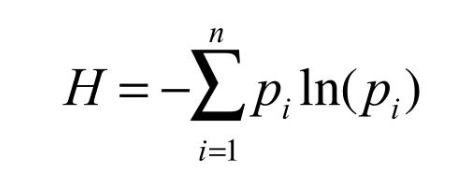Day 7 Community Structure & Dynamics
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Frederick Clements theory
communities are stable with a highly predictable composition - highly integrated and interdependent
Henry Gleasons theory
communities are a loose, ephemeral association of species, determined by chance
Communities affected by
keystone species
succession
biogeography
Keystone species
has a major effect on the composition of a community
Example of keystone species
Pisaster ochraceous starfish in intertidal communities
Effect if you remove Pisaster ochraceous starfish
barnacle and mussel populations increase
less open space for algae
chitons and limpets leave
mussels outcompete barnacles
end result is a mussel dominated community
What Pisaster ochraceous starfish mainly eat
barnacles and mussels
Disturbance
event that removes biomass (organisms) from communitythe
predictable frequency
Disturbance regime
has predictable frequency - disturbance
Succession
predictable progression of species replacements in a region
Types of succession
Primary succession
Secondary succession
Primary succession
succession pattern after a disturbance removes both organisms and soil
Secondary succession
succession pattern after disturbance removes some or all of organisms, but not soil
Pioneer species
first species to invade habitat
Pioneer species in secondary succession
R-selected
rapid growth
reach reproductive maturity quickly
produce many seeds
short life span
tolerate challenging abiotic conditions
Early successional community in secondary succession
weedy species are replaced by longer lived herbaceous species
Mid-successional community in secondary succession
shrubs and short-lived trees begin to invade
climax community in secondary succession
final stage in succession - stable community
long lived tree species at mature age
Pioneer species in primary succession
pioneer species may be slower growing but very tolerant of nutrient-poor substrate
Fire effect on communities
fire can cause communities to not reach a climax stage unless fires stop
What fires favors
fire favors grasses over non-woody plants and woody plants
Fires majorly impact these communities
invertebrate communities
Fewer fires today due to
human interference
Conservation/restoration
managed burns to maintain natural state
Species richness
number of species present in community
Species evenness
measure of similarity in abundance of each species
Species diversity
measure that incorporates richness and evenness
Shannon index
H = Shannon index of diversity
n = number of species present
i = identities of each species
pi = fraction of all species that is species i