SSS Week 2
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Risk factors for bacterial infections
skin barrier disruption (trauma, insect bites)
moist, macerated environments (common in warm, occluded areas such as the axilla and groin)
colonisation with skin flora pathogens
impaired host defenses
What causes impaired host defenses
Metabolic - diabetes mellitus
Vascular insufficiency - Peripheral arterial disease, chronic venous insufficiency (varicose veins)
Immunodeficiency - HIV/AIDS, malignancy, immunosuppressive therapy eg. glucocorticoids
Impetigo
staph
~ most common in young children (but occurs at any age)
~ less commonly caused by strep pyogenes
~ spreads in warm moist environments with close physical contact and poor hygiene
Two presentations
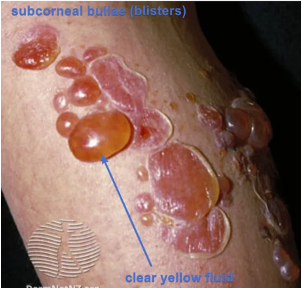
1 Bullous (SUBCORNEAL BULLAE)
~ thin-roofed bullae with clear yellow fluid which rupture quickly leaving exudative and yellow brown crust erosions
~ more likely to have systemic symptoms of malaise, fever, and lymphadenopathy
[staph attacks intracellular adhesion molecules in stratum granulosum, causing bullae formation – explored later]
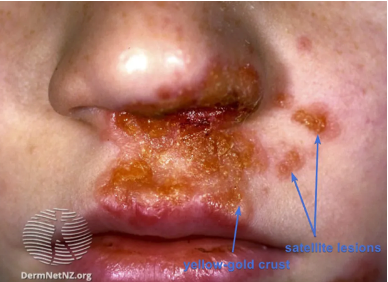
2 crusted or non-bullous (most common)
~ begins with a single erythematous macule which evolves into a pustule or vesicle
~ pustule or vesicle ruptures releasing serous contents which dries leaving honey-coloured crust
~ has satellite lesions due to autoinoculation
what areas of skin are prone to impetigo? broken by insect bites. superficial injury, excoriated eczema
complications?
Can trigger post-strep glomerulonephritis and rheumatic heart disease
Can grumble on for several weeks and lead to deeper ulcerated and scarring infection called Ecthyma
general measures - TREATMENT
cover affected areas with watertight dressing to prevent spread
hand hygiene
school exclusion (until at least 24 hours after starting appropriate antibiotic treatment)
TOPICAL: for localised non-bullous impetigo, antiseptic recommended for 5-7 days… if ineffective or not appropriate (if around eyes) topical antibiotics can be considered (fusidic acid 1st, mupirocin - reserved for MRSA infection)
SYSTEMIC: fluclox (1st)
alternatives may include trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole or erythromycin (for MRSA infection or if penicillin allergy)
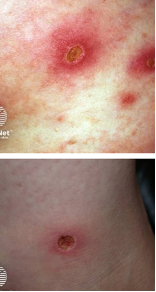
Ecthyma
Hard crusted sores beneath which ulcers form
~ begins as a vesicle or pustule on inflamed skin
~ removal of crust reveals red, swollen, indurated ulcer oozing with pus
Community-acquired MRSA
mostly occurs
~ in overcrowded places, due to frequent contact of skin and sharing things
~ in people with draining cut or sore or that are carriers of MRSA
Management
~ swab for MCS
PCR
Surgical drainage if required
Clindamycin or trimethoprim/sufamethoxazole
For severe infections vancomycin is indicated
Clinical features of hospital acquired MRSA
~ present as skin infections (abscesses, furuncles and carbuncles, impetigo and cellultiis) or as wound infections (at trauma and surgical sites)
Whereas
Clinical features of community-acquired MRSA mainly presents as bacterial folliculitis, boils, impetigo
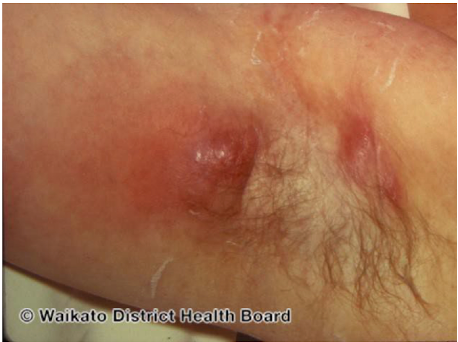
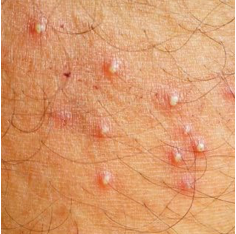
Folliculitis
Inflamed hair follicles
Presentation
~ tender red papule or pustule centred on a hair follicle
~ more common in hot weater
~ often occurs in macerated areas
~ look at centre of the inflammatory papule for protruding hair shaft

Shaving and waxing common triggers
Investigation
MCS
Skin scraping for fungus
Hair pull test (if fungal scalp involvement suspected)
Treatment
• Depending on the organism or cause.
• Physical factors such as occlusive clothing, grease or massage oils or in a child case nappies need to be managed.
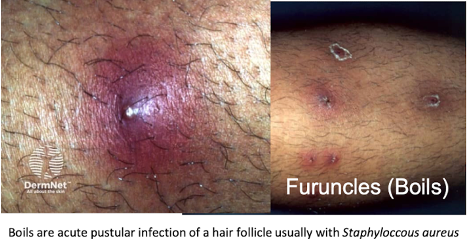
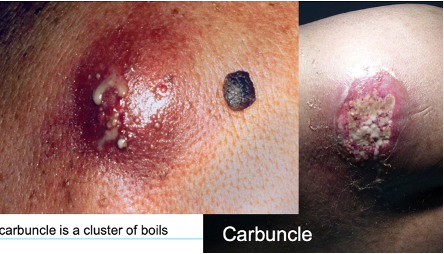
Furuncles and carbuncles
deep form of bacterial folliculitis
~ furuncles (boils) present as single or multiple tender, red, firm or fluctuant nodules or walled-off abscesses which eventually point and discharge pus from a central core
~ carbuncles are when multiple furuncles coalesce and extend to the subcutis
~ carbuncles often have systemic signs (malaise, chills, fever)
Treatment
~ apply topical antiseptic like povidone iodine or chlorhexidine cream
Then cover with gauze
~ oral antibiotics: fluclox, cephalexin
~ incision and drainage
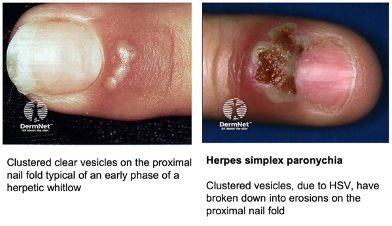
Acute vs chronic paronychia
Acute paronychia
~ common in nail biters and those with chronically wet hands
Presentation
~ nail fold becomes painful, red and swollen, sometimes yellow pus under cuticle
Treatment
~ drainage with sterile needle, application of a topical antibiotic, sometimes oral
Acute herpetic paronychia
~ caused by HSV
Chronic paronychia
~ chronic irritant dermatitis and C.albicans superinfection
~ may start on one and spreads to several others
~ affected nail fold is swollen and lifted off nail plate
~ becomes distorted and ridged as it grows. May become yellow or green and brittle
~ common in people with chronically wet hands, such as bar tenders and housewives
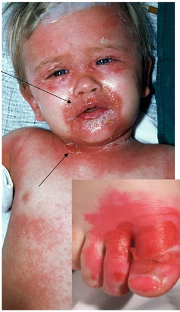
SSSS
~ characterised by erythematous painful blistering
~ skin looks like a burn or ‘scald’
~usually from a local infection eg. impetigo
Treatment: systemic antibiotics
Mechanism of Staph to cause SSSS
~ release of epidermolytic toxins A and B from staph
~ toxins target desmoglein-1 (a cell adhesion protein) in the stratum granulosum
~ leads to intraepidermal splitting
~ results in blistering, skin peeling and positive nikolsky sign
What is Nikolsky’s sign?
shearing stress of skin causes separation of skin, results in traumatic bulla
Toxic shock syndrome
~ caused by release of exotoxins from staph and can also be caused by s.pyogenes
~ presents with sudden high fever, widespread erythematous rash, and multi-organ involvement
~ may lead to circulatory collapse
~ classically linked to tampon use but can arise from skin or wound infections
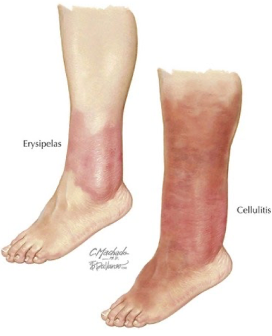
Cellulitis vs erysipelas
Cellulitis
~ acute diffuse spreading skin infection (what ur brother had)
Erysipelas
~ skin infection involving upper dermis with clearly delineated borders, eg. butterfly rash
Both present with localised redness, pain, swelling and +/- systemic symptoms (fever)
~ usually caused by s.pyogenes (GAS)
~ if around a wound, consider staph
~ periorbital cellulitis can occur in children (like ur bro) usually S.pyogenes. his was HSV, Hib is now rare due to vaccination
Cellulitis presentation
~ more raised n swollen, less marginated, favours lower legs in adults, and for children, limbs and periorbital region
Predisposition for cellulitis
On legs (lymphoedema, tinea of feet, chronic dermatitis, poor lower leg circulation arterial and venous, wounds)
On face: Herpes simplex infection, dental caries, chronic sinus infection, more common in diabetics, immunosuppression)
Treatment:
rest and elevation of area
analgesia
oral or IV antibiotics eg. cephalexin, fluclox, penicillin-dependent on sensitivities
Presentation for erysipelas
~ may see lymphatic streaking
~ blisters may develop on red plaques
~ most commonly affects lower limbs
Treatment:
Oral antibiotics or IV if severe, usually penicillin
Necrotising fasciitis
~ infection of soft tissue and fascia
~ presents as a dusky cellulitis which progresses to extensive necrosis
~ bacteria multiplies and releases toxins and enzymes that results in thrombosis in blood vessels destruction of soft tissues and fascia
~ due to mixture of staph, strep and anaerobes?
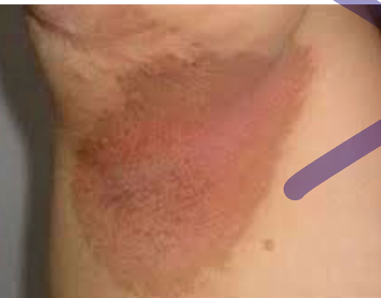
Erythrasma
~ in skin folds, axilla or groin or between the toes
~ macular wrinkled, slightly scaly, pink, brown or macerated
~ WOODS LIGHT: CORAL PINK
Treatment:
Fusidic acid cream, whitfield ointment, clindamycin solution
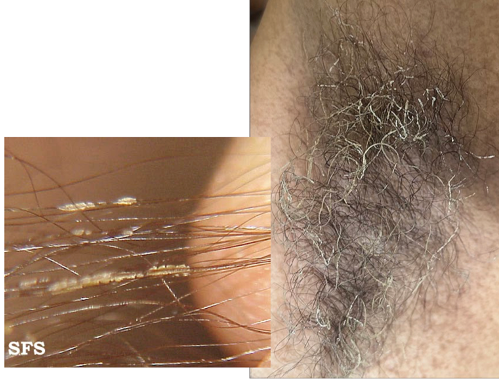
Trichomycosis Axillaris
Infection of underarm hair
~ characterised by yellow, black or red granular nodules or concretions that stick to hair shaft
~ caused by overgrowth of corynebacterium
~ topical antibiotics and shaving
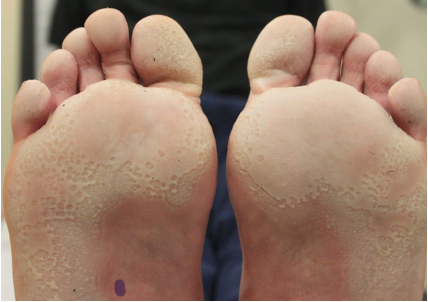
Pitted keratolysis
~ combination of unusually sweaty feet and occlusive shoes encourages growth of microorganisms that digest keratin
~ results in honeycomb like pits in webs and toe pulps, forefott and heel
~ often with offensive odour
Treatment
~ keep feet dry
~ topical clindamycin, erythromycin, fuscidic acid
~ oral macrolides