chapter 6 textbook dissociative disorders
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
dissociative identity disorder
dissociative disorder in which a person has two or more personalities or alters
each has their own distinctive traits, memories, mannerisms, even style of speech
DID three faces of eve
Eve White: main personality
timid housewife
Eve Black: alter
sexually provocative
anti social personality
Jane: merge of three
balanced
developing personality who can balance her sexual needs with demands of social acceptability
movie based off of Chris Sizemore
failed to maintain integrated personality like Eve
split into 22 personalitie
clinical features of DID
two or more distinct personalities
may have one dominant or core personality or several subordinate personalities
changes between alters may seem like possession
some personalities can show psychotic breaks
main personality can be unaware of existence of other personalities
some personalities (alter personalities) can even have different eyeglass prescriptions, allergic reactions, etc
shifting of levels of sexuality and sexual orientation is common
controversies of DID
many professionals have doubts on the existence of the disorder
very rare
Nicholas Spanos → believed DID was roleplaying until person believed it was real
72% of DID attempted suicide
dissociative amnesia
dissociative disorder in which a person experiences memory
loss without an explanation → reversible, memory can come back
divided into 5 types of problems
fugue: rare subtype — amnesia on the run
travels suddenly either purposefully or wandering
unable to recall past personal informationextbook 3
may appear normal
malingering: faking symptoms or making false claims for personal gain
localized amnesia
events occurring during a specific time period are lost to memory → person may forget events after traumatic event for a certain amount of time
selective amnesia
forget disturbing particulars that take place during a certain period of time → a soldier may remember most of battle but not the death of his friend
generalized amnesia
people forget their entire lives
continuous amnesia
forgets everything that occurred from a particular point in time up to and including the present
systematized amnesia
specific to a particular category of information, such as memory about one’s family or particular people in one’s life
depersonalization / derealization disorder
recurrent episodes and impair daily functioning
depersonalization
temporary loss or change in the usual sense of our own reality
feel detached from themselves and surroundings
may feel like a robot or dreaming
derealization
sense of unreality about the external world involving odd changes in the perception of one’s surroundings or in the passage of time
people and objects may seem to change in shape or size, sounds may sound different
associated with dizziness, fears of going insane, depression
features of DID
memories are intact, people know who they are unlike amnesia
sometimes feelings of DPDR can come on and fade
associated more with anxiety disorders
more common in US because we emphasize individualism
amok
culture bound dissociative syndrome
southeast asian and pacific island cultures
trancelike state in which a person suddenly becomes highly excited and violently attacks other people and destroys object
zar
culture bound dissociative syndrome
north africa and middle east
dissociative states used to reflect spirit possession
shouting banging head against wall
psychodynamic perspective dissociative
involve massive use of repression
disconnecting or dissociating ones conscious self from awareness of traumatic experiences or other sources of psychological pain or conflict
social cognitive theory of DD
learned response involving the behavior of psychologically distancing oneself from disturbing memories or emotions
nicholas spanos → roleplaying
brain dysfunction of DD
structural brain differences in those who have dissociative disorders
brain functioning in sleep
vulnerability-stress model of DD
people prone to fantasize are open to altered states of consciousness are more likely than others to develop dissociative experiences in the face of traumatic events
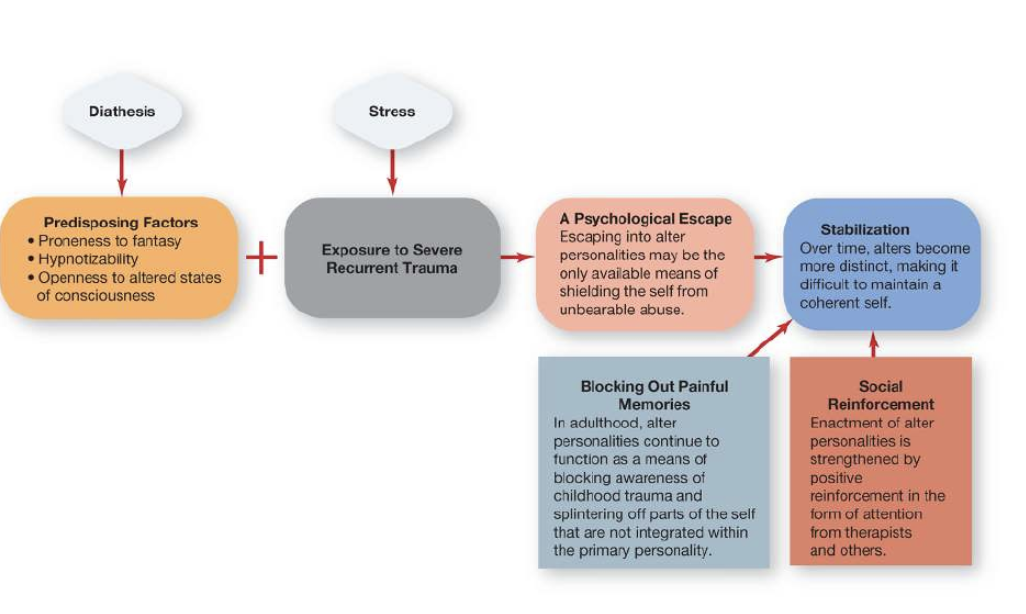
treatment of DD
help patients uncover and work through memories of early childhood trauma
therapists recommend establishing connections with dominant and alter personalities
help safely relive traumatic experiences and make them conscious
somatic symptom and related disorders
people who display physical symptoms without an identifiable physical cause orhave excessive concerns about the nature or meaning of their symptoms
symptoms significantly interfere with the people’s lives
lead them to go doctor shopping in hopes of finding a medical practitioner to explain and treat their ailments
somatic symptom disorder
excessive concern about one’s physical symptoms
somatic symptom disorder diagnosis requirements
physical symptoms that are persistent for at least 6 months or longer
associated with either significant personal distress or interference with daily functioning
SSD hypochondrasis
previously in older versions of DSM
applied to people with physical complaints who believed their symptoms were due to a serious, undetected illness, despite medical reassurance to the contrary
health anxiety-illness anxiety disorder
illness anxiety disorder
somatic symptom disorder categorized by high levels of anxiety or concerns about having a serious illness even though physical symptoms are either absent or minor
fear of what symptoms mean
subtypes of illness anxiety disorder
care-avoidant:
postpone or avoid medical visits or lab tests due to high levels of anxiety about what may be discovered
care-seeking:
doctor shopping
become angry at doctors who try to convince them their fears are unwarranted
conversion disorder
characterized by symptoms or deficits that affect ability to control voluntary movement or impair sensory functions
conversion disorder features
inconsistent or incompatible with known medical conditions or diseases
conversion or transformation of emotional distress into significant symptoms in the motor or sensory domains
named from psychodynamic belief that represents conversion of repressed sexual or aggressive energies into physical symptoms
formally called hysteria or hysterical neurosis
symptom patterns can take form of paralysis, epilepsy, problems in coordination, blindness, loss of sense of hearing or smell, loss of feeling in limb
la belle indifference: remarkable indifference to their symptoms
factitious disorder
fake or manufacture physical or psychological symptoms
sometimes take medication or injure themselves to have symptoms
symptoms don’t bring obvious gain
not the same as malingering
malingering
faking illness to avoid work or duty
subtypes of factitious disorder
factitious disorder on self
muchausen syndrome
form of feigned illness in which a person either fakes being ill or makes themself ill
factitious disorder on another
muchausen sydrome by proxy
intentionally falsify or induce physical or emotional illness or injury in another person → typically child
koro syndrome
characterizes people who fear that their genitals are shrinking or retracting into their bodies which will result in death
koro syndrome features
primarily found in china and southeast asian cultures
mainly found in young men
includes episodes of acute anxiety
physiological symptoms: sweating, breathlessness, heart palpitations
may use mechanical devices such as chopsticks to try to prevent retraction
pass with time
dhat syndrome
excessive fears over the loss of seminal fluid in nocturnal emissions, in urine or masturbation
found in India
semen is viewed to be a vital body fluid; elixir of life
hippocrates perspectives of somatic symptoms and related disorders
Hippocrates: termed the word hysteria
attributed the strange bodily symptoms to a wandering uterus resulting in internal chaos
prescribed marriage as a cure
psychodynamic theory of SSRD
believed hysteria was rooted in psychological rather than physical causes → lead freud to develop theory of unconscious mind
left over emotion is converted into physical symptoms
does not explain how energies left over from unconscious conflicts become transformed into physical symtpoms
hysterical symptoms are functional
allows person to achieve primary and secondary gains
primary gain:
allow an individual to keep internal conflicts repressed
aware of physical symptom but not of the conflict it represents
secondary gains
allow individuals to avoid burdensome responsibilities and gain
support from those around them
learning theory of SSRD
people with somatic symptom disorders also carry benefits or reinforcing properties of the sick role
people with disorders may be relieved of chores and responsibilities
women in western culture are more likely to be socialized to cope with stress by enacting a sick role
cognitive theory of SSRD
type of self handicapping → way of blaming poor performance on failing health
focuses on the role of distorted thinking
tend to exaggerate the significance of minor physical complaints
misinterpret benign symptoms which creates anxiety
brain dysfunction of SSRD
may involve disconnect or impairment to the neural connections between parts of the brain that control certain functions and other parts involved in regulating anxiety
treatment of SSRD
Behavior approach
removes sources of secondary reinforcement that may be connected with physical complaints
reinforces depended and complaining behaviors
may teach family members to reward attempts to assume responsibility and ignore nagging or complaining
CBT
challenges and corrects distorted beliefs and help replace exaggerated illness related beliefs with rational alternatives
best treatment option
psychosomatic disorders
psychological factors contribute to physical disorders (headaches, asthma)
tension headache
stress can lead to contractions of muscles of scalp, face, neck, and shoulders
develop gradually and is dull, steady pain on both sides of head, feelings of pressure or tightness
migranes
piercing or throbbing sensations on one side of head or centerned behind an eye
can be intolerable
aura: cluster of warning sensations
perceptual distorions: flashing lights, bizarre images, blind spots
leads to disturbances of sleep, mood, thinking processes
theoretical perspectives on headaches
tension headaches: increased sensitivity of neural pathways that send pain signals to brain from face and head
migraines: involve underlying central nervous symptom disorder involving nerves and blood vessels in brain
serotonin: falling levels may cause blood vessels in the brain to contract then dilate → stimulates sensitized nerve endings giving throbbing sensations with migraines
factors that trigger headache attack
emotional stress
stimuli (bright lights)
menstration
sleep deprivation
altitude
weather or seasonal change
drugs
monosodium glutamate
alcohol
hunger
treatments to headache
pain relievers : aspirin, ibuprofen
biofeedback training (BFT)
helps people gain control over various bodily functions such as muscle tension and brain waves by giving them information about these functions in form of auditory signals or visual displays
learn to make the signal change in desired direction
EMG (electromyographic biofeedback)
involves relaying info about muscle tension in forehead
thermal BFT
modifies patterns of blood flow to help control migraines
cardiovascular disease
heart or artery disease
coronary heart disease
major form of cardiovascular disease → leading cause of death for both men and women
flow of blood to heart is insufficent to meet the hearts needs
arteriosclerosis: hardening of arteries — makes artery walls become thicker, harder, and makes blood flow more difficult
atherosclerosis: underlying cause of ^ involving buildup of fatty deposits along artery walls which leads to artery clogging plaque
how can we lower risk of HD
adopting healthier behaviors
stopping smoking, overeating, heavy drinking, consuming high fat diet, leading a sedentary lifestyle
negative emotions of HD
frequent emotional distress may have damaging effects on cardiovascular system
chronic anger
linked to increased risk of coronary heart disease
Type A behavior pattern
characterizes people who are hard driving, ambitious, impatient and highly competitive
higher risk of CHD
stress of hormones
epinephrine and norepinephrine
adrenal glands
increase heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure
can damage heart and blood vessels
episodes of acute anger can trigger heart attacks with people with established heart disease
depression
places additional stress on the body
factors of HD cont
social environmental stress
factors such as overtime work, exposure to conflicting demands, assembly line labor — linked to CHD
ethnicity and CHD
european americans and african americans have highest rates of death due to CHD
racial issues → african americans do not receive as well quality care as whites
asthma
respiratory disorder in which main tubes of windpipe— the bronchi— constrict and become inflamed and large amounts of mucus are secreted
features of asthma
may feel like suffocating
effects about 26 million people
can last from a few minutes to several hours and vary in intensity
theoretical perspectives of asthma
causal factors
allergic reactions, exposure to environmental pollutants, and genetic and immunological factors
stress, anxiety and depression
treatment of asthma
reduction of exposure to allergens
desensitization therapy (allergy shots)
inhalers or drugs ( help bronchial passages during asthma attacks
antiinflammatories
behavioral techniques help develop breathing and relaxation skills to improve breathing
cancer
involves development of aberrant, or mutant cells that form growths (tumors) that spread to healthy tissue
causes of cancer
genetic factors
exposure to cancer causing chemicals
exposure to some viruses
unhealthy habits
smoking, high fat intake, excess body weight, alcohol consumption, not exercising, and sun exposure
stress and cancer
weakened immune system may increase susceptibility to cancer
psychological counseling and group support programs can improve the quality of life of patients and help them cope with serious emotional consequences of cancer
avoidant type of coping → more likely to become depressed
pairing relaxation, pleasant imagery, and attention distraction can help reduce nausea associated with chemotherapy
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
AIDS
caused by HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)
attacks the immune system, leaving it helpless to fend off diseases it normally would hold in check
how hiv is stransmitted
sexual contact
direct infusion of contaminated blood
accidental pricks from needles used previously on infected person
infected mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or through breast feeding
adjustment of people with HIV and AIDS + coping skills
because of the nature of the diseases, many people develop psychological problems — most commonly anxiety and depression
coping skills
CBT can improve body’s immune response, reduce anxiety and depression, enhance self care behaviors and ability to handle stress, and improve quality of life
treatment of HIV and AIDS
stress management techniques
relaxation training
positive mental imagery
cognitive strategies to control intrusive negative thoughts
antidepressant medication
psychological interventions to reduce risky behaviors
spreading awareness of unsafe sexual and injection behaviors