psych 1100 exam 3 lundquist *non-cumulative*
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
long term memory
(duration and storage capacity)
duration: permanent
storage capacity: infinite (hypothetically)
short term memory
(duration and storage capacity)
duration: seconds to minutes
storage capacity: 7+/- 2 chunks
working memory
short term memory
chunks
organized packets of info in STM
3 aspects of memory process
acquisition
storage
retrieval
acquisition
In order to remember, you must learn something
storage
to be remembered, an experience must leave some record in the nervous system
memory trace
record of experience
retrieval
the process through which you retrieve info from memory in response to some cue or question
2 kinds of retrieval
recall and recognition
recall
type of retrieval that requires you to produce an item from memory in response to a cue or question
recognition
type of retrieval that requires you to judge whether you have encountered a stimulus previously
acquisition
the processes of gaining new info and placing it in memory
intentional learning
placing new info into memory in anticipation of being tested on it later
incidental learning
learning w/out trying to learn, and often without awareness that learning is occurring
primacy effect
early part of list recalled better than middle part
is recalled from LTM- more time for rehearsal
recency effect
last part of list is recalled better then middle part
is recalled from STM- still part of chunks
how to reduce primacy
present words faster
how to reduce recency
elongate time before recall
maintenance rehearsal
mechanical process of repeating the memory items over and over, giving little thought to what the items are or whether or not they form a pattern
importance of active engagement
help to expand capacity of LTM
*penny example
shallow processing
an approach to memorization that involves focusing on the superficial characters of the stimulus, such as the sound of a word or the typeface in which it was printed
ex: is the word printed in capital letters
deep processing
an approach to memorization that involves focusing on the meaning of the stimulus
ex: would it fit into this sentence?
Craik and Tulving's findings
deep processing results in the best recall
relative context allows for better meaning processing and therefore better recall
memory trace
physical record in the nervous system that preserves memory
memory consolidation
biological process through which memories are transformed from a fragile status to a more permanent and robust state, according to most researchers, consolidation occurs over the course of several hours
retrograde amnesia
a memory deficit, often suffered after a head injury, in which the patient loses memory for events that occurred before the injury
STM
phonological- based on speech sounds
will confuse boat with coat
LTM
semantic- based on meaning
confuse "boat with ship"
STM neural code
dynamic- pattern of activity among a group of cells
LTM neural code
structural- pattern of connections within a group of cells
retrieval
process of searching for a memory and finding it
retrieval failure
apparent forgetting
tip of the tongue (TOT) effect
partial retrieval
the condition in which one remains on the verge of retrieving a word or name but continues to be unsuccessful
information is in storage but it is inaccessible
retrieval cue
hint or signal that helps one to recall a memory
retrieval paths
mental connections linking one idea to the next that people use to locate a bit of information in memory
example of good and bad retrieval paths with list of words studied based on sound
was there a word that rhymed with log? good retrieval path to dog
was there a word that is an animal with sharp teeth? bad retrieval path to dog
contextual reinstatement
way of improving retrieval by re-creating the state of mind that accompanied the initial learning
is it the return to an environment that improves recollection?
no, it is the recreation of the mental context of learning
just thinking about the original environment will help retrieval
retention interval
the time that elapses between learning and retrieval
Ebbinghaus
tested his memory by studying random syllables and testing himself
plotted a forgetting curve
forgetting curve
graphic pattern representing the relationship between measures of learning and the length of the retention interval; as the retention interval gets longer; memory decreases
effect of retention interval
(2 ideas for why old memories are lost)
1. passage of time itself- memory decays over time
2. new learning- new info getting added to long term memory somehow disrupts the old info that was already in storage
intrusion errors
memory mistakes in which elements that were not part of the original info get mixed into ("intrude into") someone's recall
misinformation effect
result of a procedure in which, after the experience, people are exposed to questions or suggestions that misrepresent what happened. The term refers to people's tendency to include the misinformation as part of their recall of the original experience
what can lead to the misinformation effect?
misleading questions and giving false details
schema
an individual's mental representation that summarizes her knowledge about a certain type of event or situation
example of intrusion from schematic knowledge:
most professor's offices have books
>may recall seeing a bookshelf that was not there
DRM paradigm
common procedure for studying memory, in which participants read and then immediately recall a list of related words, but the word providing the theme for the list is not included
example of intrusion from semantic associations:
given a list of words: bed, rest, tired, blanket, snooze, nap, snore
when asked to recall list> most falsely recall sleep since it is a common word/idea that shares significance with the list
familiarity
general sense that a certain stimulus has been encountered before
recollection
recall of the context in which a certain stimulus was encountered
do familiarity and recollection learning processes occur in the same place?
no- can lead to issues of one failing but the other succeeding
explain: staged crime example
Witness a stage crime > shown mugshots (none of which from crime) > brought in for a line up- will usually identify someone from the mugshots because of sense of familiarity- where they are remembering them from is wrong
familiarity is successful but recollection is failing
STM forgetting
displacement and or decay
LTM forgetting
misplacement and or retrieval failure
proactive interference
old info affect new
retroactive interference
new info affects old
working memory is not a limit on storage capacity, but rather a limit on...
processing capacity
maintenance rehearsal: STM or LTM?
elaborative rehearsal: STM or LTM?
m: STM
> repeating a phone number until you dial it
e: LTM
> thinking about meaning and how it would fit into a sentence
explicit memory
conscious memories that can be described at will and can be triggered by a direct question
implicit memory
memories that we may not recall consciously, but that are still demonstrable through an indirect test
episodic memory
form of explicit memory
memory for specific events and experiences
semantic memory
form of explicit memory
memory for facts (including word meanings); these memories are not tied to any specific time or place
example of episodic memory
my 7th birthday was at Funplex
example of semantic memory
George Washington was the first president of the United States
flashbulb memories
form of episodic memory; vivid, detailed memories said to be produced by unexpected and emotionally important events
why are flashbulb memories remembered so vividly?
Most likely rehearsal (the story being told over and over) that makes it memorable
anterograde amnesia
a memory deficit suffered after some kinds of brain damage, in which the patient seems unable to form new explicit memories; however, memories acquired
what kind of memory is lost and which is preserved with anterograde amnesia
explicit memory is lost
implicit memory is preserved
patient HM
had hippocampus and amygdala removed to treat epilepsy
> Epilepsy was treated
> Could not put new memories into long term
declarative memory
knowledge of info that can be expressed in words
example of declarative memory
knowing cars run on gas
procedural memory
knowledge of how to do something, such as riding a bike; expressed in behaviors rather than in words
example of procedural memory
knowing how to ride a bike
diff. between explicit and implicit
explicit is a reference to prior knowledge- requires retrieval
implicit has no conscious awareness of remembering- is a result of priming
diff. between episodic and semantic/generic
episodic: events or events of memory
semantic/generic: common knowledge you have gained, but you don't remember gaining it
diff. between declarative and procedural
declarative: information you know that you can explain
procedural: skills you know, but it would be hard to explain how to do
priming effect
An encounter with a stimulus leaves us better prepared for that stimulus the next time we meet it
perceptual learning
another form of implicit memory; having to "recalibrate" your perception to the world
ex: getting new glasses and your eyes learning to adjust to them
propositions
statements relating to a subject and a claim about that subject
node
in network-based models of mental representation, a "meeting place" for the various connections associated with a particular topic
the symbol
association link
in network-based models of mental representation, connections between the symbols (or nodes) in the network
spreading activation
the process through which activity in one node in a network flows outward to other nodes through associative links
presented with 2 strings of letters and told to determine if both strings are real words
Will say yes faster for NURSE-DOCTOR than GARDEN-DOCTOR
>Nurse activated association link that is closely connected to doctor
Form of priming*
sensation
basic, primitive mental state corresponding to energies in environment; experience in the world
perception
mental state corresponding to properties of objects and events in environment; knowledge of the world
distal stimulus
an object of event in the outside world; typically at a distance from the perceiver
proximal stimulus
energies from the outside world that directly reach our sense organs
empiricist's view
learning- experience teaches us how to interpret 2D proximal stimulus
active perceiver concept
mind organizes sensory info into pre existing categories
pyschophysics
approach to perception that relates the characteristics of physical stimuli to the sensory experiences they produce
absolute threshold
smallest quantity of a stimulus that an individual can detect
difference threshold
smallest amount that a given stimulus must be increased or decreased so that an individual can detect the difference
just-noticeable difference (jnd)
smallest difference that an organism can reliably detect between 2 stimuli
Weber's Law
observation that the size of the difference threshold is proportional to the intensity of the standard stimulus
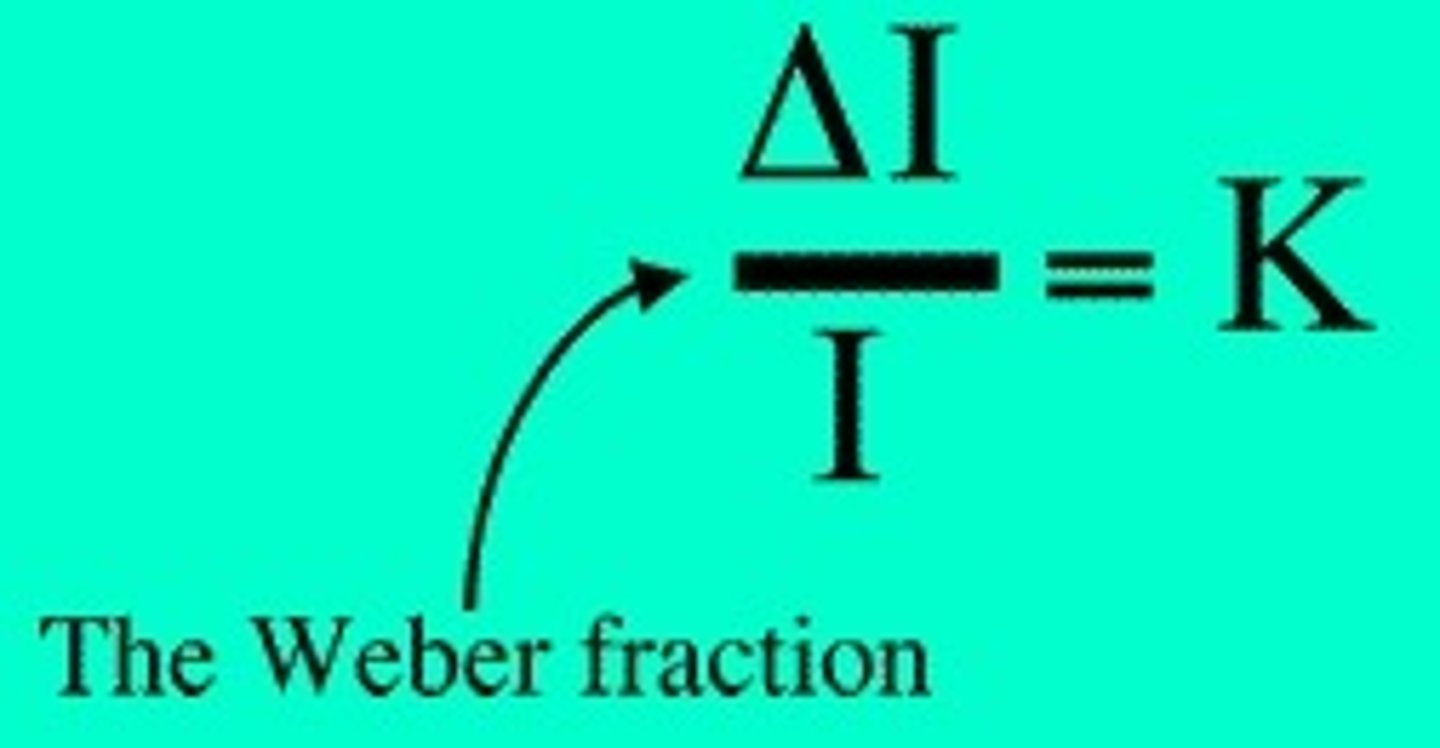
what is weber's law used for?
to compare sensitivities of different sensory modalities
the smaller the weber fraction
the more sensitive the sense modality is
Fechner's law
observation that the strength of a sensation is proportional to the logarithm of physical stimulus intensity
transduction
process through which a physical stimulus is converted into a signal within the nervous system