Materials Testing Final
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Quality assurance (QA)
the owner’s responsibility to ensure the materials meet specifications
Quality Control (QC)
the developer’s (or contractor, producer) responsibility to regulate the processing to ensure the material will meet specs
What are the 2 main sizes of aggregates, and what sieve size separates them?
Coarse and fine, #4 sieve
Compute the wet density (pcf) and dry density (pcf) of a soil sample with the following data from a Standard Proctor Compaction Test:
· Mass of Mold: 8.45-lb
· Volume of Mold: 0.033-ft3
· Mass of Wet Soil + Mold: 12.85-lb
· Moisture Content: 15.53%
Wet Density (pcf) = Mass of Wet Soil / Volume of Mold = (12.85 lb – 8.45 lb)/ 0.033 ft3 = 133.33 pcf
Dry Density (pcf) = Wet Density/1+Moisture Content = 133.33 pcf / (1 + 15.53%) = 115.41 pcf
Calculate the Plasticity Index of the following test results:
· Plastic Limit Trial 1 – Moisture Content 12.5%
· Plastic Limit Trial 2 – Moisture Content 13.7%
· Plastic Limit Trial 3 – Moisture Content 14.0%
· Based on graphical data, Liquid Limit is determined to be 55.3%.
Plastic Limit = (12.5+13.7+14.0)/3 = 13.4%
Plasticity Index = LL - PL = 55.3 - 13.4 = 41.8 > round up to 42
True or False
A concrete beam is the best material to span curve
False (steel is)
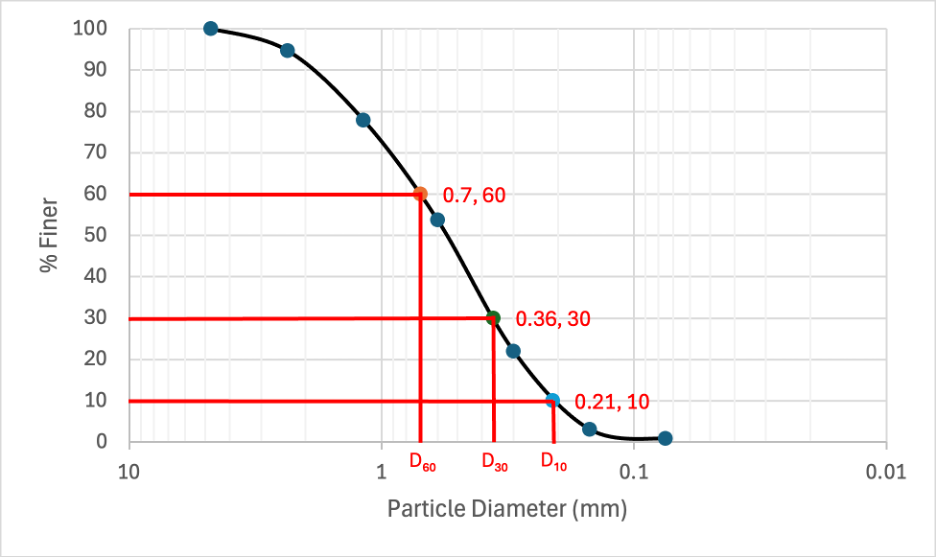
Given this Particle-Size Distribution Curve, find Cu and Cc.
Cu = D60/D10 = 0.7/0.21 = 3.3
Cc = D30²/(D60 x D10) = 0.36²/(0.7 × 0.21) = 0.88
True or False
Mix pavement is less expensive than rigid pavement.
True
For Wood Science, what is the definition of the Fiber Saturation Point?
The Fiber Saturation Point is the point at which cell walls are completely saturated, but cell cavities are empty.

True or False
Shrinkage in wood happens most along the width (radial).
False (it happens most along height (tangential)
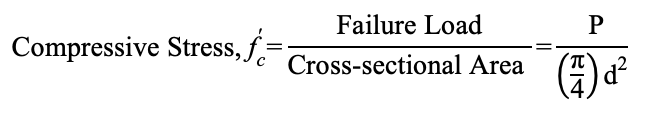
Find the compressive Stress (psi) given the following information:
diameter of cylinder is 4 inches
Maximum Load is 43,250 pounds
Area = pi/4 × 4² = 12.57
Compressive Stress = Maximum Load / Area = 43,250 / 12.57 = 3,440 psi
What is the difference between plans and specifications?
The plans focus on what and where to build. The specifications focus on how to build it.
What are the 3 basic geological classifications?
Igneous
Sedimentary
Metamorphic
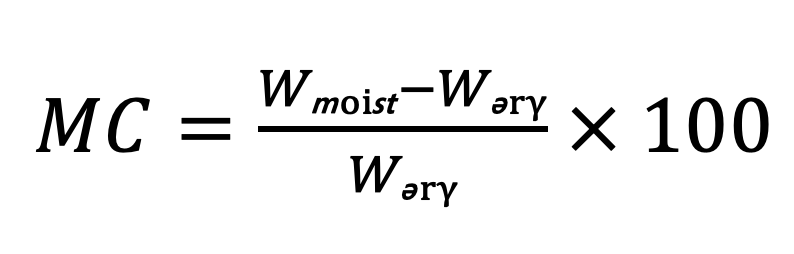
A sample of coarse aggregate is taken in the lab and the initial weight is 1,520-g (Wₘₒᵢₛₜ). After drying to a constant weight, the sample weighs 1,498-g. What is the moisture content? Report to the nearest 0.1%.
MC = (W moist - W dry) / W dry x 100%
MC = (1,520 - 1,498) / 1,498 × 100% = 1.469% > round up to 1.5%
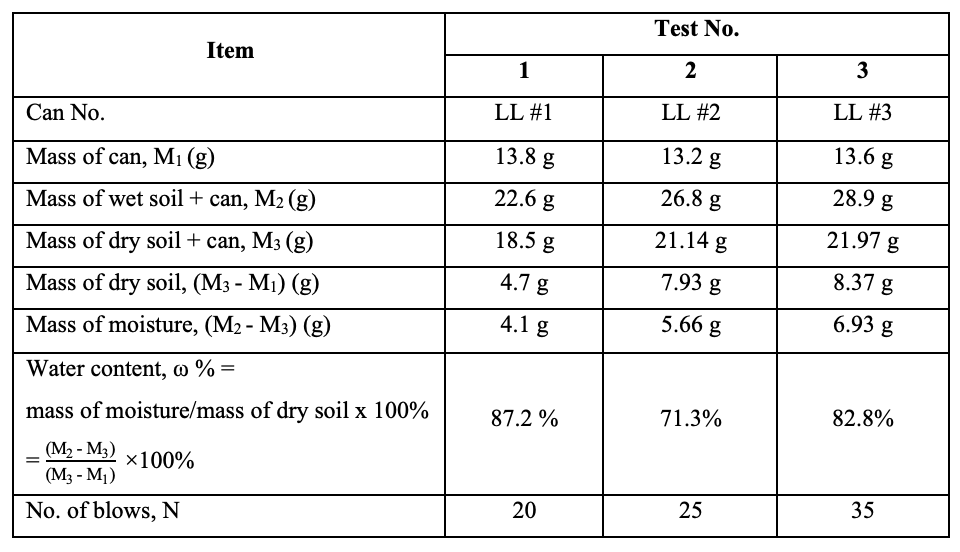
Plastic limit trial chart
Mass of dry soil= (mass of dry soil + can) - can
Mass of moisture= (mass of wet soil + can ) – (mass of dry soil + can)
Moisture content= (mass of moisture/mass of dry soil)*100
Cohesive Soil
any soil whose grain stick together upon wetting AND drying, and some force is required to separate because they are in clumps
Cohesionless Soil
any soil whose grain may stick together ONLY WHEN wet, but they fall apart upon drying
What are the 4 necessary components of concrete?
Water, Fine Aggregate, Coarse Aggregate, Cement
True or False
For concrete design, as the water to cement ratio goes up the strength of the concrete goes up.
False
What are the 2 stages of hydration?
Setting and Hardening
(when mixed with water, cement first sets and then rather slowly hardens)
What are the three criteria that establish the required minimum sampling frequency for concrete?
Not less than once each day
Not less than once for each 150 cubic yards of concrete placed
Once for each 5000 square feet of surface area of slabs or walls placed
Find the maximum load needed to reach a Compressive Strength 42.20 psi given a 6×12 inch concrete cylinder.
Area = pi/4 × 6² = 28.27
Compressive Stress = Maximum Load / Area
42.20 = Maximum Load / 28.27
Maximum Load = 42.20 × 28.27 = 1,192.99
Determine the flexural strength of a concrete beam
that is 6×6×18 and had a maximum load of 6420 pounds.
MOR = (Failure load x Span length) / (Width x Depth²)
MOR = (6420 × 18) / (6 × 6²) = 535 psi
What are the types of joints in concrete?
Contraction Joints - to control cracking due to shrinkage, a shallow groove ¼ the depth of slap is made to encourage cracks to form along that line
Construction Joints - used when concrete pouring is stopped in order to join further concrete placements, has sealer on top
True or False
30-gals of water will not change the mix design of concrete.
False
What is the required compressive strength the producer should design to?
4,000 psi standard + 1,200 safety margin = 5,200psi
Select the Max aggregate size in each situation
a 9”x5’x30’ slab
a sidewalk 4” thick
2” of space between reinforcing forms
Maximum aggregate size should not exceed:
1/5 of the narrowest dimension of the form,
1/3 the depth of slabs.
3/4 of the clear space between reinforcing bars or forms
Answers:
9” is the narrowest dimension » 1/5 of 9” = 1.8”
4” deep » 1/3 of 4” = 1.3
2” of space » ¾ of 2”= 1.5
What is the correct amount of mixing water for 4” slope and 1.5” aggregate
285 » or 300
What processes must be accounted for when integrating Construction Materials Testing into a CPM schedule?
Lead time / Procurement time
Testing
Submittal process
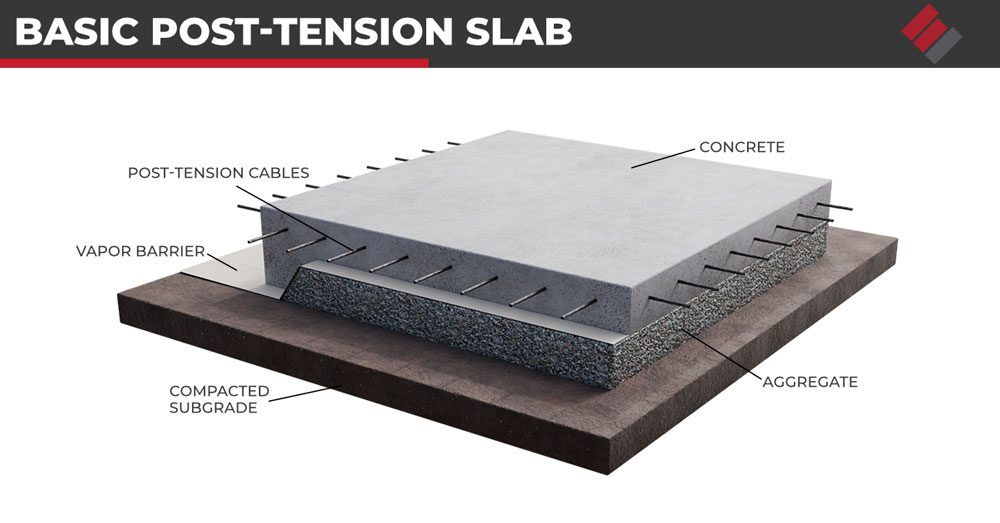

Determine the type of construction depicted in the image
Post-tensioned concrete:
helps combat foundation problems by making the slab stiffer and more resistant to cracking. If movement occurs, the entire slab tends to move together, reducing the risk of differential settlement compared to a regular slab.