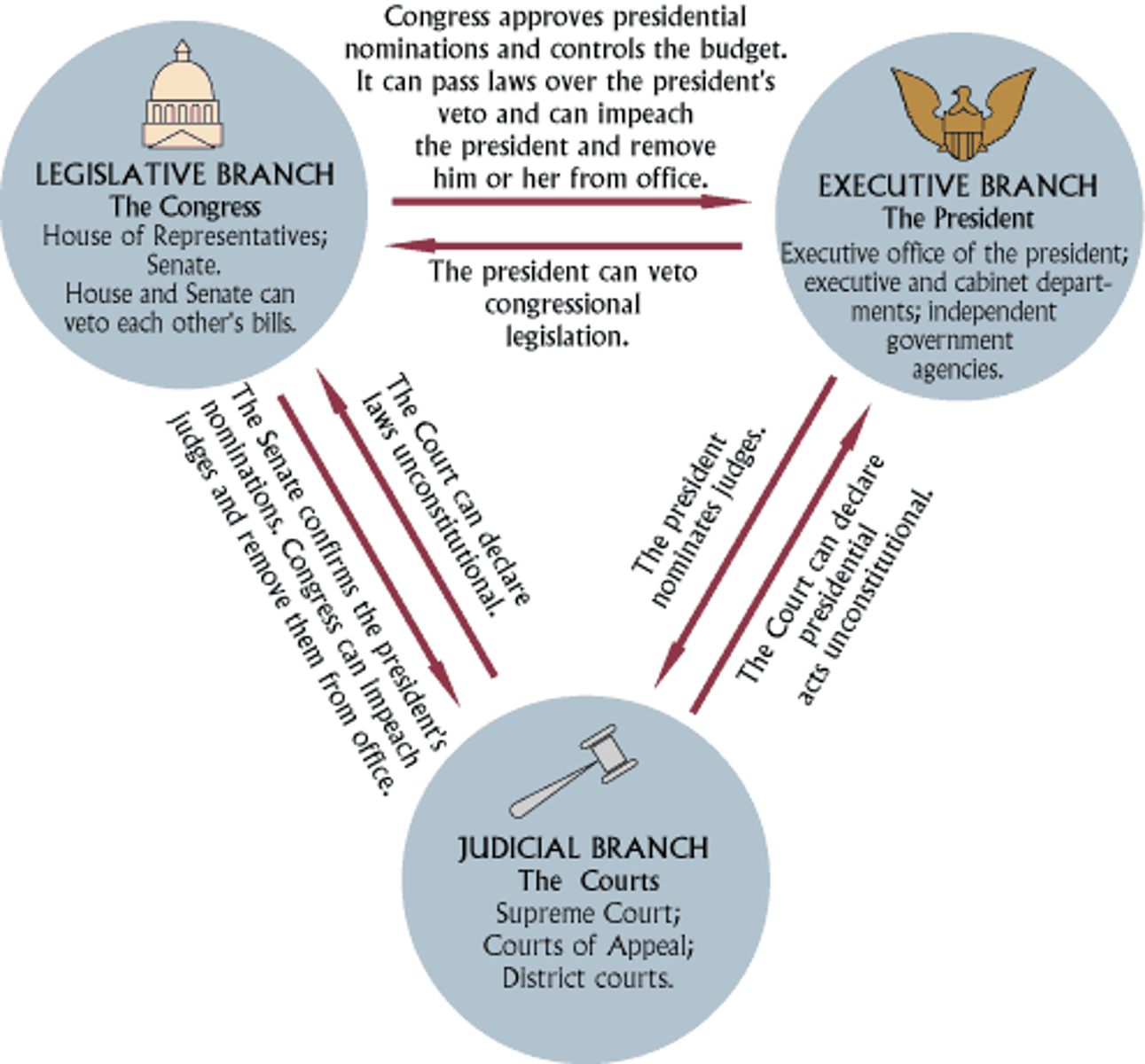
Limited Government
A principle of constitutional government; a government whose powers are defined and limited by a constitution.

Individual Rights
rights guaranteed or belonging to a person

Bill of Rights
First 10 amendments to the U.S. Constitution

1st Amendment
Freedom of Religion, Speech, Press, Assembly, and Petition

2nd Amendment
Right to bear arms

3rd Amendment
Restricts quartering of troops in private homes.

4th Amendment
Freedom from unreasonable searches and seizures

5th Amendment
Right of Accused Persons/ Indictment of Grand Jury (1) No Self-Incrimination (Miranda) (2) No Double Jeopardy (defendant cannot be tried again on the same, or similar charges) (3) No deprivation of life liberty or property without "due process of law" (fair treatment) (4) Eminent domain

6th Amendment
Criminal Proceedings; Right to a speedy trial; Right to Attorney; Right to fair impartial jury

7th Amendment
Right to jury in civil trials.
8th Amendment
No cruel and unusual punishment
Amendment that prohibits excessive bail amounts and cruel and unusual punishment.

9th Amendment
Citizens entitled to rights not listed in the Constitution

10th Amendment
Powers not expressly given to federal government by the Constitution are reserved to states or the people. Also known as "reserved powers amendment" or "states' rights amendment"

George Washington (as president)
Set many precedents such as 2 terms in office, creating a cabinet, and giving a farewell address

John Adams
America's first Vice-President and second President. Sponsor of the American Revolution in Massachusetts. During his presidency, Congress passed the controversial Alien and Sedition Acts

Thomas Jefferson
3rd President of the United States , He was a delegate from Virginia at the Second Continental Congress and wrote the Declaration of Independence. He later served as the third President of the United States.

James Madison
Father of the Constitution
4th President
President during the war of 1812

Monroe Doctrine
A statement of foreign policy which proclaimed that Europe should not interfere in affairs within the United States or in the development of other countries in the Western Hemisphere.
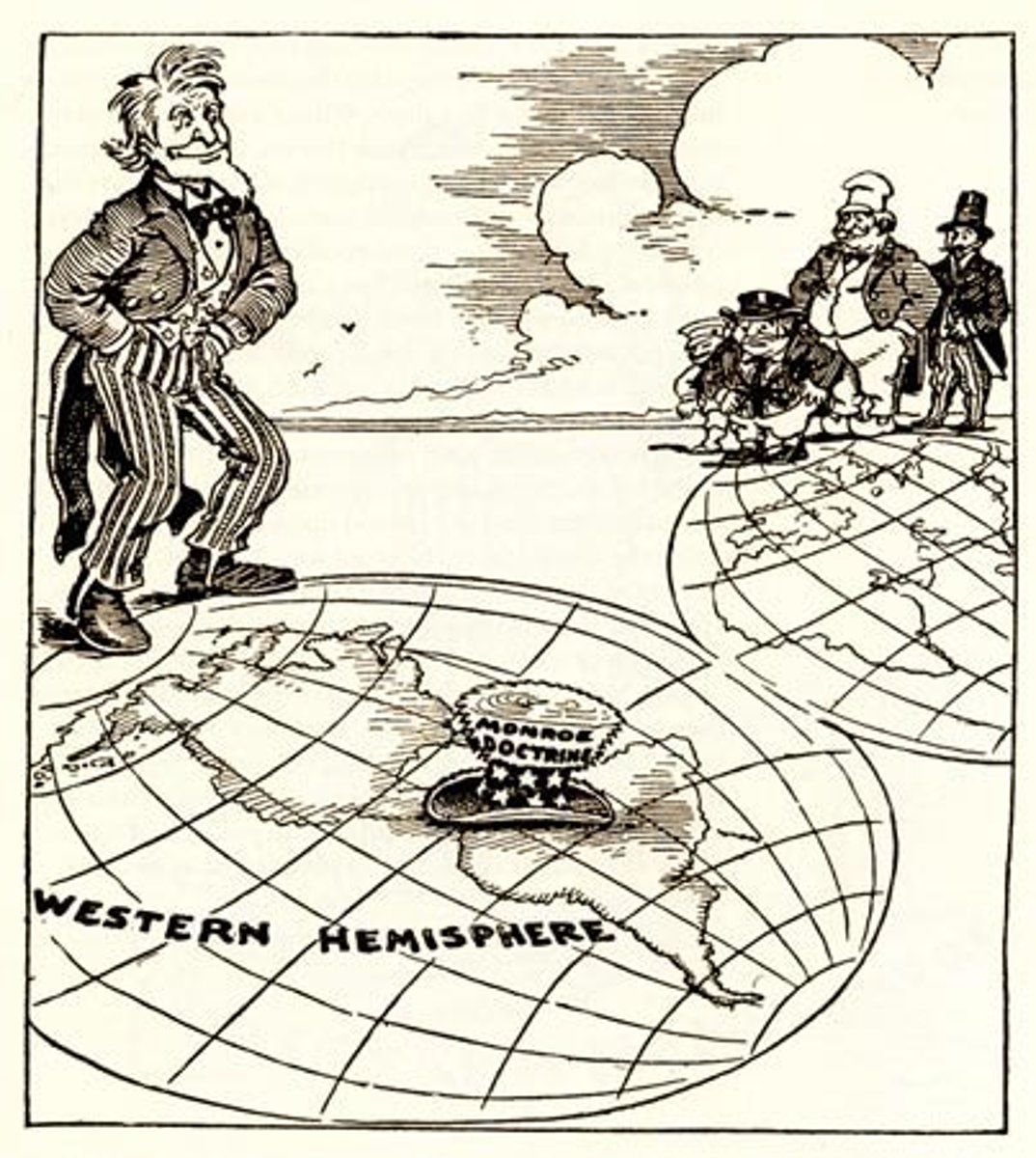
James Monroe
5th President
1816 and 1820; Democratic-Republican; his time in office is described as "The Era of Good Feelings," notable events include the Missouri Compromise, the establishment of the Monroe Doctrine, the acquisition of Florida from Spain, and several internal improvements such as The Cumberland Road

Mexican War
1846-1848
after disputes over Texas lands that were settled by Mexicans the United States declared war on Mexico in 1846 and by treaty in 1848 took Texas and California and Arizona and New Mexico and Nevada and Utah and part of Colorado and paid Mexico $15,000,000
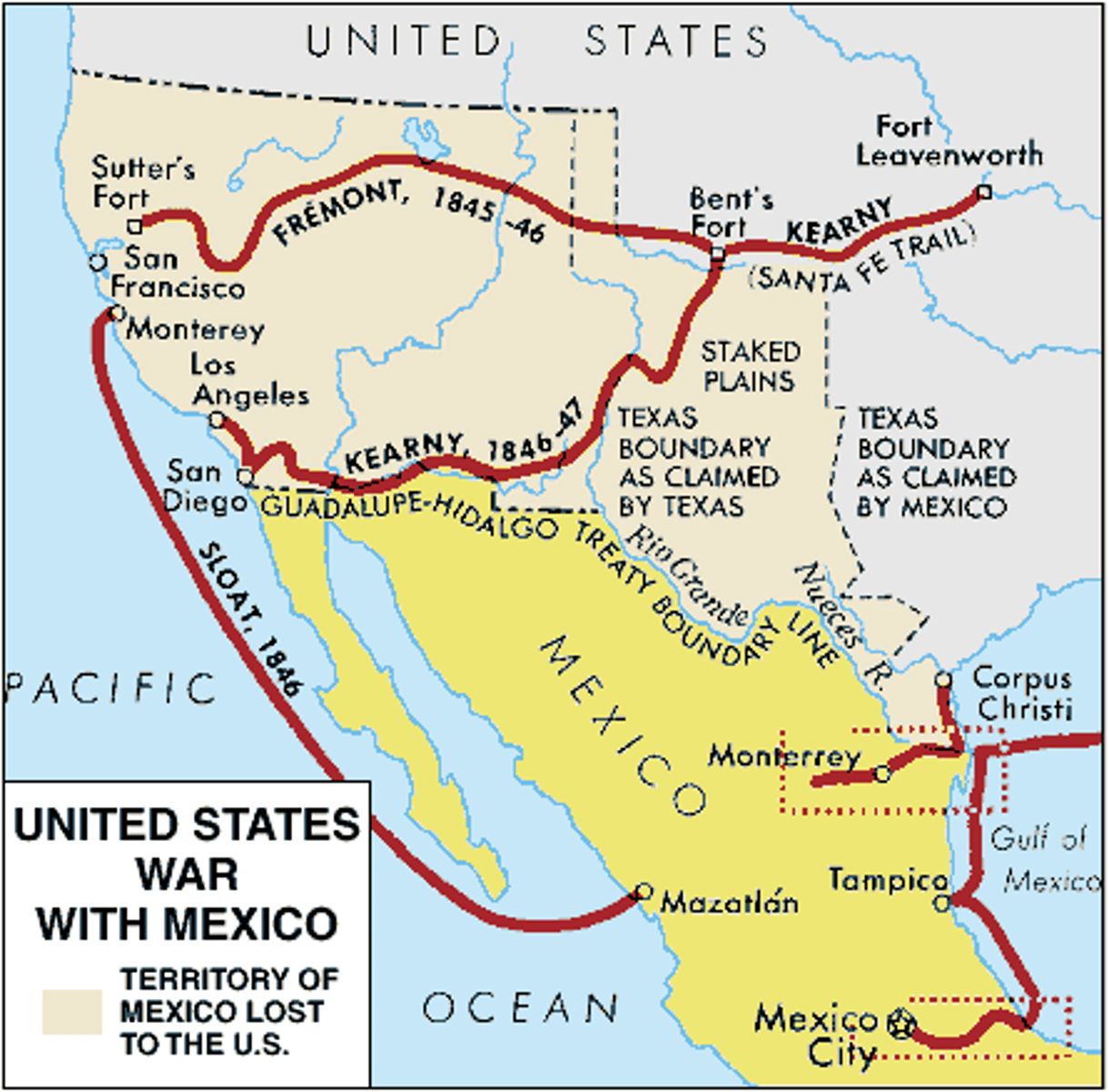
James K. Polk
president in March 1845. wanted to settle Oregon boundary dispute with Britain. wanted to acquire California. wanted to incorporate Texas into union.

Jacksonian Democracy
A policy of spreading more political power to more people. It was a "Common Man" theme.

Industrialization
The development of industries for the machine production of goods.

Mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by controlling the trade of their colonies
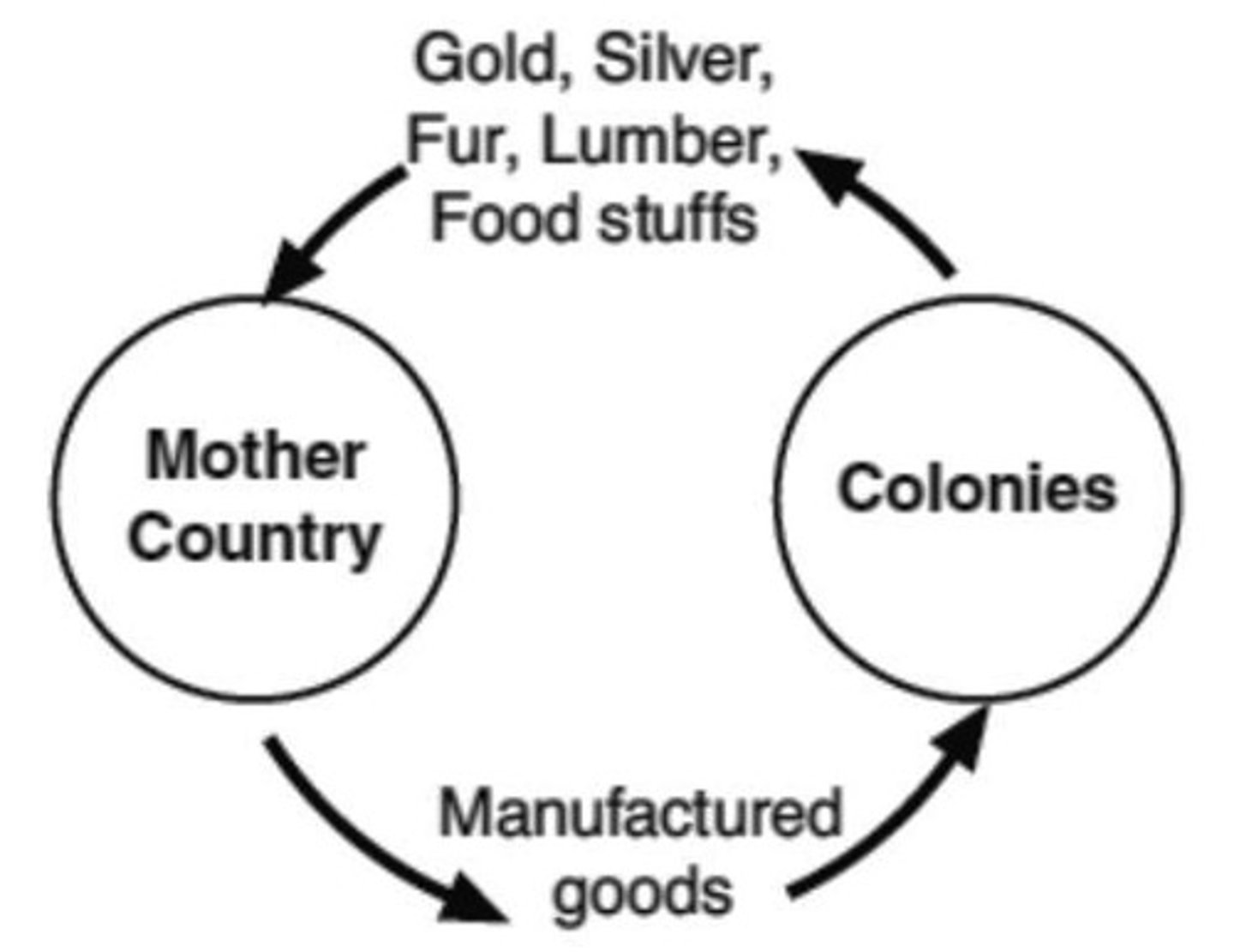
Free Enterprise
Economic system in which individuals and businesses are allowed to compete for profit with a minimum of government interference

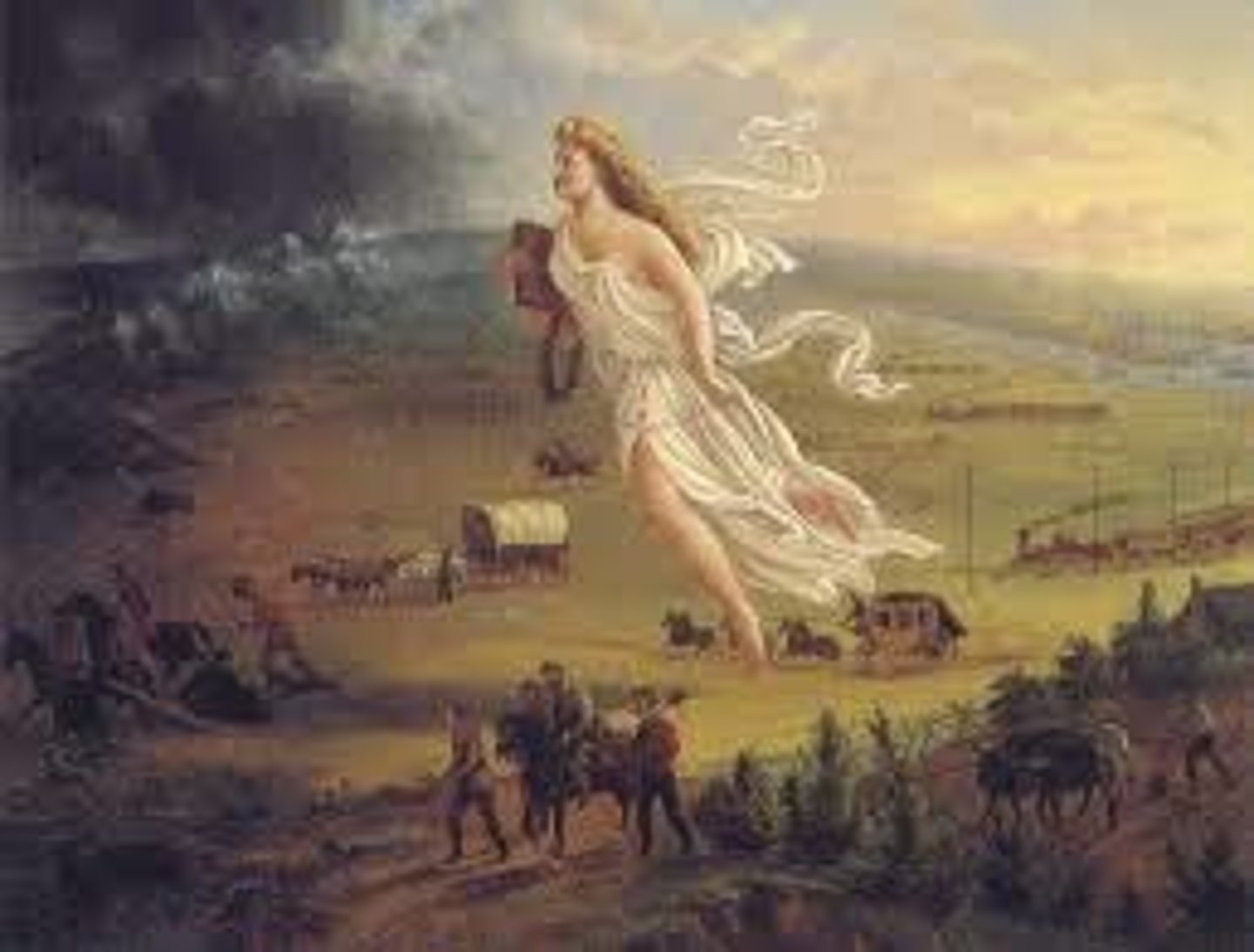
Manifest Destiny
A notion held by a nineteenth-century Americans that the United States was destined to rule the continent, from the Atlantic the Pacific.

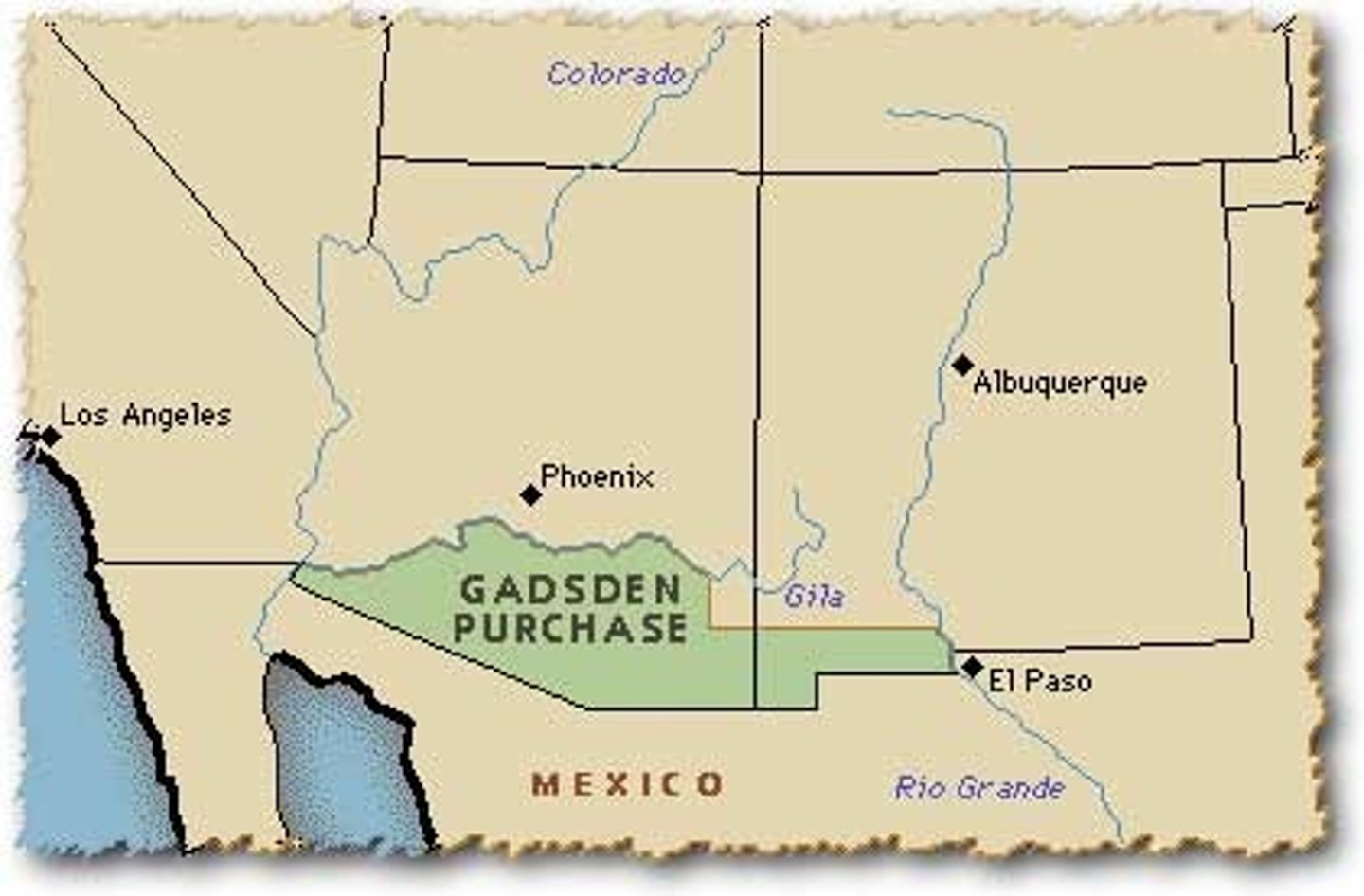
Gadsden Purchase
Agreement w/ Mexico that gave the US parts of present-day New Mexico & Arizona in exchange for $10 million; all but completed the continental expansion envisioned by those who believed in Manifest Destiny.
Florida Cession
1819
The United States gained this area from Spain with the Adams-Onis Treaty

Abolition Movement
the campaign against slavery and the slave trade

Public Education Movement
Led by Horace Mann, called for free public schooling for all students regardless of background.

Labor Reform Movement
movement to improve working conditions and working hours; led by the Lowell Mill Girls who initiated the first strike.
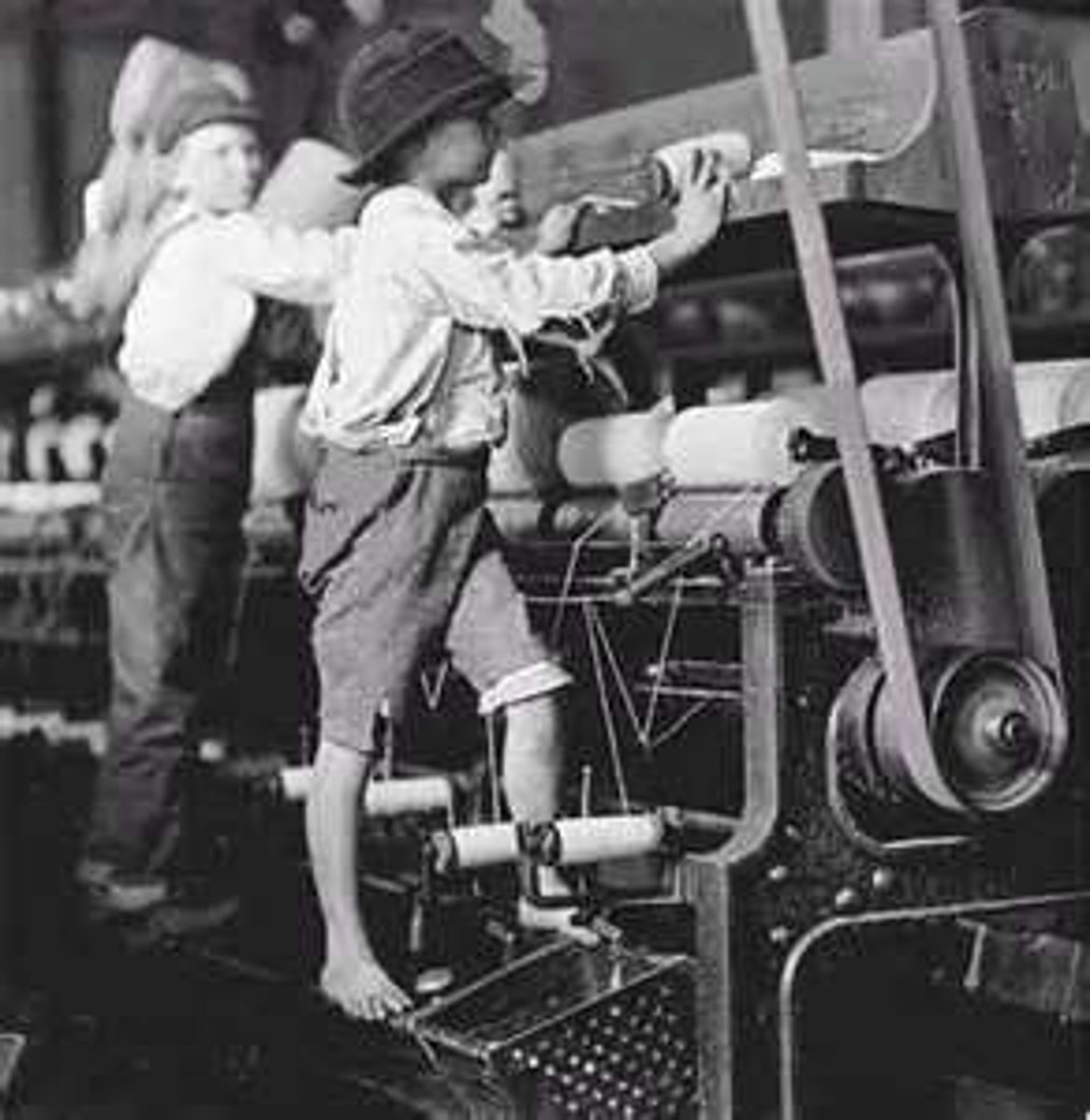

Women's Rights Movement
an organized effort to improve political, legal and economic status of women in American society
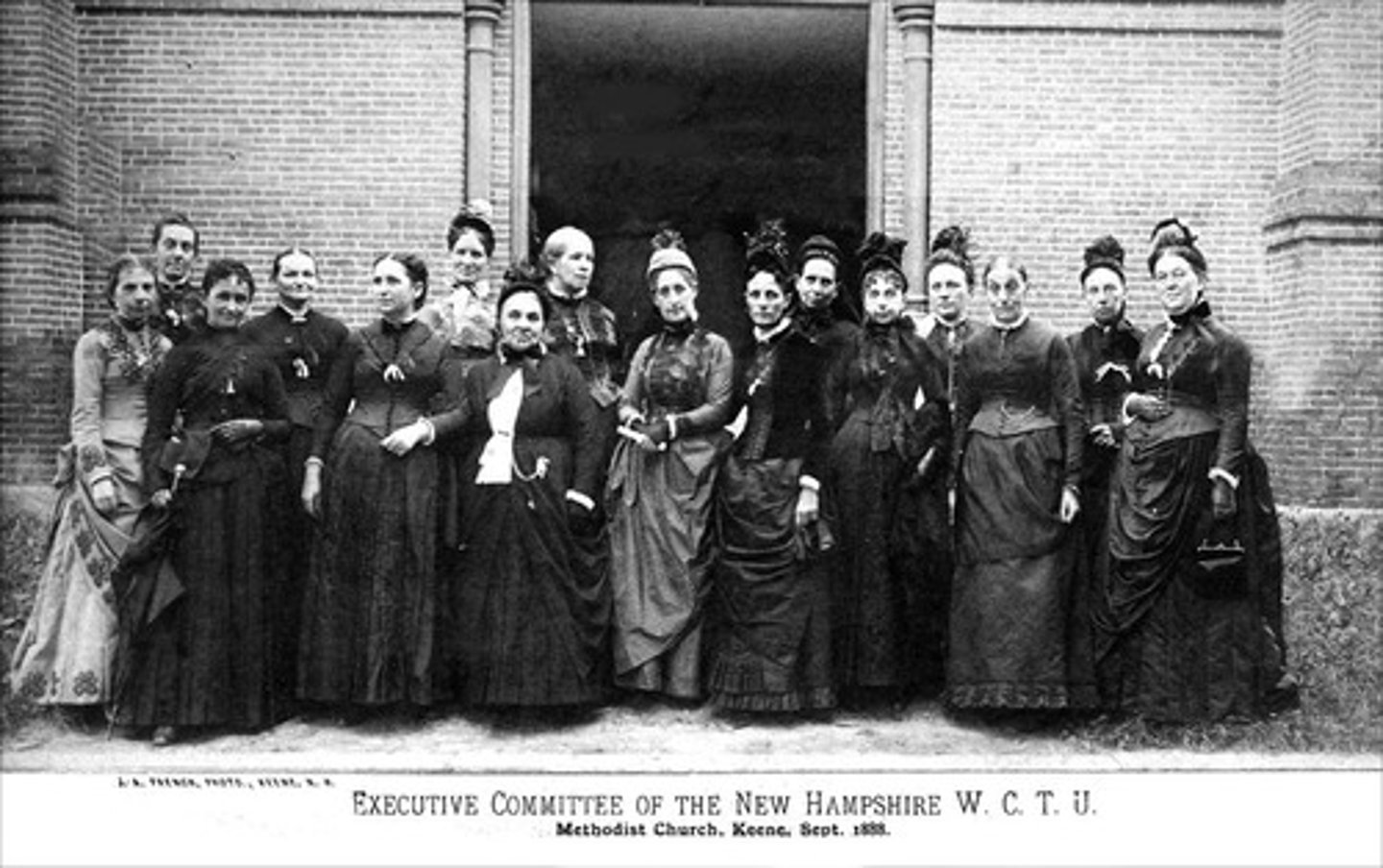

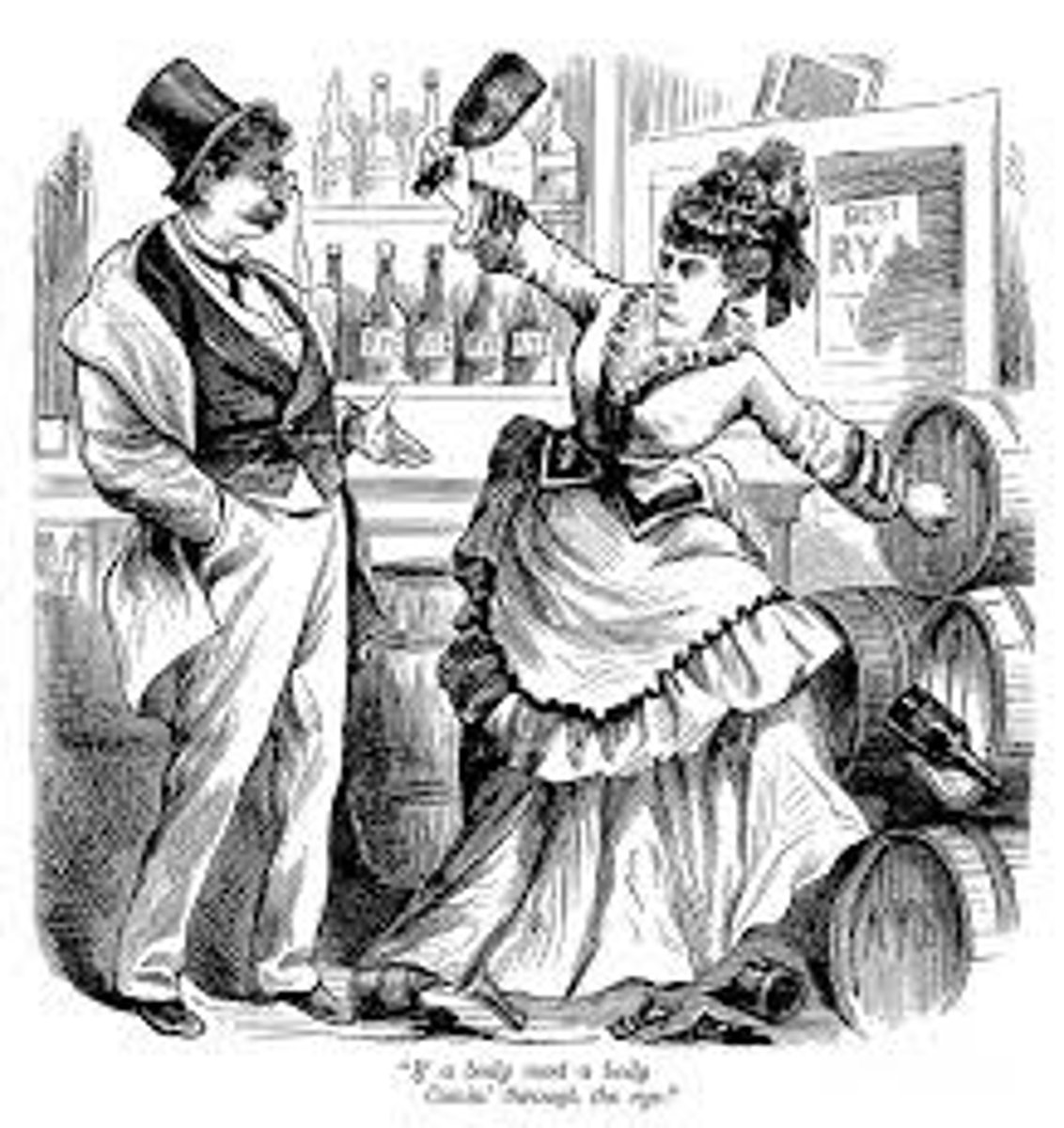
Temperance Movement
An organized campaign to eliminate alcohol consumption

Sectionalism
An exaggerated loyalty to a particular region of the country
Bleeding Kansas
(1856) a series of violent fights between pro-slavery and anti-slavery forces in Kansas who had moved to Kansas to try to influence the decision of whether or not Kansas would a slave state or a free state.
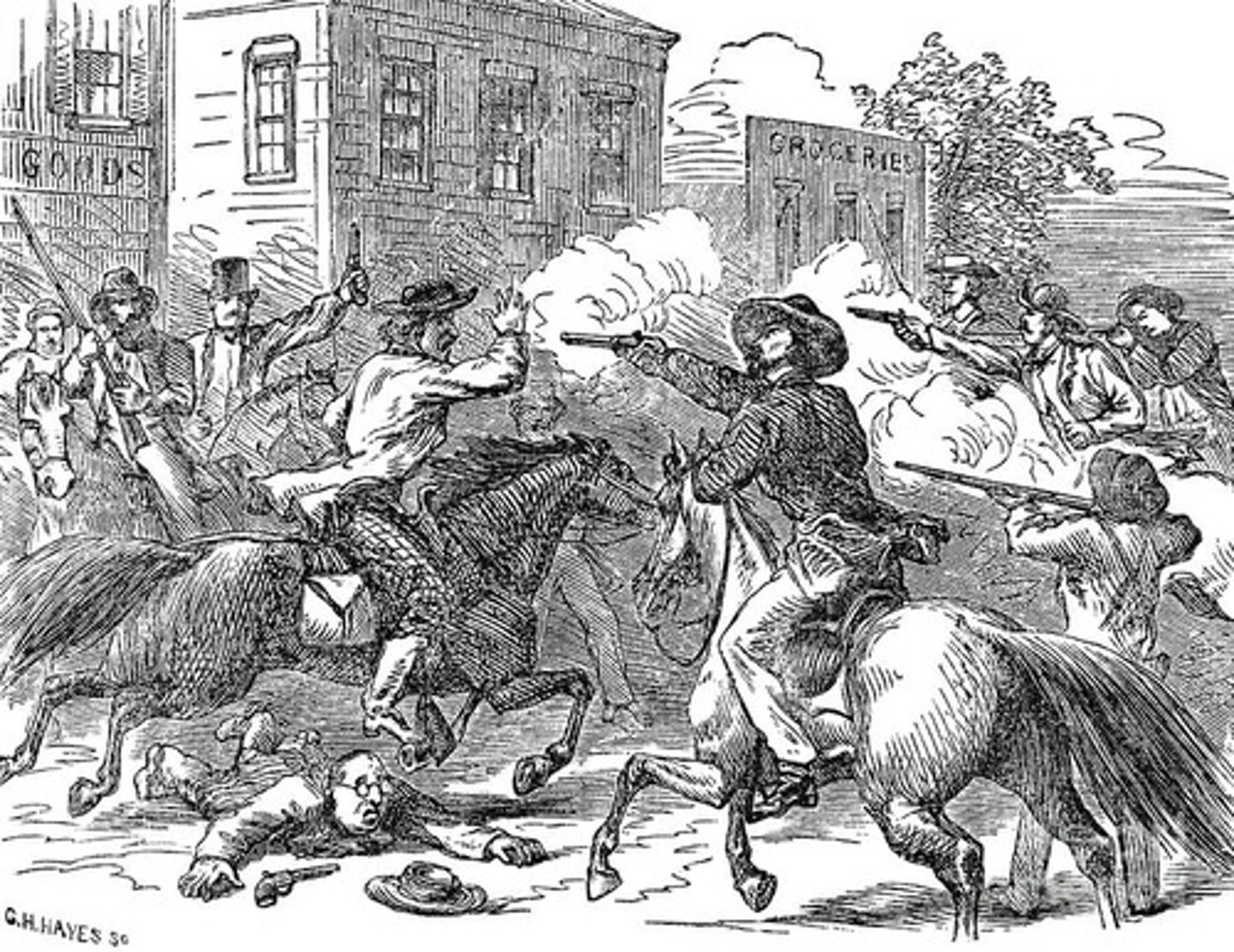

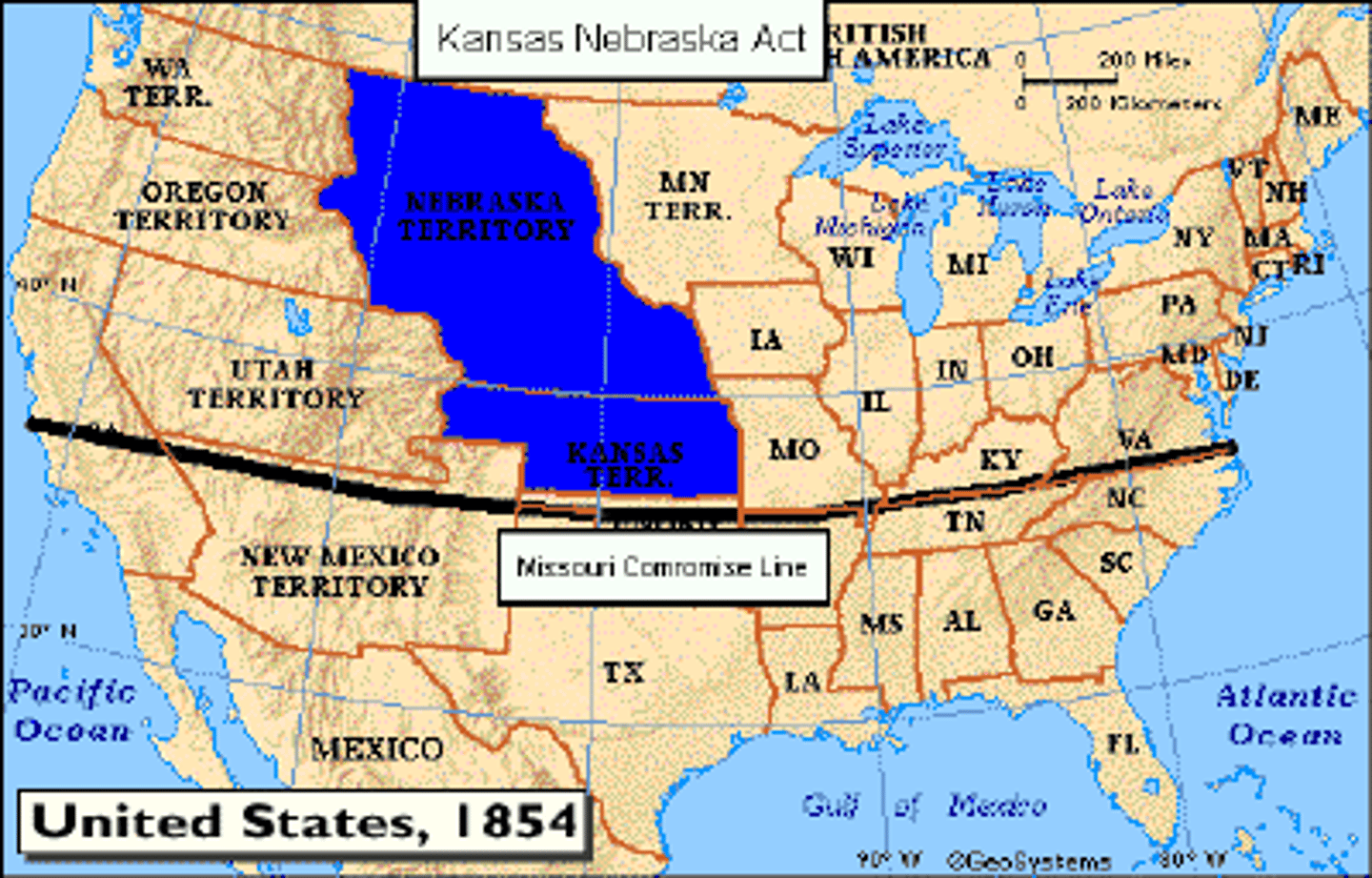
Kansas-Nebraska Act
1854 - Created Nebraska and Kansas as states and gave the people in those territories the right to chose to be a free or slave state through popular sovereignty.
Susan B. Anthony
social reformer who campaigned for womens rights, the temperance, and was an abolitionist, helped form the National Woman Suffrage Assosiation
