GI Medications and Influences on Oral Cavity (Dr. Singh)
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
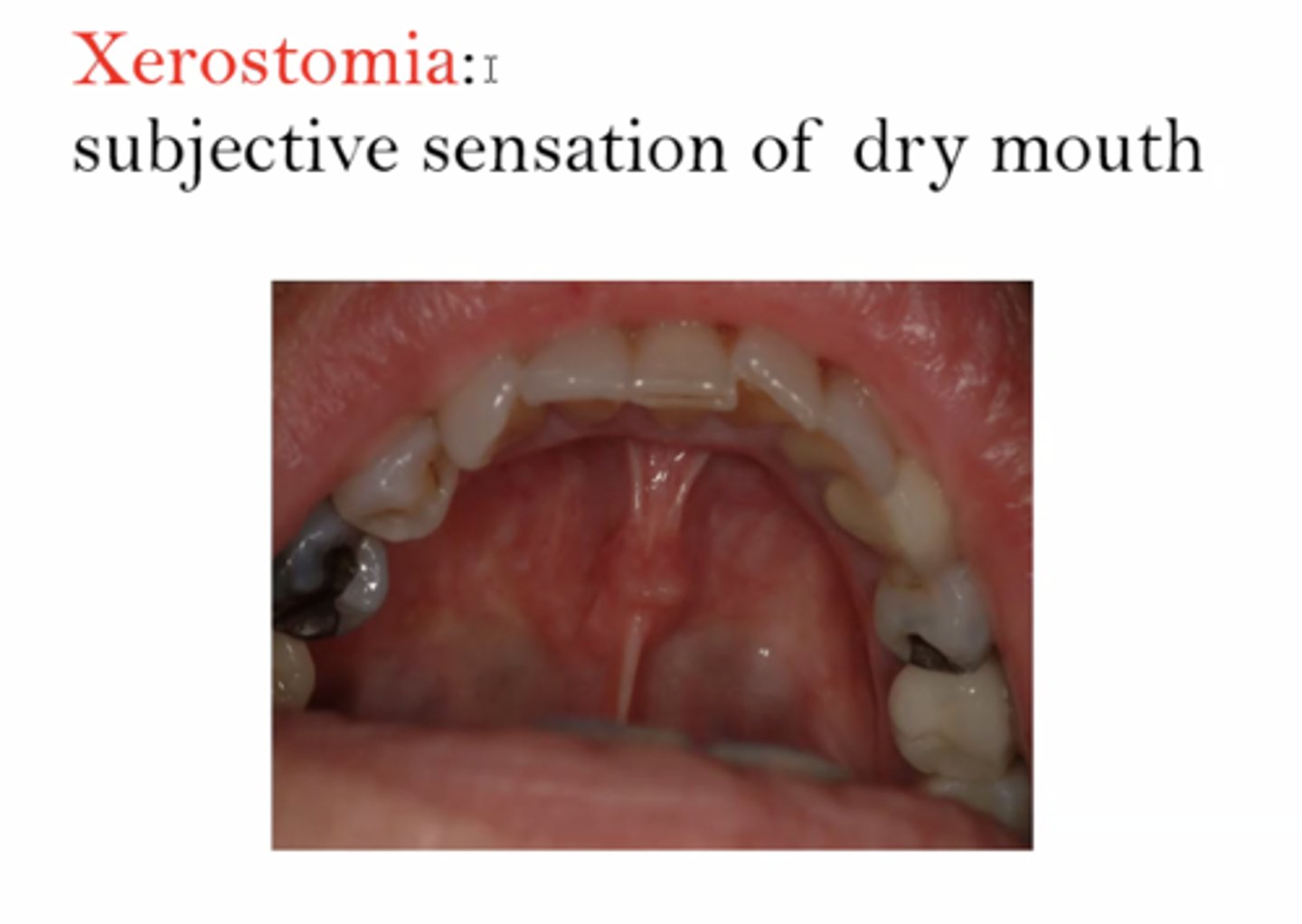
subjective sensation of dryness of mouth:
xerostomia
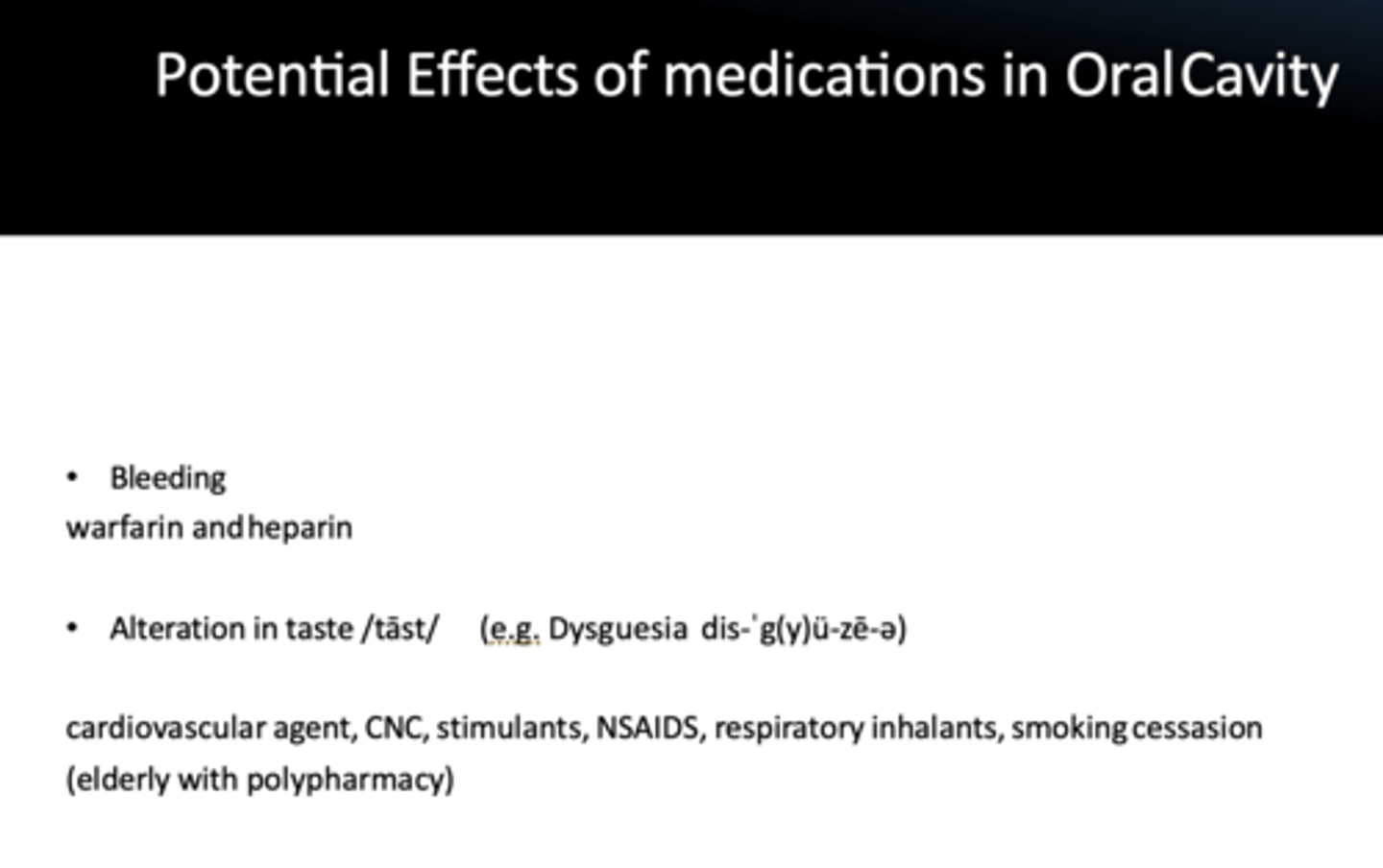
wafarin and heparin can potentially cause what side effect?
bleeding

cardiovascular agent, CNC, stimulants, NSAIDS, respiratory inhalants, smoking cessasion can potentially cause what side effect?
alteration in taste
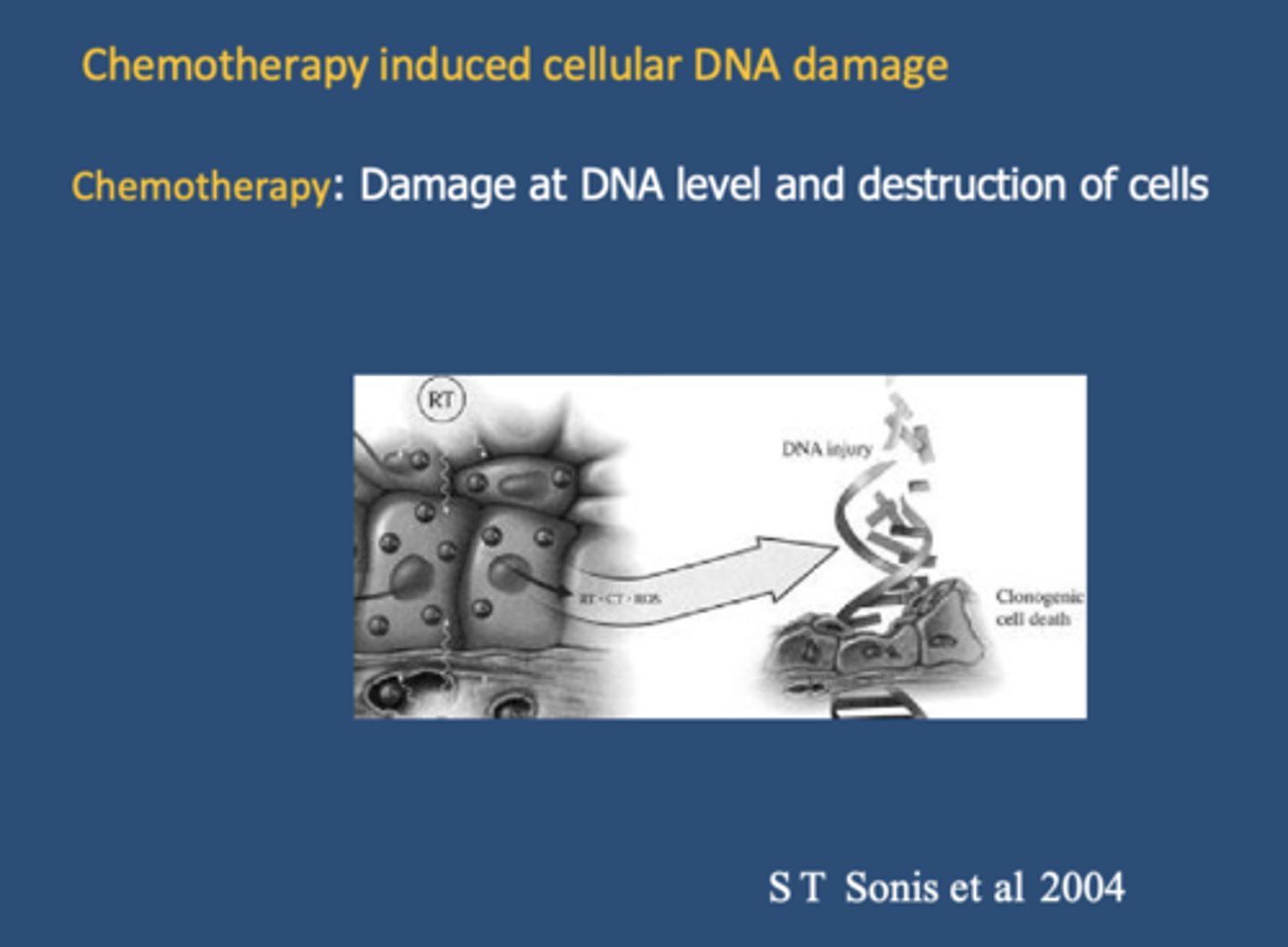
____________ causes damage at DNA level and destruction of cells
chemotherapy
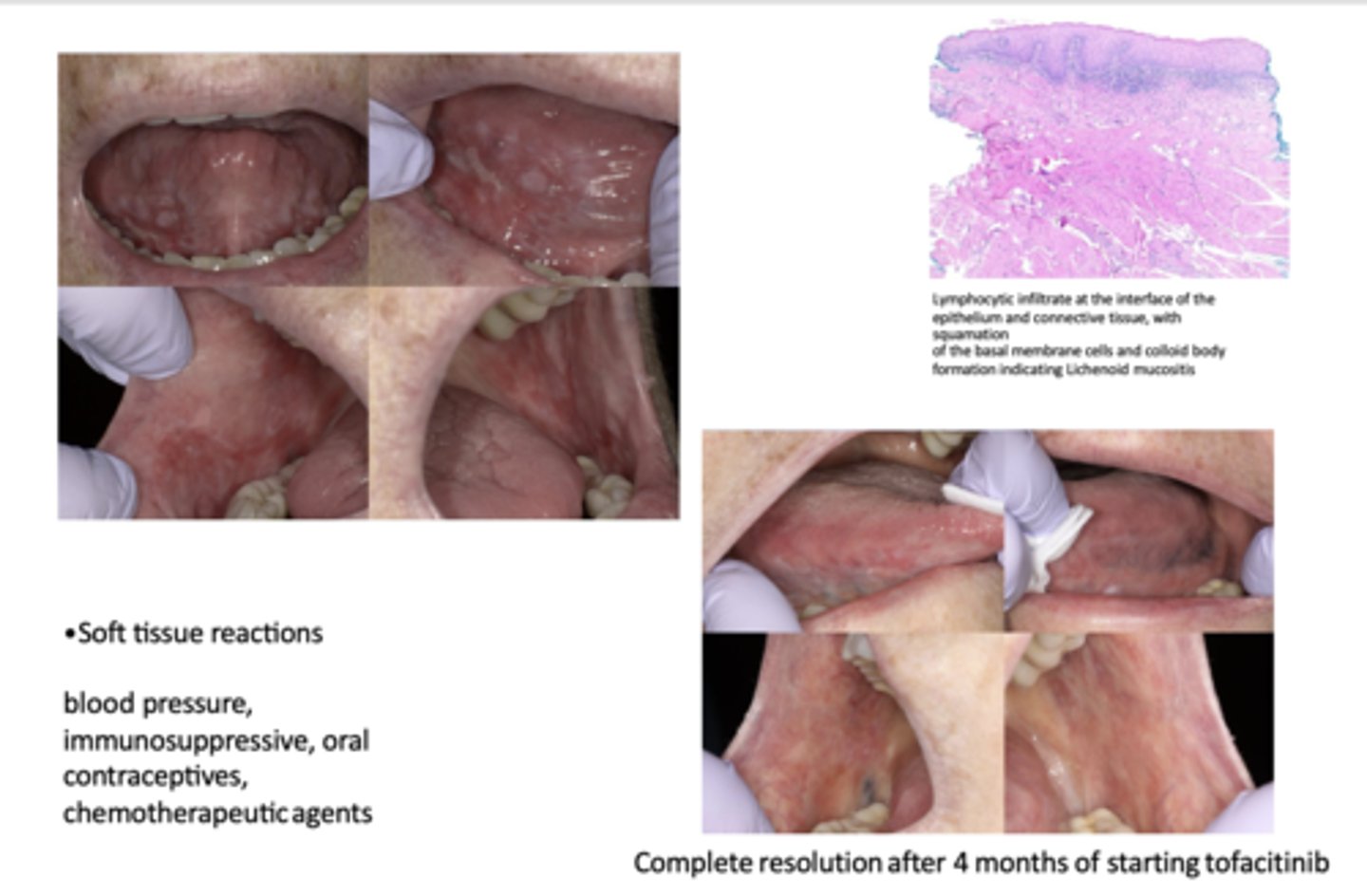
Soft tissue reactions can have complete resolution after 4 months of starting _____________
tofacitinib
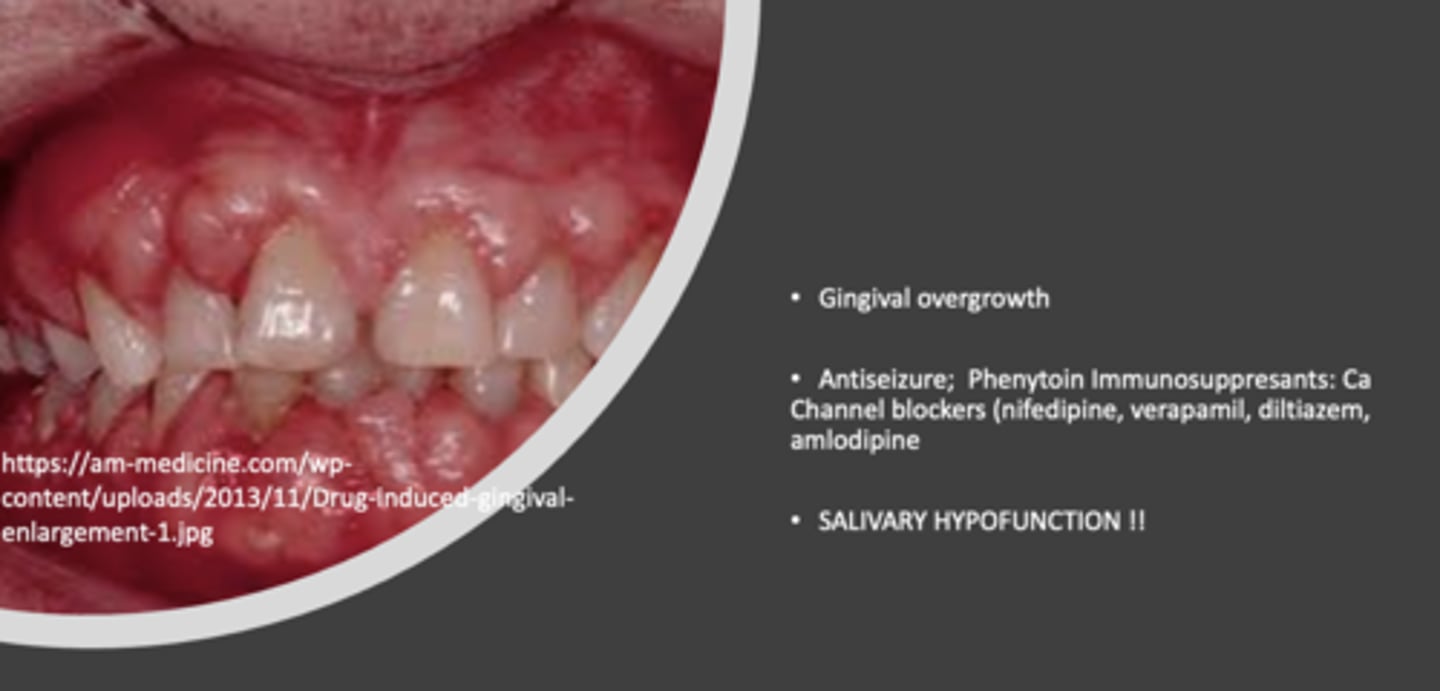
In addition to gingival overgrowth, which oral side effect is commonly associated with the use of antiepileptics, phenyotin immunosuppressants, and calcium channel blockers?
Salivary hypofunction
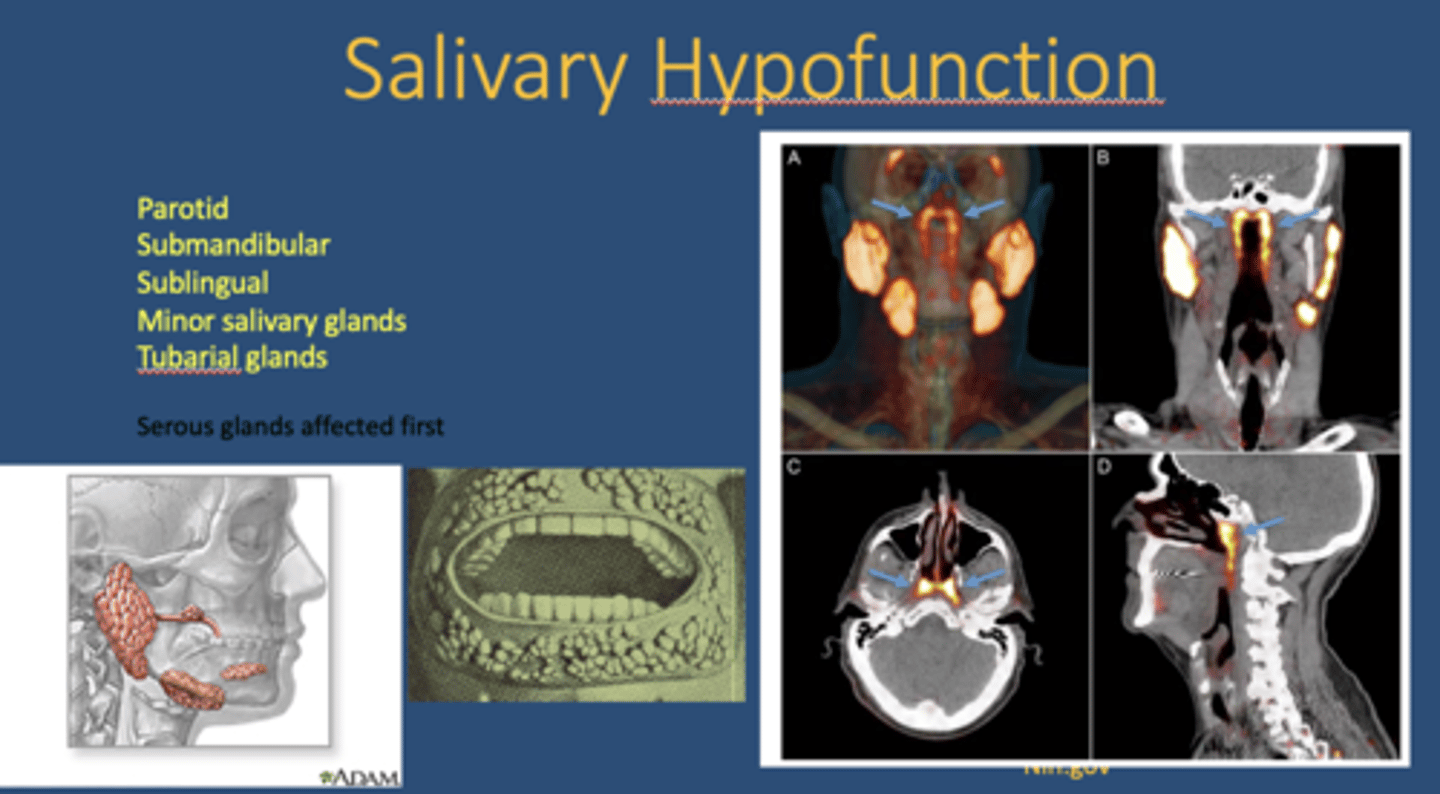
In xerostomia, which glands are affected first?
serous glands
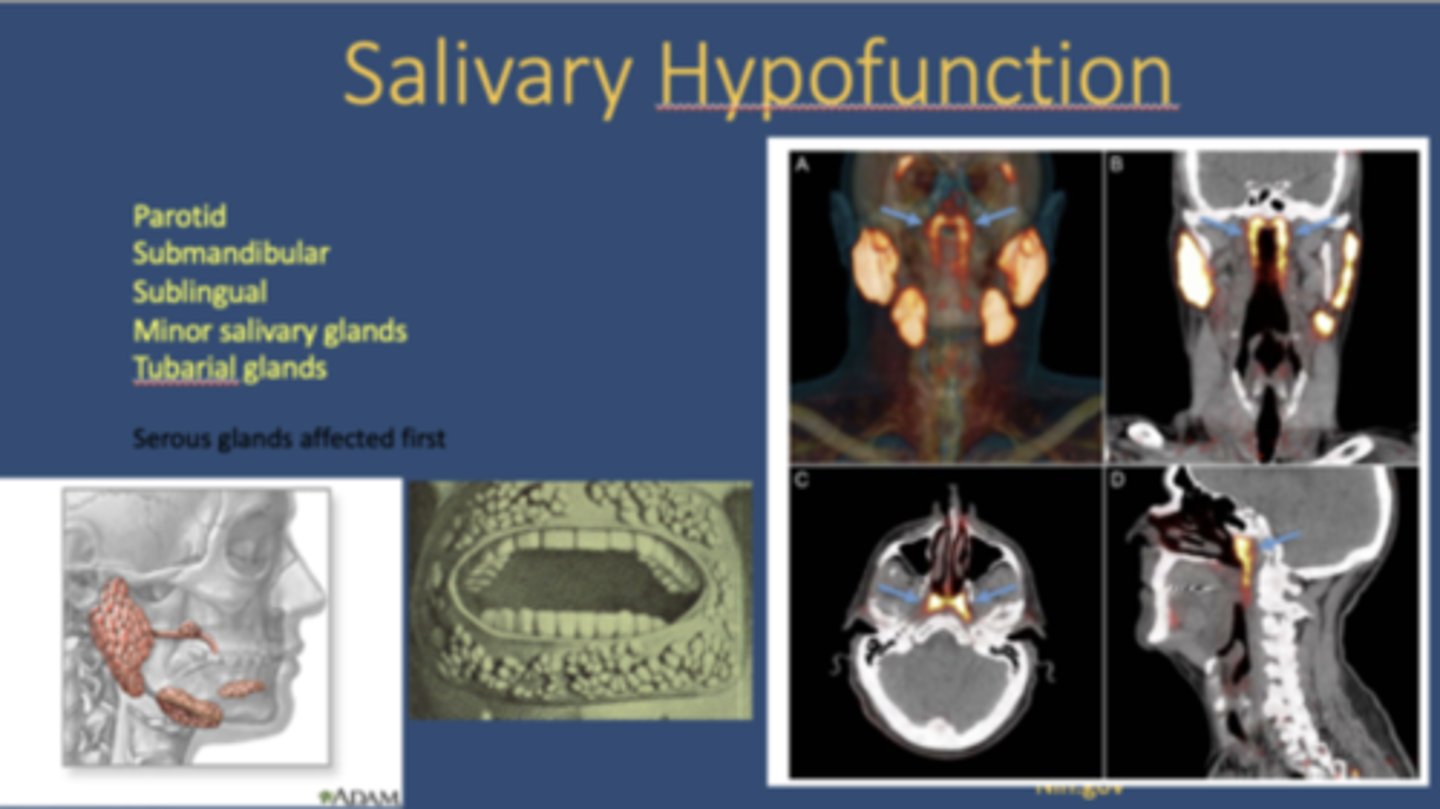
What is a newly discovered salivary gland?
Tubarial glands
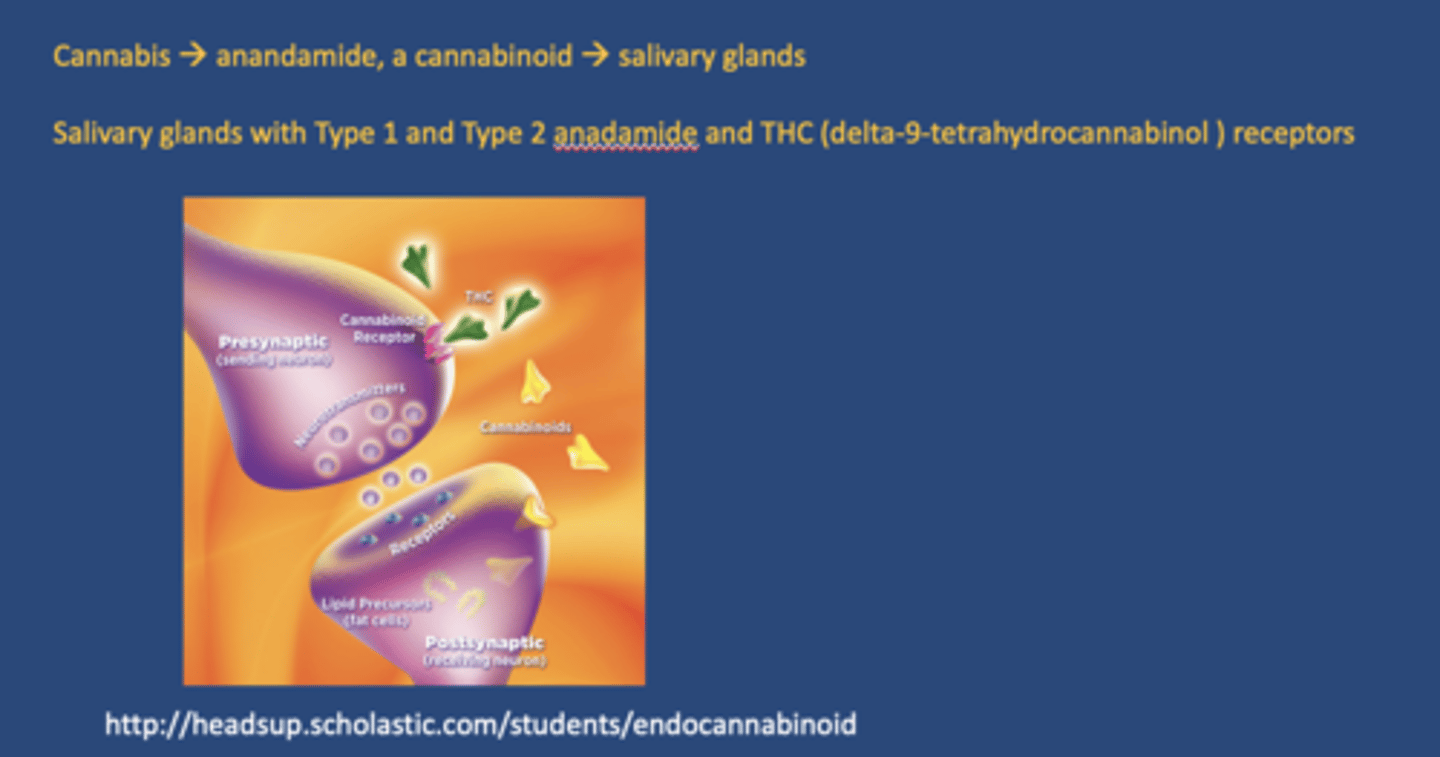
What endogenous cannabinoid is produced in response to cannabis use and affects salivary glands?
Anandamide
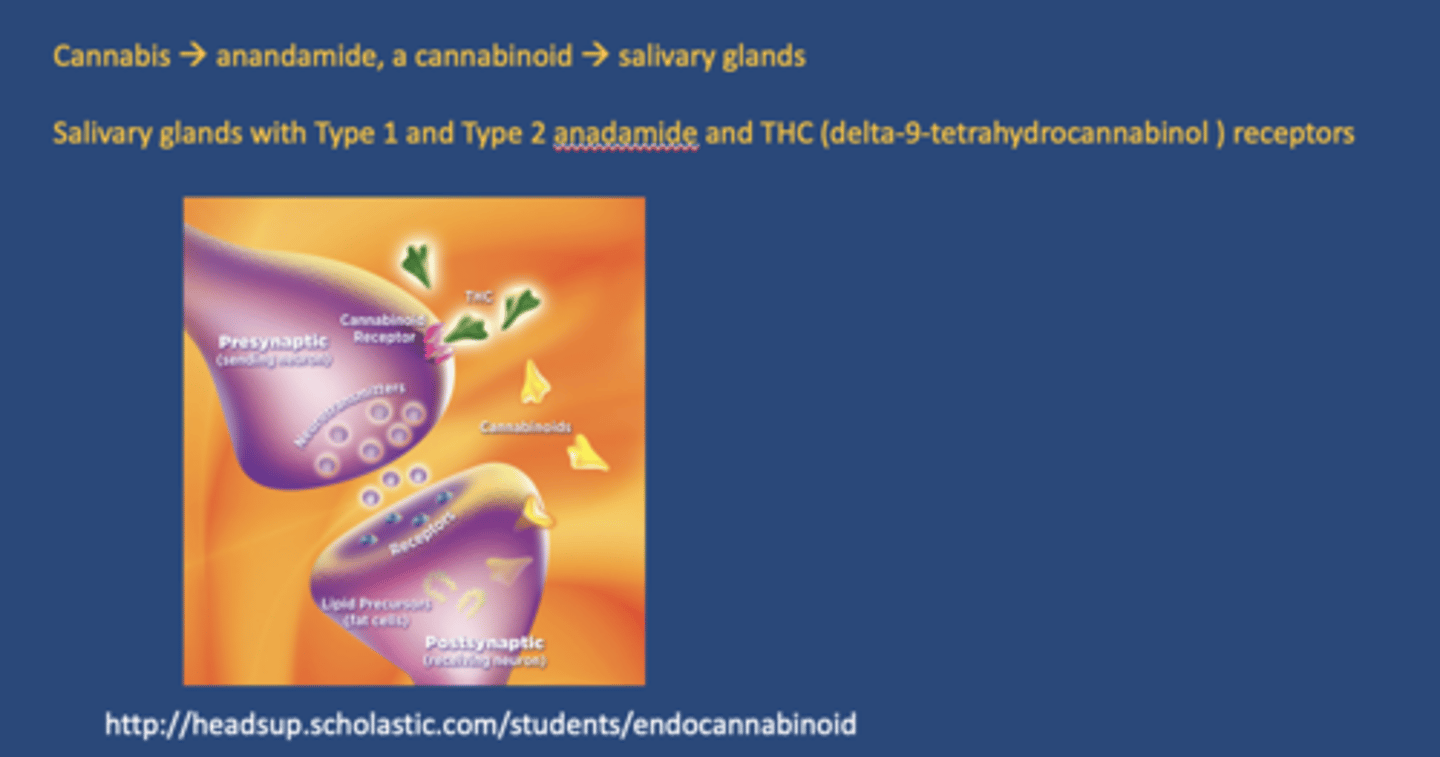
Where are cannabinoid receptors found in relation to salivary glands?
- Type 1 and Type 2
- THC
sensation of having too much saliva in the mouth even though there is volumetric decrease in the saliva and resulting in thick, ropey, stringy, foamy and viscous saliva is known as ____________
subjective sialorrhea

_______________ is the main neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system, which is largely responsible for stimulating saliva production
Acetylcholine

what type of drugs effect the serous production of saliva by competing with or blocking acetylcholine receptors on M1 - M3 (muscuranic receptors)?
anticholinergic drugs

MOA of Anti-cholinergic medications:
compete/blocking acetylcholine receptors on M1 - M3
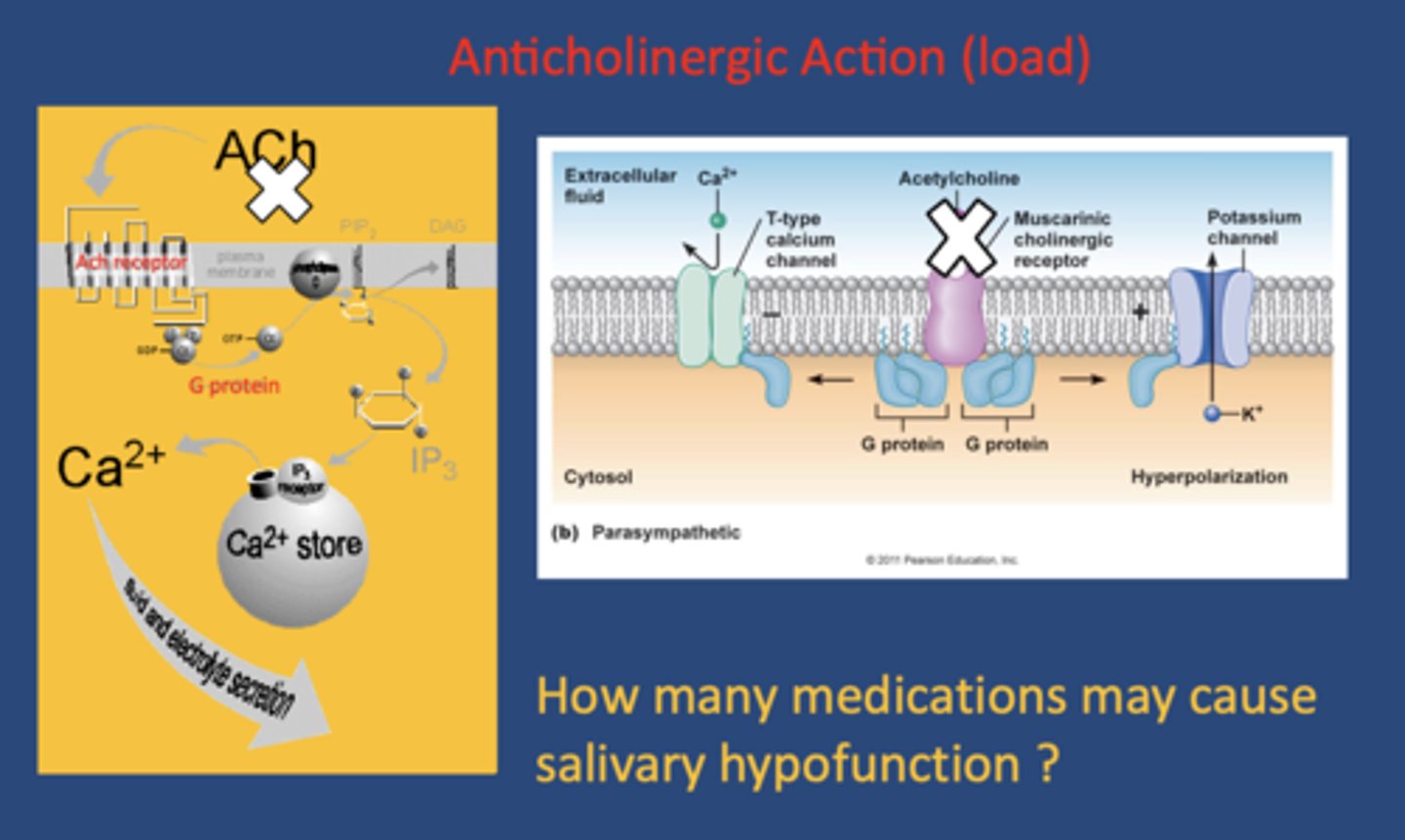
How many medications may cause salivary hypofunction?
400-800 (700+)
unstimulated normal salivary production/flow rate:
~0.3 mL/min

unstimulated hyposalivation salivary production/flow rate:
<0.16 mL/min

oral complication/critical salivary production/flow rate:
<0.10 mL/min

stimulated normal salivary production/flow rate:
1.5 mL/min

stimulated hyposalivation salivary production/flow rate:
<0.5mL/min

How to distinguish irreversible salivary gland destruction vs medication induced salivary hypofunction?
Irreversible: Apoptosis or DNA damage (stimulated and unstimulated saliva is low)
Medication: No damage to salivary glands (Unstimulated flow may be reduced, stimulated is partially preserved)

The salivary flow rate with medication induced salivary hypofunction will be at the ________ (0.3) when the salivary glands are stimulated by mimicking chewing process.
normal level

sialogogues activate the __________ nervous system
parasympathetic
What are the main functions of saliva?
Food: Digestion, taste, bolus formation
Teeth: Buffer, protection against demineralization, remineralization, lubrication
Microorganisms: Anti-viral, anti-fungal, anti-bacterial
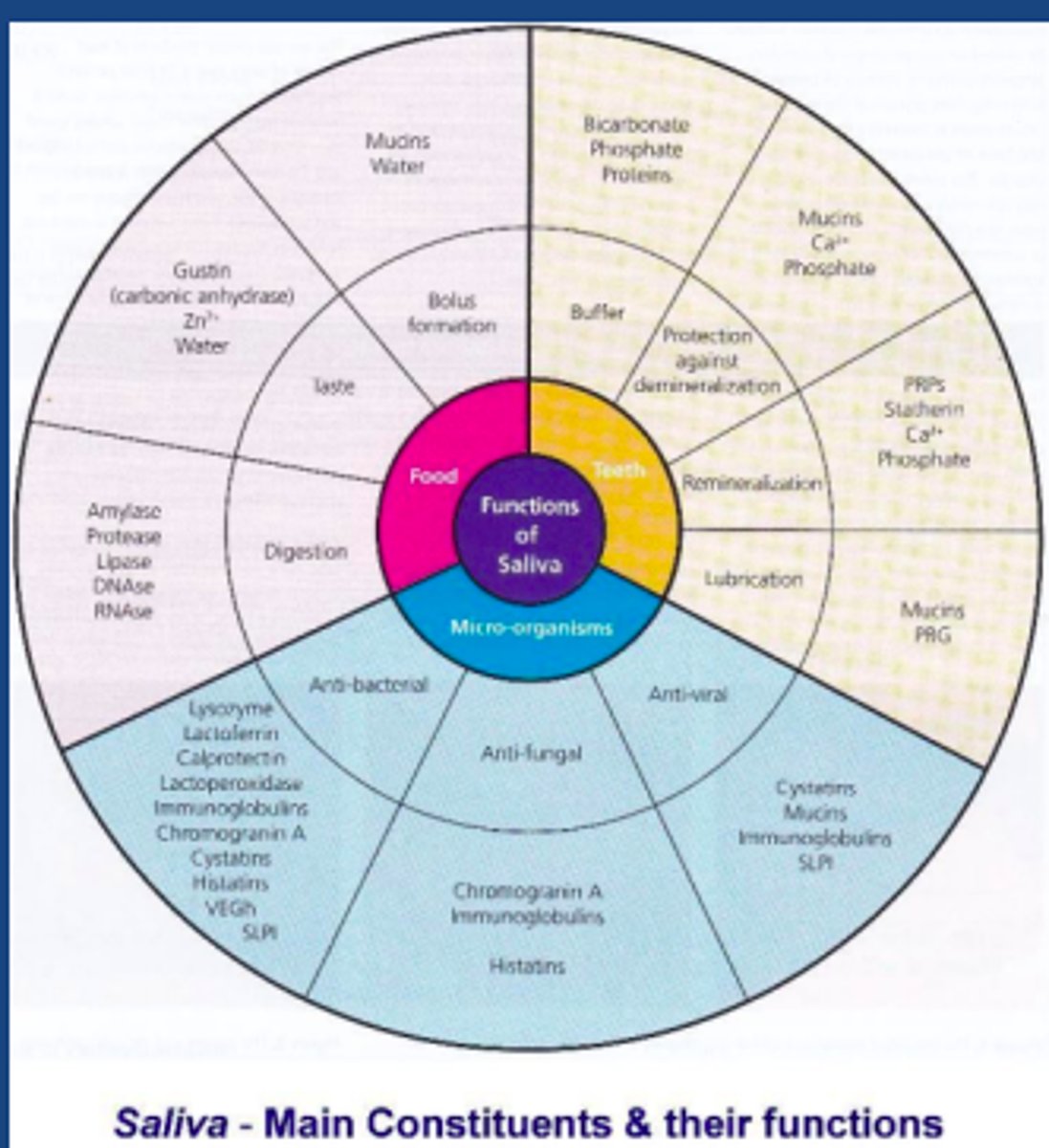
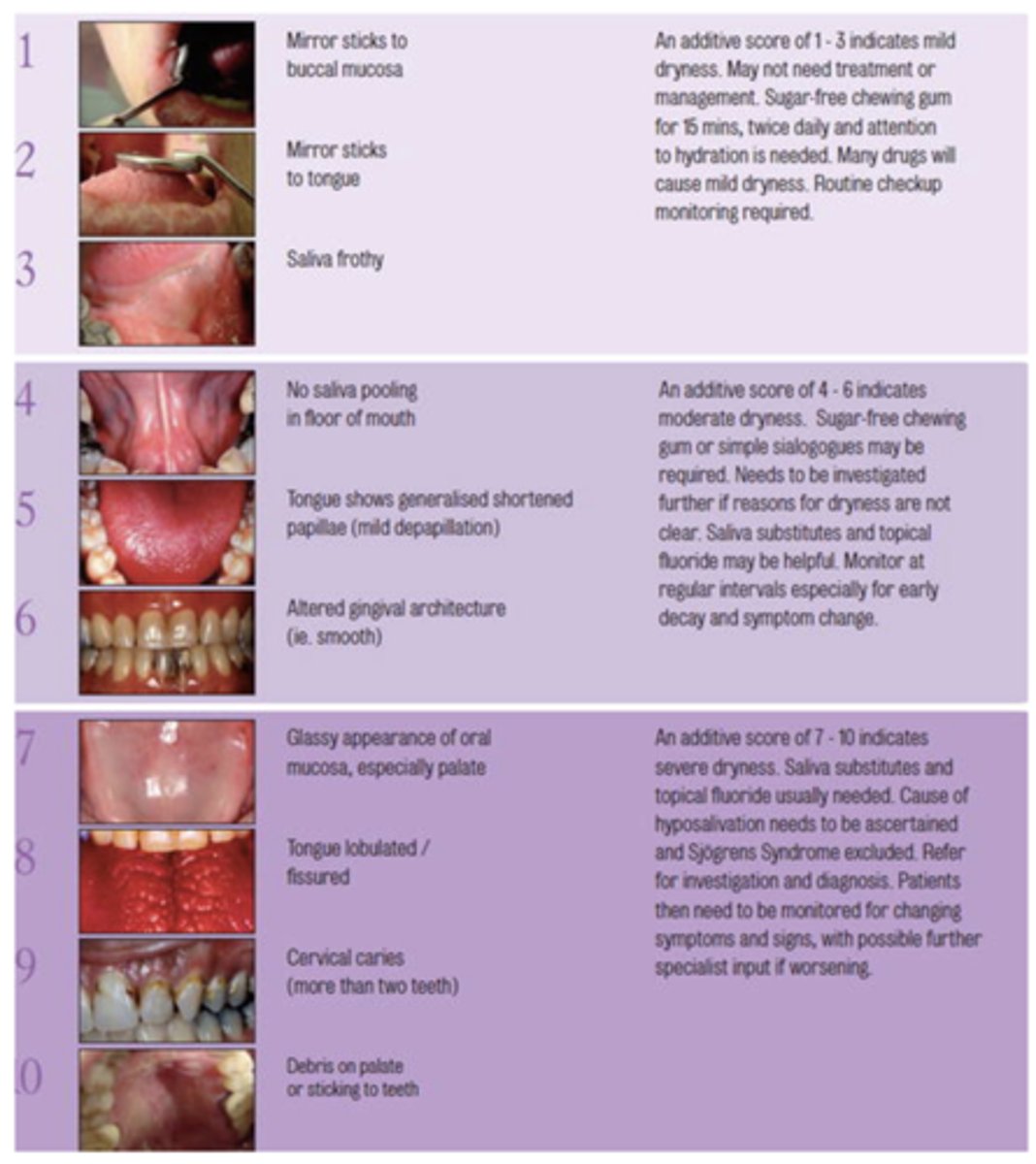
What challacombe scale is the following description?
Mirror sticks to buccal mucosa
1
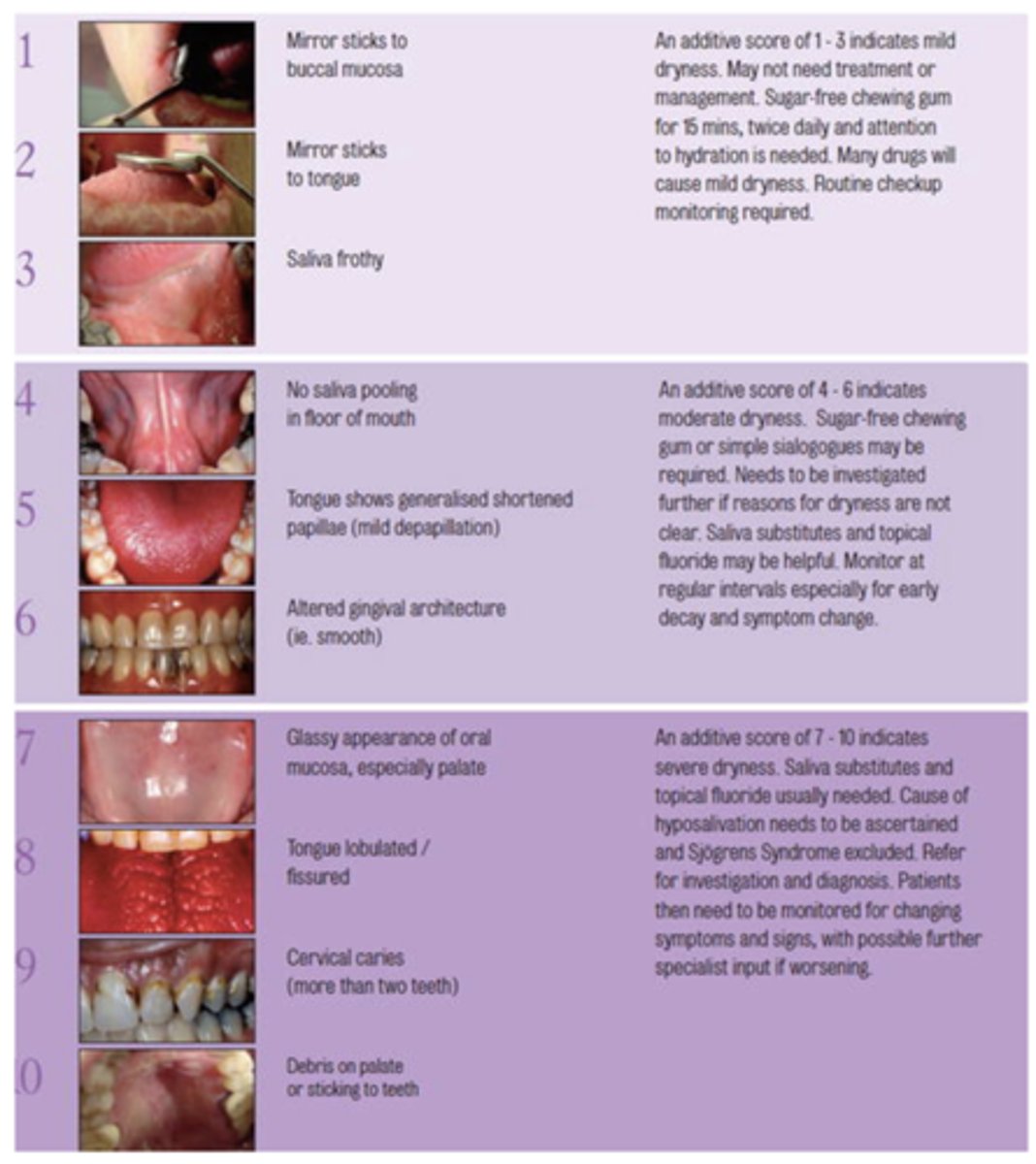
What challacombe scale is the following description?
Mirror sticks to tongue
2
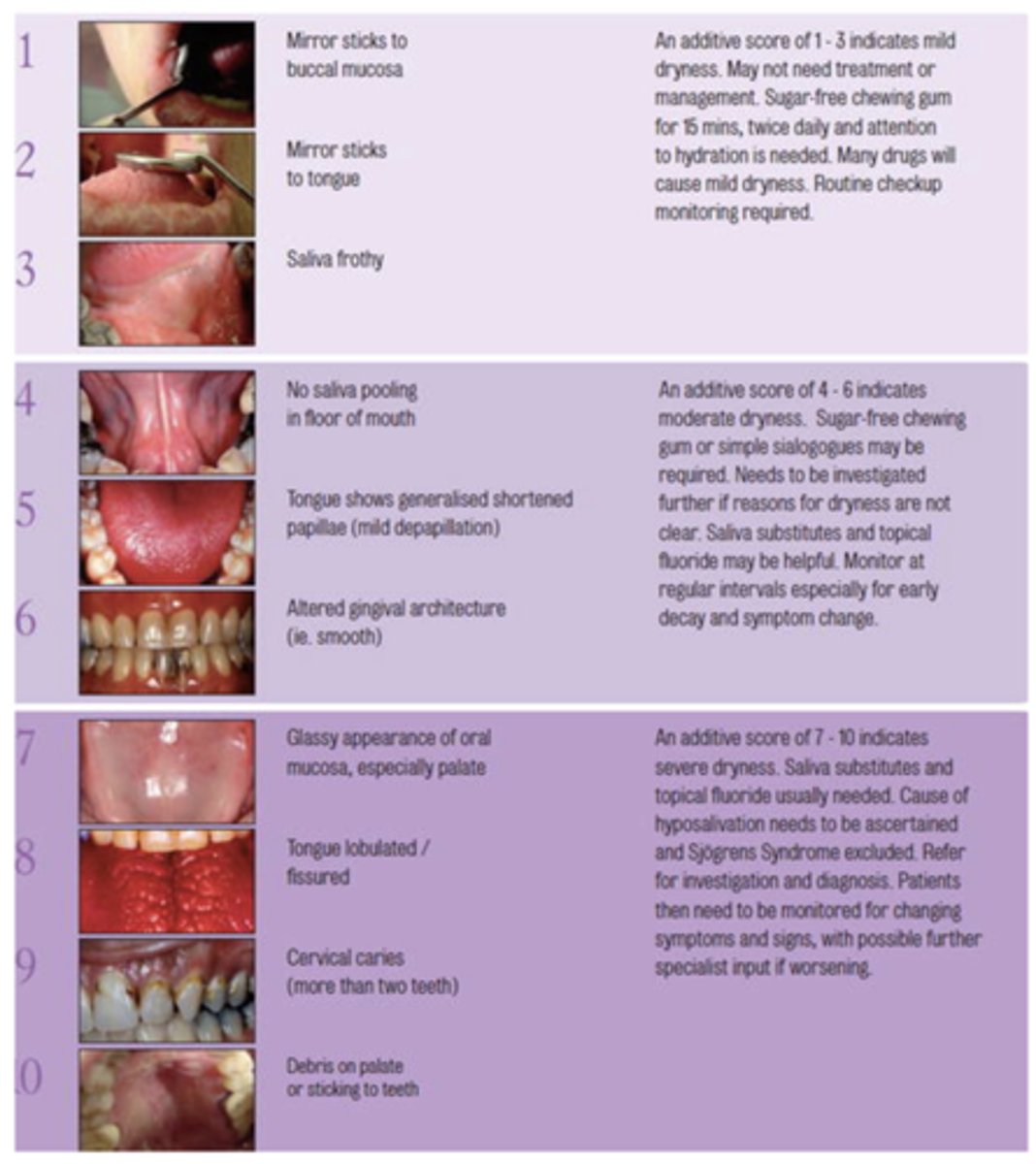
What challacombe scale is the following description?
Saliva frothy
3
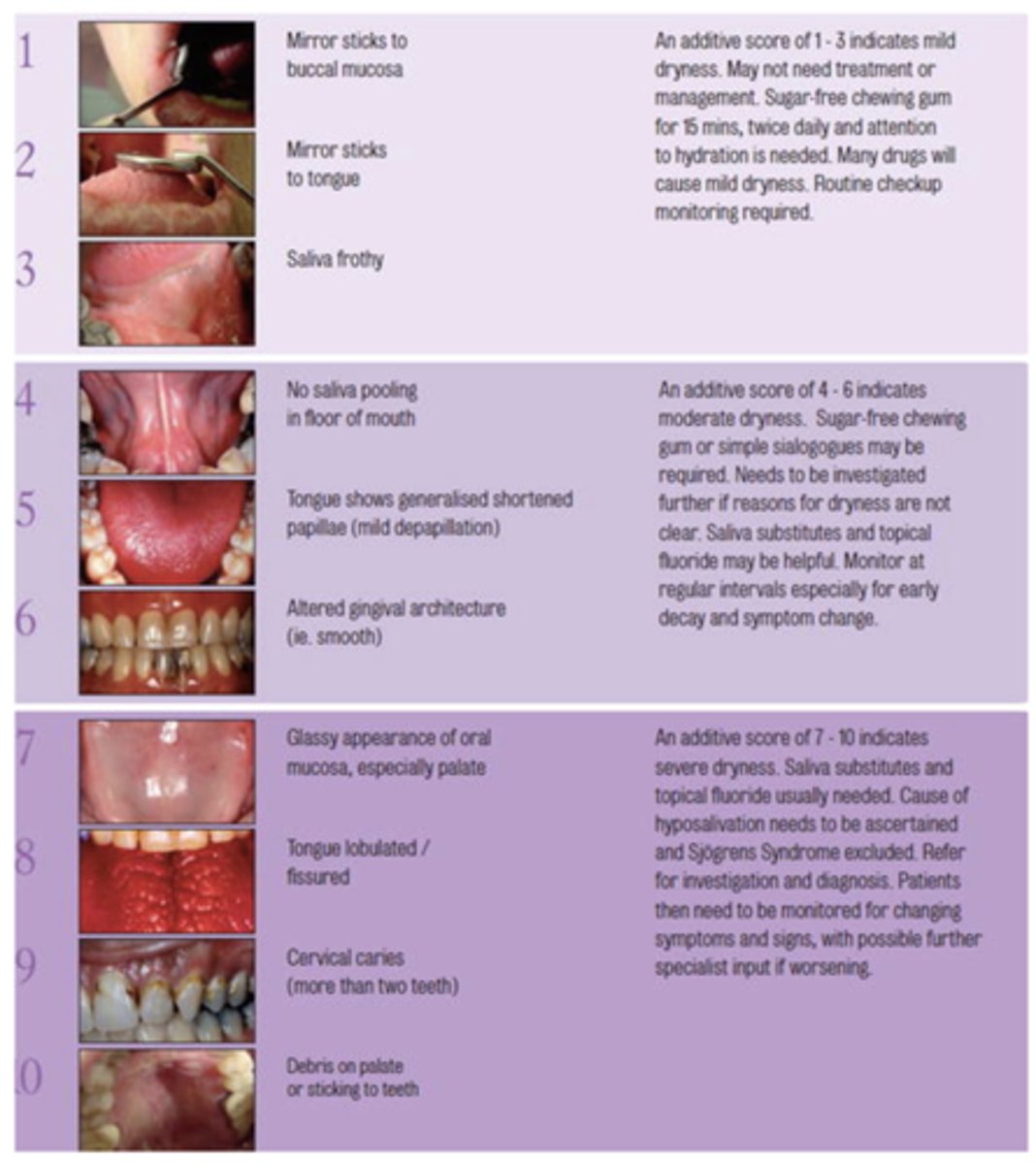
What challacombe scale is the following description?
No saliva pooling in floor of mouth
4
What challacombe scale is the following description?
Tongue shows generalized shortened papilla (mild depapillation)
5
What challacombe scale is the following description?
Altered gingival architecture (ie. smooth)
6
What challacombe scale is the following description?
Glassy appearance of oral mucosa, especially palate
7
What challacombe scale is the following description?
Tongue lobulated/fissured
8
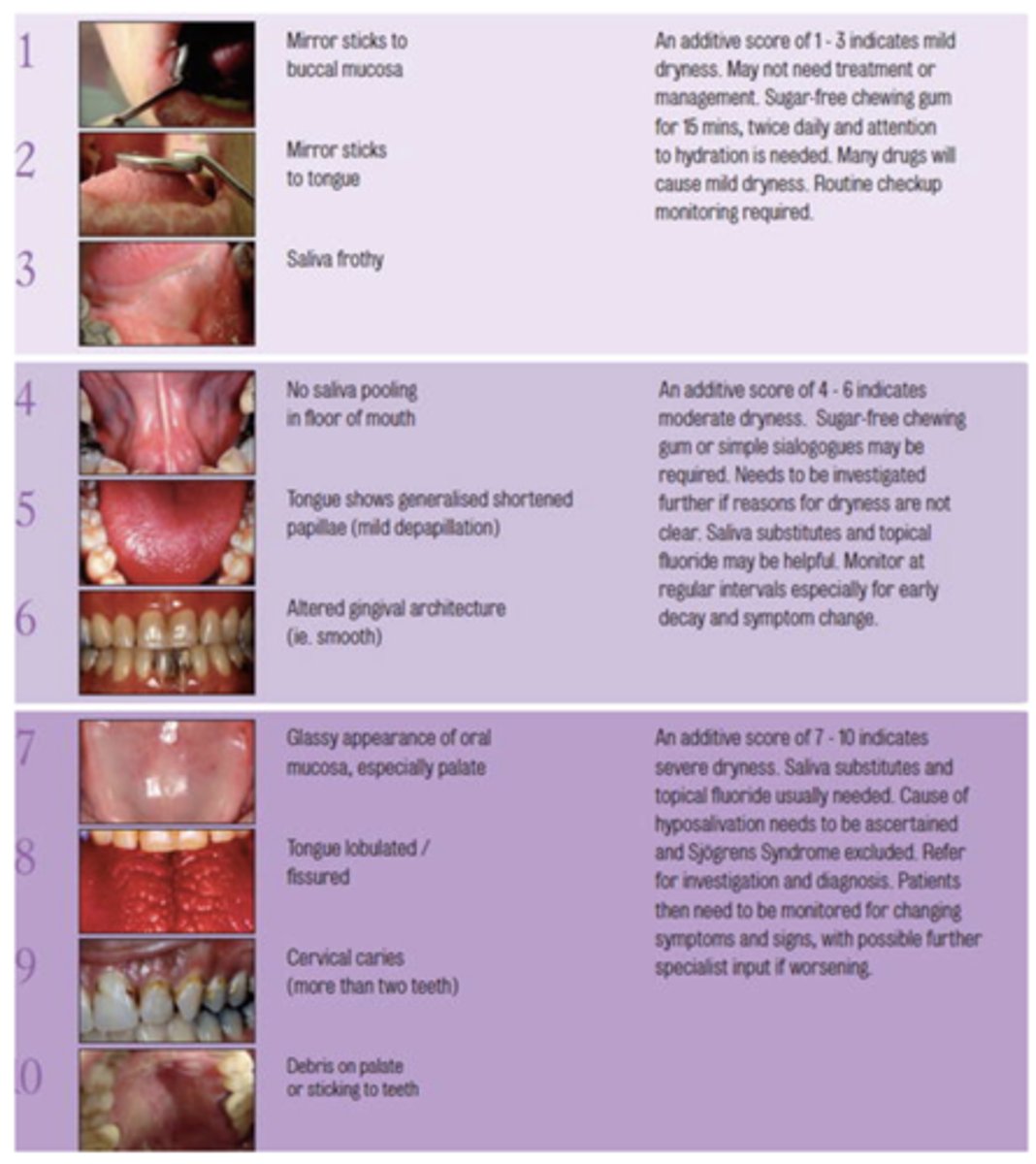
What challacombe scale is the following description?
Cervical caries (more than two teeth)
9
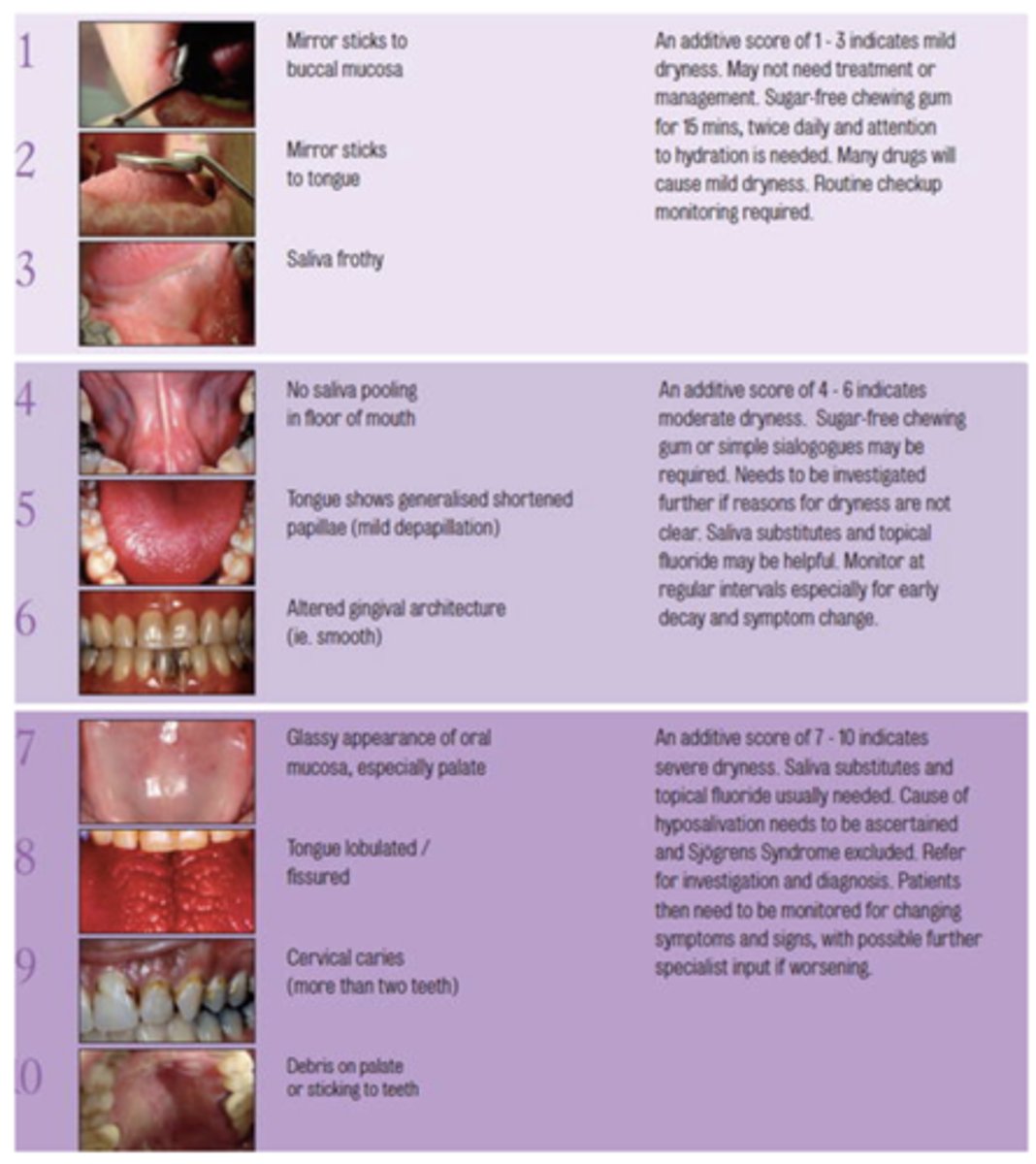
What challacombe scale is the following description?
Debris on palate or sticking to teeth
10
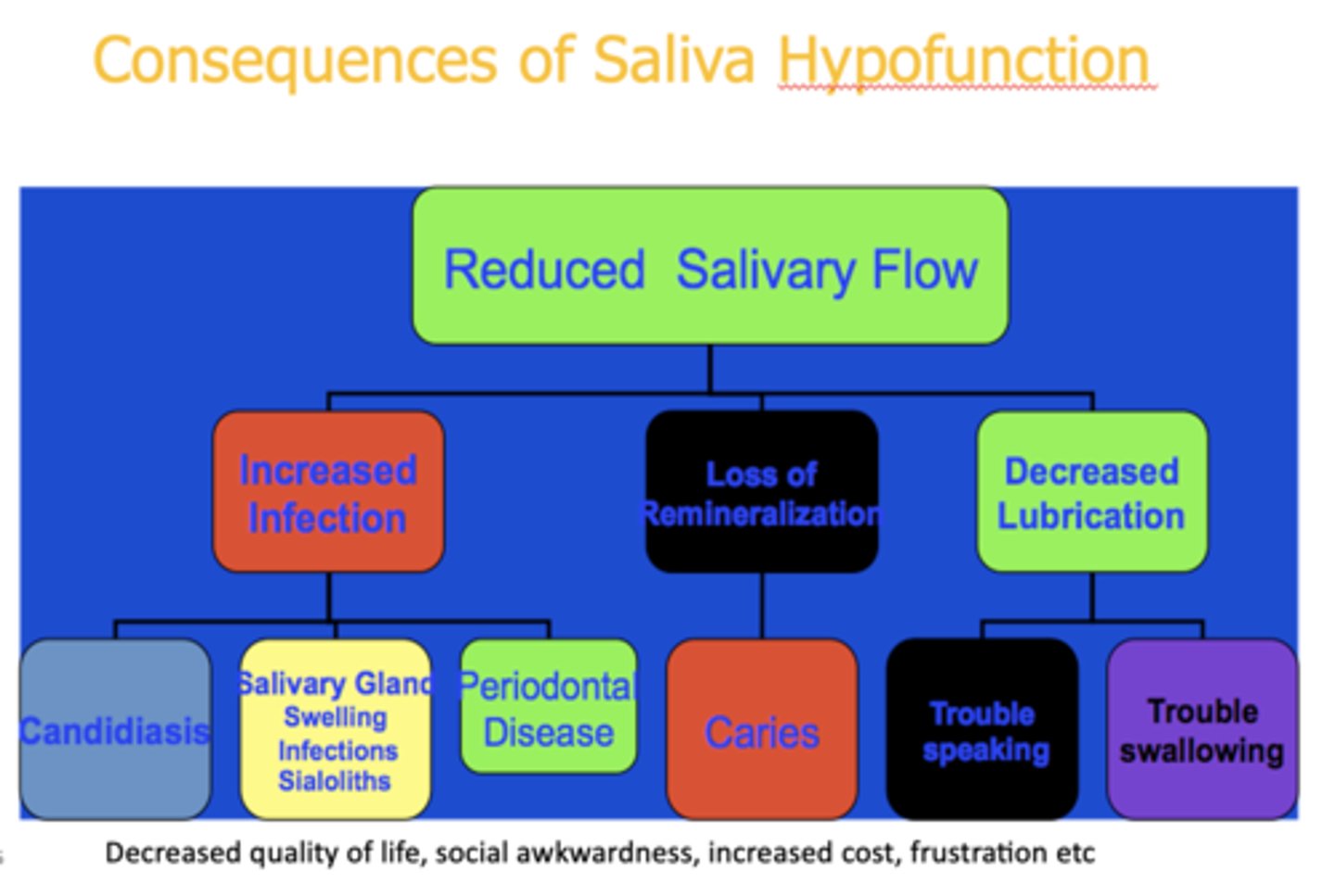
What are the 3 consequences of reduced salivary flow?
- Increased infection
- Loss of remineralization
- Decreased lubrication
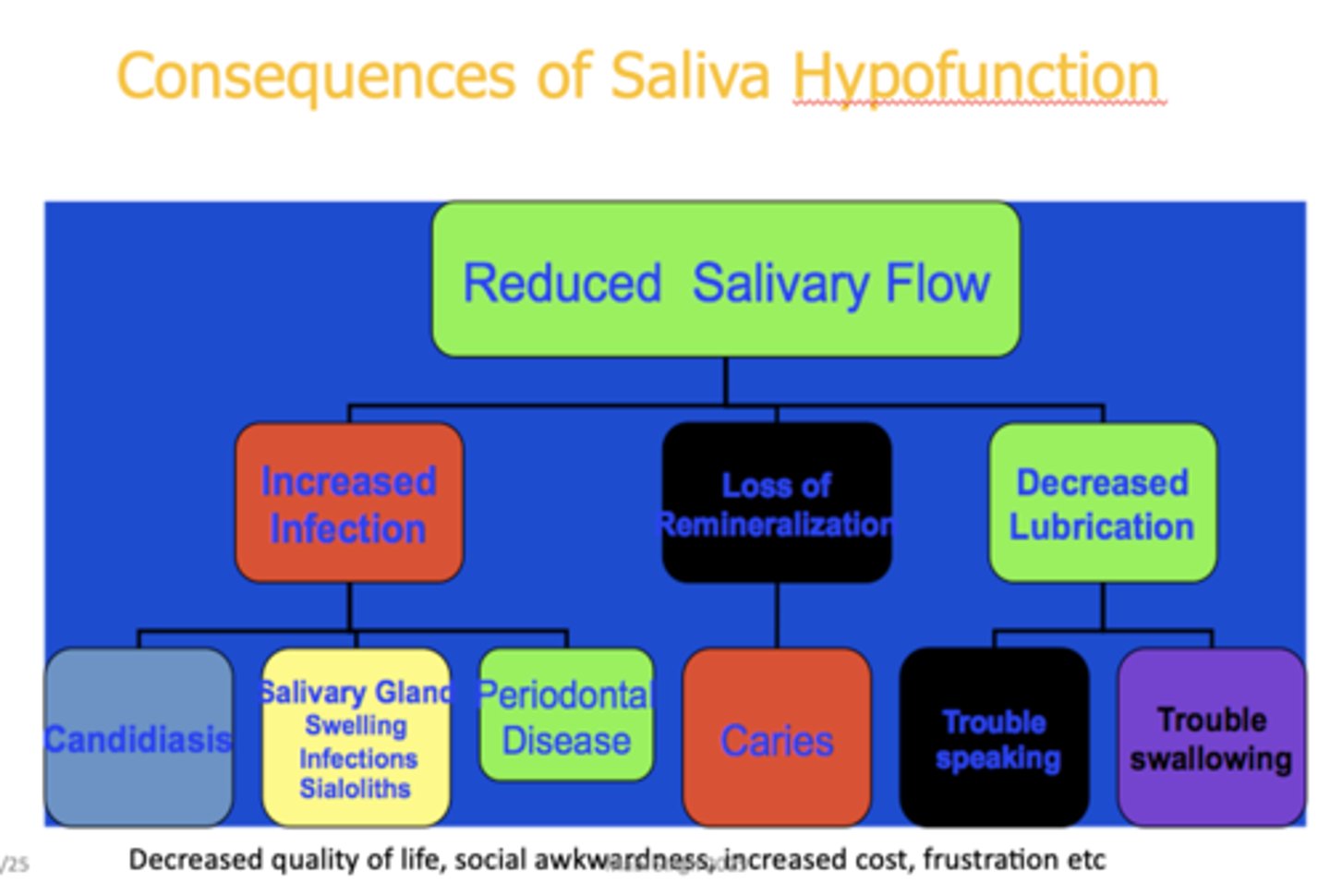
t/f: Decreased quality of life, social awkwardness, increased cost, frustration are all consequences of salivary hypofunction
true
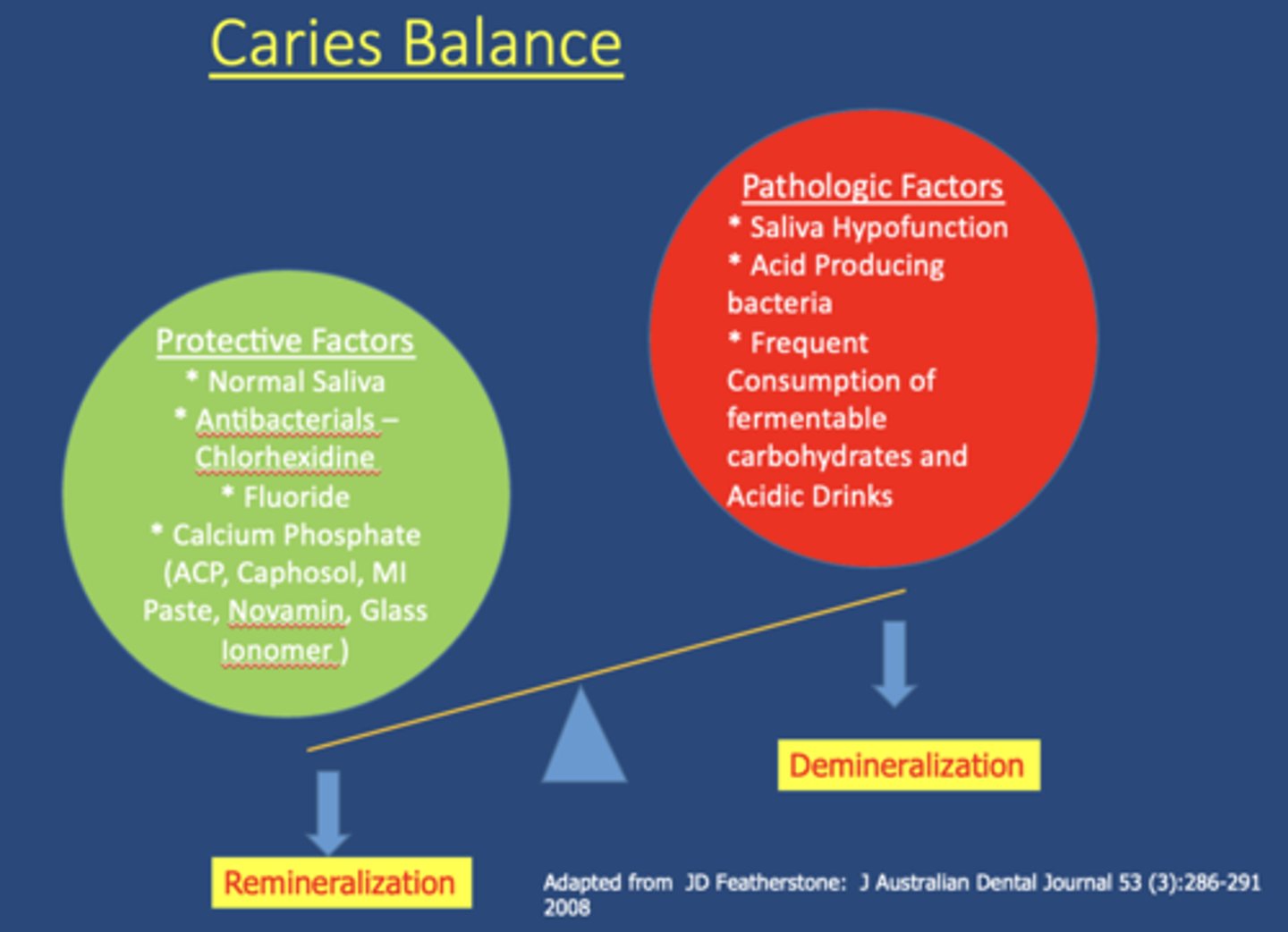
Which of the following are protective factors of saliva?
a. contain buffers that neutralize acids
b. flow for clearance purposes
c. fluoride from topical
d. antibacterial agents
e. salivary proteins and lipids form pellicle and protect tooth surface
f. calcium & phosphorous
g. all of the above
g. all of the above
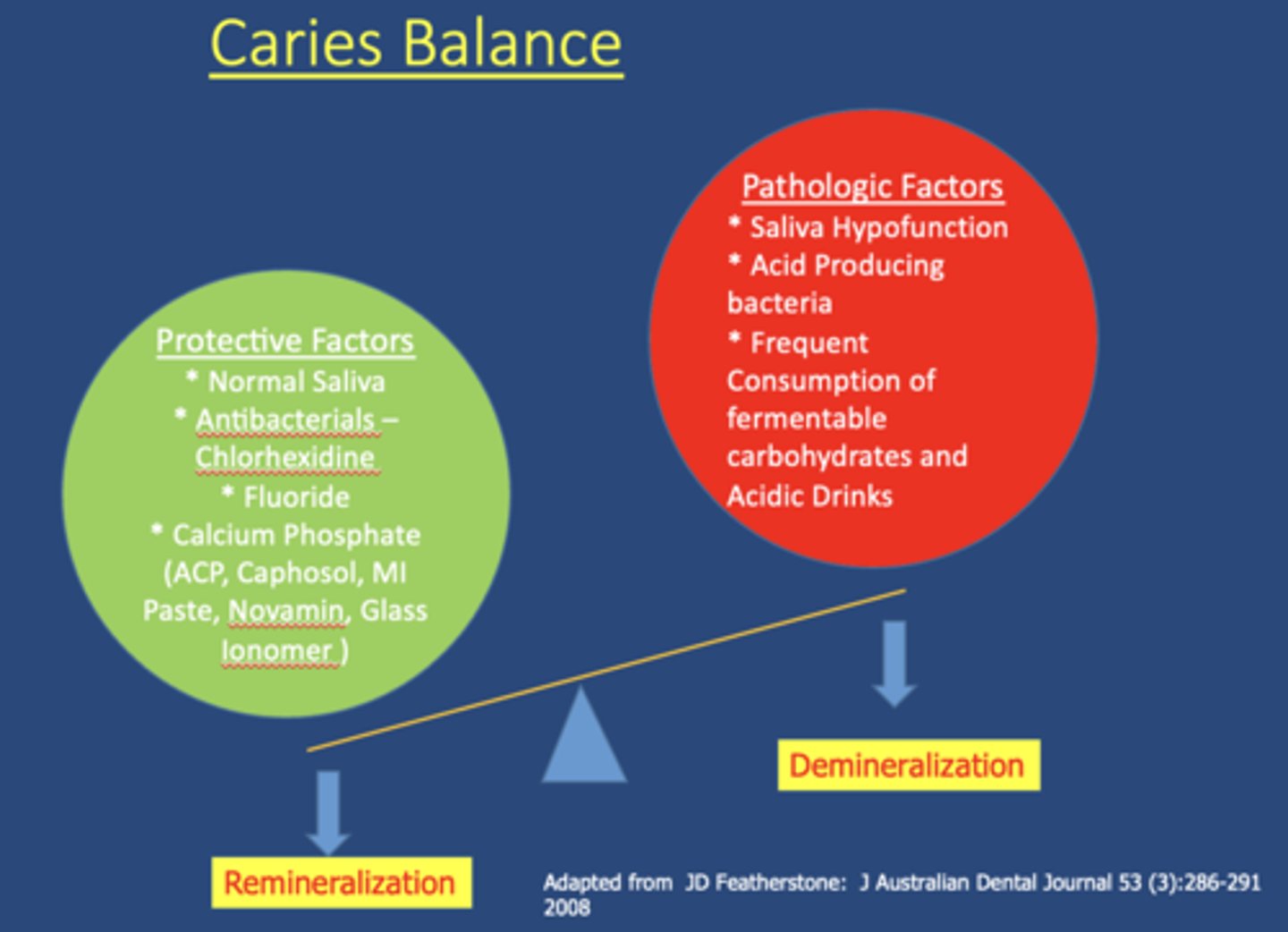
Which of the following are pathologic factors of saliva?
A. Saliva Hypofunction
B. Acid Producing bacteria
C. Frequent Consumption of fermentable carbohydrates and Acidic Drinks
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
What are the two options to overcome complications of salivary hypofunction due to medications?
1. Change medications (if possible)
2. Sialogogues
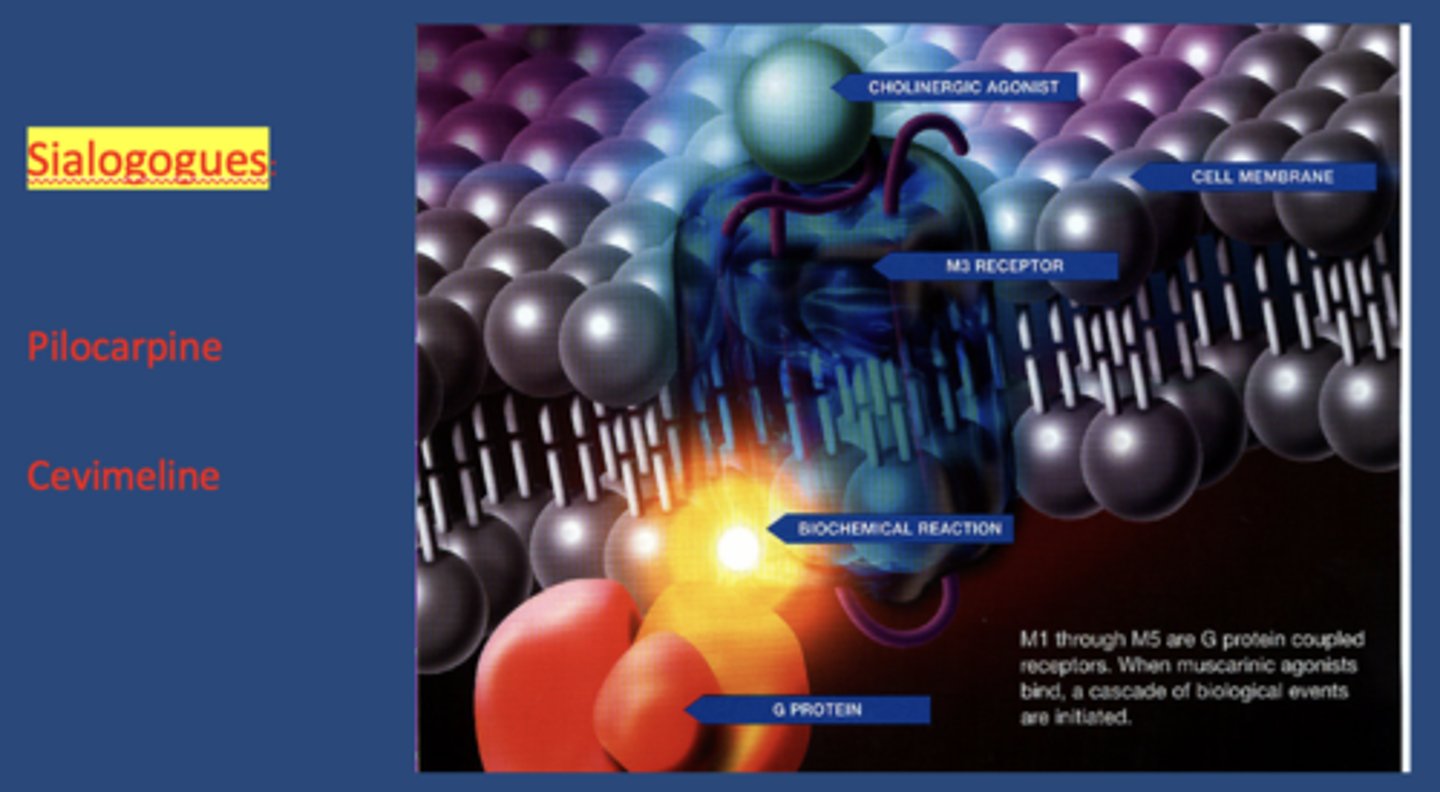
sialogogues act on mostly on _________ receptors
M3 muscarinic
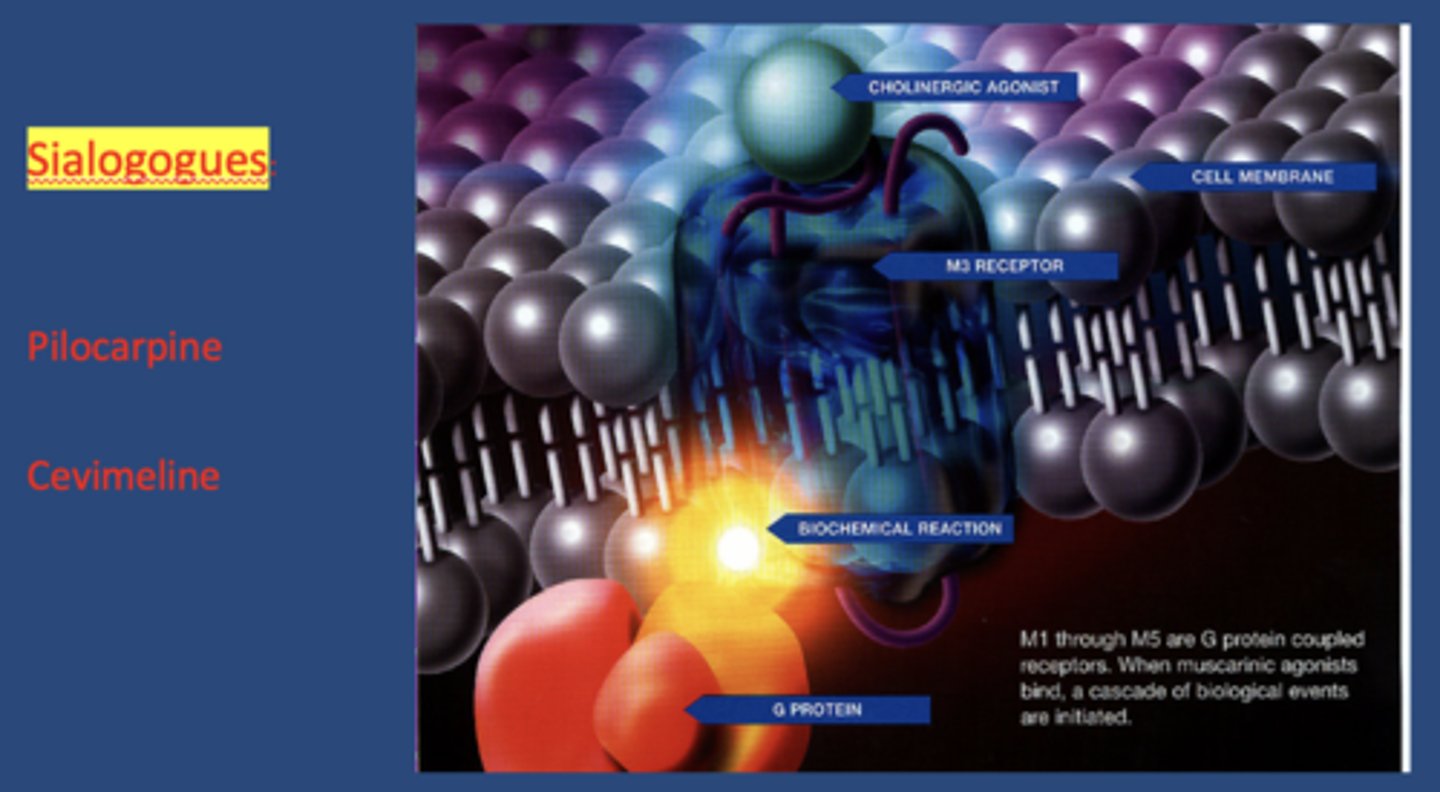
name 2 commonly prescribed sialogogues:
- Pilocarpine HCl
- Cevimeline HCl
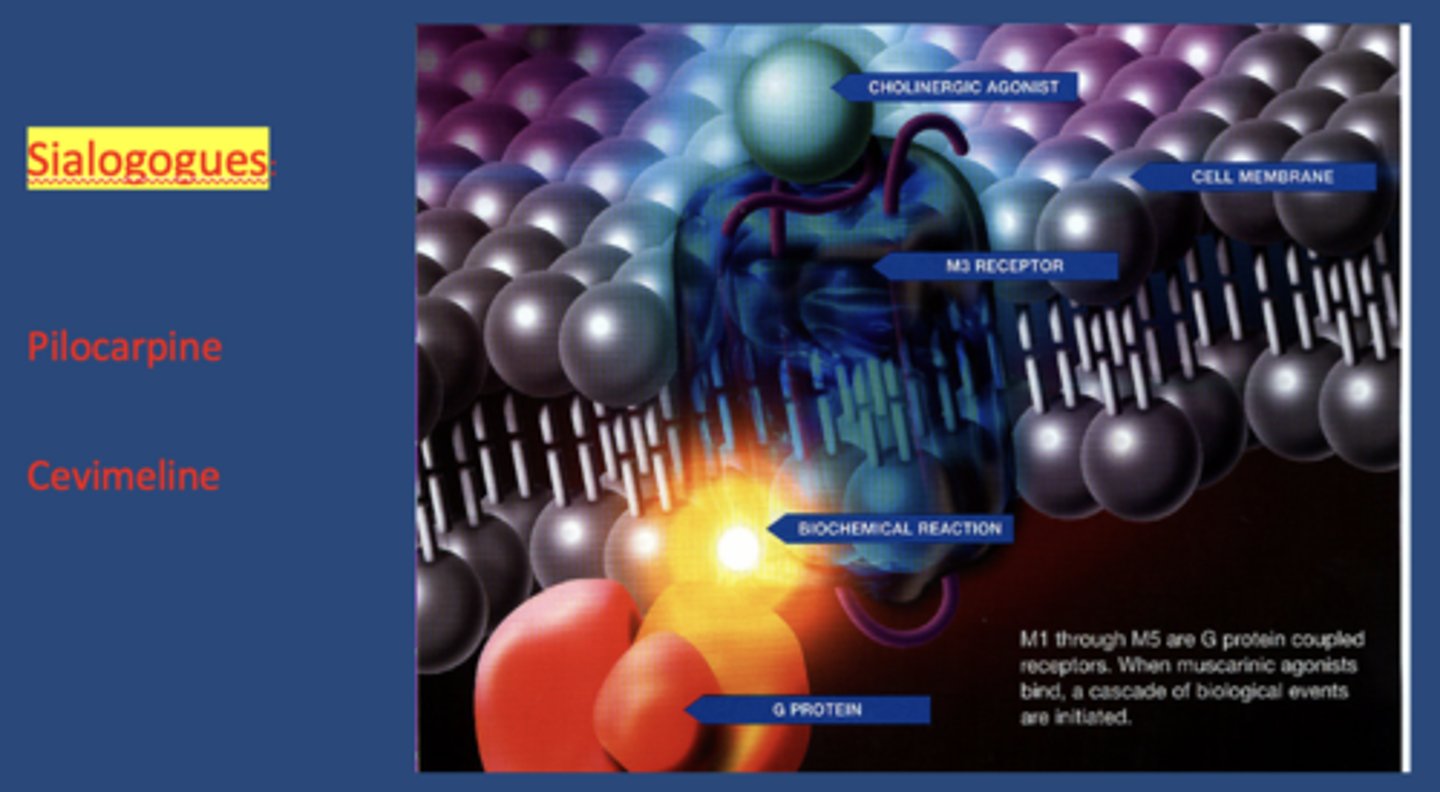
the half-life of Pilocarpine HCl is:
3 hours
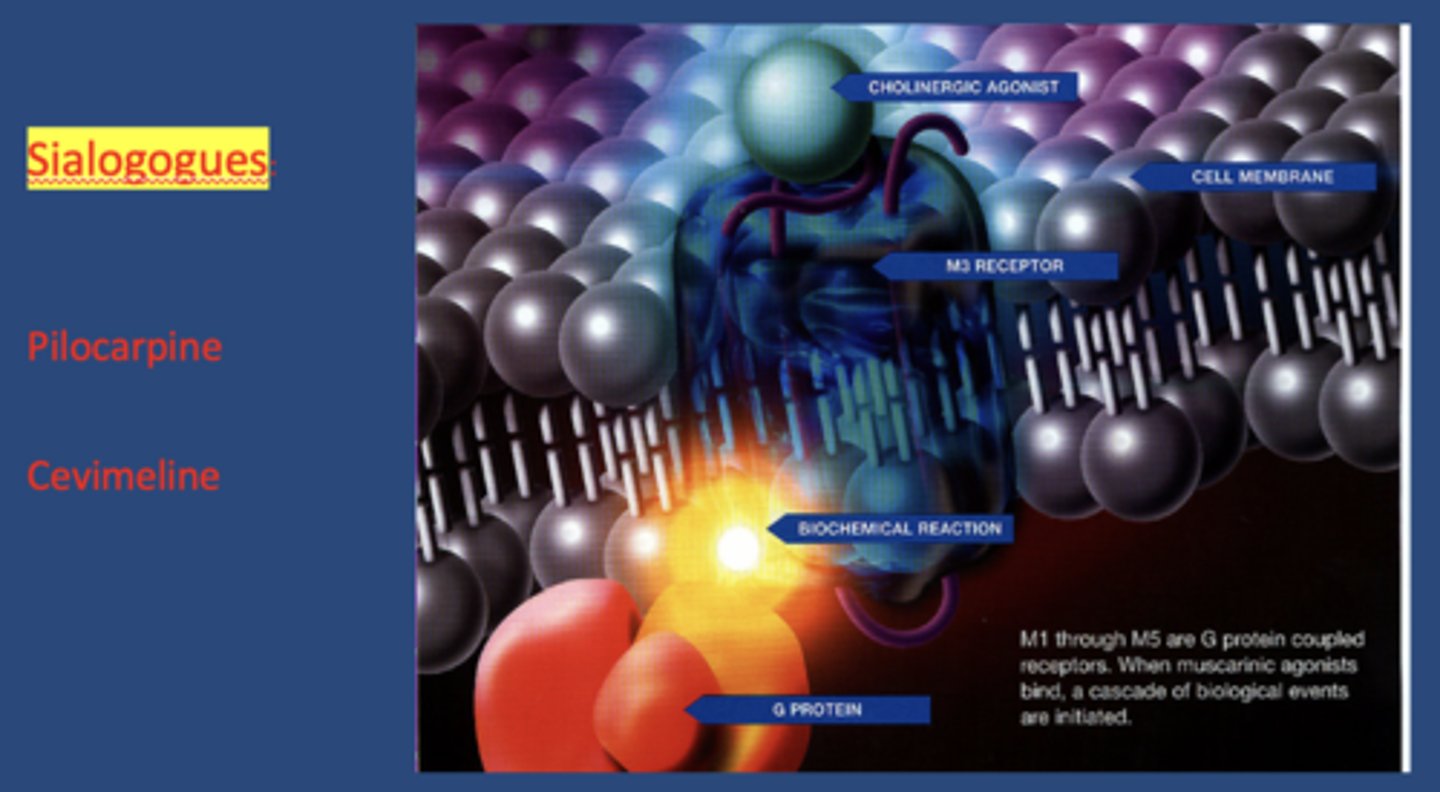
the half-life of Cevimeline HCl is:
5-6 hours
Which substrate is metabolized to produce ammonia and help buffer oral pH?
Arginine
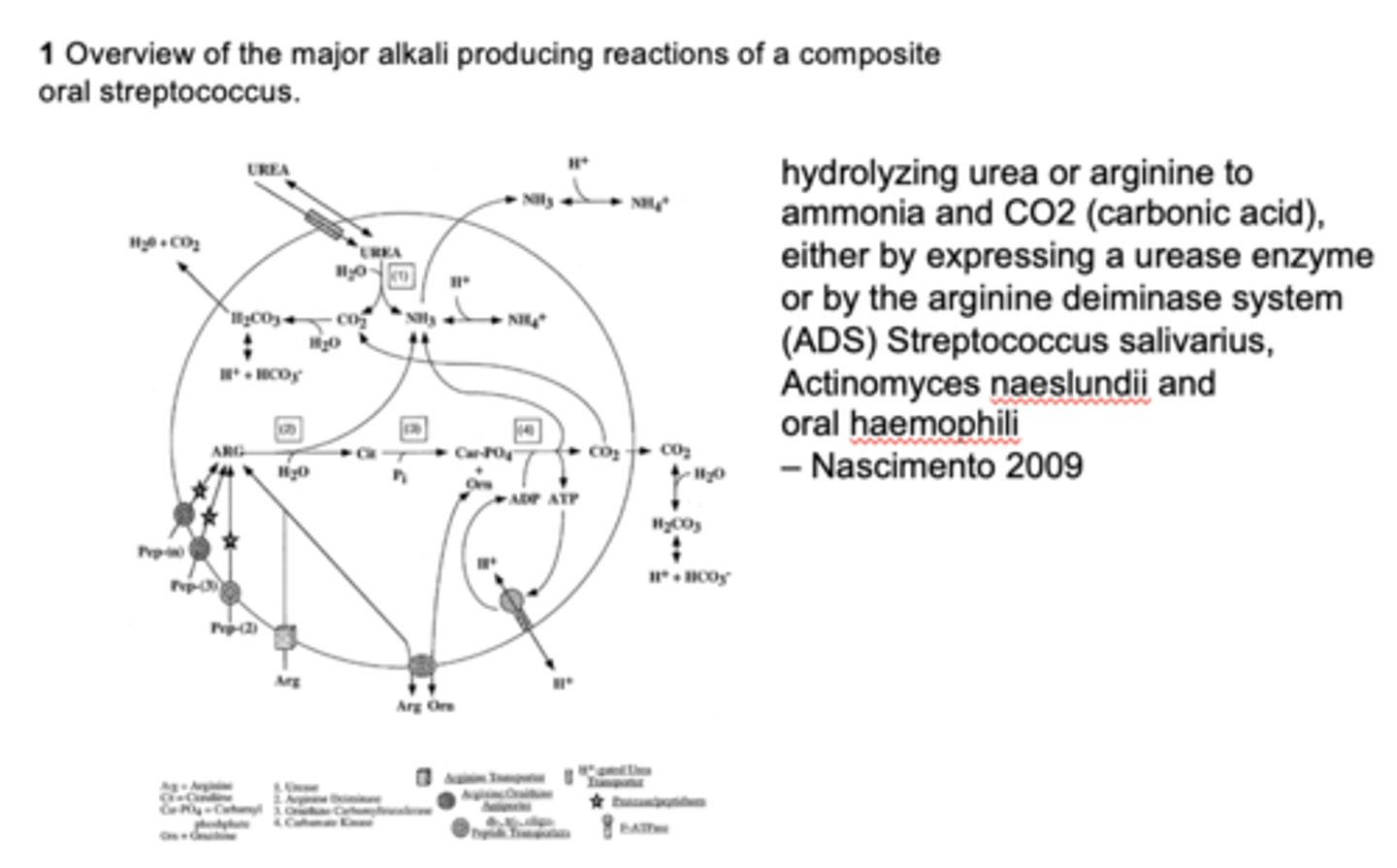
What is the primary role of alkali generation in the oral cavity?
Buffers acids and protects against caries
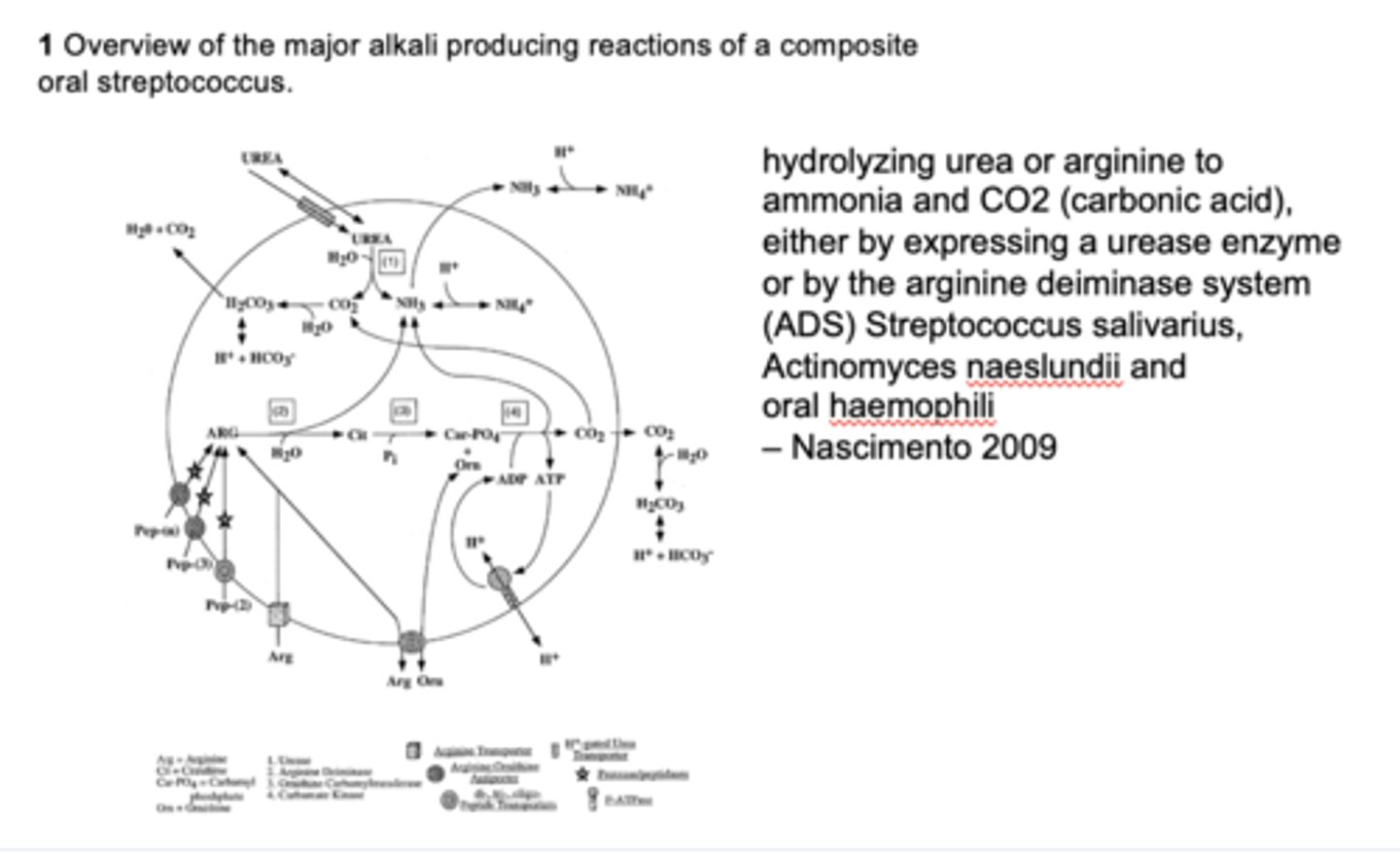
How does arginine change pH?
Increases pH (bc of ammonia production and alkali generation)
How does xylitol affect saliva?
Increases saliva volume (reduces caries risk)
What is a major limitation of artificial saliva?
It is quickly removed during swallowing

Why are salivary substitutes considered palliative rather than curative?
Their effects are short-lived and do not mimic natural protective functions

What are drawbacks of salivary substitutes?
A. Short duration of effect
B. Removed quickly during swallowing
C. Do not provide protective functions of natural saliva
D. All of the above
D. All of the above

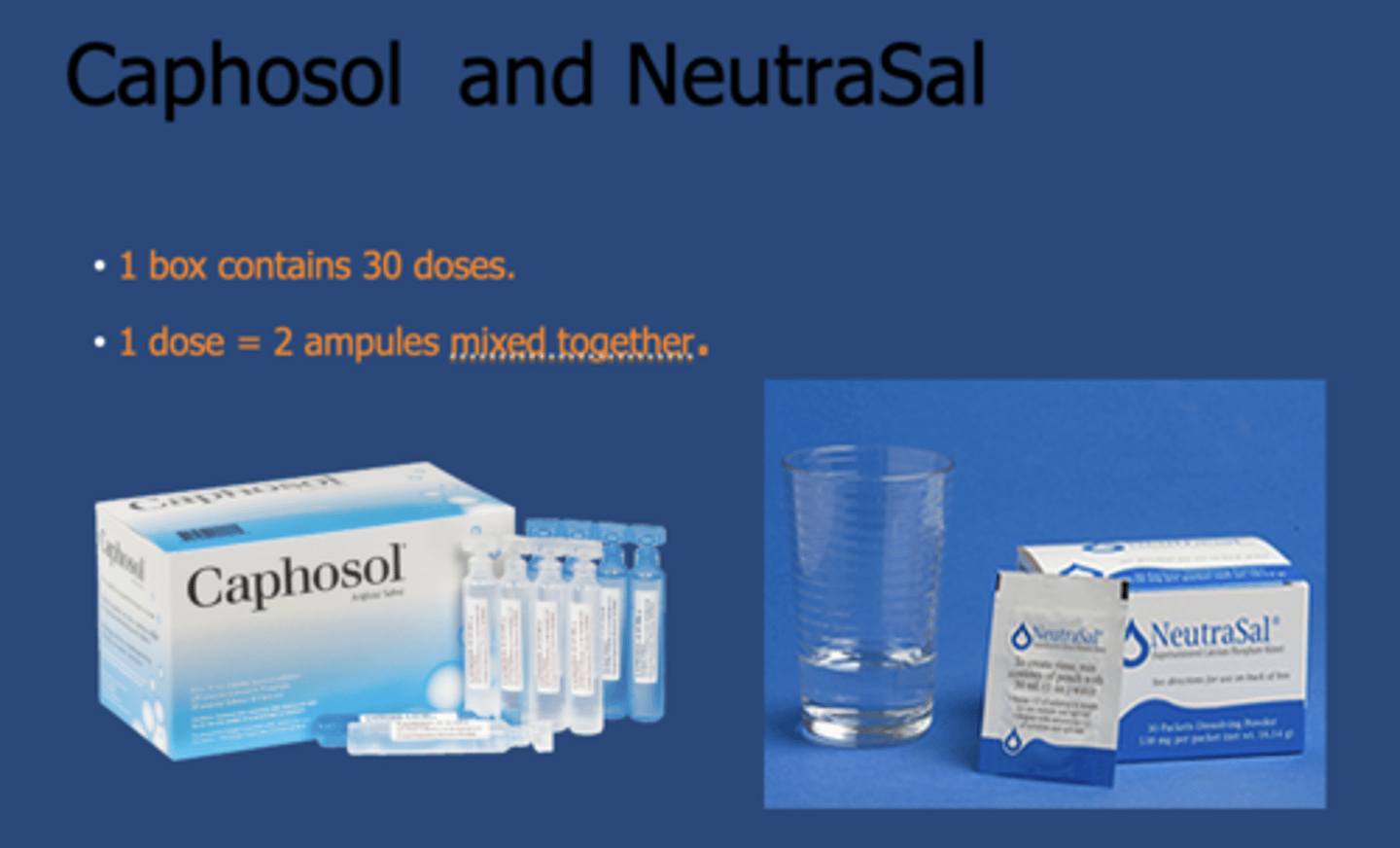
What is the role of caphosol and neutrasal with saliva?
Provide palliative relief for dry mouth by hydrating tissues, buffering pH, and supporting tissue repair
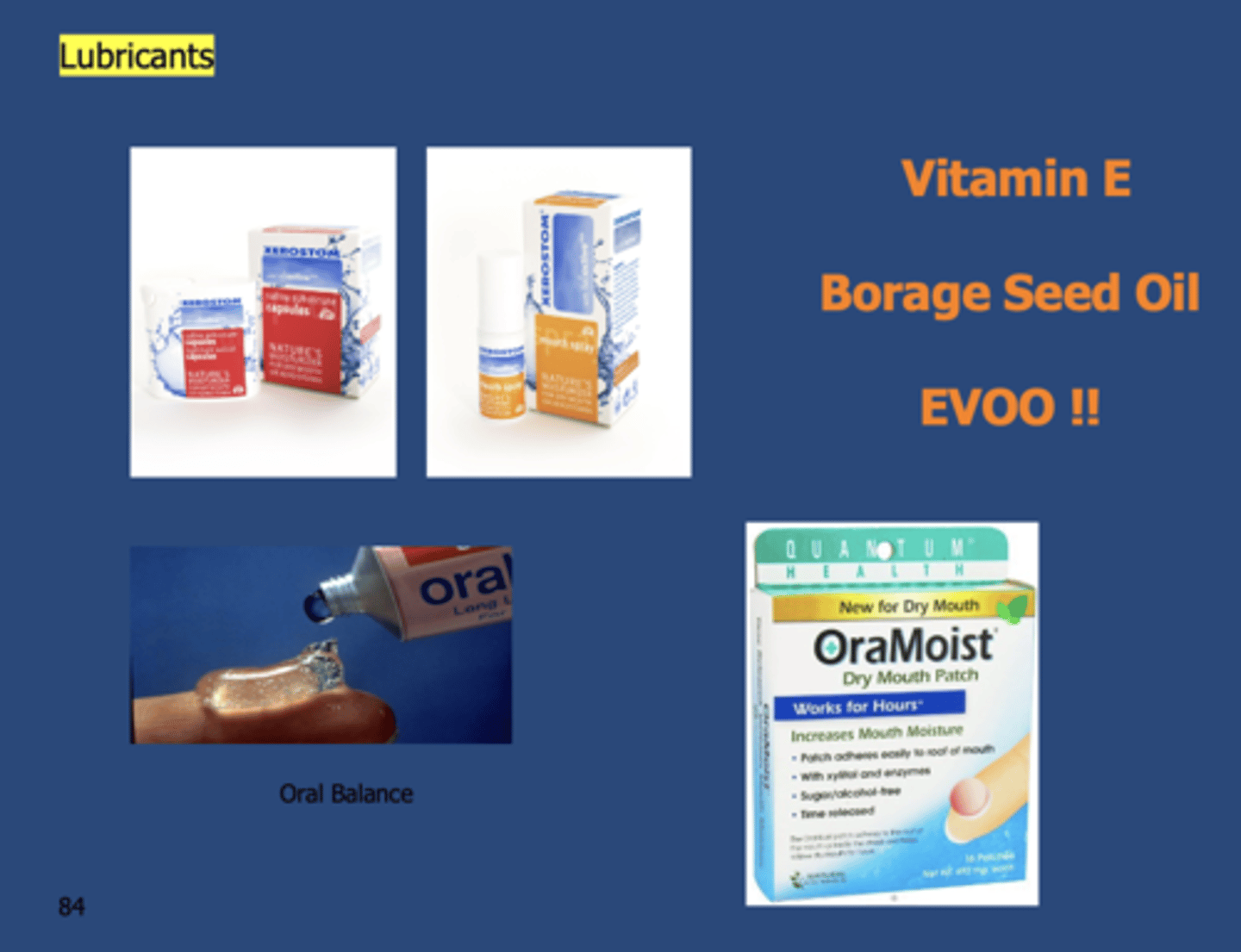
What are 3 examples of lubricants for the oral cavity?
- Vitamin E
- Borage Seed Oil
- EVOO !!
What is the purpose of high fluoride toothpaste?
It promotes the formation of fluorapatite crystals, which are more resistant to acid demineralization, thereby helping to strengthen enamel and prevent caries.

T/F: Silver ion is bactericidal
True

What promotes mineral remineralization both enamel and dentine caries (protection of the collagen matrix from degradation)?
Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF)

What is the benefit of biotene?
Does not have abrasives and irritants so is good to use toothpaste during treatment

T/F: Xylitol gum helpful in stimulating saliva without increasing caries
True
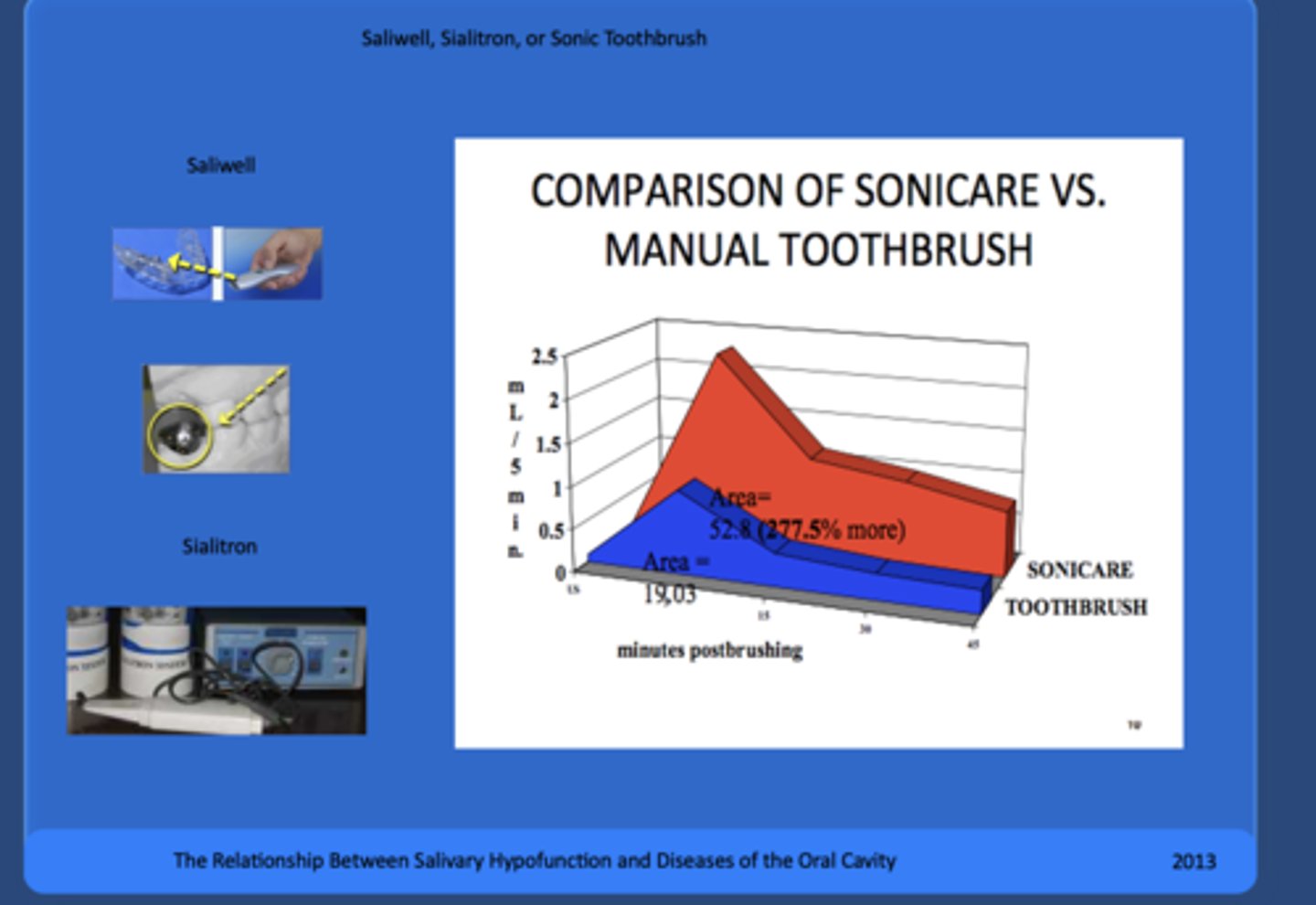
What type of tooth brush can be helpful dislodging biofilm from mucosal surfaces?
Electric toothbrushes
Which class of medications are most likely to cause xerostomia/dry mouth?
Psycholytics
t/f: taste buds need saliva to solubilize chemicals in food
true
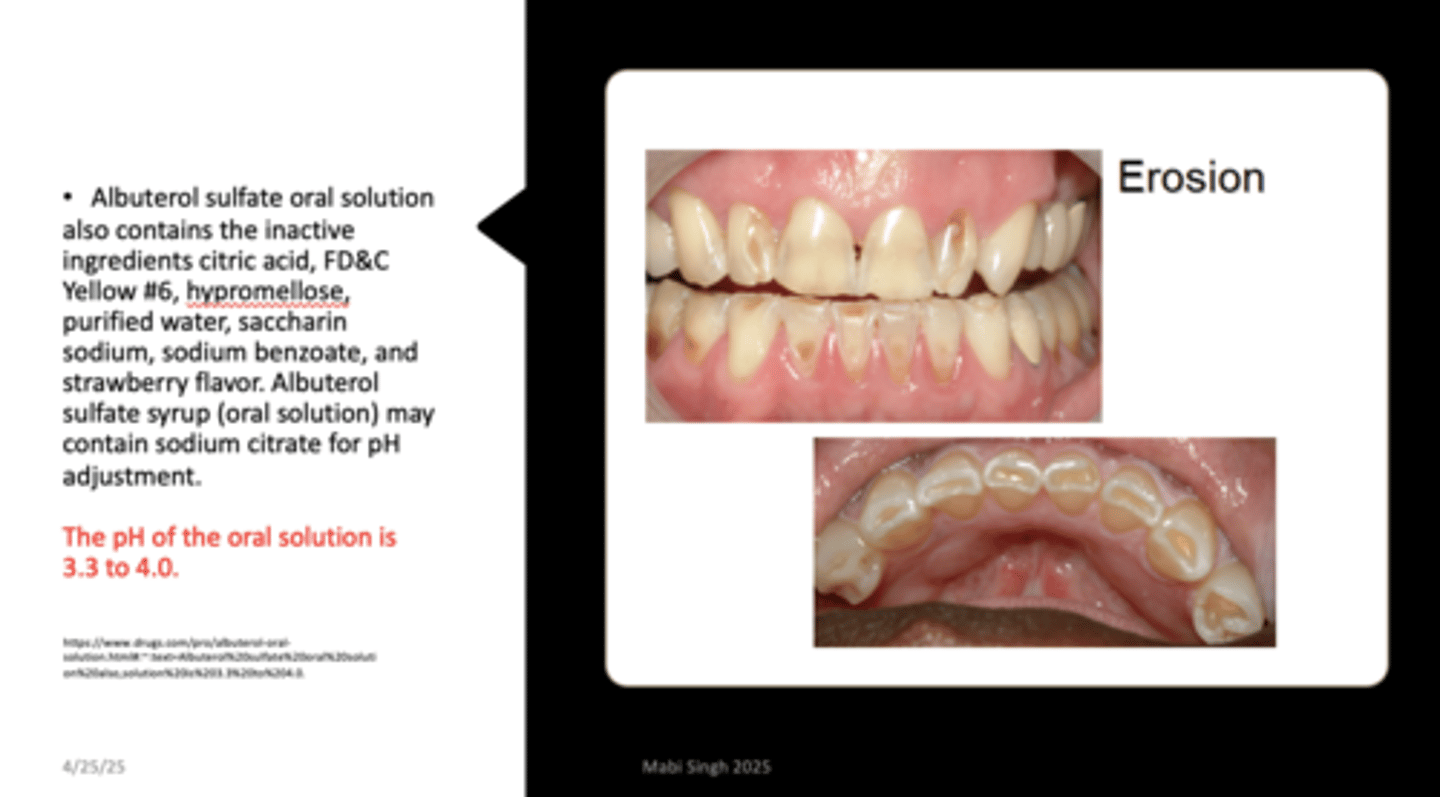
What is the pH of Albuterol sulfate oral solution?
3.3 to 4
Prevalence of caries is increased in what 3 conditions discussed in lecture (highest to lowest prevalence)?
Radiation > Sjogrens > Medication
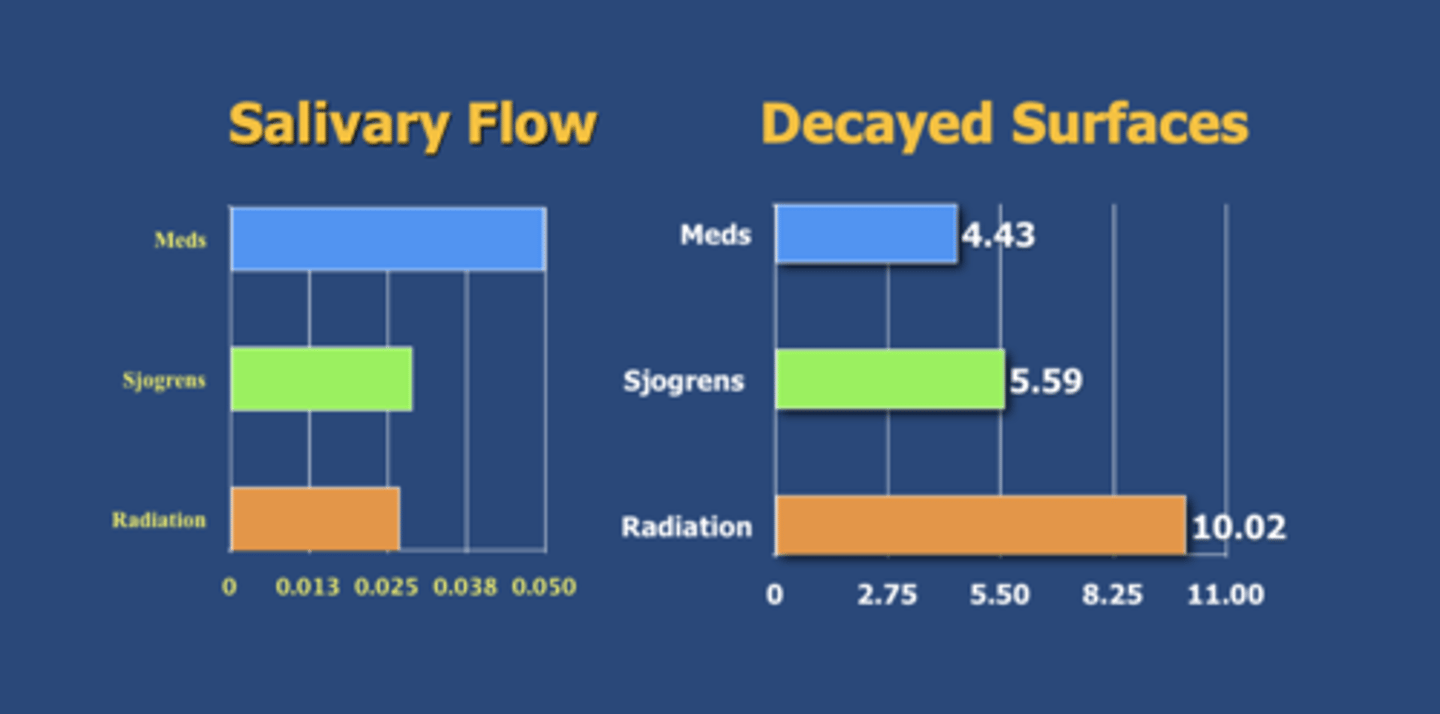
T/F: Children who used their medication greater than twice daily were significantly more likely to experience dental disease in both the primary and mixed dentitions
True
