Disasters/Emergency Preparedness Environmental Health
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch. 9 & 17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Defining Disasters
Any natural or human-made incident that causes disruption, destruction, or devastation requiring external assistance.
Type and timing predict subsequent injuries and illnesses.
Disasters with little or no advance notice, such as terrorism events, will often have more casualties because those affected have little time to make evacuation preparations.
Disasters with warnings also carry their own dangers, because individuals can be injured attempting to prepare for the disaster or while evacuating.

Disaster Events
Range from affecting individuals to entire communities
Continue to rise worldwide
Disproportionately strike at-risk individuals
Consistently more costly to recover from
Disasters can affect one family at a time, as in a house fire, or they can kill thousands and result in economic losses in the millions, as with floods, earthquakes, tornadoes, hurricanes, tsunamis, and bioterrorism.
Factors Contributing to the Potential for Disaster
Epidemiologic triad
Host Factors:
Age, general health, mobility, psychological factors, and even socioeconomic factors
Agent Factors:
Natural or technologic element that causes the disaster
Environment Factors:
Those that could potentially contribute to or mitigate a disaster
Characteristics of Disasters: Scope
Range of its effect, either geographically or in terms of the number of victims.
Characteristics of Disasters: Intensity
The level of destruction and devastation it causes.
Victims of Disasters
Direct Victims: people experiencing event; dead and survivors
Displaced persons: forced to leave to escape effects of disaster; usually temporary
Refugees: people forced to leave homeland due to war or persecution
Indirect Victims: relatives or friends of direct victims
What are the 4 Phases of a Disaster?
Prevention or Mitigation
Preparedness
Response
Recovery
Phase 1: Prevention (Mitigation & Protection)
Prevention:
No disaster expected or anticipated
To identify community risk factors and to develop and implement programs to prevent disasters from occurring
Prevention Against Natural Disasters:
* Prevention can include structural measures, such as protecting buildings and infrastructure from the forces of wind and water, and nonstructural measures, such as land development restrictions.
Structural measures
Protecting buildings and infrastructure
Threats include forces of wind and water
Nonstructural measures
Land development restrictions
Prevention Against Human-Made Disasters:
Heightened inspections
Improved surveillance and security operations
Public health and agricultural surveillance and testing
Immunizations
Isolation
Quarantine
Halting of chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, and explosive (CBRNE) threats
Masking/social distancing
Phase 2: Preparedness
Personal Preparedness:
Disaster kits for home, workplace, and car
Professional Preparedness:
National Disaster Medical System (NDMS)
Medical Reserve Corps (MRC)
Community Emergency Response Team (CERT)
Community preparedness (Drills, plans)

Phase 3: Response
Occurs immediately after the onset of the disastrous event and during the emergency.
Put plans into action to save lives and prevent further damage.
Rescue, triage, on-site stabilization, transportation of victims, and treatment at local hospitals.
Phase 3: Response—Additional Info.
First level: First Responders
Mobilization of local responders
Fire department, law enforcement, public health, and emergency services
National Response Framework (NRF)
Emergency support functions (ESFs)
National Incident Management System (NIMS)
Response to biological incidents
Biodefense programs:
BioWatch, BioSense, Project BioShield, Cities Readiness Initiative, Strategic National Stockpile (SNS)
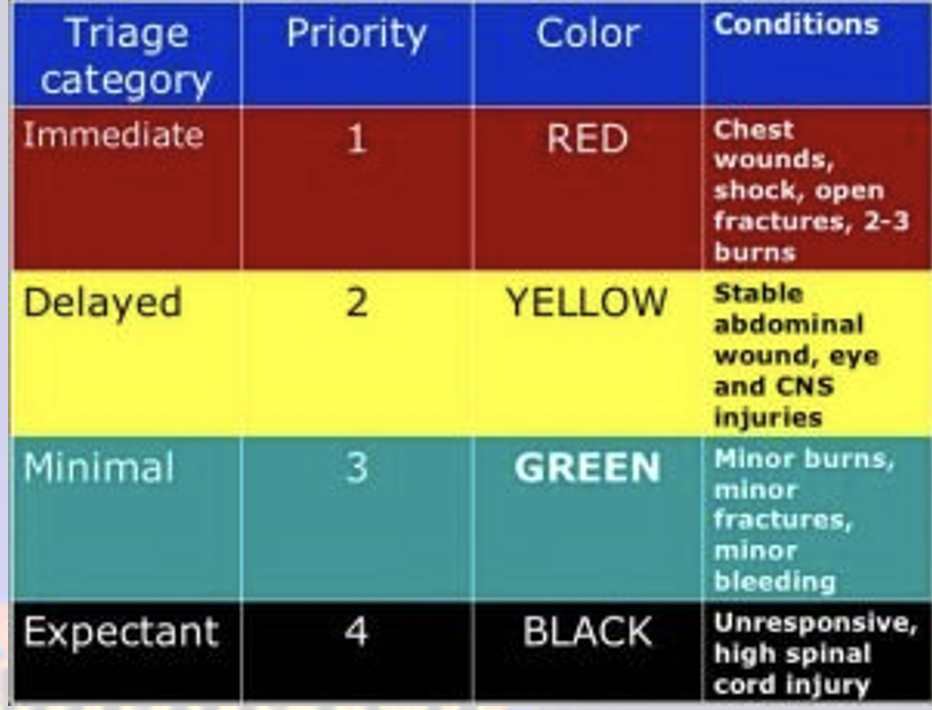
Phase 3: Response—Triage
Tags: (in order of priority)
Red—Immediate: Chest wounds, shock, open fractures, 2-3 burns, etc.
Yellow—Delayed: Stable abdominal wound, eyes and CNS injuries, etc.
Green—Minimal: Minor burns, minor fractures, minor bleeding, etc.
Black—Expectant: Unresponsive, high SCI. etc.
**Know what each of the colors represent, in terms of the patient’s status
Phase 4: Recovery
Returning to the new normal:
Community balance of infrastructure and social welfare near the level that it would have had if the event had not occurred
Hardest part of a disaster
Federal assistance: (FEMA)
Rebuilding and restoring after large-scale event
Gradual shift in support:
From short-term aid to long-term support for communities: sustainment of effort
Community’s Stress Reactions
Stress reactions in individuals:
Exacerbation of a chronic disease/illness
Older adult’s reactions dependent on health, independence, income, and so on…
Regressive behaviors in children
Role of the CHN
Preventing Disasters:
Primary level, Secondary level, and Tertiary level
Preparing for Disasters (Primary Prevention):
Disaster planning; personal preparation; assessment for risk factors and disaster history
Establishing authority, communication, and transportation
Mobilizing, warning, and evacuating
Responding to disasters (Secondary prevention):
Rescue
Triage immediate treatment and support
Care of bodies; family notification
Supporting recovery (Tertiary prevention):
Long-term treatment
Long-term support
Need for self-care (critical incident stress debriefing [CISD])
Terrorism is…
Unlawful use of force and violence against persons or property to intimidate or coerce a government, the civilian population, or any segment thereof, in furtherance of political or social objectives (U.S. FBI)
Agents for terrorism:
Bioweapons (mustard gas, sarin and VX gas, anthrax)
Nuclear agents
Chemical warfare
Factors Contributing to Terrorism
International Terrorism: political factors
Anti-American sentiment
Anti-Western sentiment
Domestic Terrorism: extremist views
Social
Environmental
Racial
Political
Religious
Trauma From the Warfront
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI):
Characteristic injury of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars
Most common causes: blast, object hitting head, falls
Associated with: depression, PTSD, suicidal ideation
Important for C/PHNs to assess for in veterans
Future of Disaster Management
Nurses continue to plan and train
All-hazards environment
All specialty practices must participate.
Public health nurses = critical members of disaster team
Population-based focus
Expertise in epidemiology and community assessment
Stay current in disaster training and committed to the following:
Community planning activities
Exercise participation
Actual disaster work
Ecology, the Human and the Environment
Ecology is the study of the interactions and relationships between living organisms and their environments.
Ecosystems are dynamic communities that no organism including humans can exist outside of.
The scientific study of ecosystems provides an understanding of the relationship between humans and the environment and why knowledge of environmental health is so important for nurses.
Environmental Health
The purpose of environmental health is to ensure the conditions of human health and provide healthy environments for people to live, work, and play.
Accomplished through…
Risk assessment
Prevention
Intervention
Using Critical Theory Approach
Uses “thinking upstream” framework.
Raises questions about oppressive situations.
Involves community members in the definition and solution of problems.
Facilitates interventions that reduce health-damaging effects of environments.
Asks critical questions about clients’ work and home environments to help discern the contributions of specific hazards to health.
Benefits of an Environmental Health History
Increased awareness of environmental/occupational factors
Improved timelines and accuracy of diagnosis
Prevents disease and aggravation of conditions
Identifies potential work-related environmental hazards and/or environmental hazards in and around clients’ homes
I PREPARE: Environmental Exposure History
I – Investigate potential exposures
P – Present work
R – Residence
E – Environmental concerns
P – Past work
A – Activities
R – Referrals and Resources
E – Educate
**Remember what each of the letters stands for!
Areas of Environmental Health
Built environment (man-made)
Work-related exposures
Outdoor air quality
Healthy homes
Water quality
Food, safety, and waste management
Major Global Environmental Concerns: Overpopulation
Effects: food scarcity, water shortages, and depletion of other vital resources
Demographic entrapment: population > ability of ecosystem to support it or acquire needed support or when population exceeds its ability to migrate to other ecosystems in a manner to preserve its standard of living
Government’s role: solutions possibly controversial depending on culture, religious beliefs, personal values, and convictions
Nurse’s role: teaching about birth spacing, preventing high-risk pregnancies, preventing growing epidemic of HIV/AIDS, providing family planning education, and providing prenatal care
Major Global Environmental Concerns: Air Pollution
One of the most hazardous sources of chemical contamination; adverse effects including costs to property, productivity, quality of life, and human life
Difficulty establishing actual cause and effect
Certain geographic areas more susceptible to ill effects due to weather or physical terrain
Major Global Environmental Concerns: Dusts, gases, and naturally occurring elements + Acid precipitation
Dusts—silica dust, asbestos; gases—sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, chlorine, ozone, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide; naturally occurring elements— radon Pollen, volcanic ash, and airborne microorganisms
__________________________________________
Air contaminants + precipitation = sulfuric and nitric acid (acid rain)
Effects: killing small life forms; danger to forest and freshwater ecologies
Major Global Environmental Concerns: Ozone Depletion + Global Warming
Effects: increased risk for skin cancer and cataracts; indirectly damaging food chain, increasing exposure to vector-borne diseases, raising of ocean levels, and negative impact on crop production
Government’s role: clean air legislation, reduction of greenhouse gases
Nurse’s role: detection, community education, and lobbying for appropriate legislation
Major Global Environmental Concerns: Water Pollution
Surface water (lakes and streams); underground sources
Effects: cause of disease; contamination of streams, lakes, and wells; contamination of fish; and upset of ecosystem
Government’s role: legislation for water quality testing; groundwater protection
Nurse’s role: examining household or city drinking water, identifying increased incidences of water-related diseases, and promoting safe healthy water
Major Global Environmental Concerns: Deforestation, Wetlands Destruction, and Desertification
Effects: upset of ecosystem; gases contributing to ozone depletion; geographic changes/landslides; drought, famine, and starvation
Government’s role: saving wetlands and forests
Nurse’s role: acting as a voice at the local level; leading and collaborating to initiate grassroots efforts to save wetlands and forests
Major Global Environmental Concerns: Energy Depletion
Nonrenewable sources primarily used today; nuclear energy still controversial, including building of plant and disposal of nuclear waste
Government’s role: discovery, rediscovery, or tapping of other renewable sources of energy; use of environmentally friendly sources
Nurse’s role: education about energy conservation, alternative energy sources; encouragement to become interested in and knowledgeable about potential energy depletion
Major Global Environmental Concerns: Unhealthy or Contaminated Food
Inherently harmful foods, contaminated foods, and foods with toxic additives
Food irradiation/cold pasteurization—for global food safety
Government’s role: regulatory agencies and monitoring
Nurse’s role: education about proper food storage, cooking, and handling
Major Global Environmental Concerns: Waste Disposal
Issues involving disposal of human waste, garbage, and hazardous waste
Government’s role: establishment of standards for safe waste disposal; monitoring and enforcing compliance
Nurse’s role: educating public and lobbying for enabling legislation; encouraging use of recyclable products; avoiding use of aerosol sprays, plastics, and other non-recyclable items
Major Global Environmental Concerns: Insect & Rodent Control
Effects: irritation/discomfort; direct threat to health via attack; contamination of food; vectors for disease transmission (mosquitoes, flies, ticks, roaches, fleas, rats, mice, and ground squirrels)
Government’s role: vector surveys, research, control; community awareness; and pest control programs
Nurse’s role: increasing awareness of threat; remaining alert to evidence of insects/rodents; educating persons; notifying proper authorities; surveying communities; and influencing policy makers
Major Global Environmental Concerns: Safety in Home, Worksite, and Community
Exposure to toxic chemicals, radiation, noise pollution, biologic pollutants; injury hazards; and psychological hazards
Government’s role: standards and regulation; monitoring of chemical use and production; public education and community safety programs
Nurse’s role: monitoring; preventive measures for injuries; safety education; promotion of first-aid/CPR; noise education; active lobbying for crime prevention, reduction of workplace stressors, and development of educational and support programs
Critical Community Health Nursing Practice
Approach environmental health at the population level
Take a stand; advocate for change
Ask critical questions
Facilitate community involvement
Form coalitions
Using collective strategies
Alliance of Nurses for Healthy Environments (ANHE)
The Mission of ANHE:
Promoting healthy people and healthy environments by educating and leading the nursing profession, advancing research, incorporating evidence-based practice, and influencing policy.
Strategies for Nursing Action in Environmental Health
Learn about possible environmental health threats.
Assess clients’ environment and detect health hazards.
Plan collaboratively with citizens and other professionals to devise protective and preventive strategies.
Assist with the implementation of programs.
Take action to correct situations in which health hazards exist.
Educate consumers and assist them to practice preventive measures.
Take action to promote the development of policies and legislation that enhance consumer protection and promote a healthier environment.
Assist with and promote program evaluation to determine the effectiveness of environmental health efforts.
Apply environmentally related research findings and participate in nursing research.
B. Heat exhaustion
Which is an individual health consequence during an extreme high temperature condition?
A. Adequate hydration
B. Heat exhaustion
C. Hyperactivity
D. Uncontrollable chills