Skull and Spine Radiology
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
How to radiograph the skull or spine of small animals?
- Anesthesia/heavy sedation required
- accurate positioning is essential
- Lateral, VD/DV, obliques,rostrocaudal
• Vertical beam
• Understand the way tomake images
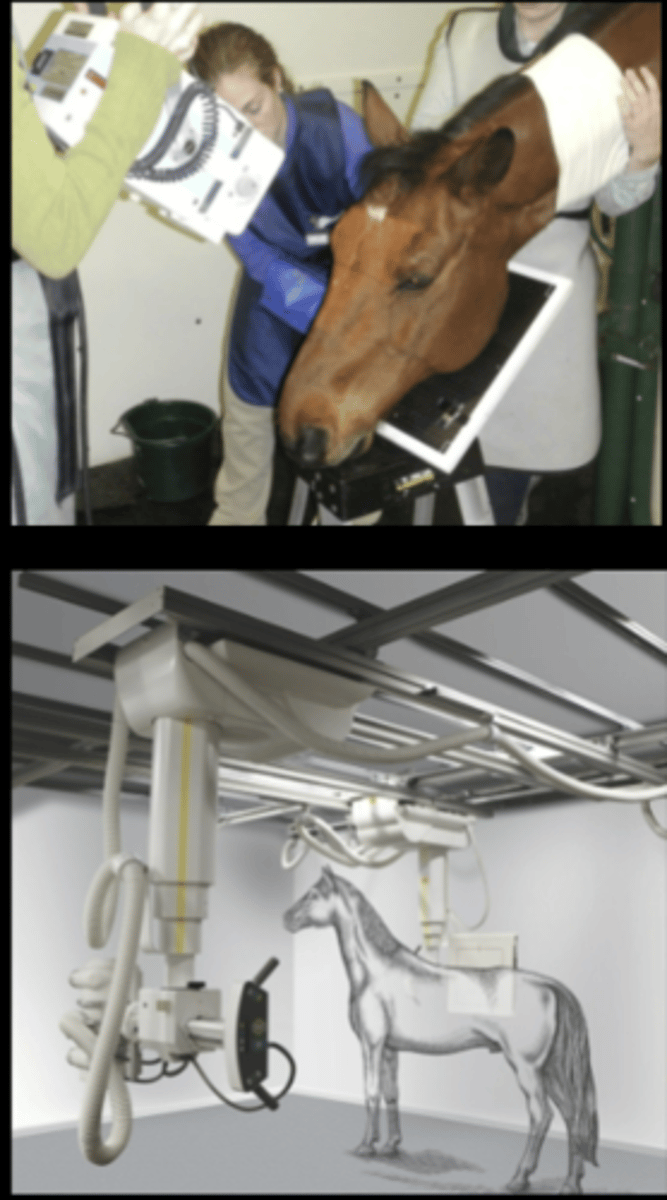
How to radiograph the skull or spine of large animals?
- Sedation necessary
- done standing (rarely recumbent)
- Lateral, DV, obliques
• Horizontal Beam (mostly)
- Overhead tube
- Portable generator
• Understand the way to make images

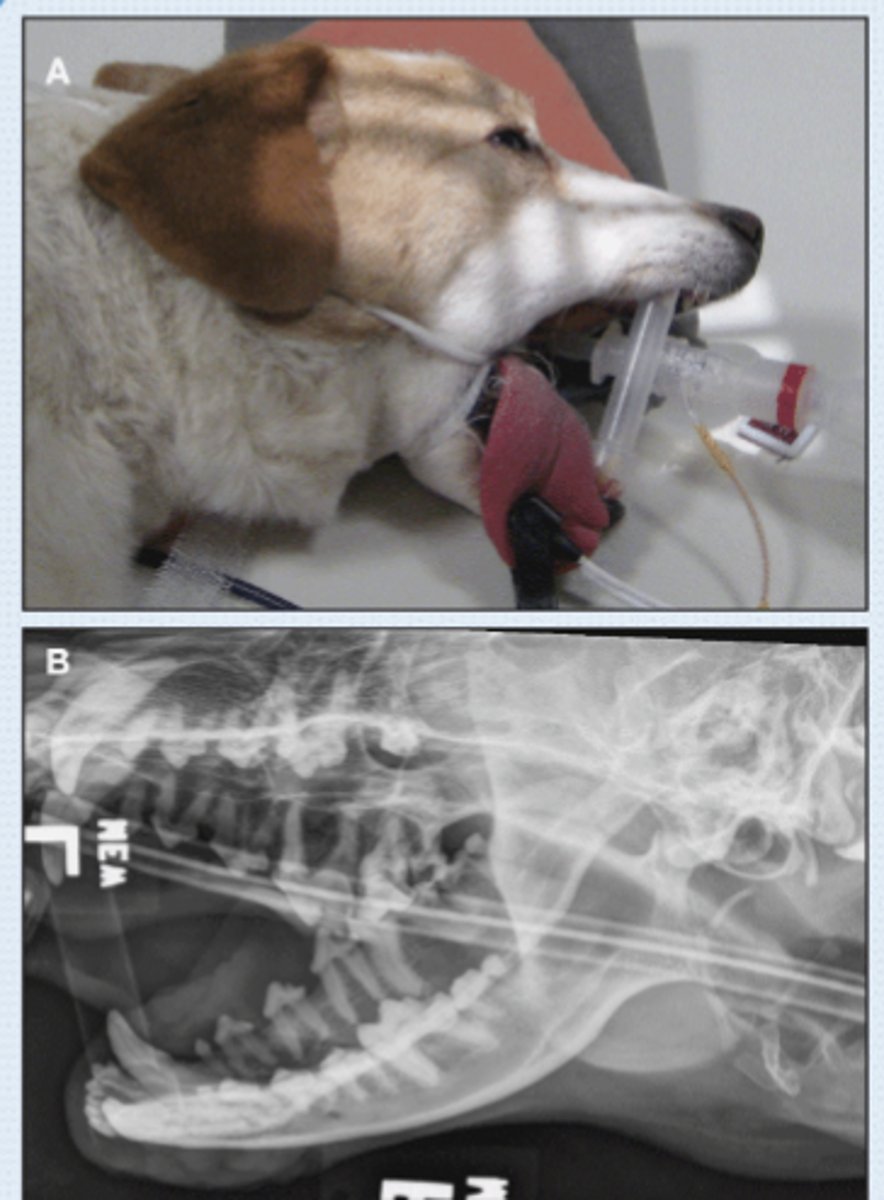
SM Animal- Lateral Image
• Patient in lateral recumbency
• Marker to indicate laterality of patient
SM Animal Skull- VD image
• Patient in dorsal recumbency
• Markers to indicate laterality
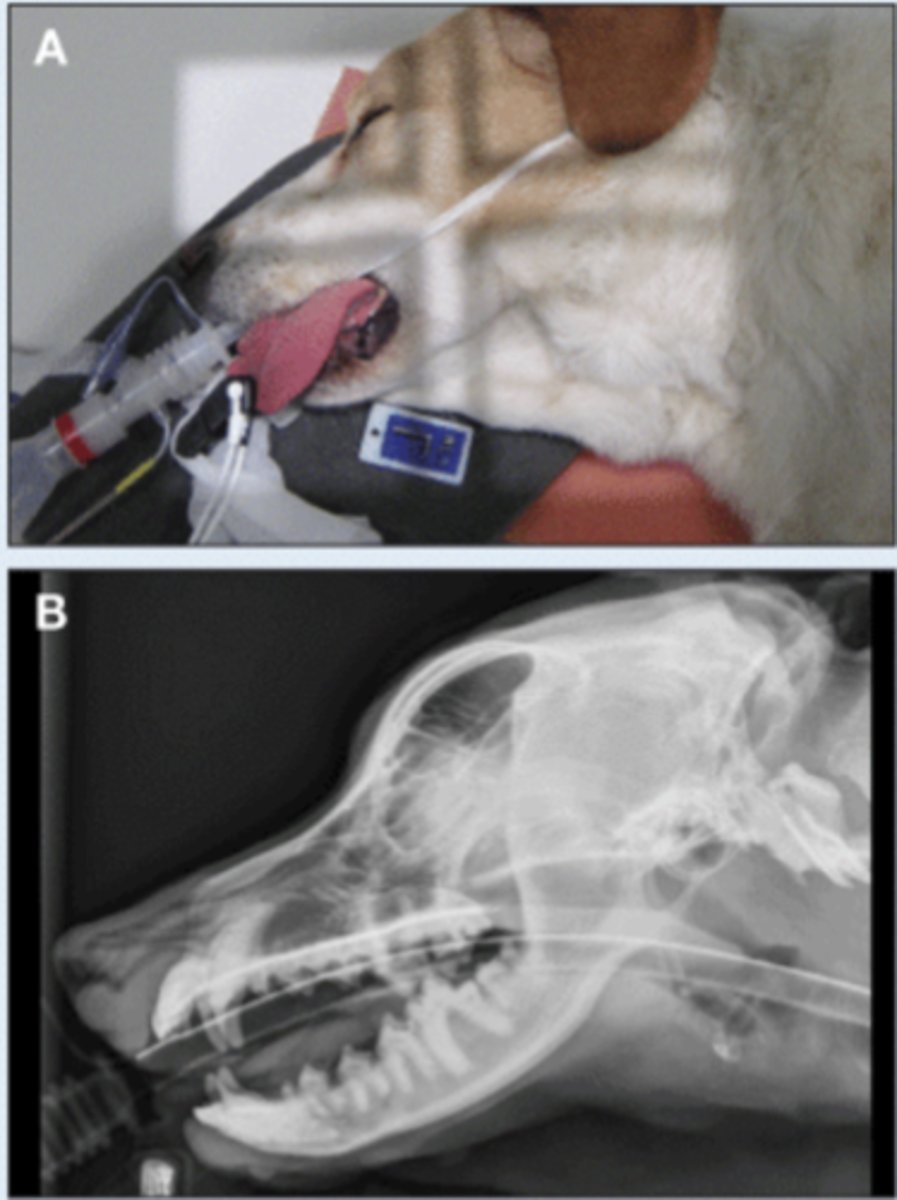
SM Animal Skull- Open mouth VD image
• Patient in dorsal recumbency
• Mouth open
• Tube angled toward nose
• Markers to indicate laterality

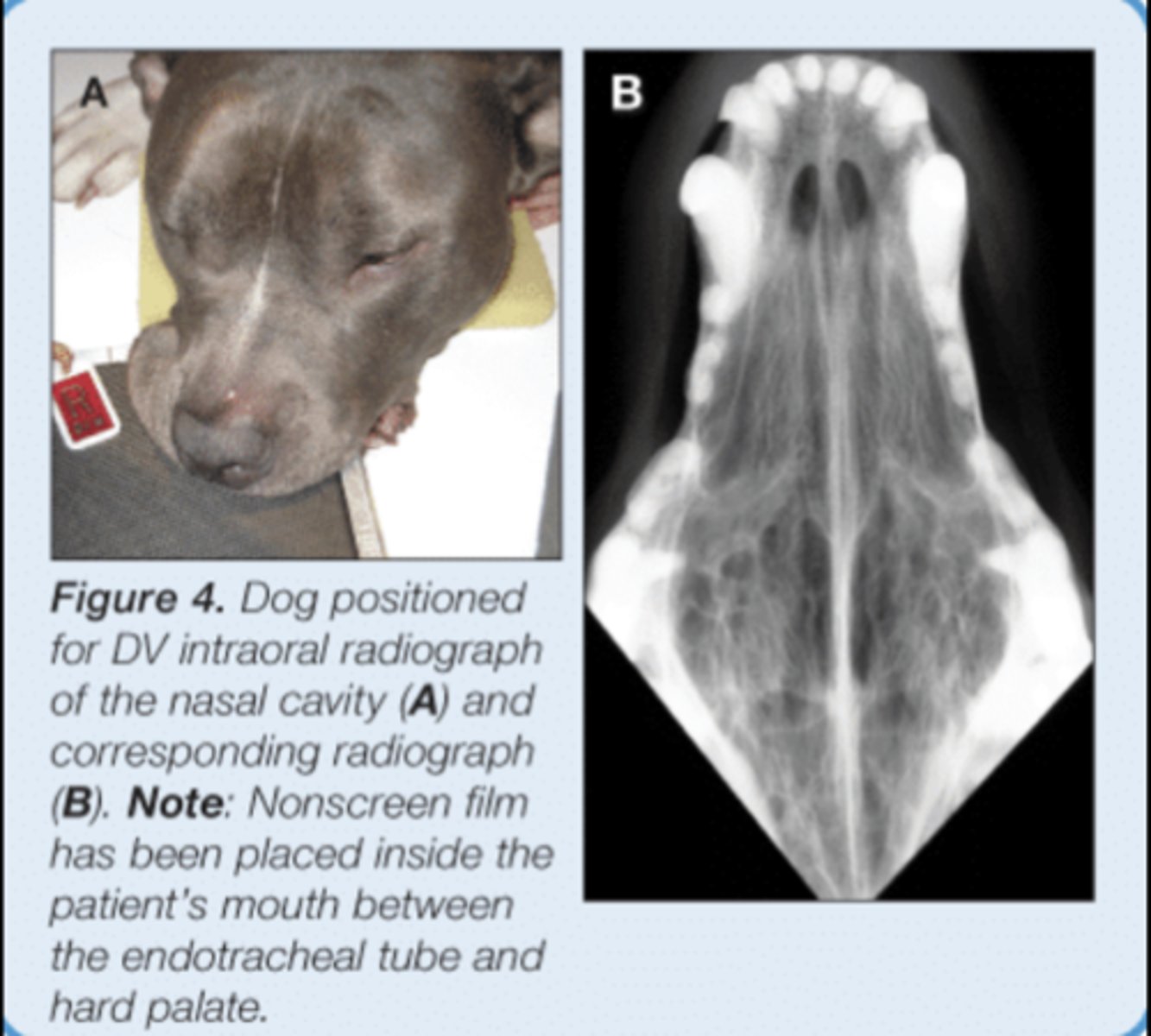
SM Animal Skull - Intraoral DV image
• Patient internal recumbency
• Plate in mouth - May not be possible with digital plates
• Markers to indicate laterality
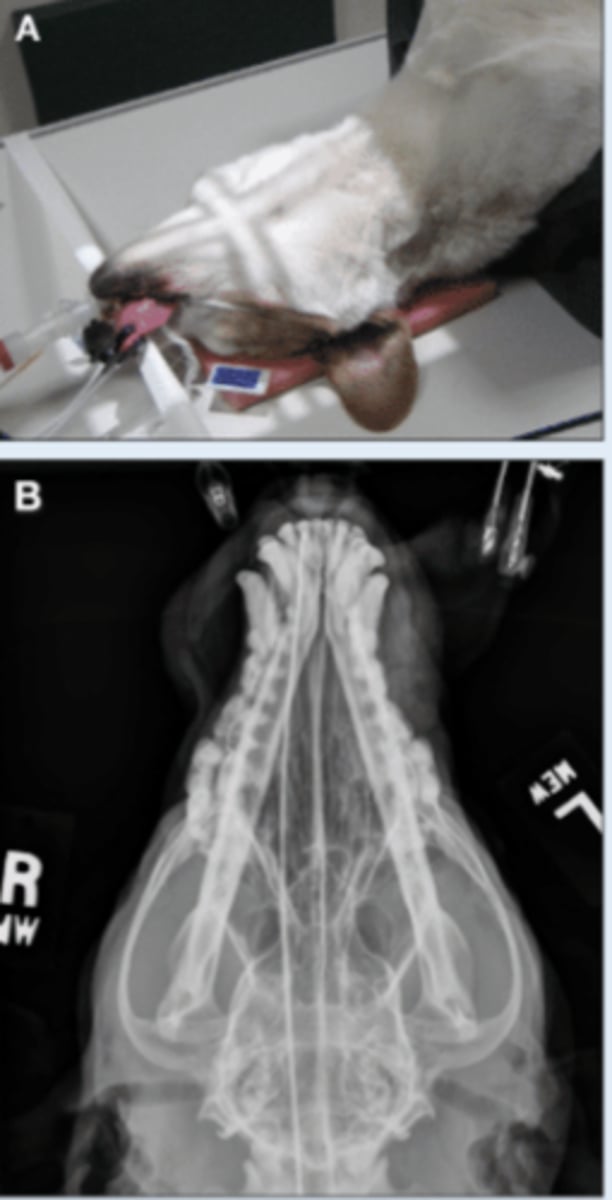
SM Animal Skull - Rostrocaudal image
• Patient in dorsal recumbency
• Nose pointed at tube
• Markers to indicate laterality
• Specifically for frontal sinuses
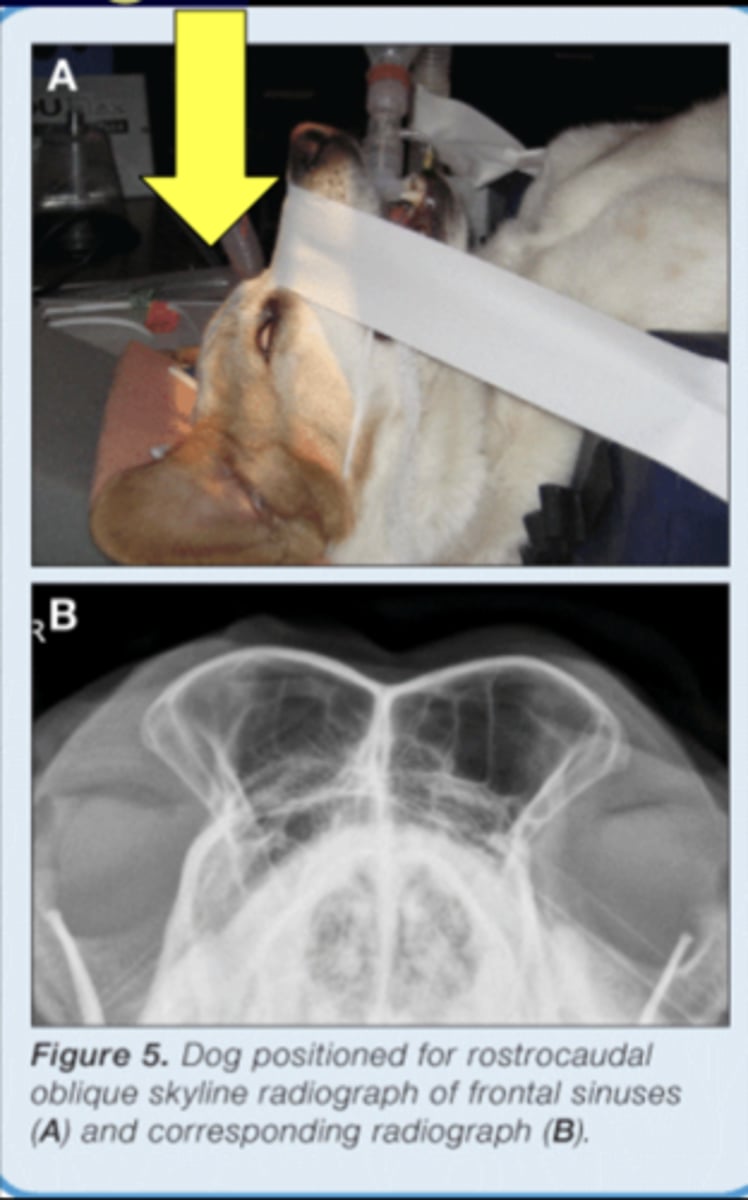
SM Animal Skull- Rostrocaudal image (tympanic bullae)
• Patient in dorsal recumbency
• Nose pointed at tube, slightly angled
• Markers to indicate laterality
• Similar view can be made with mouth open
SM Animal Skull - DV Oblique image
• Patient in lateral recumbency
• Obliqued (rolled) to offset sides
• Markers to indicate laterality
- Marker closest to anatomy indicates the side
• Maxilla or mandible
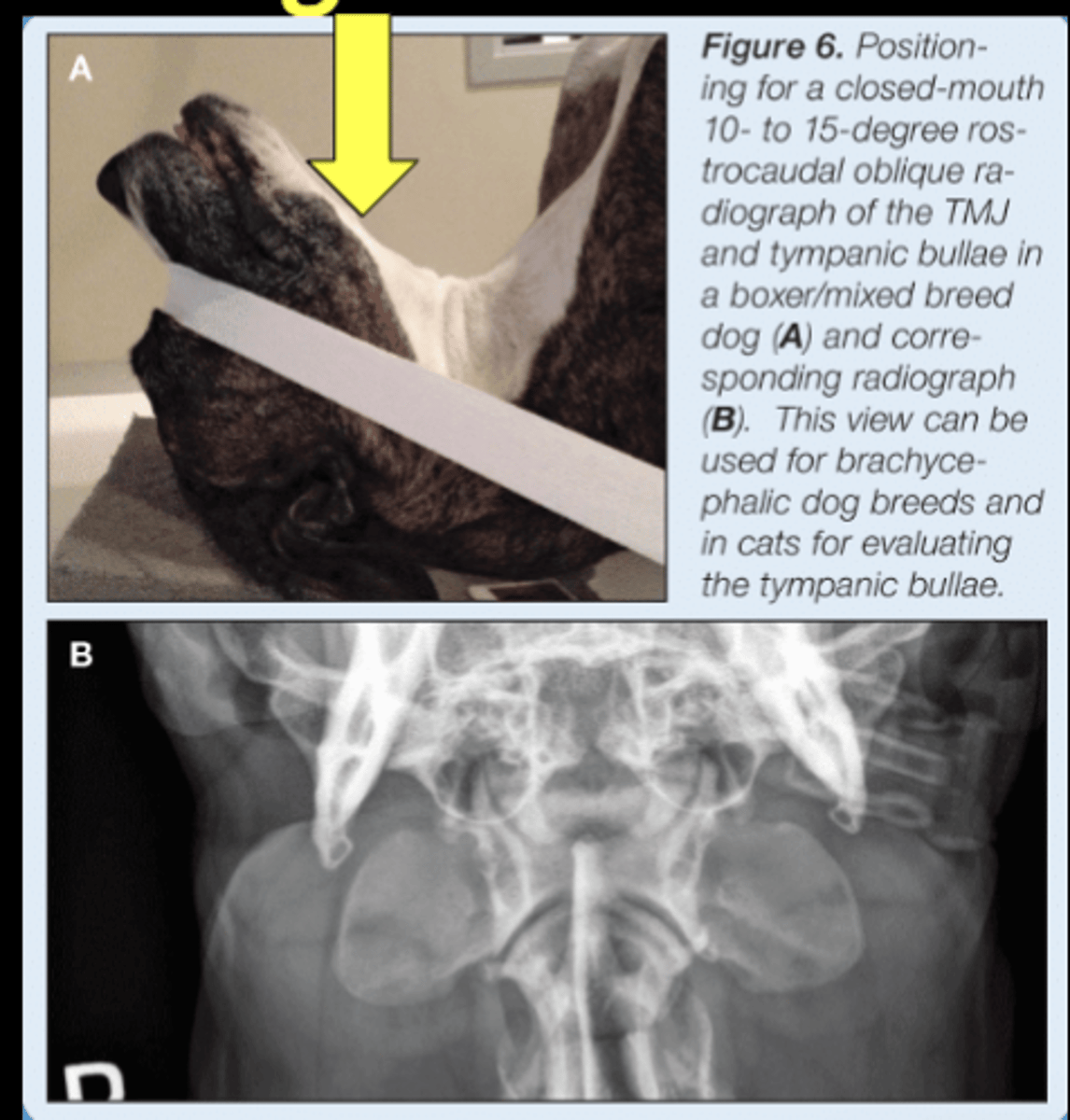
SM Animal Skull - Rostrocaudal Oblique image
• Patient in lateral recumbency
• Nose elevated
• Patient rolled DV slightly
• Markers indicate anatomy that is closest
• Tympanic bulla or TMJRL

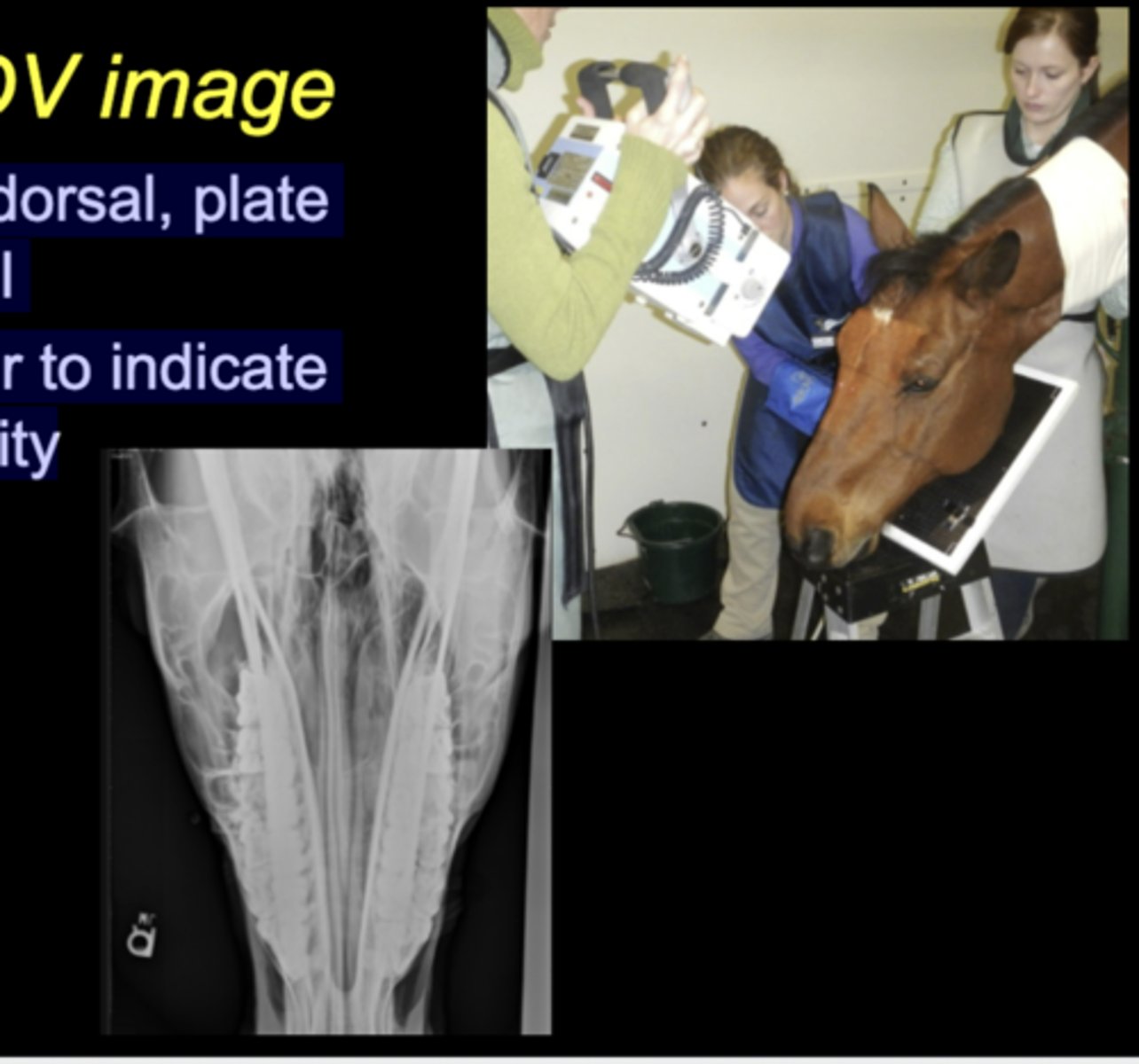
LG Animal Skull - DV image
• Tube dorsal, plate ventral
• Marker to indicate laterality
LG Animal Skull - Lateral image
• Tube on one side, plate on the other
• Marker to indicate laterality closest to plate
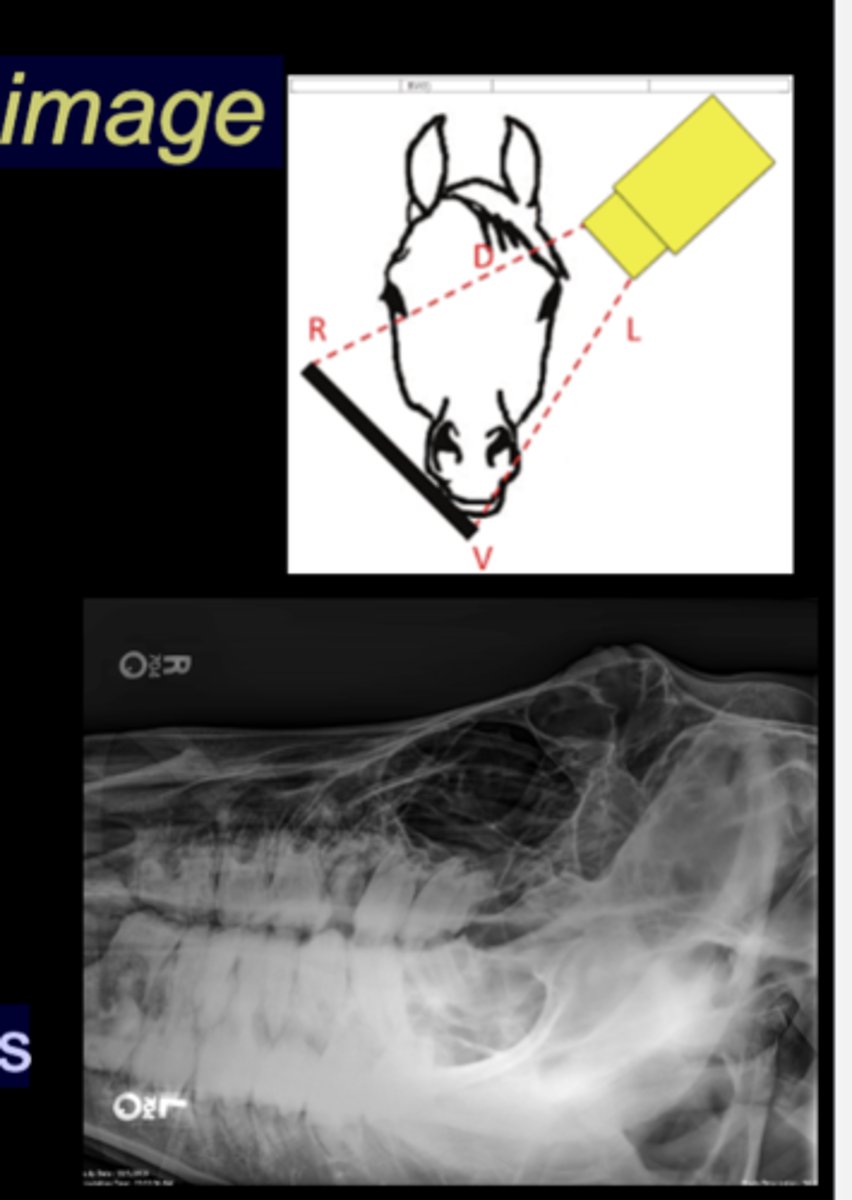
LG Animal Skull - DV Oblique image
• Tube on one side, plate on the other
• Tube angled in DV plane, plate held perpendicular
• Markers indicate anatomy that is closest
• Maxillary or mandibular structures
When to image
• Trauma• Masses/swelling
• Otic disease
• Tooth disease
• TMJ disease
• Nasal and paranasal sinus disease - EQ
• Neurologic signs localized to the brain or cervical spine
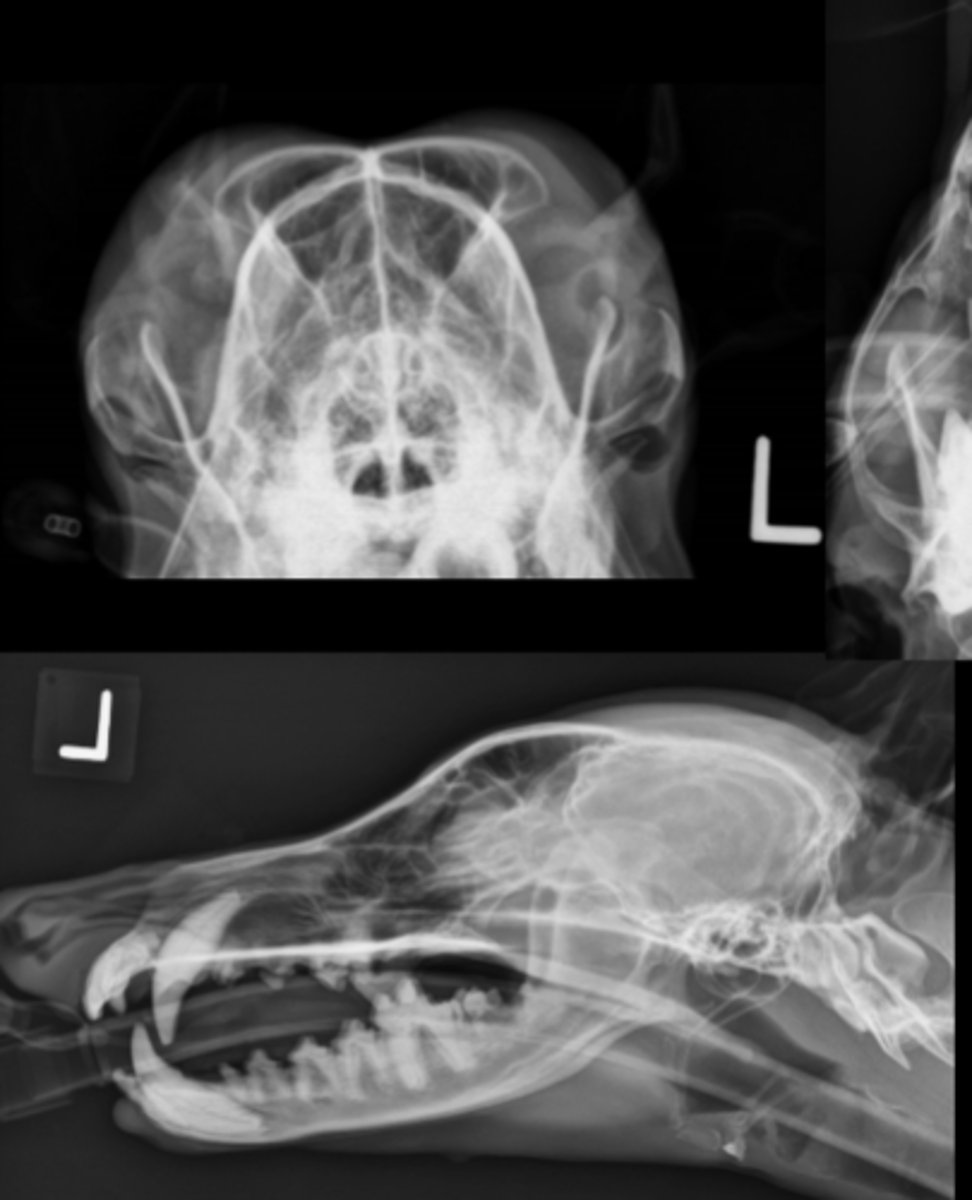
Canine Skull
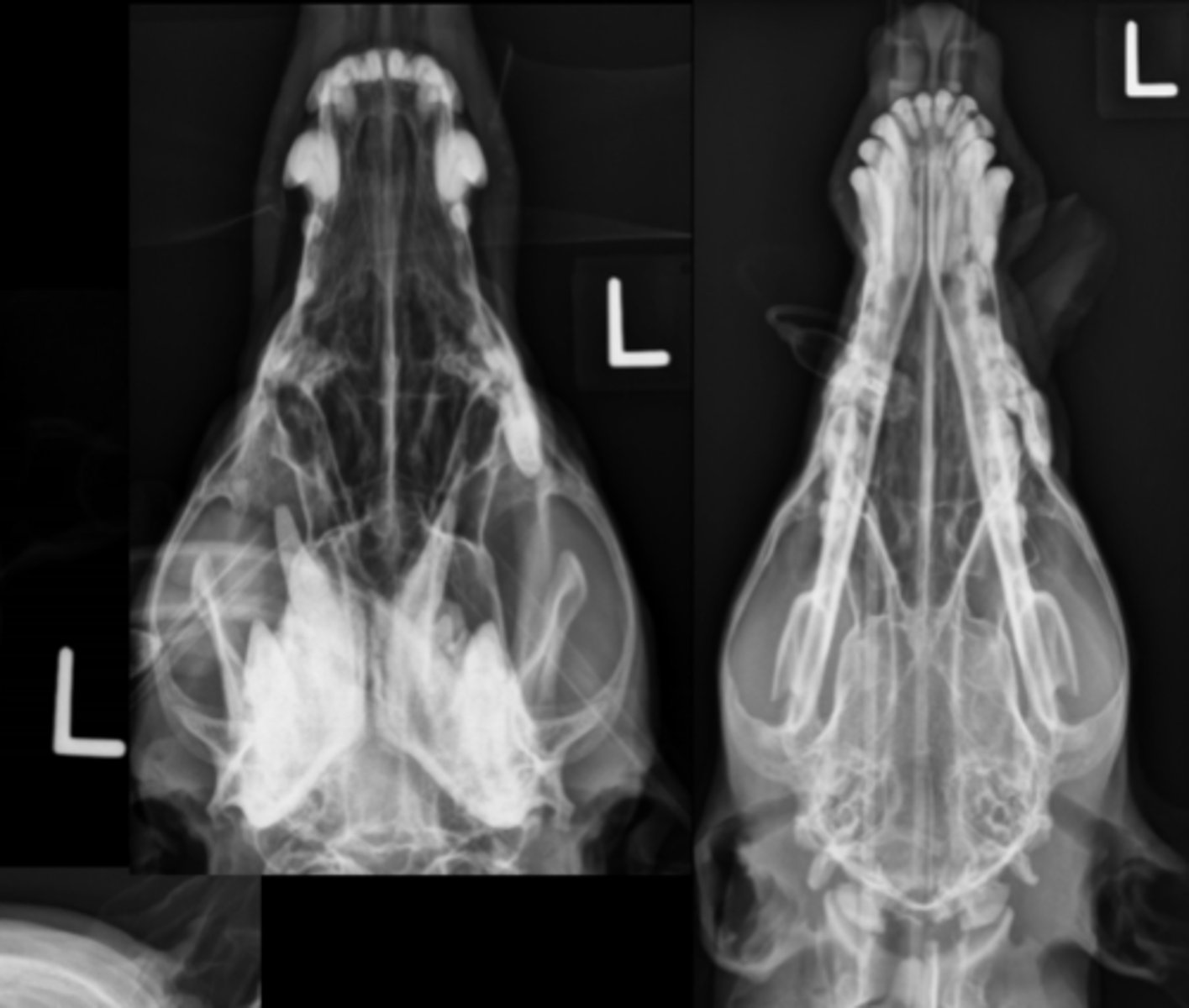
Canine Skull
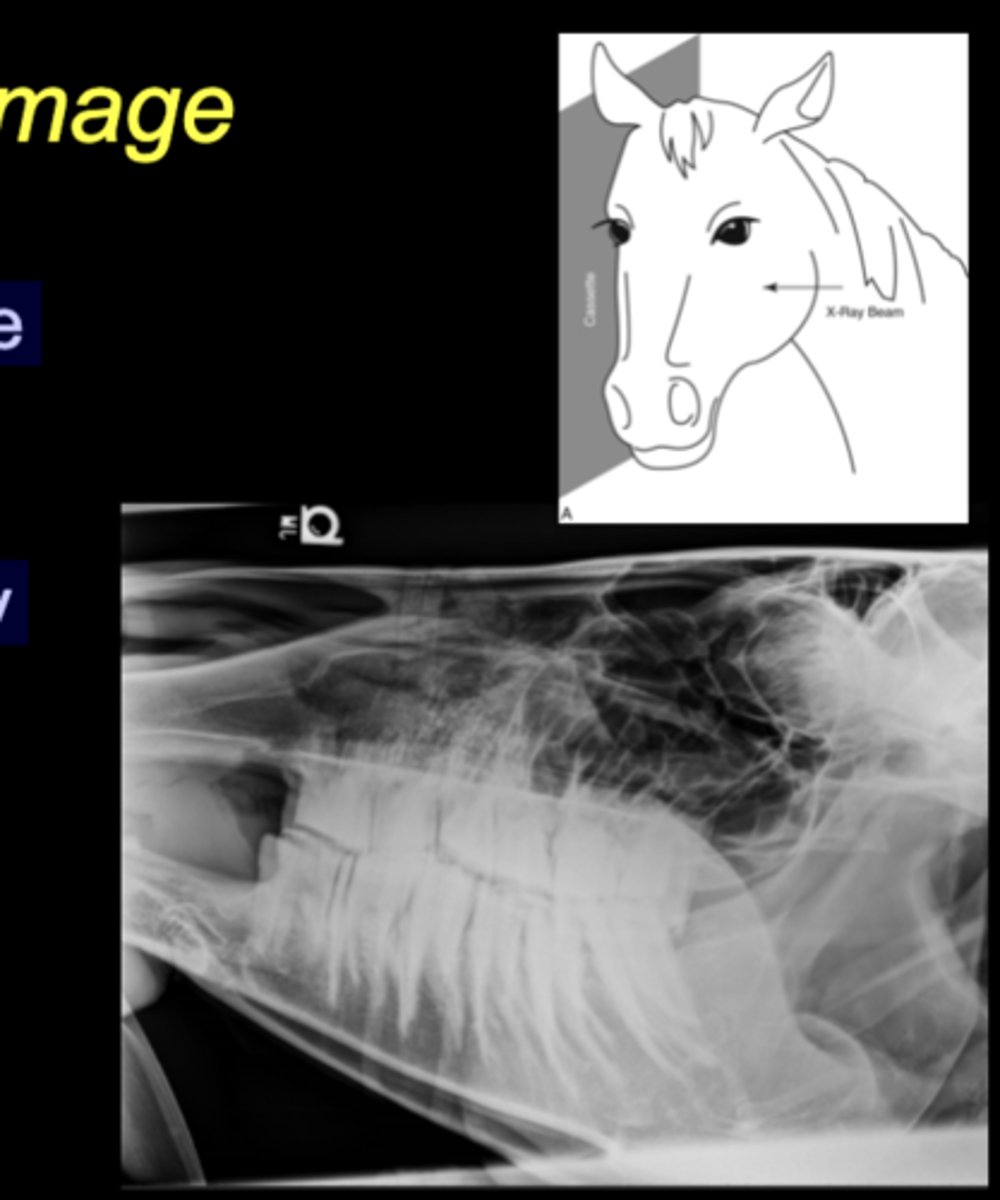
Equine Skull
Equine Skull

Equine skull

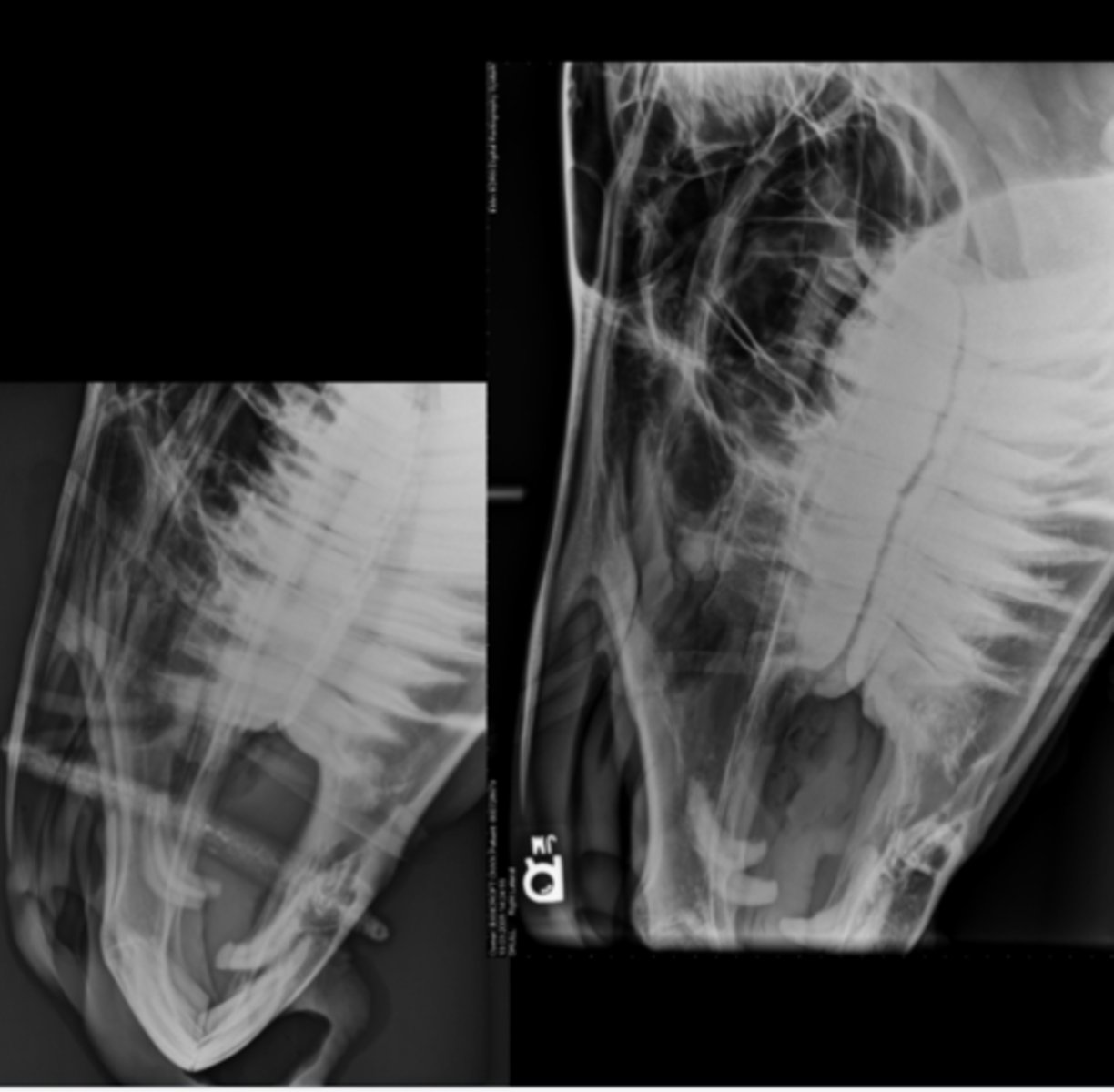
SM Animal Spine- Lateral Image
• Patient in lateral recumbency
• Center on region of interest - Cervical - CT junction
• Marker to indicate the laterality of patient
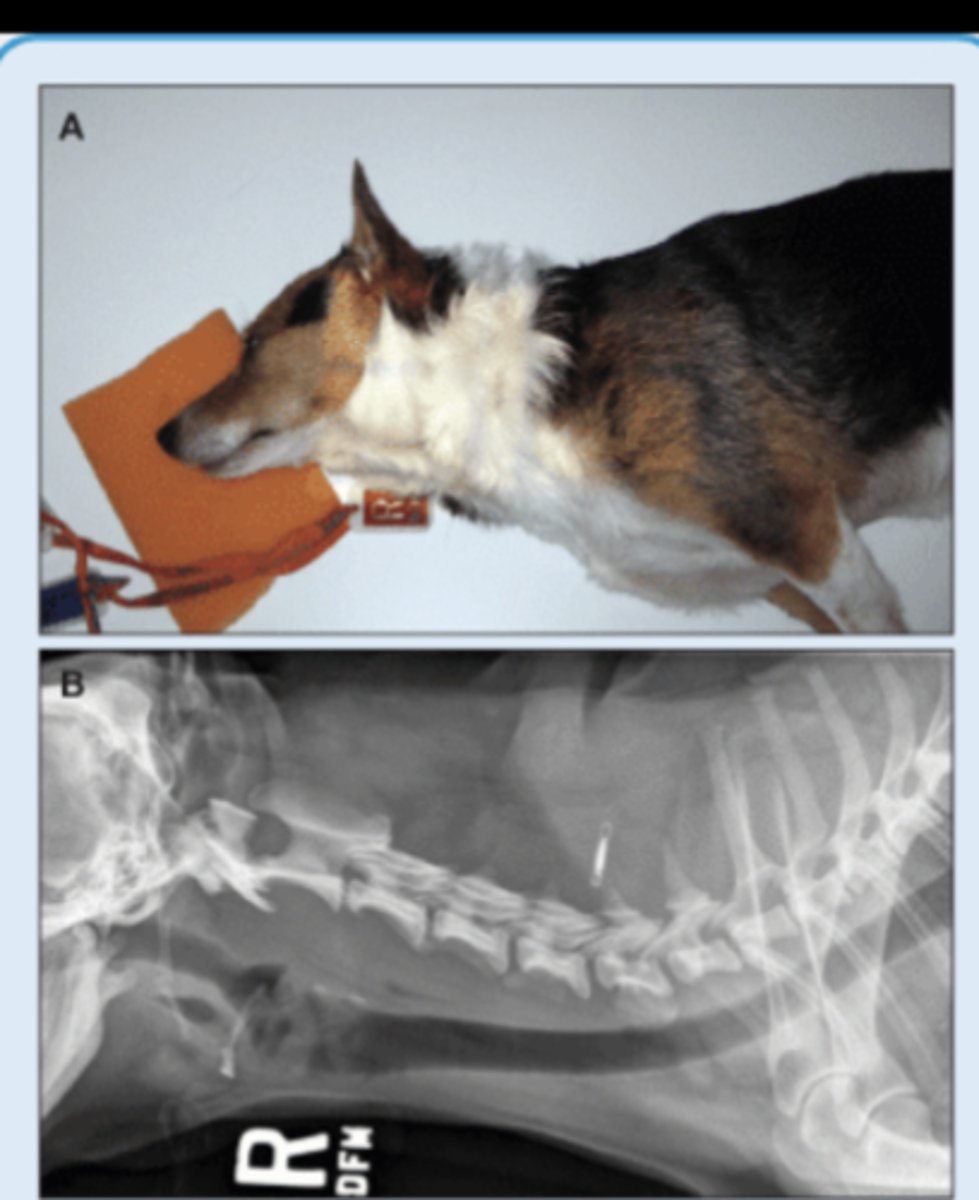
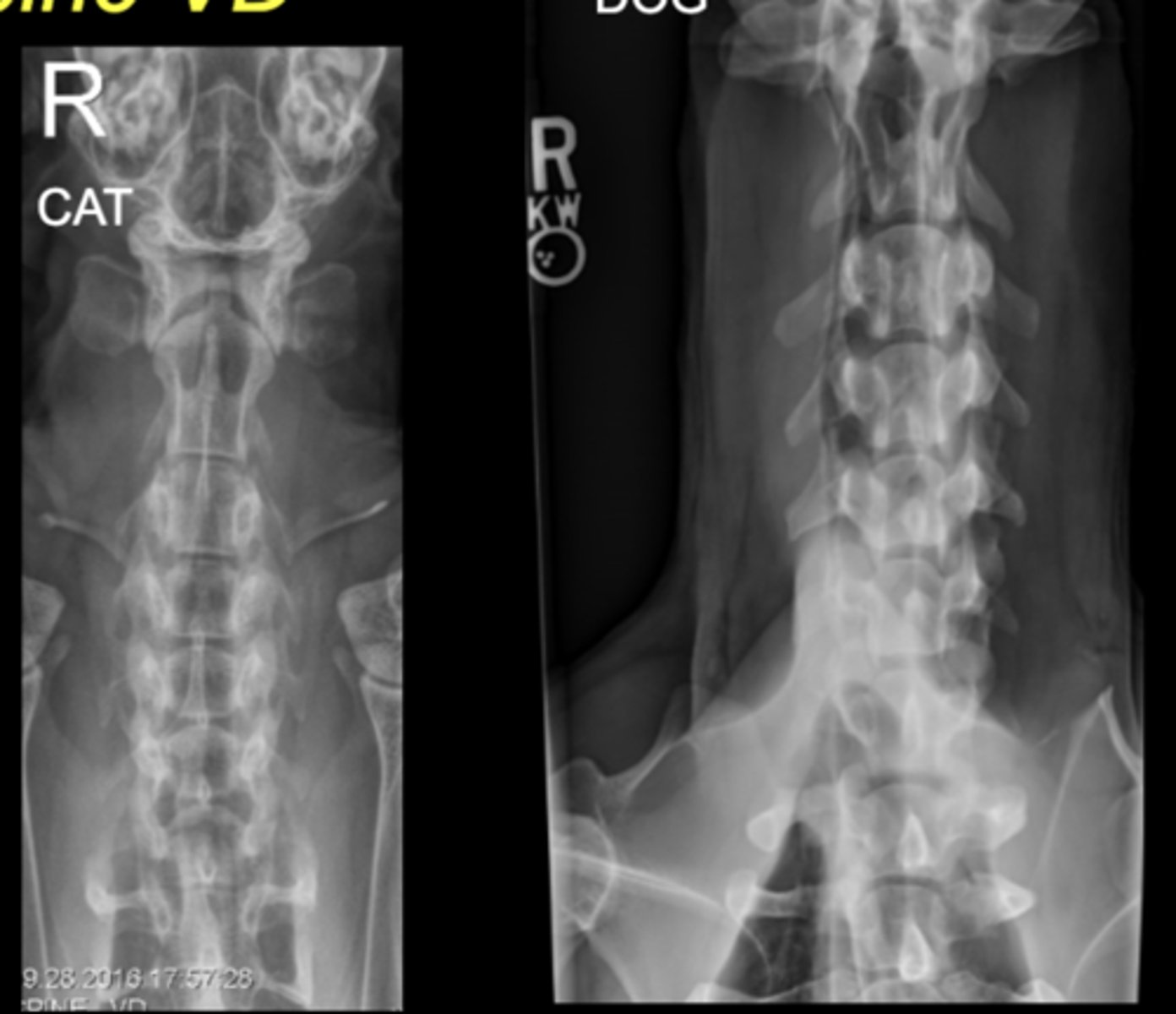
SM Animal Spine - VD image
• Patient in dorsal recumbency
• Centered on area of interest
• Angle beam toward thorax to image through caudal discspaces*
• Marker to indicate laterality of patient*
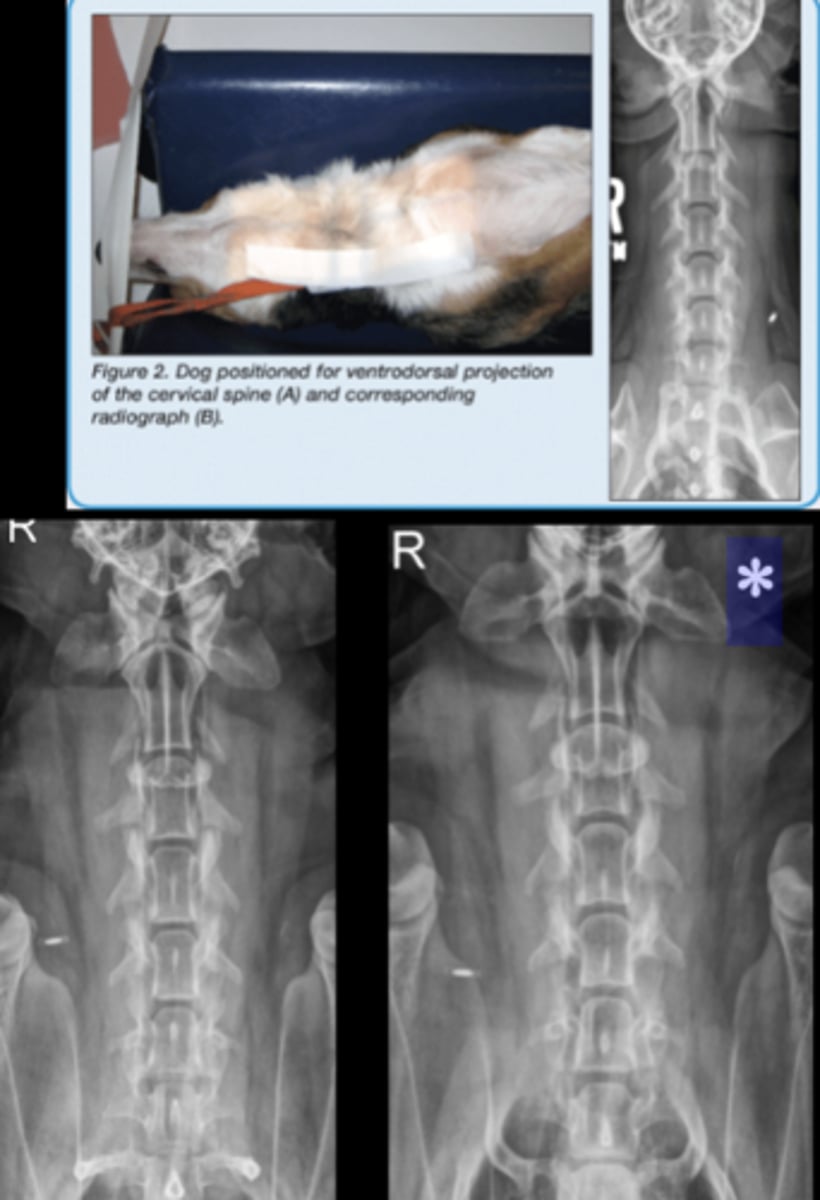
SM Animal Spine - VD Oblique images
• Patient in dorsal recumbency, tipped right or left
• Center on the area of interest
• Marker to indicate laterality of patient
• Only rarely used as needed
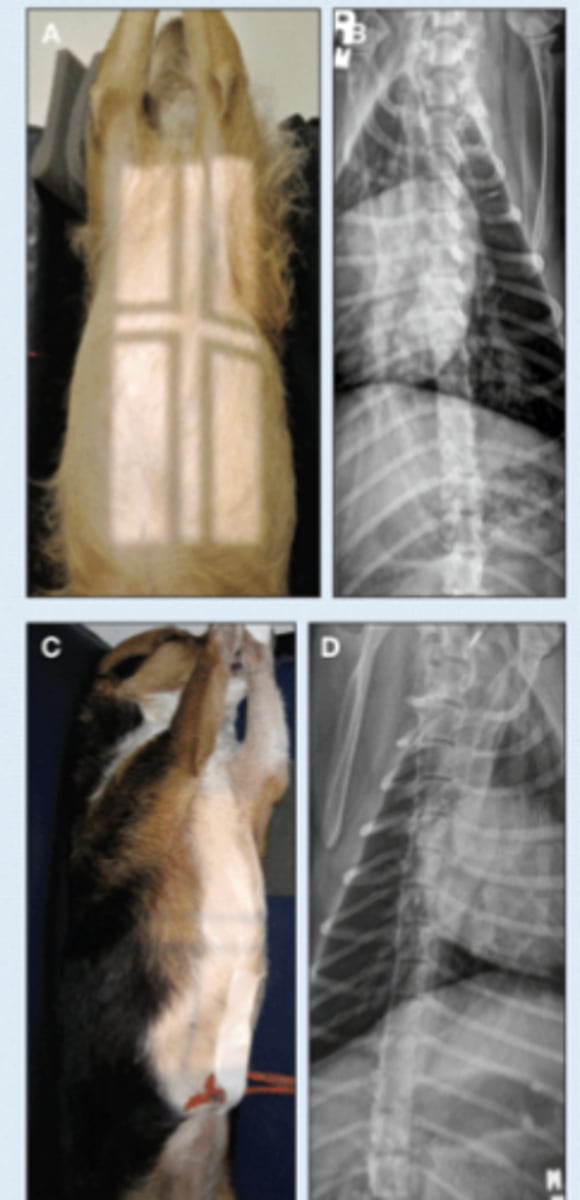
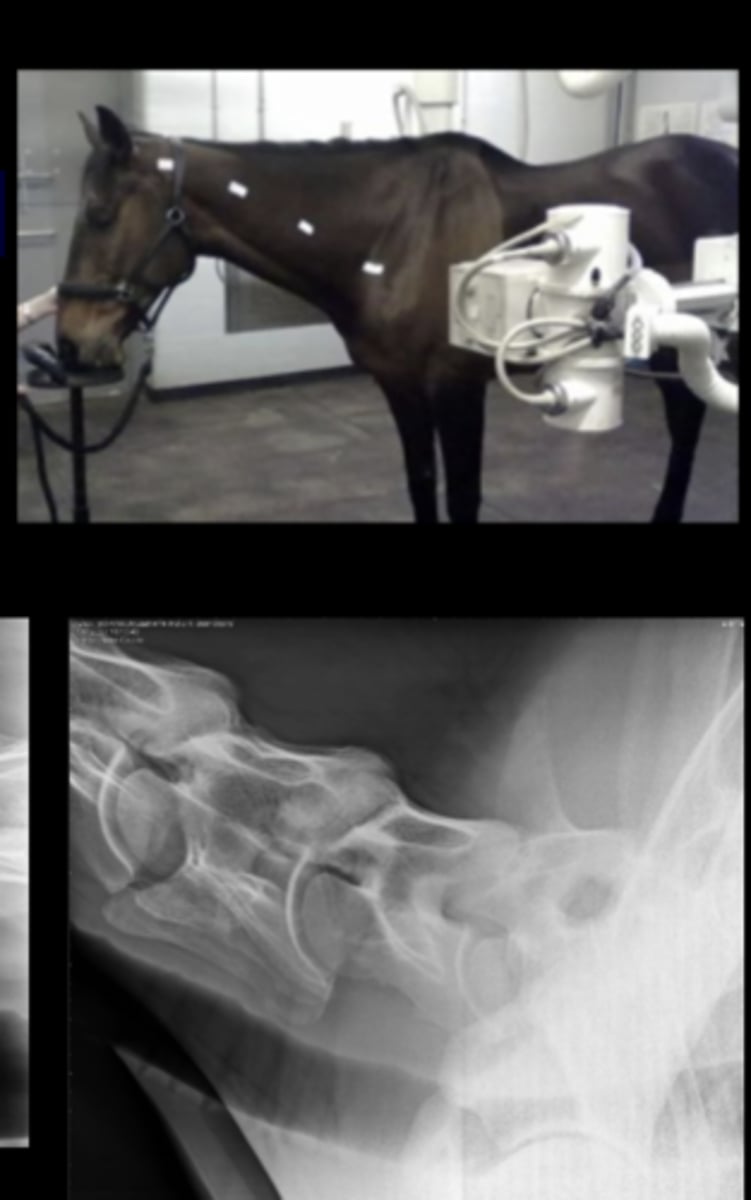
LG Animal Spine - Lateral image
• Patient usually standing
• Marker to indicate laterality of patient
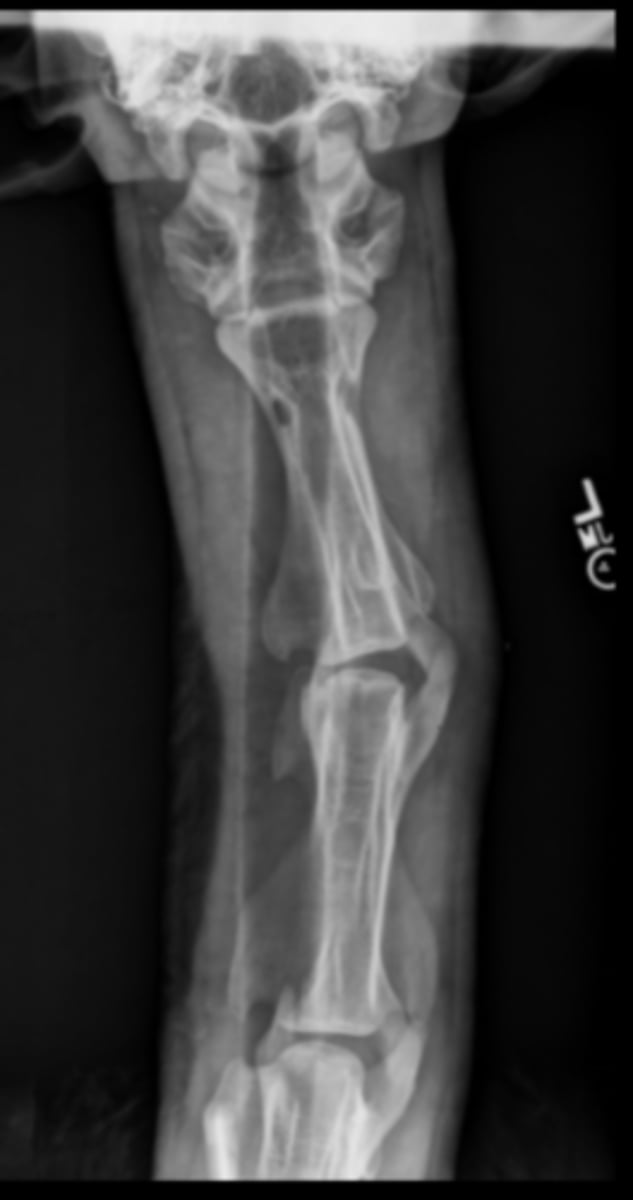
LG Animal Spine - DV/VD image
• Only in smaller patients due to size
• Patient standing or under GA in sternal or dorsal recumbency
• Marker to indicate laterality of patient
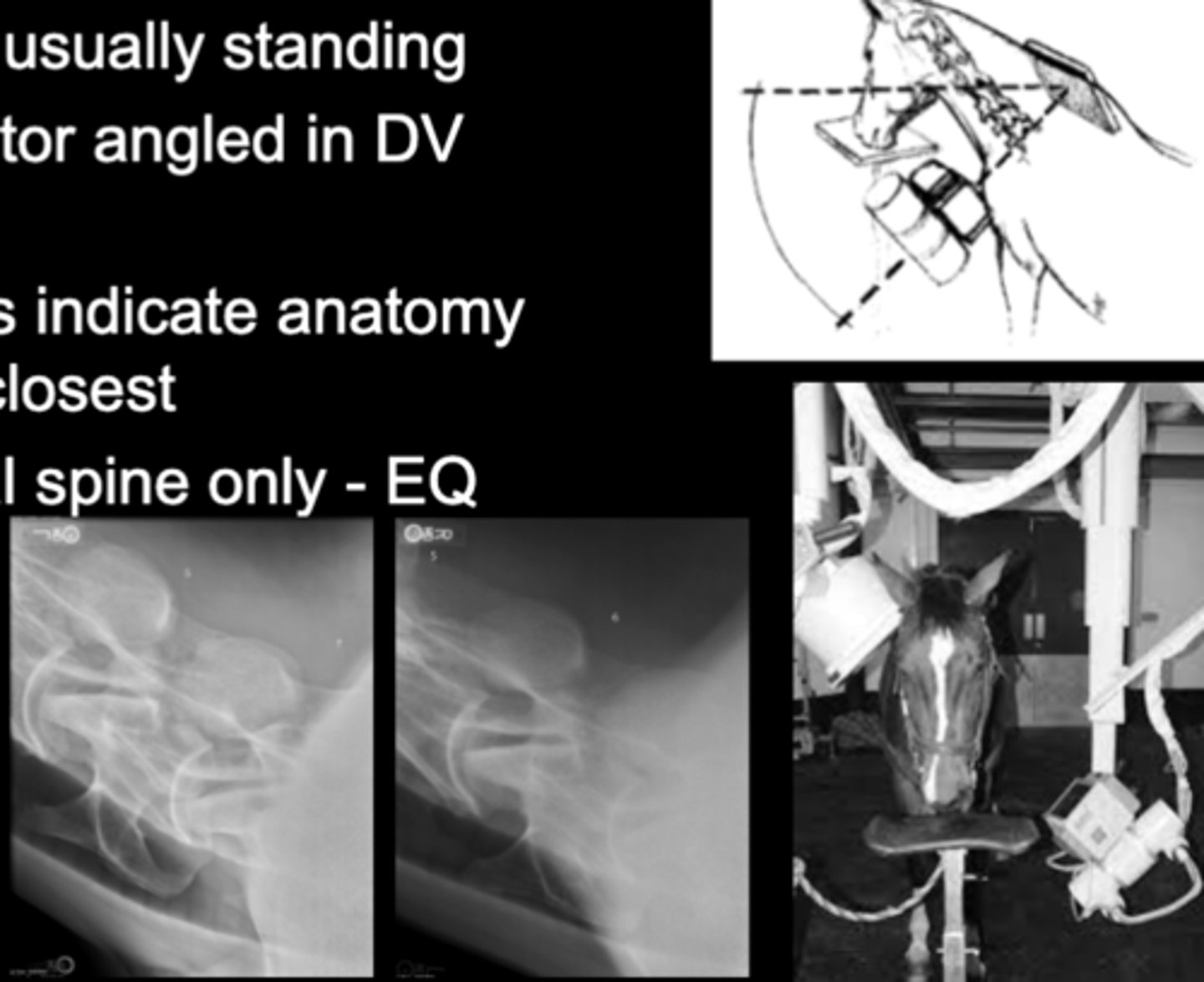
LG Animal Spine - DV Oblique image
• Patient usually standing
• Generator angled in DV plane
• Markers indicate anatomy that is closest
• Cervical spine only - EQ
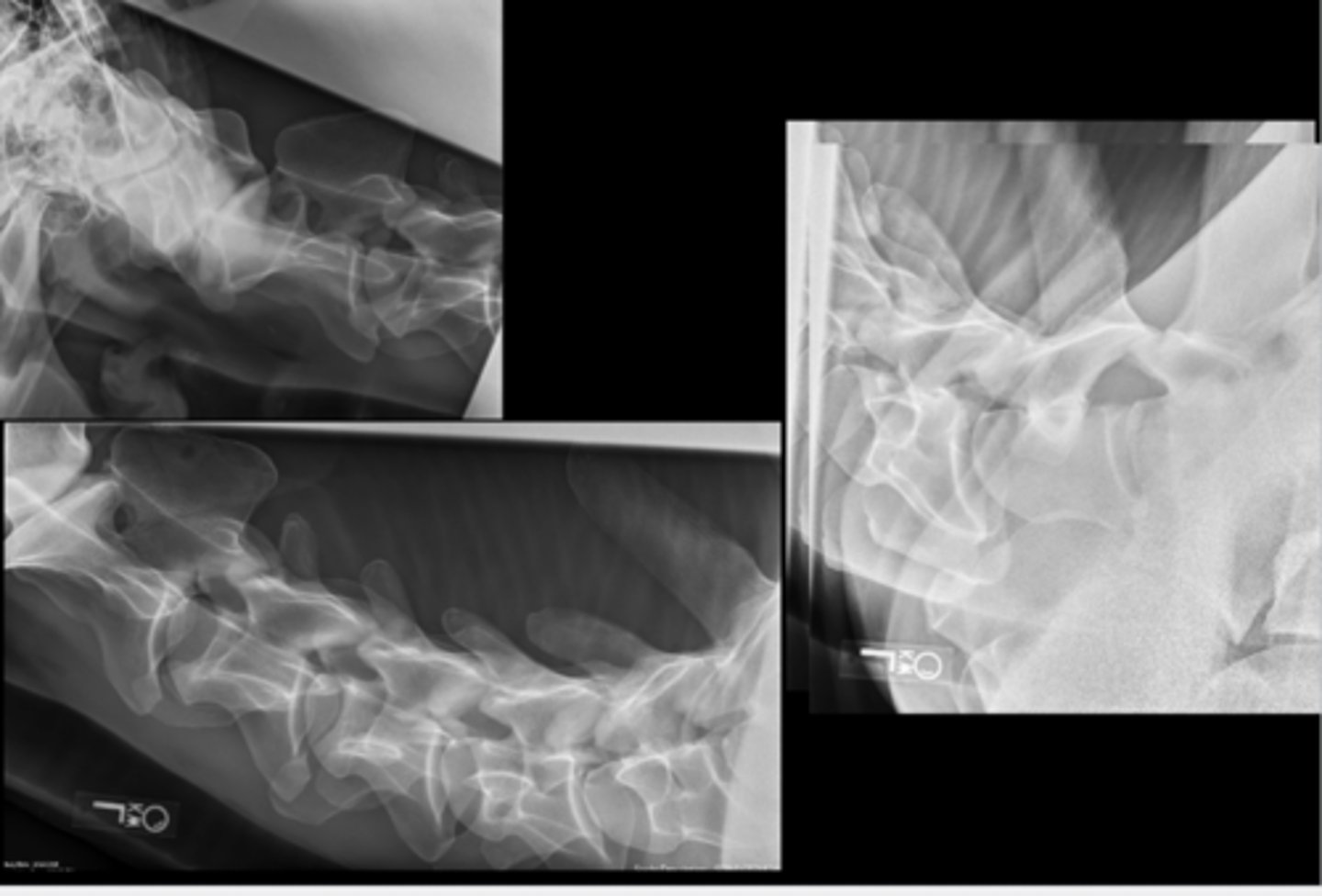
SM Animal Spine Lateral
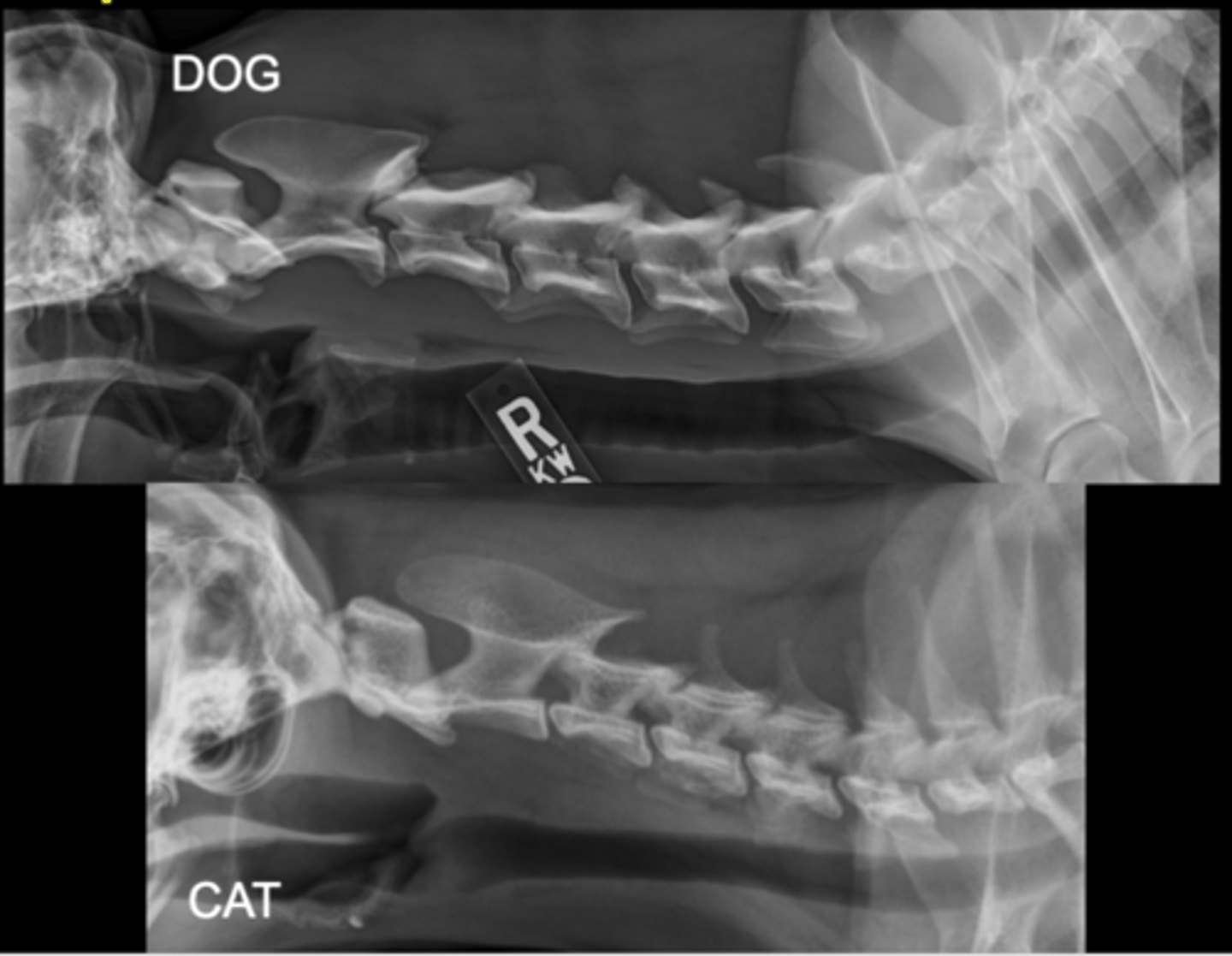
SM Animal Spine VD
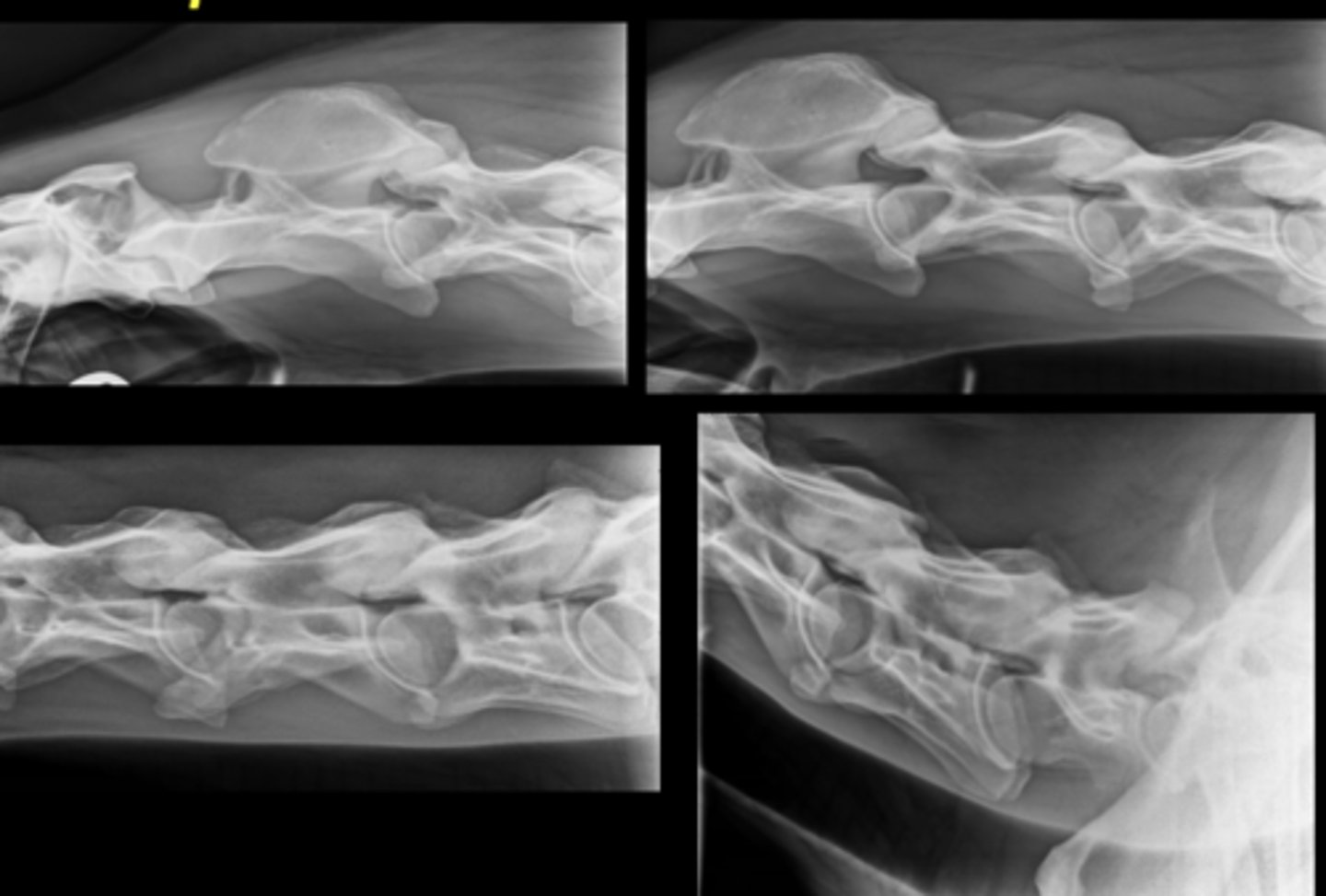
Equine Spine Lateral
Llama Spine Lateral
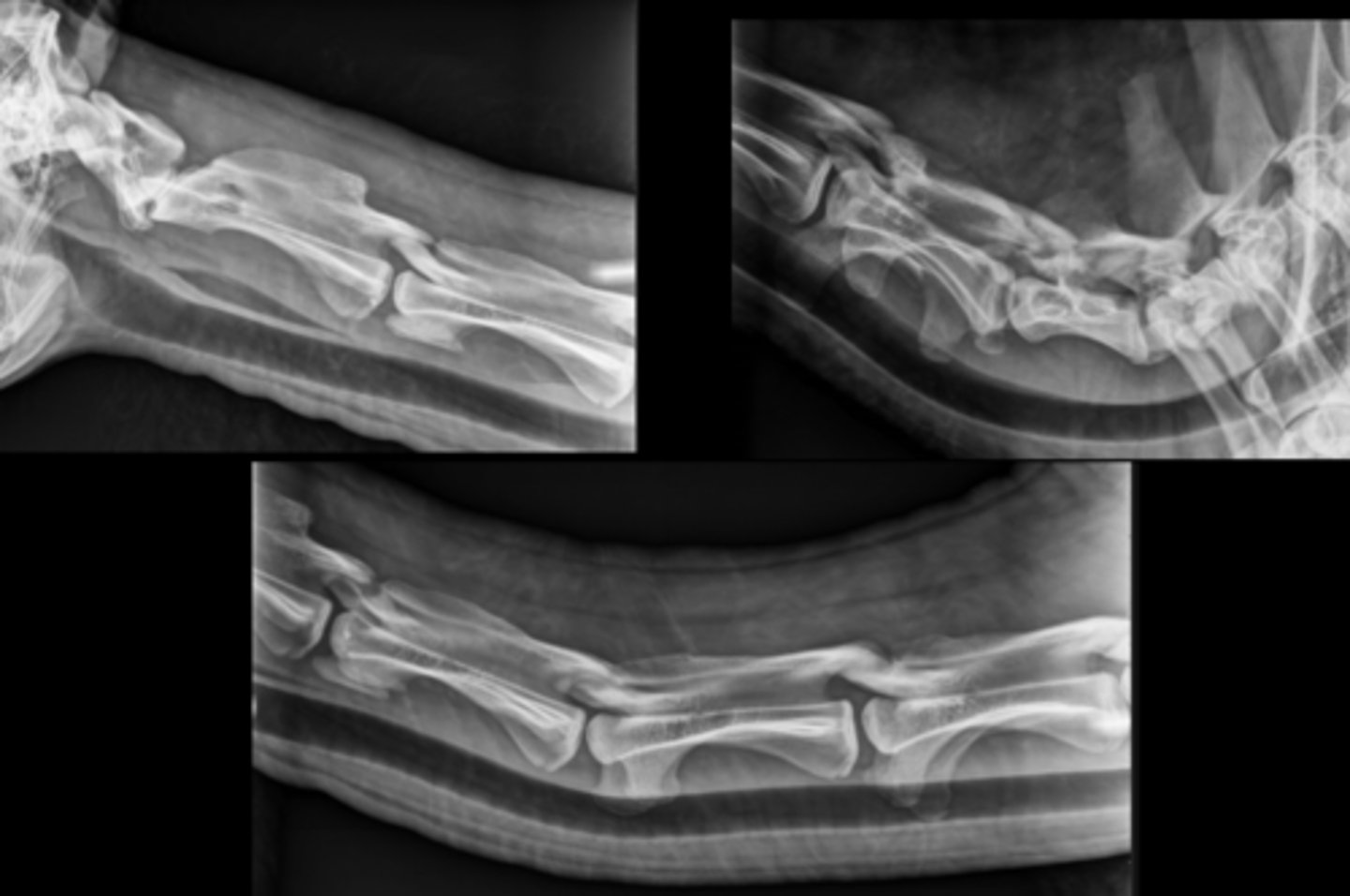
Bovine Spine Lateral