6: Reabsorption of Water: Collecting Ducts
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
The main 2 functions of the distal tubule is to?
Regulate secretion of K+ into the Urine
The absorption of Na+ out of the filtrate
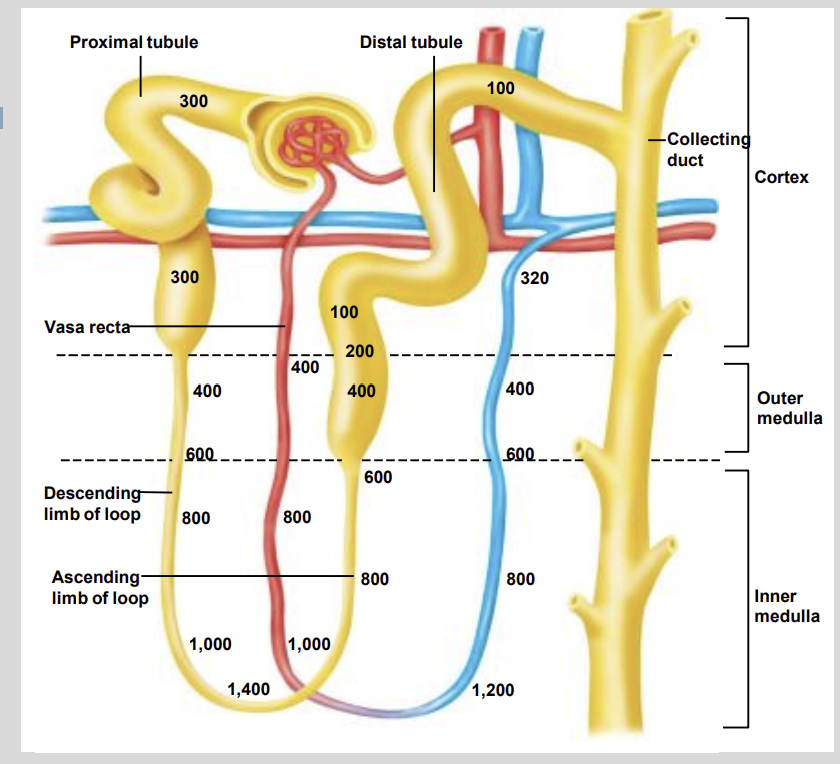
In the distal tubule, more…?
NacI is absorbed.
there are no aquaporins present so no water is absorbed from the filtrate
The collecting ducts first form in the?
Cortex
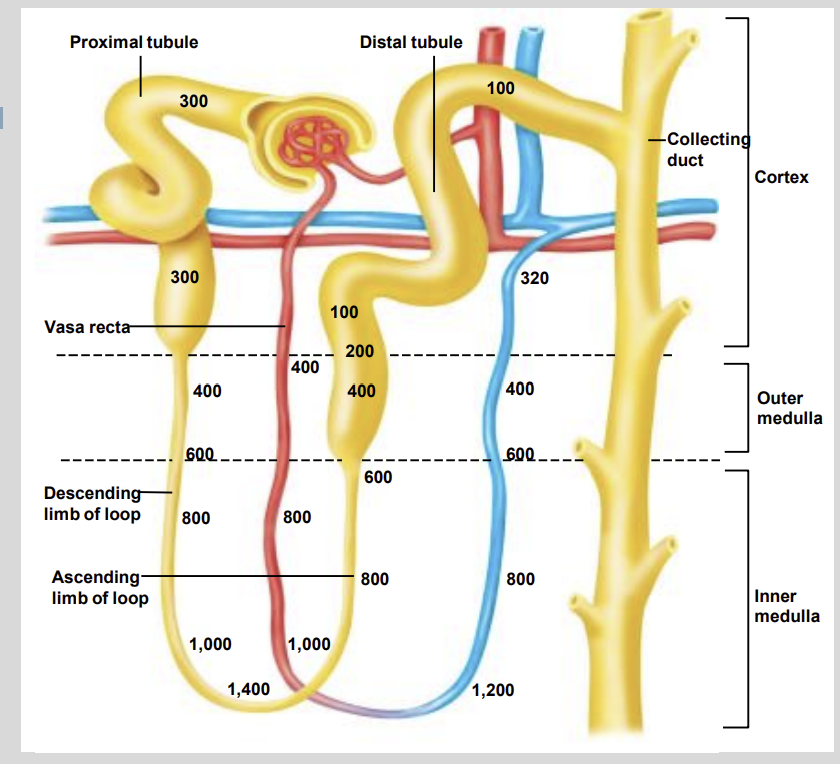
What forms the collecting ducts ?
Convergence of Many Distal Tubules
The collecting ducts must pass through the hyper?
Hypertonic Renal Medulla
What can the collecting ducts pass after passing through the Hypertonic Renal Medulla?
Can pass Urine into the Calyces
The fluid of that enters the collecting duct is normally very?
Hypertonic (≈100mOsm)
Why is the fluid than enters the collecting duct Hypertonic?
due to the actions of the distal tubule removing more solutes
The collecting duct is permeable to water but completely?
Completely Impermeable to NacI
the high concentration of NaCl in the renal medulla interstitial fluid cannot move?
Into the collecting ducts.
The hypertonic environment of the renal medulla is usually?
Constant
the permeability of the collecting duct varies depending on the?
Hydration Status of the body
In the collecting duct, hormones maintain whole?
body salt/water balance by regulating the rate of water reabsorption.
the permeability of the collecting duct is altered by the number of?
Aquaporins
present in the plasma membrane of the collecting duct epithelial cell
The more aquaporins there are in the apical plasma membrane, the?
Permeability of the Membrane
Fluid not reabsorbed that leaves the collecting duct….?
Becomes Urine
Aquaporins diagram
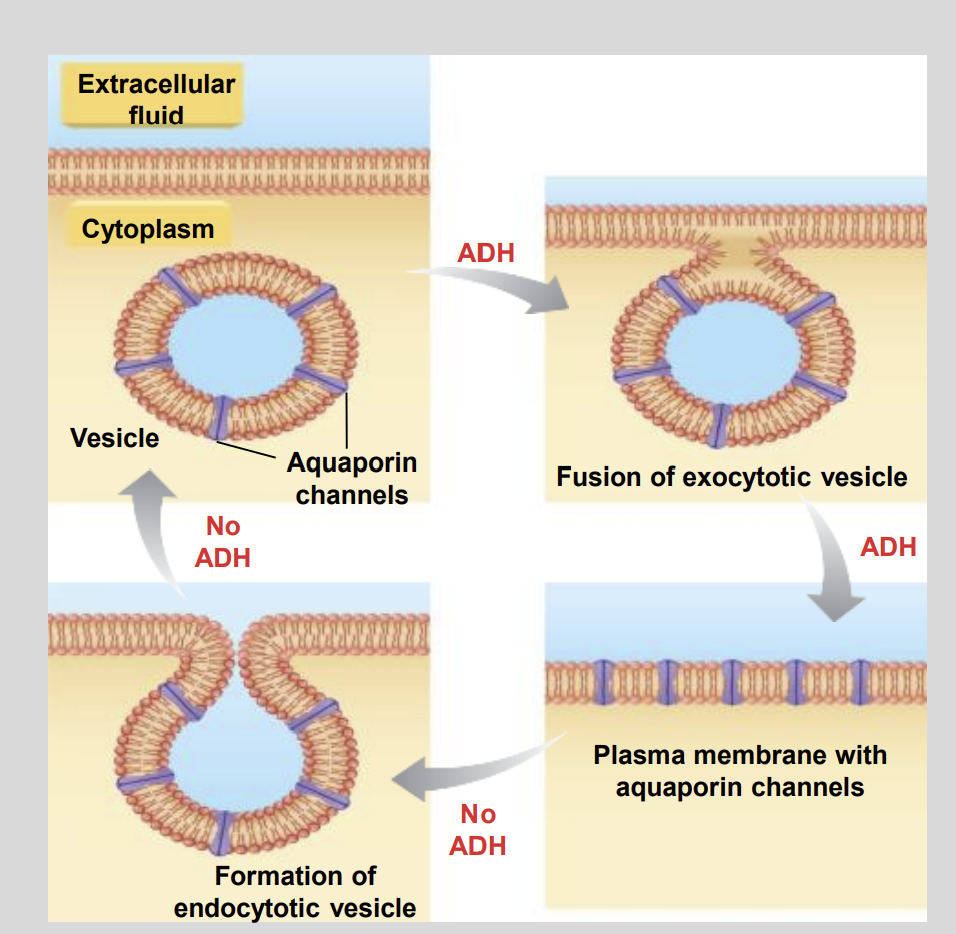
Aquaporins (water channels) can be stored in?
Internal Vesicles
The posterior pituitary gland secretes anti?
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
When is ADH released?
During a state of Dehydration
As little as ..% increase in plasma osmolality can induce increased ADH release?
1%
When ADH binds to its receptors on the epithelial cell surface, cAMP acts as a….?
Second messengers,
Triggering Aquaporins.
The process of Exocytosis does ?
Insert the aquaporins into the plasma membrane
does not result in the release of any contents into the extracellular fluid
In the absence of ADH, the aquaporins are removed from the?
Removed from the Plasma Membrane
Via Endocytosis
ADH Water Balance Diagra,
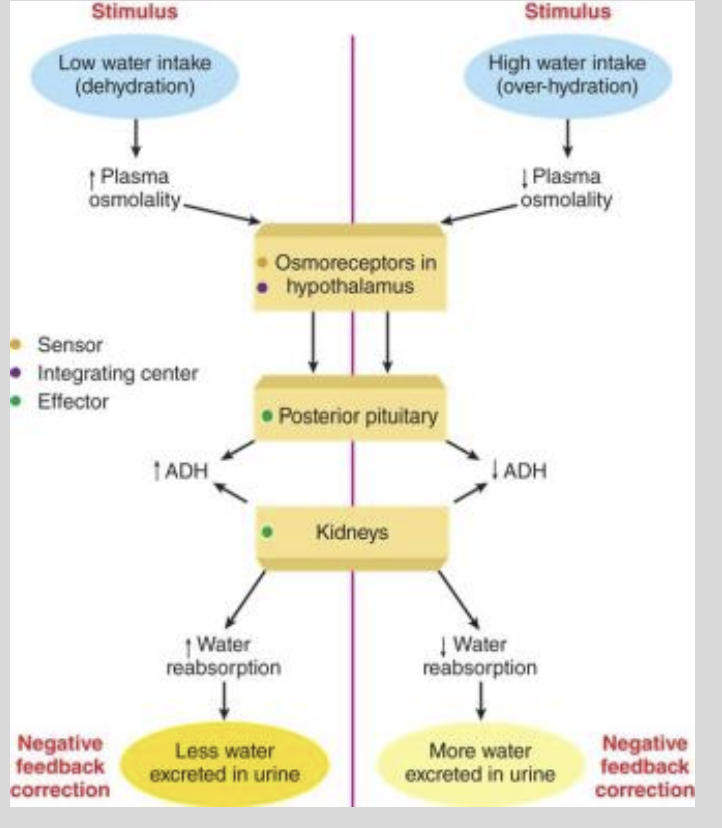
Bullet point describe Dehydration and irs ADH effect on Water Balance?
Dehydration = ADH Release
ADH increases Concentration of Aquaporins.
More Water Retained in Collecting Ducts
Urine = More Concentrated?
Bullet point describe Over-Hydration and irs ADH effect on Water Balance?
Overly Hydrated Inhibits ADH Production
Lack of ADH promotes the internalisation of aquaporins in the collecting ducts.
Less water is retained from the collecting ducts
Urine is more Diluted.
The highest possible urine osmolarity is equivalent to the osmolarity?
of medullary interstitium (≈1,400mOsm).
Under normal conditions how much Urine is produced daily?
1.5 L
minimum of 400ML
Diabetes insipidus is a?
Rare Disease
not linked to T1D or T2D
Diabetes insipidus is characterised by?
Polyuria
Chronic Thirst
What are the 2 Types of Diabetes Insipidus?
central diabetes insipidus
nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Describe Central Diabetes Insipidus?
Central diabetes insipidus results from the insufficient secretion of ADH
Describe Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus develops when the kidneys do not respond to ADH circulating
Can occur due to Lithium perscription.