Animal Reproduction: Terminology and Processes
1/221
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
222 Terms
Androgen
A male sex hormone, such as testosterone; a type of hormone that promotes the development and maintenance of male sex characteristics.
Artificial insemination (AI)
When semen is placed into the cervix.
Conceptus
The production of conception being the embryo/fetus together with the surrounding membranes(s).
Corpus luteum
Produces progesterone that in turn allows and maintains pregnancy.
Estrous
An adjective describing the estrous cycle.
Estrus
A noun denoting the time of heat.
Function of the gonads
To produce gametes and sex hormones.
Gonad
The ovary in females and testis in males; the primary reproductive organ.
Libido
The desire to mate.
Monoestrous
Where there is a single estrus followed by an absence of ovarian activity.
Polyestrous
Where an animal will show repeated estrus separated by 16-23 days depending on the species.
Reflex ovulators
Show estrus but require mating to ovulate.
Pregnancy recognition
When the conceptus signals its presence to the mother to allow pregnancy to continue.
Primordial germ cell
Migrates to the site destined to be the gonad; cells become gonocytes in the developing gonad and ultimately become gametes.
Progesterone
The hormone that is essential to the maintenance of pregnancy.
Sertoli cells
In the seminiferous tubules of the testis; they function as 'nurse cells' for developing spermatozoa.
Testis
The primary male reproductive organ because it produces spermatozoa and the male reproductive hormone testosterone.
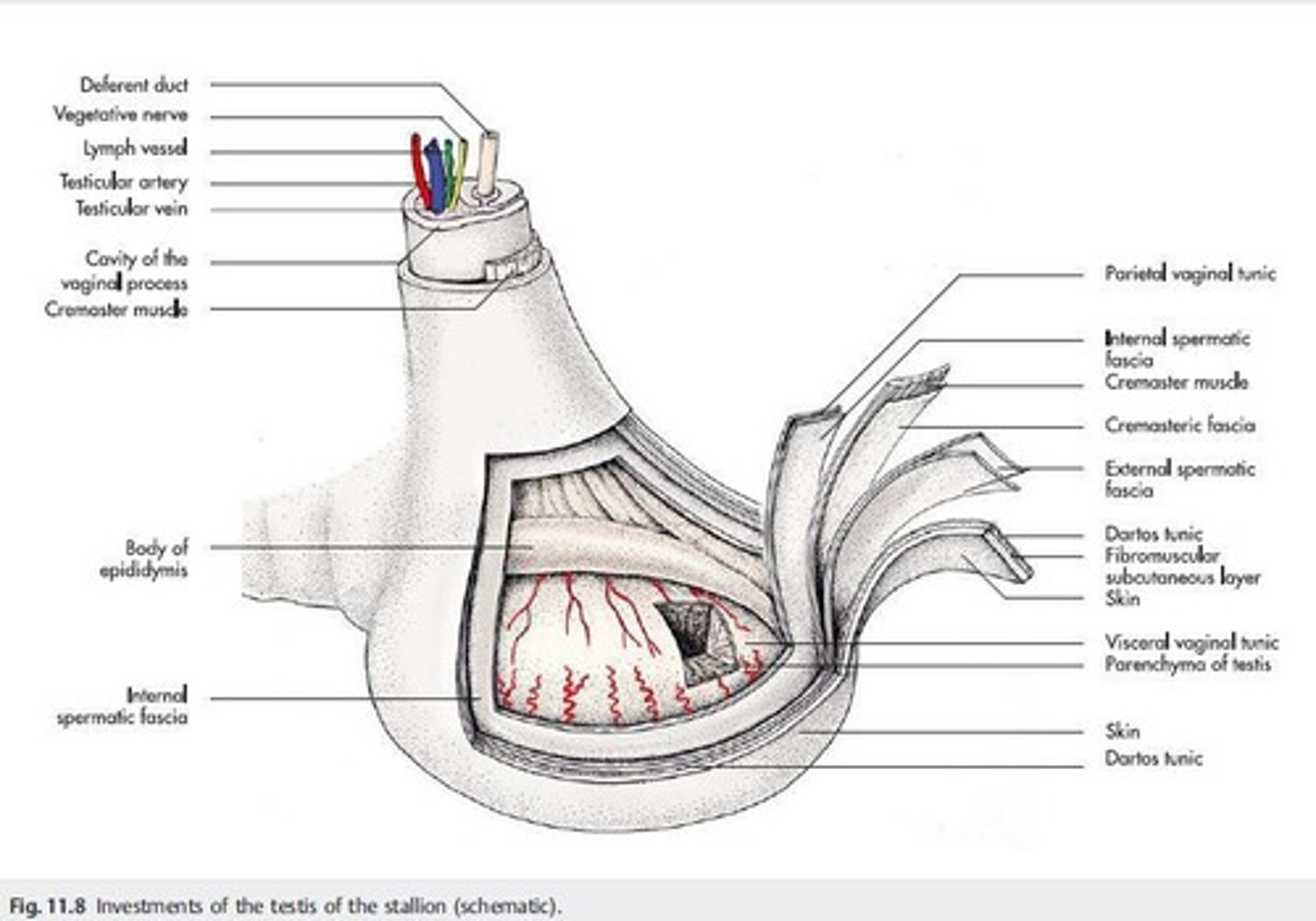
Vas deferens
Connects the epididymis with the urethra; provides an environment suitable for survival of spermatozoa and the additions of the secretions of the accessory glands resulting in semen.
Seminiferous tubules
Hollow structure in which the germ cells differentiate to spermatozoa.
Epididymis
A coiled structure also in the scrotum; functions include storage of quiescent but live spermatozoa before ejaculation, maturation of spermatozoa, and addition of nutrients to the semen for spermatozoa to use for movement.
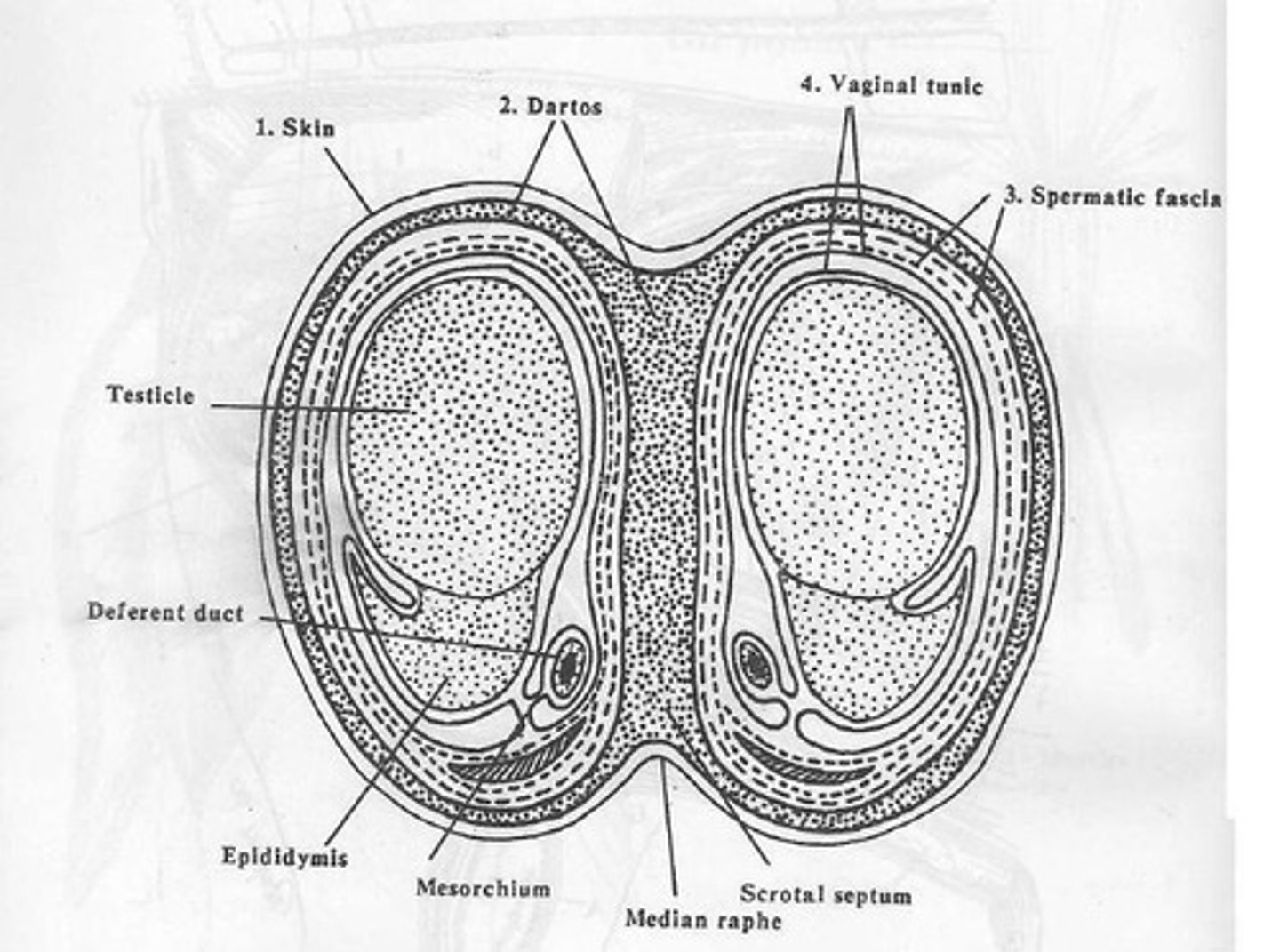
Male accessory sex glands
Situated along the pelvic portion of the urethra; comprises of vesicular gland, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands; it varies depending on species.
Ampullary gland
Surrounds the terminal part of the ductus deferens.
Seminal vesicles
Produces secretions that are added to the spermatozoa.
Capacitation
The process that spermatozoa undergo to gain the ability to fertilize an egg after ejaculation.
Fructose
A sugar present in seminal fluid that provides energy for spermatozoa.
Prostaglandins
Compounds in seminal fluid that stimulate contraction of the female reproductive tract.
Prostate Gland
Gland that produces slightly alkaline secretions added to spermatozoa to neutralize lactic acid.
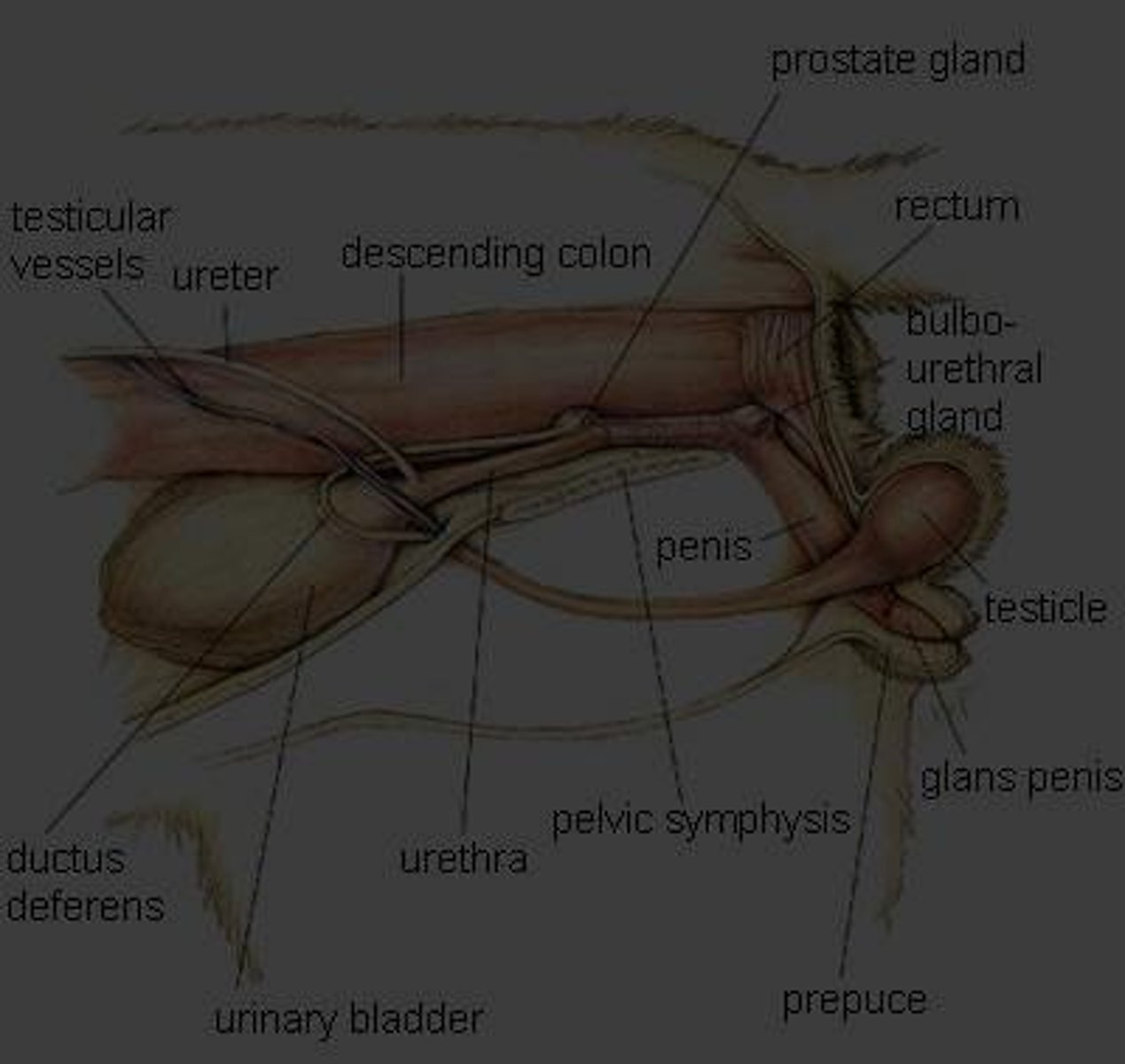
Bulbourethral Gland
Gland found in all domestic animals except dogs, located in the dorsal aspect of the pelvic urethra.
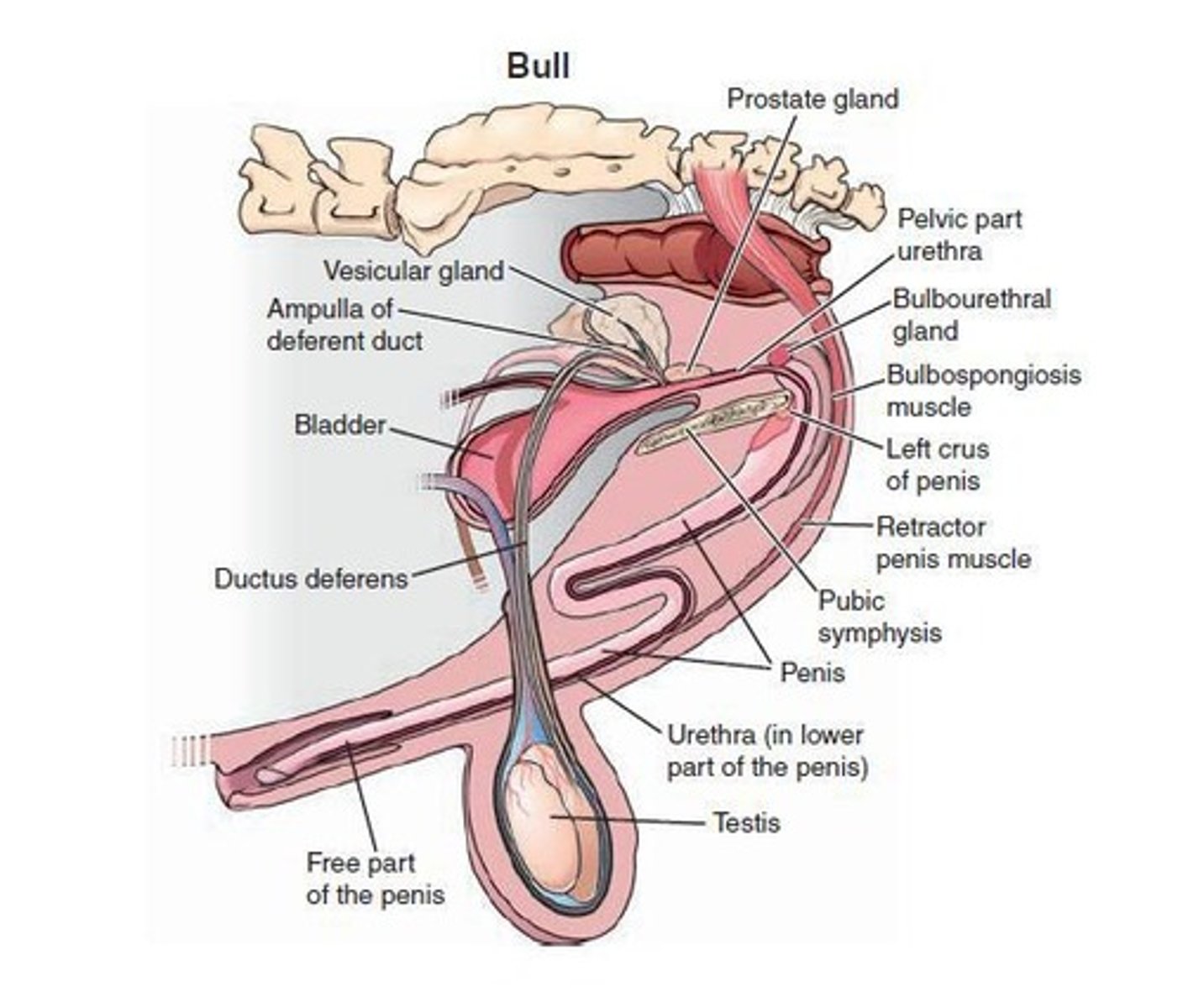
Accessory Sex Glands
Glands with well-developed soft tissue capsules and internal septum, rich in smooth muscle fibers responsible for expelling secretions.
Urethra
Tube that connects the bladder and vas deferens, through which urine and semen are expelled.
Corpus Cavernosum
Spongy tissue surrounding the urethra in the penis that becomes rigid during sexual arousal.
Sigmoid Flexure
A structure in bulls, rams, and boars that aids in extending the penis from the sheath.
Os Penis
A bone found in the penis of dogs, cats, and most primates that facilitates erection.
Fibroelastic Penis
Type of penis with small blood spaces divided by tough fibroelastic tissue, enclosed by thick tunica albuginea.
Musculocavernous Penis
Type of penis with larger blood spaces and a more delicate tunic, requiring a larger volume of blood for erection.
Prepuce
The cutaneous sheath around the free part of the penis in a quiescent state.
Cowper's Gland
Gland also known as the bulbourethral gland, which secretes fluid to clean the urethra.
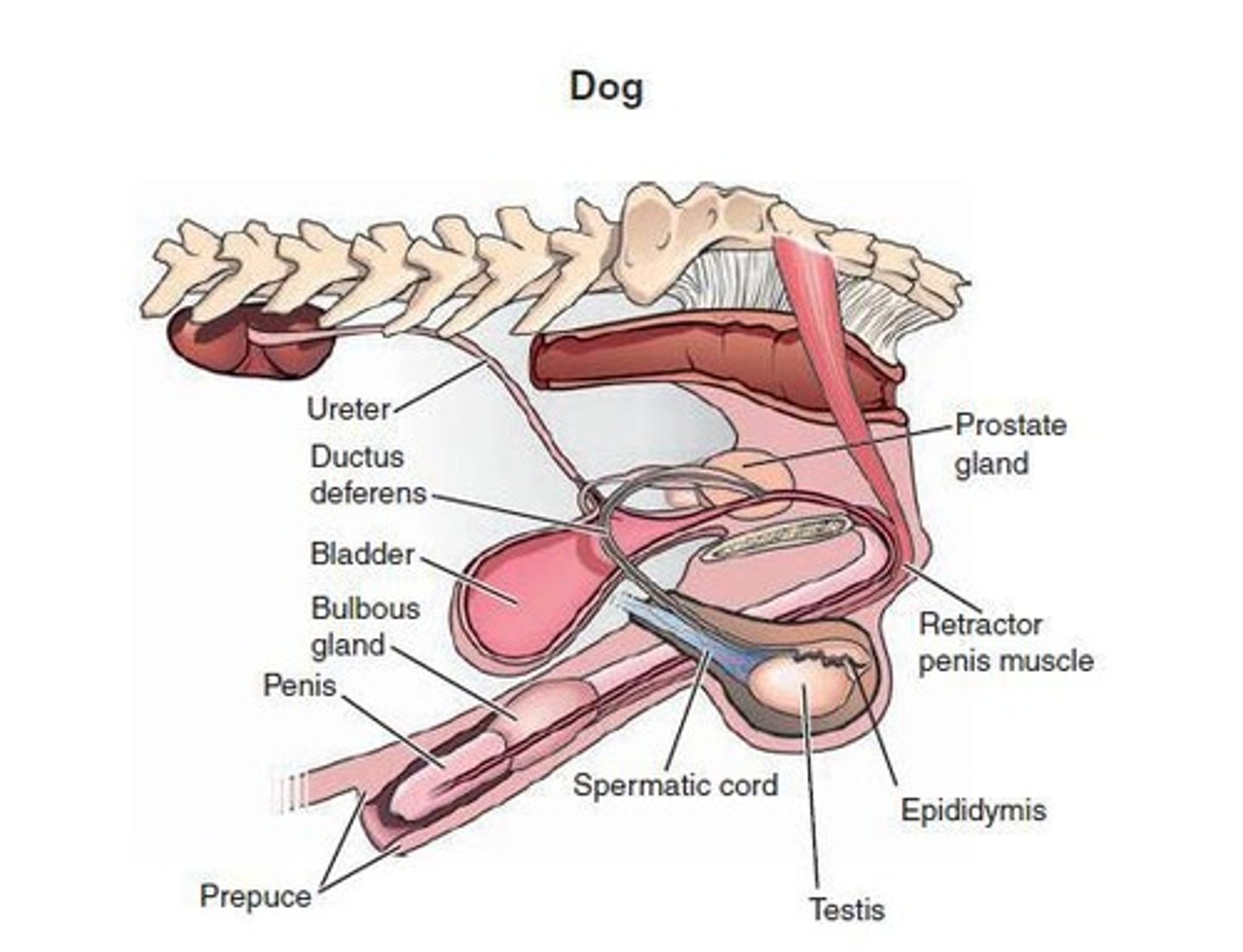
Pudendal Nerve
Nerve that delivers sensory input to the spinal cord, playing a role in erection and ejaculation.
Nitric oxide
Activates relaxation of corporal cavernosal smooth muscle tissue resulting in increased blood flow into the penis resulting in an erection.
Autonomic nerves
Involved with emission of seminal fluid.
Motor input
To the bulbospongiosus muscles causes expulsion of seminal fluid.
Spinothalamic nerves
Involved with integrating complex signaling related to reproduction.
Avian male reproductive tract
Entirely inside the body.
Testes
Produce sperm and then sperm travels through a vas deferens to the cloaca.
Papillae
Serve as the mating organs in avian males.
Castration in roosters
Called caponization.
Ovary
Principal function is to produce ova; develops in follicles associated with other cells.
Follicle development stages
Develops from primary, to secondary, to tertiary follicle.
Graafian follicle
Fully mature follicle that produces estradiol.
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Stimulated by estradiol and triggers ovulation of ova.
Zona pellucida
Thin membrane surrounding the ovum during ovulation.
Corpus hemorrhagicum
Remnants of a follicle after ovulation that first forms a bloody or red body.
Luteolysis
Process by which the corpus luteum breaks down for the corpus albicans.
Infundibulum
Catches the ovum in the oviduct.
Oviduct
Functions to move the ovum to the uterus and is the site for fertilization.
Zygote
The ovum after fertilization.
Uterus
Site where the embryo implants and the fetus develops.
Endometrium
Glandular layer of the uterus.
Myometrium
Layer of smooth muscles in the uterus.
Bicornuate uterus
Has two large uterine horns, a uterine body, and a single cervix, found in porcine, canine, feline, ruminants, and equine.
Pyometra
Life-threatening, inflammatory bacterial infection of the uterus in mature intact female canines.
Cervix
Barrier between the uterus and vagina, normally constricted with a mucus plug.
Vagina
Site for insemination and becomes part of the birth canal during the birth process.
Vulva
External opening consisting of labia majora, labia minora, and clitoris.
Hen reproductive system
In almost all species of birds, only the left ovary and oviduct are functional.
Magnum
It functions by adding concentrated egg white proteins and membranes to the egg. The ovum spends 2-3 hours here.
Isthmus
It functions by adding fluid to egg white. The ovum spends 1-2 hours here.
Germ cells
Cells that give rise to gametes and play a key role in sexual differentiation by affecting gonad development.
Sex-determination system
A biological system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism.
XY sex chromosomes
Mammals having XY (or much less commonly XXY) sex chromosomes will develop testes.
XX or X0 individuals
Develop as a female with two ovaries.
Sry gene
The principal gene controlling the sex of a mammal, located on the Y chromosome, which in virtually all cases leads to the development of testes.
W and Z chromosomes
Female birds have a W and Z chromosome, and males have two Z chromosomes.
Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
A modified peptide with 10 amino acid residues, also called LH-releasing hormone.
Gonadotropin Inhibiting Hormone (GnIH)
Inhibits the release of both gonadotropins, LH and FSH, in both mammals and birds.
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
A glycoprotein hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland.
Testosterone
The male sex hormone, a steroid synthesized from cholesterol.
Estrogens
Female sex hormones such as estradiol, estrone, and estriol, produced by the follicle before ovulation.
Oxytocin
A peptide hormone produced by the posterior pituitary gland that causes uterine contractions during the birthing process and milk to be let down from the mammary gland.
Gametogenesis
A biological process by which diploid or haploid precursor cells undergo cell division and differentiation to form mature haploid gametes.
Spermatogenesis
Occurs throughout the life of the male animal, except in seasonal breeders when it is restricted to the breeding season.
Oocytes
The number of oocytes in the ovary is established at birth.
Follicular Atresia
Loss of oocytes after ovulation or by cell death.
Cell Division
Requires duplication of the genome by mitosis (or meiosis).
Nuclear Mitochondria Replication Factors
Released from the nucleus to stimulate mitochondrial multiplication.
Meiosis
A type of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms that reduces the number of chromosomes in gametes (the sex cells, or egg and sperm).
Hormones Required for Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis requires the hormone FSH and testosterone.
Processes of Spermatogenesis
Involves three distinct processes as the cells progress from primary spermatocytes, to secondary spermatocytes, to spermatids, to sperm.
Oogenesis
Begins when the 2n oogonium undergoes mitosis, producing a primary oocyte.
Primary Oocytes
Arrest in prophase I before birth.
Secondary Oocyte
Results from meiosis of one oocyte per menstrual cycle, arrests in metaphase II and produces a polar body.
Completion of Meiosis
Occurs upon ovulation and sperm entry, resulting in a polar body and a fertilized egg.
Development of the Follicle
Maturation of a follicle proceeds from primordial follicles.
FSH and LH Roles
FSH stimulates the growth of a tertiary follicle, and LH stimulates the production of estrogen by granulosa and theca cells.
Mature Follicle
Ruptures and releases the oocyte.
Corpus Albicans
A scar on the surface of the ovary that is a remnant of ovulation.
Primary Follicle
The oocyte is surrounded by a single layer of cuboidal cells and a basement membrane.
Bovine Oocytes Size
Normally about 0.1 mm in diameter.
Secondary Follicle
Located near the surface of the ovary, with the oocyte usually about 120 μm in diameter.
Pre-ovulatory Follicle
Bulges from the surface of the ovary before ovulation and contains the ovum surrounded by zona pellucida and cumulus oophorus.