3B
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Circulatory.immunity, nephron
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What happens during sarcomere contraction? What happens to the length of thin and thick filaments? What about their distance to one another?
Filaments will not change length but will overlap each other more
actin- thin
myosin: thick
What is a motor unit pool?
Number of motor units that a muscle can recruit for contraction
The size of a motor unit pool is ____ related wit muscle contraction
Directly
As muscle cells contract, motor units will increase the amount of Calcium _____. When relaxing, muscle cells ____ Ca.
Released, reuptake
What are the components of plasma (4)
Proteins, nutrients, salts and hormones
What are the proteins within plasma (3)? What are their functions?
Albumin: Major osmo regulatory protein (maintains fluid/stay hydrated
Fibrinogen: Clots our blood
Immunoglobulins: OUR ANTIBODIES, made by B cells!
What do RBC/erythrocytes lack?
Nuclei and membrane bound organelles?
Do RBCs have mitochondria? Why or why not?
They DO NOT have mitochondria because they would utilize the O2 they need for themselves!
How many subunits does myoglobin have? What does that effect?
It has ONE which, INCREASEES oxygen affinity
This means that myoglobin get saturated MORE QUICKLY than hemoglobin!
Myoglobin has a ___ curve due to ____while hemoglobin has a ____ curve due to ___.
Hyperbolic: Having one subunit
Sigmoidal: Cooperative binding
From what kind of cells do lymphoid and myeloid stem cells come from?
hematopoietic stem cells
What are the stem cell origins of the innate and adaptive immune system respectively?
Myeloid, lymphoid stem cells
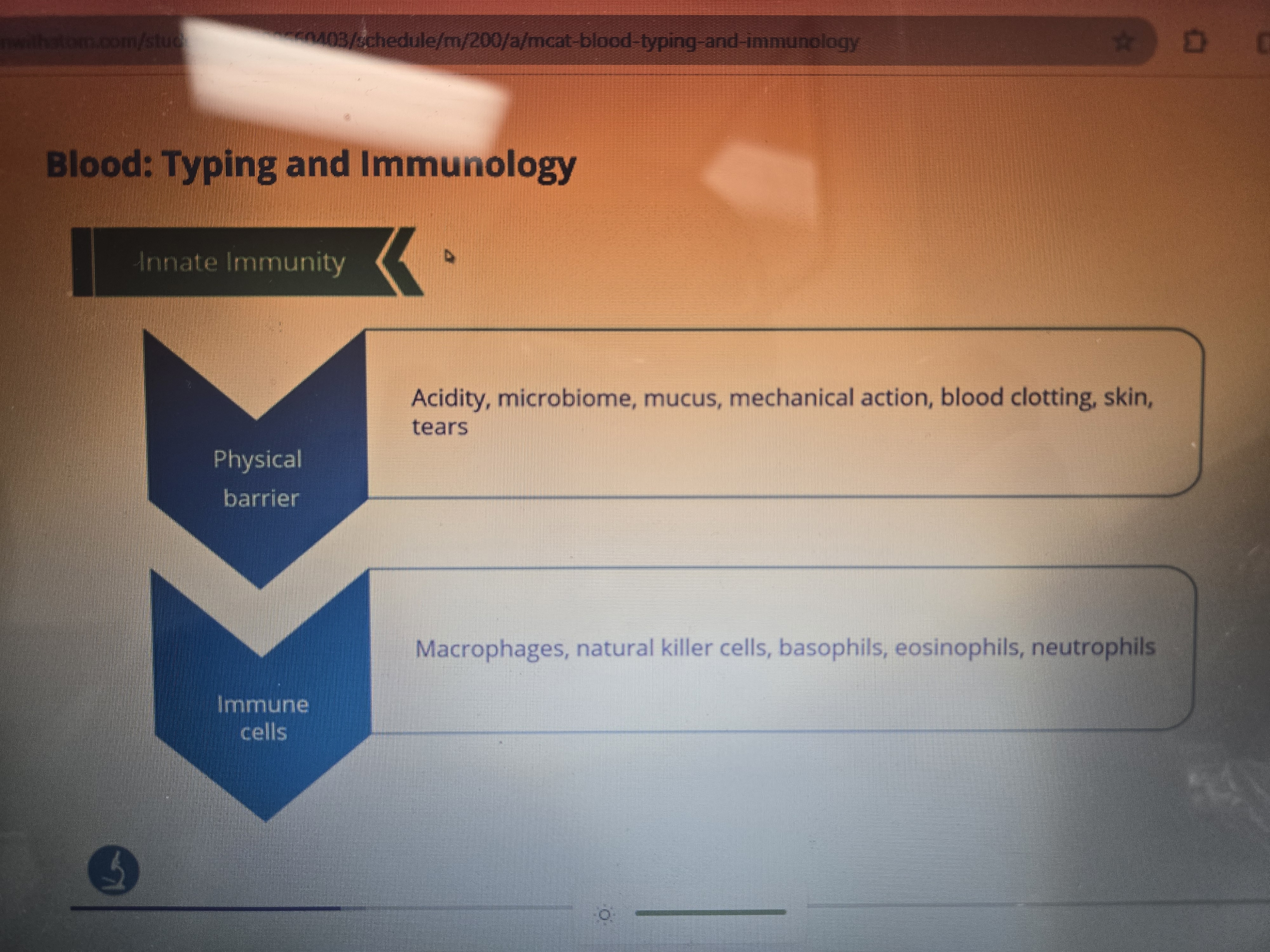
What are the two main components of INNATE immunity? What are the components of each? What are the ways of action for the components found in #2? Basically fill in the chart and take note of actions within them.
Granulocytes
Basophils: Mediate allergic responses
Eosinophils: Mediate allergic responses and respond to parasitic infections
Neutrophils: Ingest bacteria, particularly those marked with antibody
Monocytes
Macrophages: Ingests deadcellls, phagocytoses pathogen and displays antigen
Dendritic Cells: Phagocytoses pathogen and displays antigen on MHC-II
NK Cells: Attack cells not presenting MHC molecules Self MHC-I
What is the difference between active and passive antibodies?
Active: Trained B cells create the antibody
Passive: Made by somebody else like mother’s milk or the placenta
Why does a second exposure to virus have a much quicker immune response?
At that point B cells have been trained (specific antibody)and have proliferated and are recruited by helper T cells
What is hemolysis?
When blood cells rupture because blood has foreign antigens that antibodies can’t recognize
Antigens in blood are directly related to their _____. What are the antigens for each?
A: A antigens
B:B antigens
AB: Both antigens
O : No antigens
Antibodies in blood will be made against ____. Can you give examples?
Since A presents A antigens, there are no B antigens so they produce B antibodies (Way to recognize a foreign blood antigens like B)
Meanwhile AB would not have any antibodies since they recognize A and B antigens! That’s why it can only be donated to another with AB blood because we have to make sure there are no antibodies against like in B blood there is a A antibody which would go against the A antigens in AB but they can recieve from all blood types!
O blood type would have A and B antibodies since there are no antigens! With no antigens, they are a UNIVERSAL donor. But they can only recieve blood from O type.
What kind of antibodies are in co dominate blood type? What about Rh factor?
IgM, IgG
What kind of inheritance is Rh factor? How do we distinct antigens? Explain issues with this blood type in mother and newly born child?
Dominant inheritance
Positive or negative, negative meaning no antigens.
You only make antibodies when exposed to a foreign Rh antigens (mixing of blood)
So if mom has B- and their baby is B+ the 1st baby is safe if they mix blood during a procedure but if the mother has a second child with B+ the infant will die due to hemolysis
Increasing the influx of interstitial fluid into the blood stream would ____ blood pressure
Increase
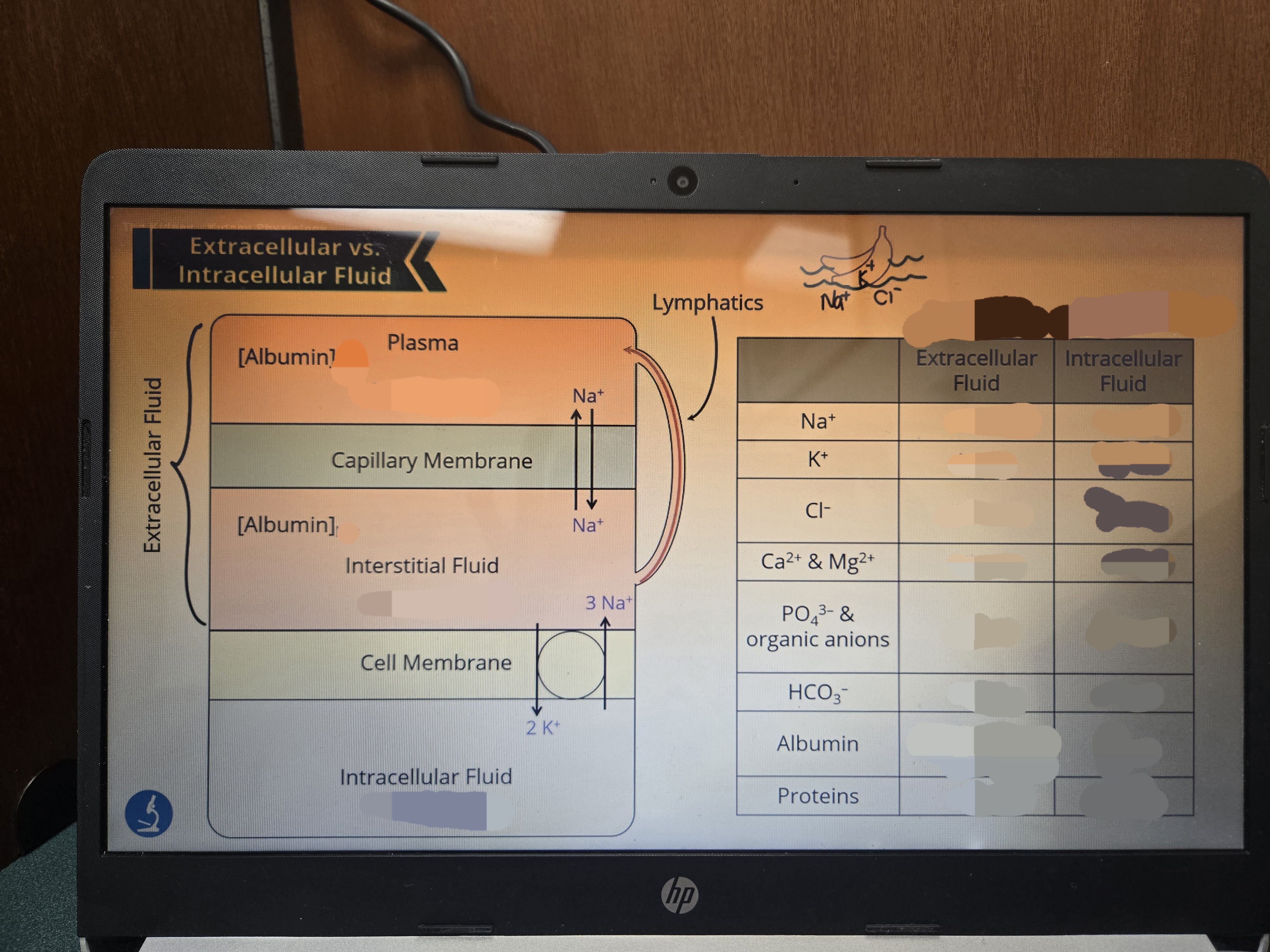
Fill out the table!
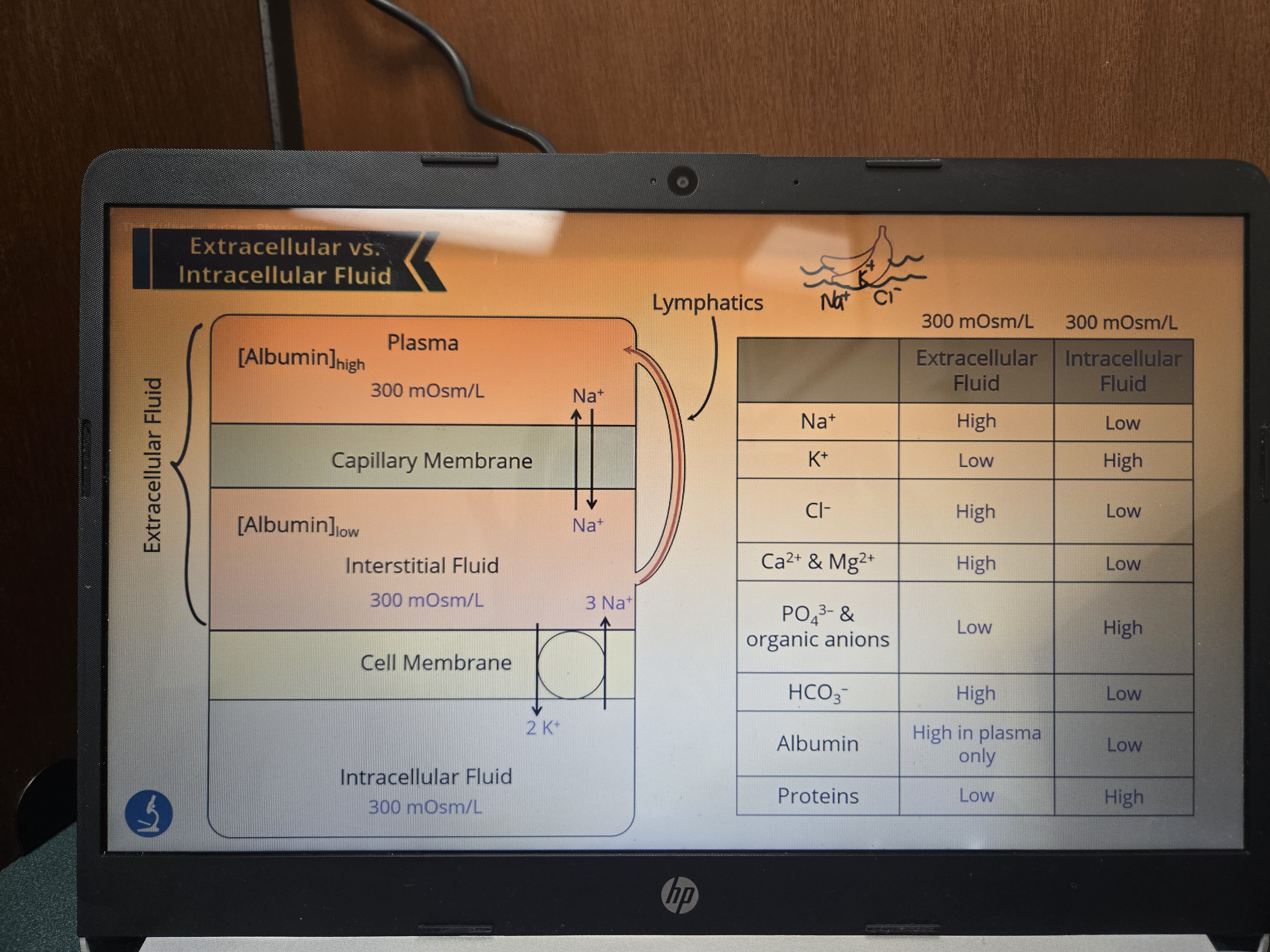
A higher osmolarity means that the fluid _____.
Has more solutes in it!
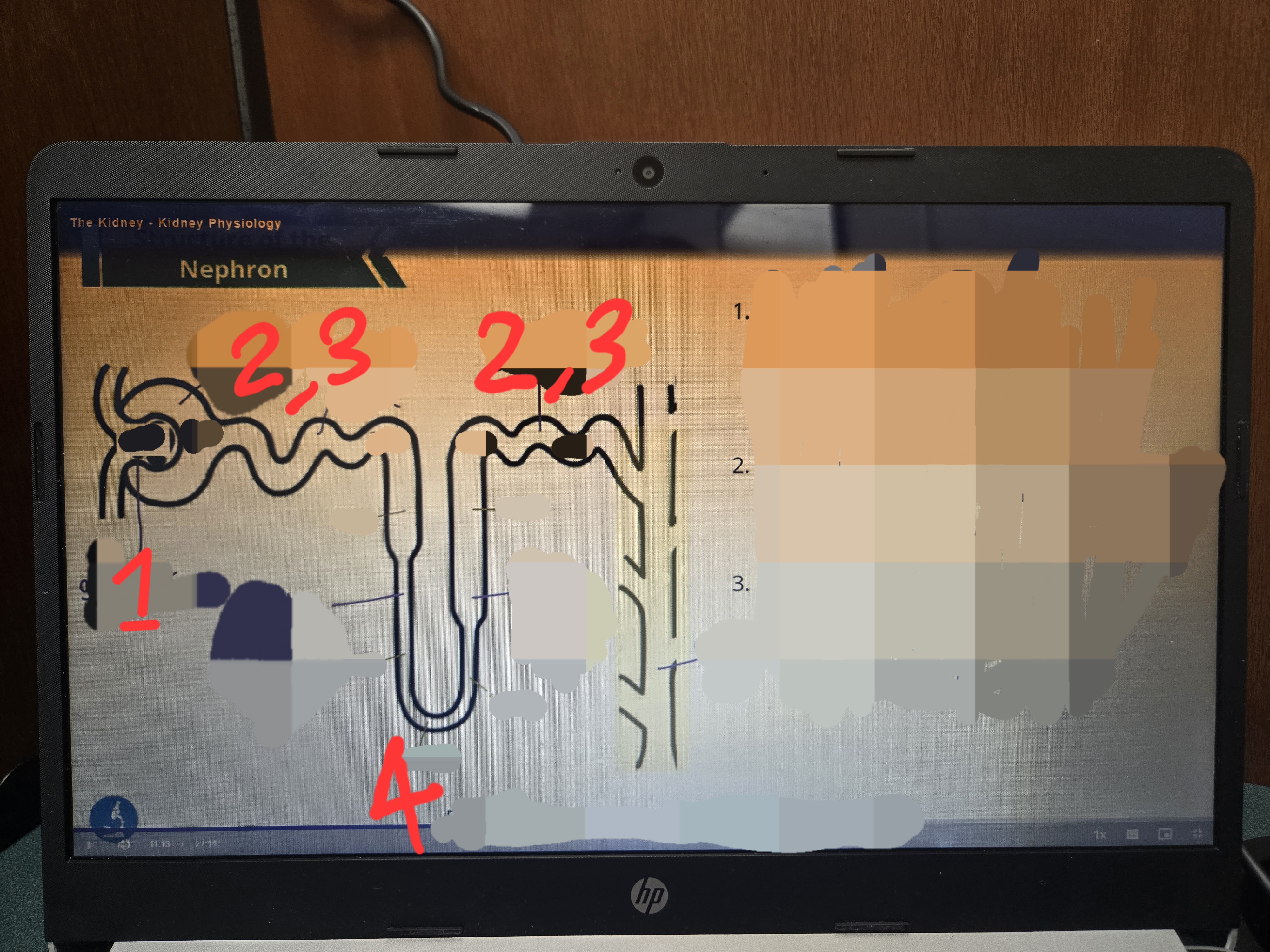
Label the names of each structure, their step, relative osmolarities
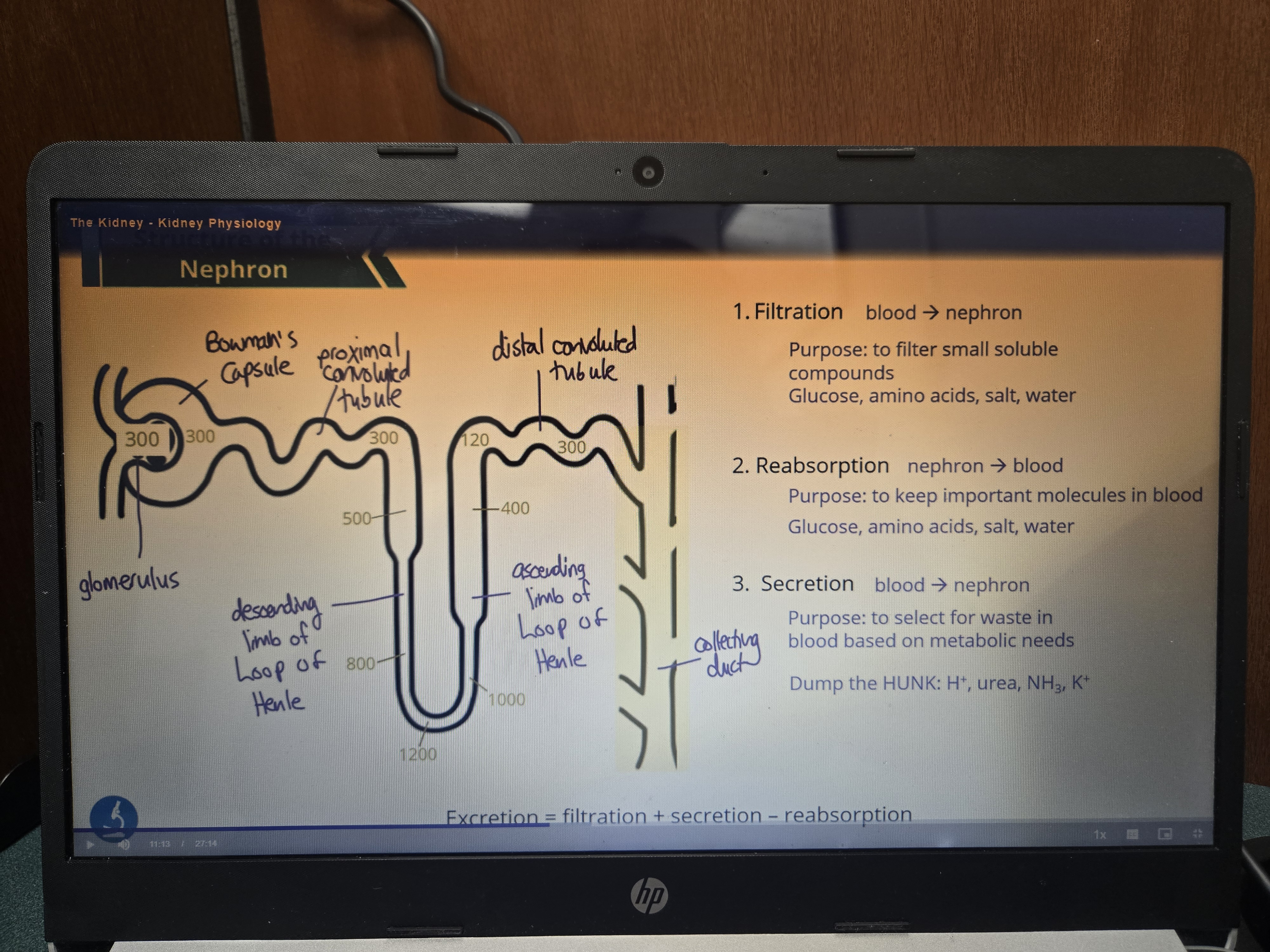
The higher the concentration of glucose in the plasma, the __ the rate of filtration into the nephron. How does this relate to reabsorption and excretion?
Higher
Although reabsorption will increase eventually there will not be enough transporters (transport maximum), then at that point there will be an increase in glucose excretion otherwise known as more sugar in URINE
How does the osmotic and hydrostatic pressure of the glomerular capillary and Bowmans space compare?
Hydrostatic pressure of the capillary is much greater due to the amount of blood coming in, and the oncotic pressure is higher because albumin is too big to filter into the nephron
The hydrostatic pressure of the Bowman capsule on the other hand is much lower. Oncotic pressure is also lower due to less albumin being filtered through.
What contributes to the net flow of fluid into the nephron
The higher hydrostatic pressure from the glomerular capillary!
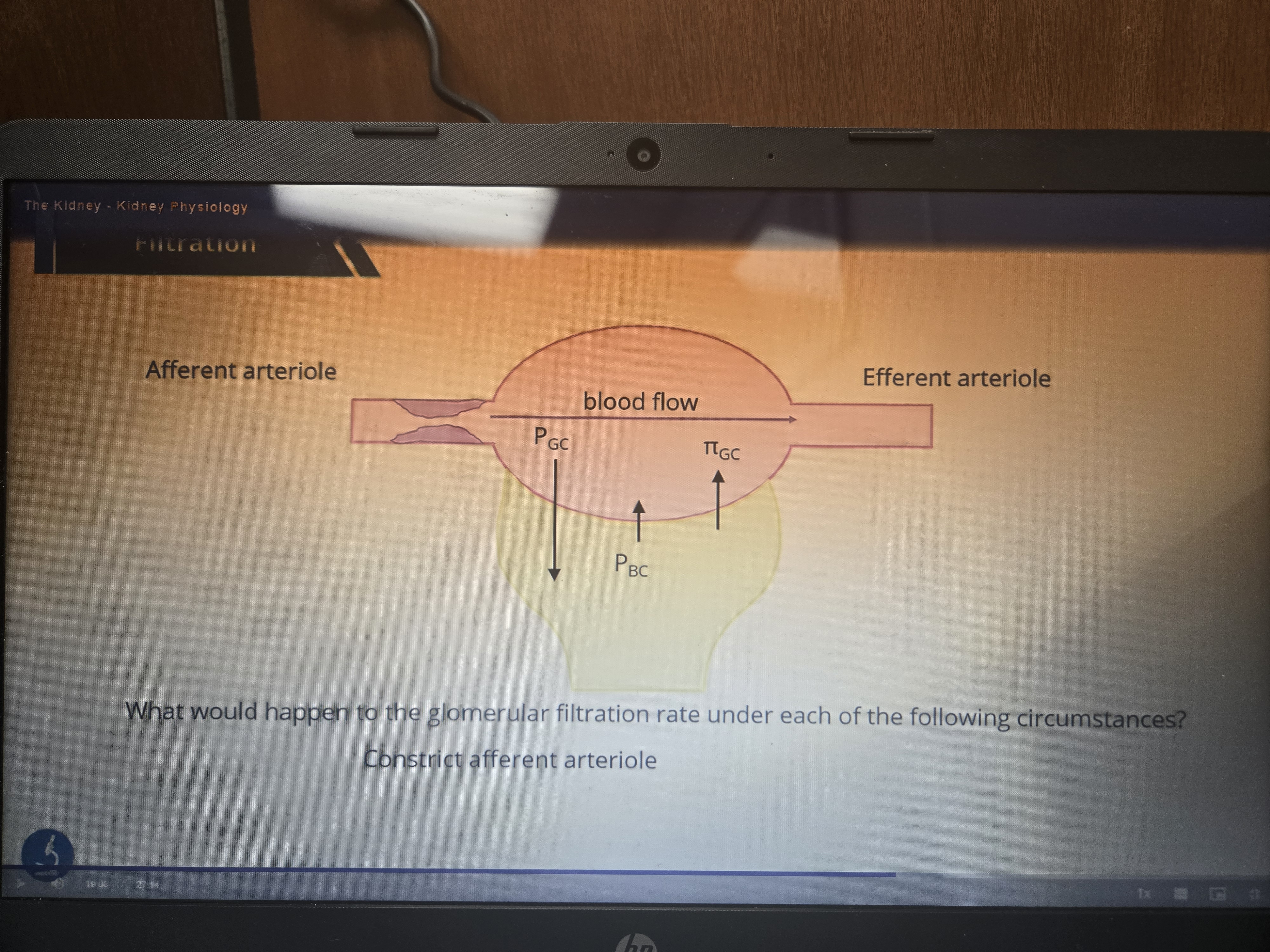
What happens and why?
Decreases in hydrostatic pressure so less fluid will make it to the glomerulus to be filtered

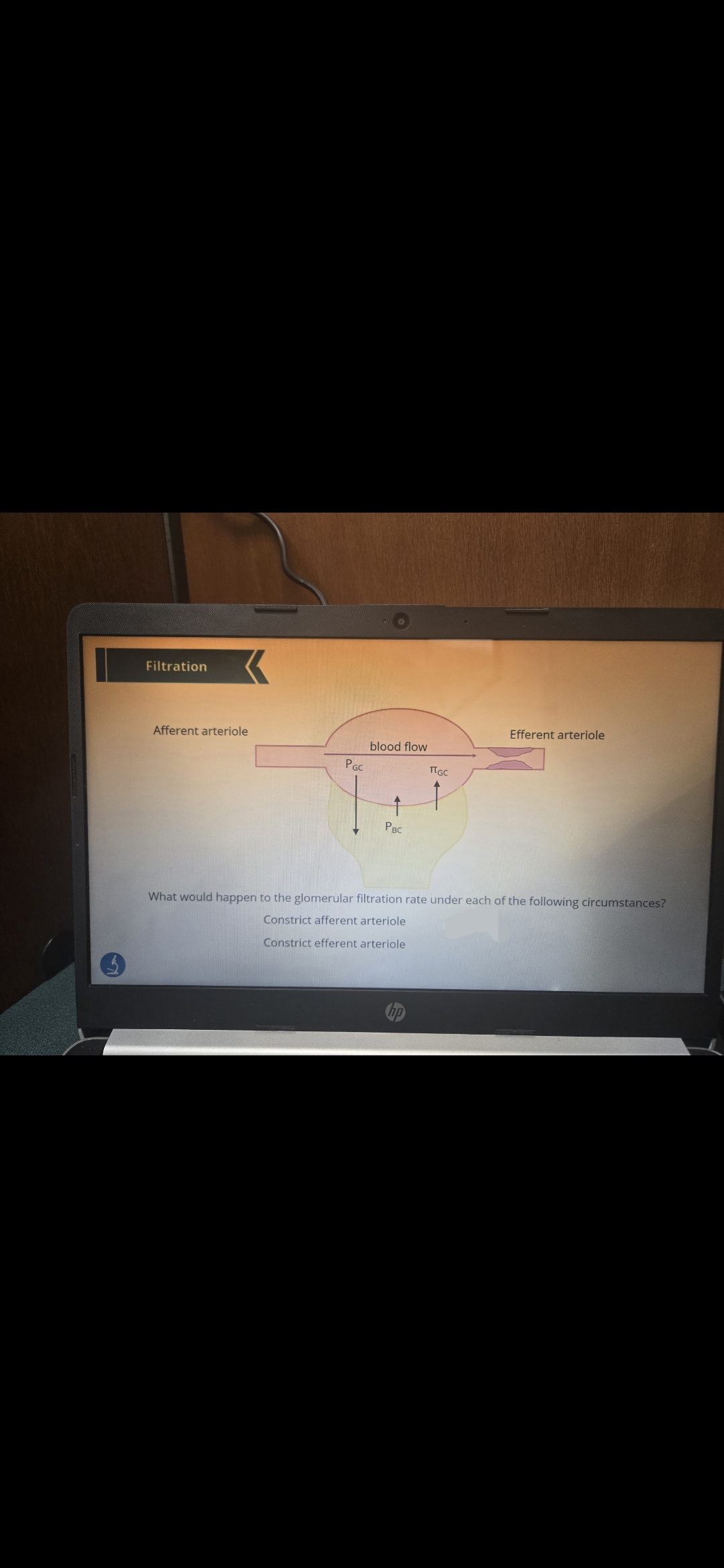
What happens here and why?
Back flow in glomerular capillary increases which increases ist hydrostatic pressure
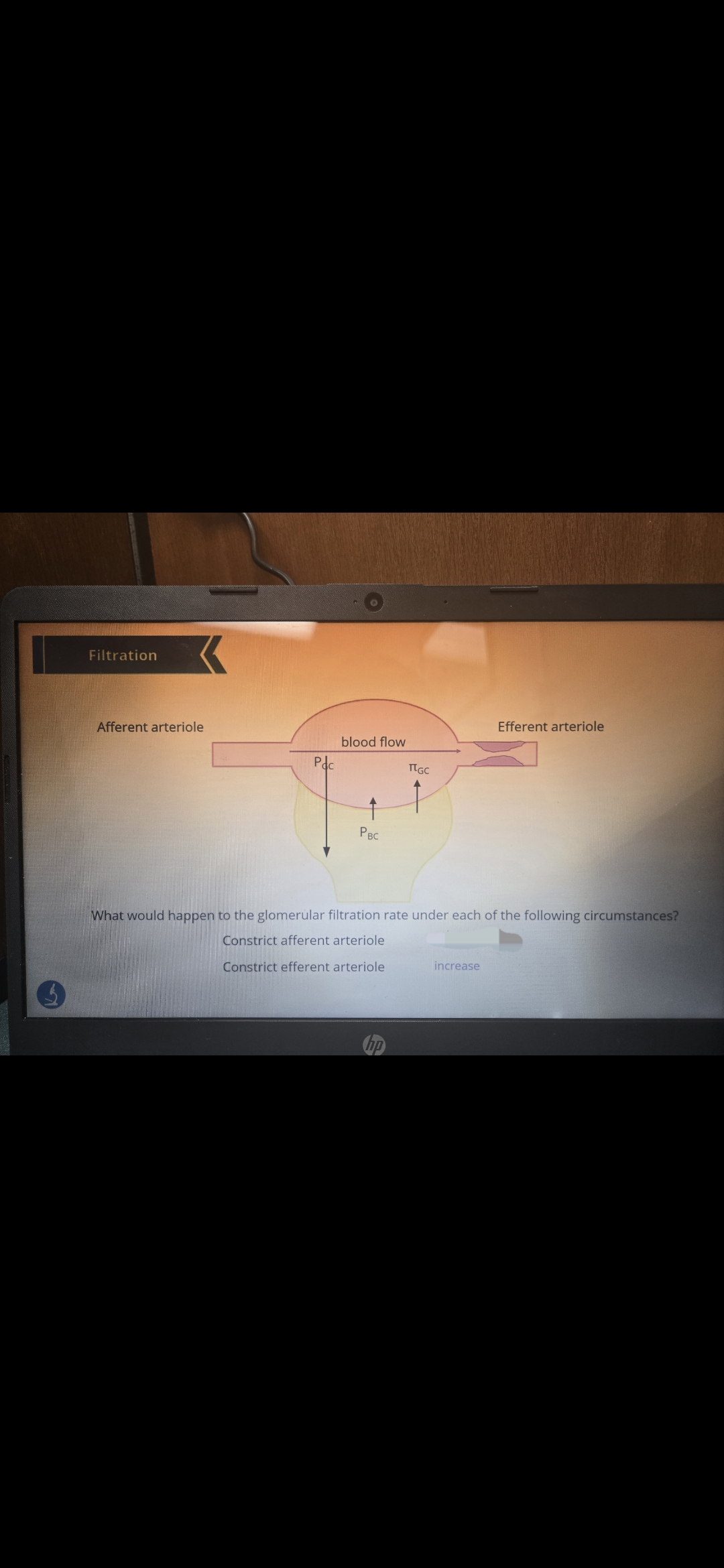
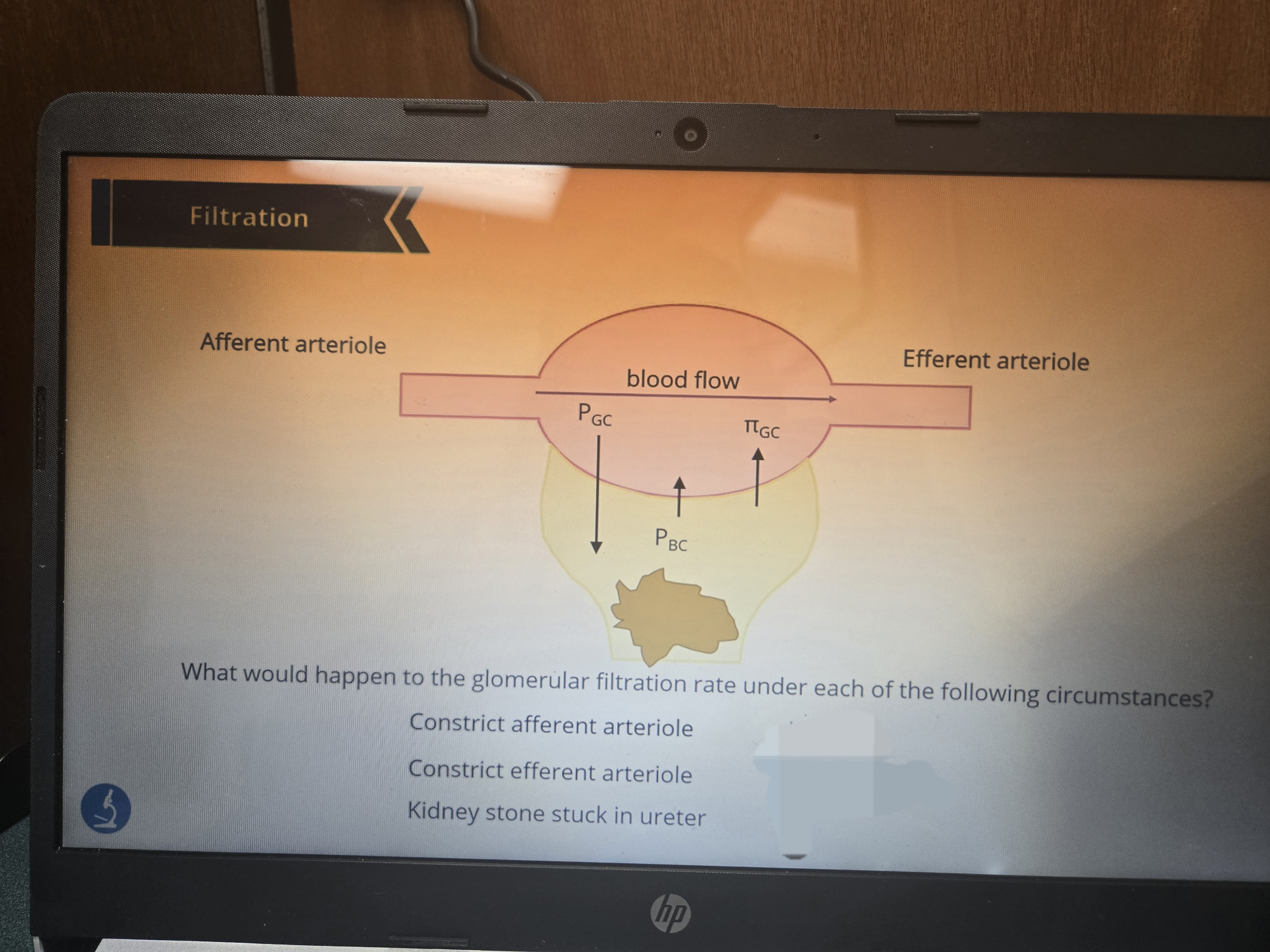
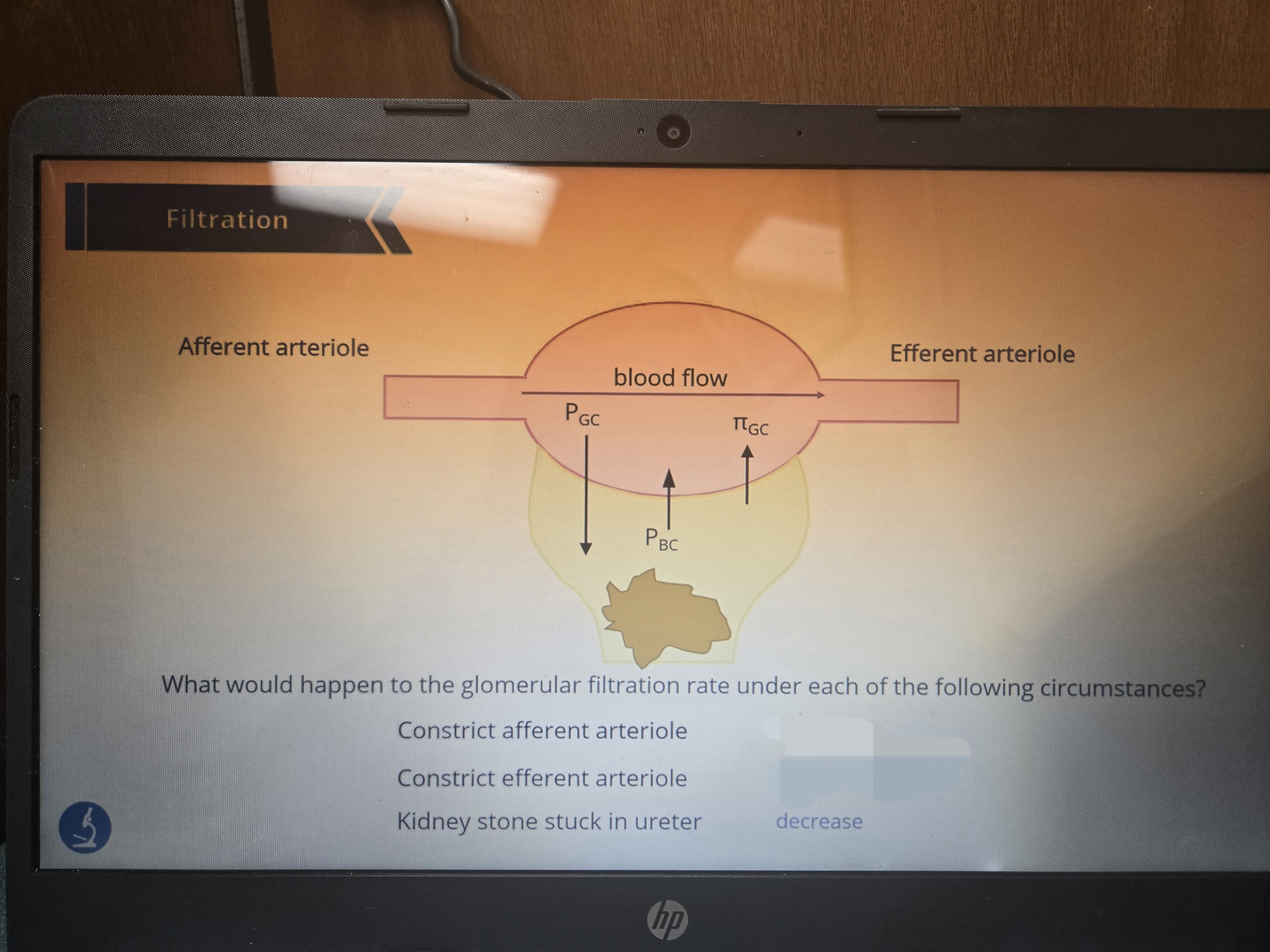
What if there was a kidney stone?
Back up of fluid in the nephron resulting in increasing hydrostatic pressure of the Bowman space, decreasing filtration
Aldosterone versus vasporessin/ADH(antidiuretic hormone). What regulation do they MOSTLY do?
Aldosterone:Reabsorption water and ION
Regulation: Plasma volume AND pressure
Vasopressin: Reabsorption of water ONLY
Regulation: Plasma osmolarity
The loop of Henley is ____ likely to be longer than the collecting duct
More
How do cytotoxic (CD8⁺) T cells kill infected cells?
🧠 Step 1: Recognize infected cell via MHC I + foreign antigen
🔫 Step 2: Kill via
Perforin + Granzymes → poke & trigger apoptosis
Fas-FasL interaction → activate cell's death pathway
➡ Result: Target cell undergoes apoptosis, not messy lysis
✅ Keeps infection from spreading without harming nearby cells
What is the difference between the MHC complexes?
💍 Engagement Proposal Analogy:
MHC Type | Analogy | Who Sees It | What Happens |
|---|---|---|---|
MHC-I | Private proposal: cell shows internal problem (ring) | CD8⁺ cytotoxic T cell | T cell says “this is toxic” → kills the cell |
MHC-II | Public proposal: APC shows external problem (ring) | CD4⁺ helper T cells | T cells say “let’s rally help!” → immune response activated |
🧬 Summary:
MHC-I = Endogenous (inside), kills cell
MHC-II = Exogenous (outside), activates immune help
What kind of circulatory system do humans have? Blood flow is ____directional which is aided by the ______ and ____ from atrium to ventricle and ____ from ventricles to vasculature
Closed , unidirectional
Atrioventricular valves :Tricuspid and Mitral/Bicuspid valve
Semilunar valves : Pulmonary and aortic valve
The atriums of both sides _____ and the ventricles of both sides ____
Both contract together to squeeze through their respective semilunar valves
What happens during diastole? What about during systole?
Diastole: heart is relaxed and fills blood in both atria
Systole: Atriums contract and ventricles then contract
In systemic circulation blood is _____ and heads to the ____ while in pulmonary circulation, blood is _____ and heads to the ____.
Oxygenated, body
Deoxygenated, lungs
In the lungs the partial pressure of O2(pO2) is ___, which allows for them to ___. The pO2 of the tissues is ____ causing ___
High, bind to heme
Low, be released from heme
The primary driving force for respiration in healthy individuals is ____ pH which is indirectly influenced by _____ levels in the blood.The following equation explains this relation ship: ______.
An increase in carbon dioxide results in a _____ in hydrogen ions which corresponds to a _____ in pH.
Decreased
Carbon dioxide
CO2 +H2O ←→ H2CO3←→ +H + HCO3-
Increase
Decrease
In order to raise the osmolarity of the filtrate as it descends into the medulla, the ____ can _____. As filtrate ascends from the medulla, osmolarity is lower so initially ___ but _____. Once at the cortex the distal conv tubule ____, but once it approaches the collecting duct it ___. The collecting duct generally
Proximal convoluted tubule secrete solutes into the filtrate, specifically HUNK
Na and Cl are reabsorbed passively, but since the ascending loop is impermeable to water, they decrease solute concentration through active transport.
Only reabsorbs NaCl, and water through aldosterone since the filtrate is much more dilute, but just before it gets to the end it gets more concentrated by dumping the HUNK
Becomes more concentrated by reabsorbing water ONLY through ADH activating aquaporins
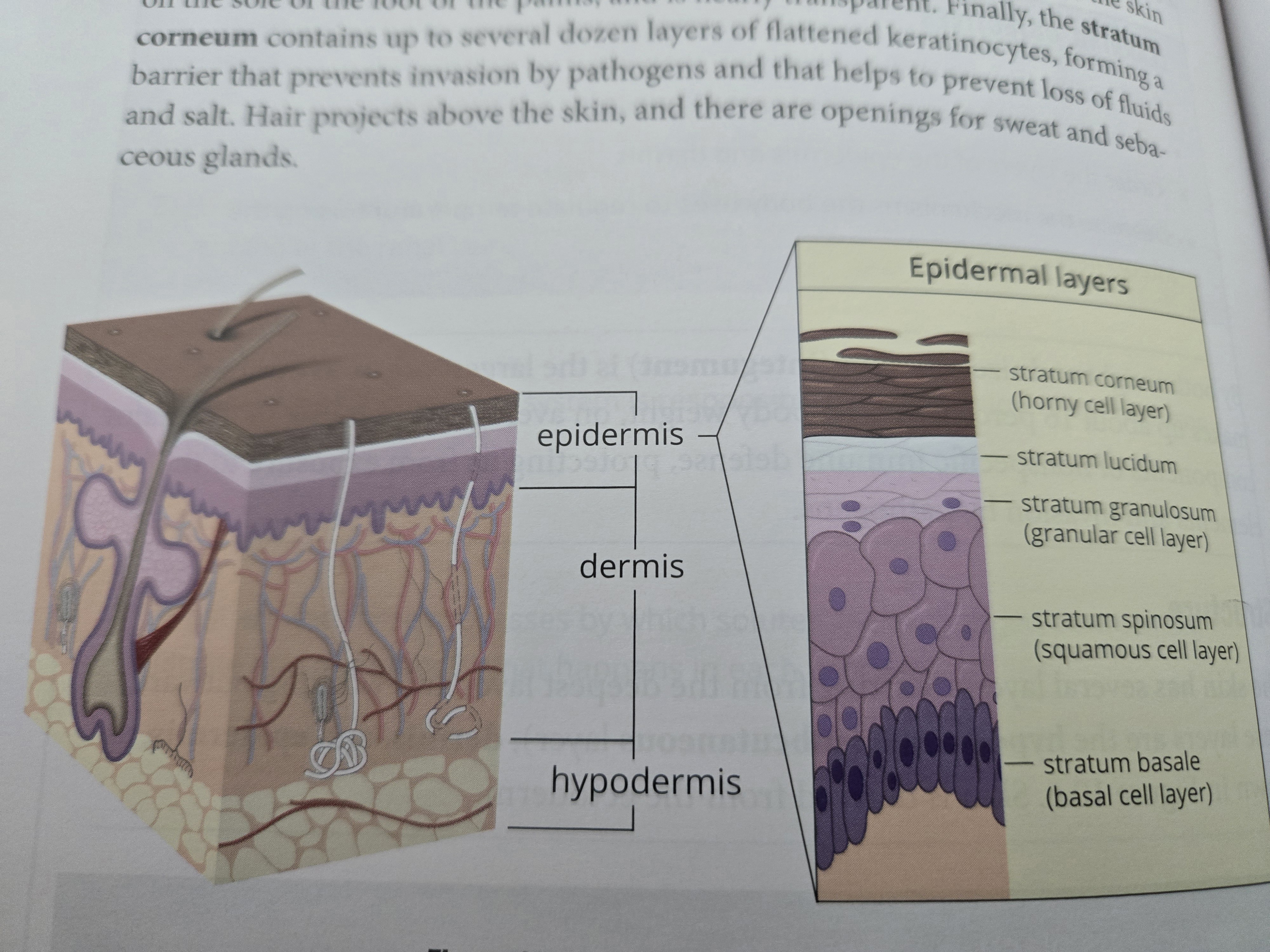
What are the main layers of skin?
What are the epidermal layers
Good mnemonic for epidermal layers:
Come Let’s Get Sun Burned
How does hydrostatic and oncotic pressure work at capallaries?
Arteries drive blood away from the heart, so the arteriole portion would be higher in hydrostatic pressure. As a result little fluid remains at the venous end which will increase albumin concentration, therefore increasing oncotic pressure which will draw fluid back!
How does Oxygen passively dissolve from the air tin the alveoli into the alveolar capillaries? What about PCO2 ?
PO2 in the ambient air must be higher than the PO2 in the alveoli, and the PO2 in the alveoli must be higher than the PO2 in the alveolar capillaries.
PCO2 is highest in the capillaries and lowest in the lungs!
Bile salts are essential for ___ and are therefore important for ___.
Emulsification for fatty compounds
fat soluble vitamin absorption
What is the function of trypsin?
Digestion of proteins
What is the function of secretin?
Secretin is a hormone released by the duodenum in response to acidic chyme from the stomach.
It:
📤 Stimulates bicarbonate secretion from the pancreas (neutralizes acid)
⛔ Inhibits gastric acid secretion
🐌 Slows gastric emptying
🧴 Stimulates bile production in the liver
💡 Hint: Secretin "secretes" base and slows the acid flow!
What kind of drug could affect macrophages or any other cell like it?
Immunosuppressive drugs
Why do we pee out less than we drink? Also why does our pee get concentrated more than our blood?
We lose water through our sweat and lungs
NOT through blood
We increase water conservation through our kidneys
Whats the point of the blood brain barrier? What cell connection is it like?
Blocks harmful stuff from blood stream to enter brain
TIGHT JUNCTION