Kin 211 motor labs
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
MAKE SURE KNOW WHAT FORMULAS MEAN, WHEN TO APPLY, DISTINGUISH THEM
MOTOR LAB 1: what does constant, absolute and variable error measure
constant = msr bias
--> postive or negative
absolute = msr accuracy
--> always positive
variable = msr consistency
MOTOR LAB 2
Hicks Law describes what
how woudl increase curvilinearly and linearly
how to find RT
LINEAR to find RT = RT increase linearly as # stimulus responses double or incr in 1 bit
as N(choices) increase, Rt incre curvilinearly
RT = a + b[log2(N)]
![<p>LINEAR to find RT = RT increase linearly as # stimulus responses double or incr in 1 bit</p><p>as N(choices) increase, Rt incre curvilinearly</p><p>RT = a + b[log2(N)]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9b67f596-68e3-458a-bb89-e3e96ae151b5.jpg)
MOTOR LAB 3
STM duration and capacity
3 things that affect duration and capacity
Graph of short-term sensory store, showing how we will forget shi
STM = 30 sec duration, 7 chunks of info
rehearsal = incr duraction by repetitions of info
interference = decr duration BO limited capacity and inability to rehearse
Chunking = incr capa by linking info tgt
as time where asked to name the letters(the cue) INCREASES, worse @ memorize letters
MOTOR LAB 4
what is bottle neck theory
what is occurring and AKA what
at some pt attn info processing becomes serial...2nd task is slower
delay = pschological refractory period (PRP)
SOA = time between S1 and S2
decr SOA -> incr RT (moves quicker in succession -> harder to guard)
MOTOR LAB 5
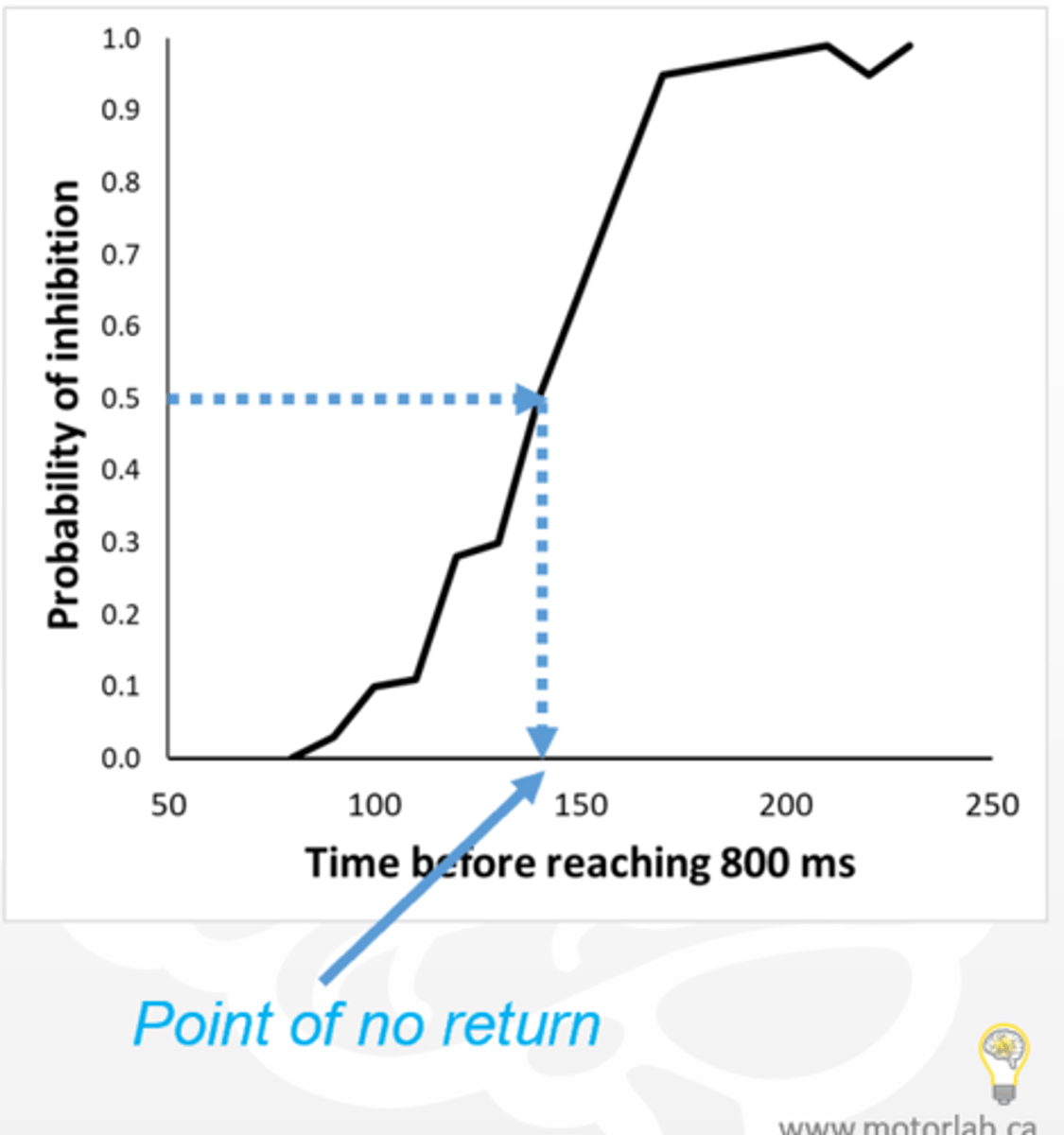
what is a motor program
what is the PONR
how to find
what ahppens if constant error
pre-structured, organized in advance set of neural commnads -> mvmt sequence
point of no return
-> release of motor commands and prob of inhibting release is 50%(a time)
if CE(constantly over time) -> add to time
MOTOR LAB 6
FITTS LAW... found what...equation
ID = ___
MT increase linearly as index of difficulty (ID) incr
-->MT = a + b[log2(2A/W)]
ID = log2(2A/W)
-->A = mvmt amplitude
W= target width
![<p>MT increase linearly as index of difficulty (ID) incr</p><p>-->MT = a + b[log2(2A/W)]</p><p>ID = log2(2A/W)</p><p>-->A = mvmt amplitude</p><p>W= target width</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7664a77b-95de-4615-b25b-389db639eca1.jpg)
Motor Lab 7
what constant and variable practice
which one better in acquisition and retention & transfer
constant = only rhearse one variation of skill in prac
variabe = rehearse many variation of skill in prac
acquisition btter for constant practice
variable better for retnetion and transger
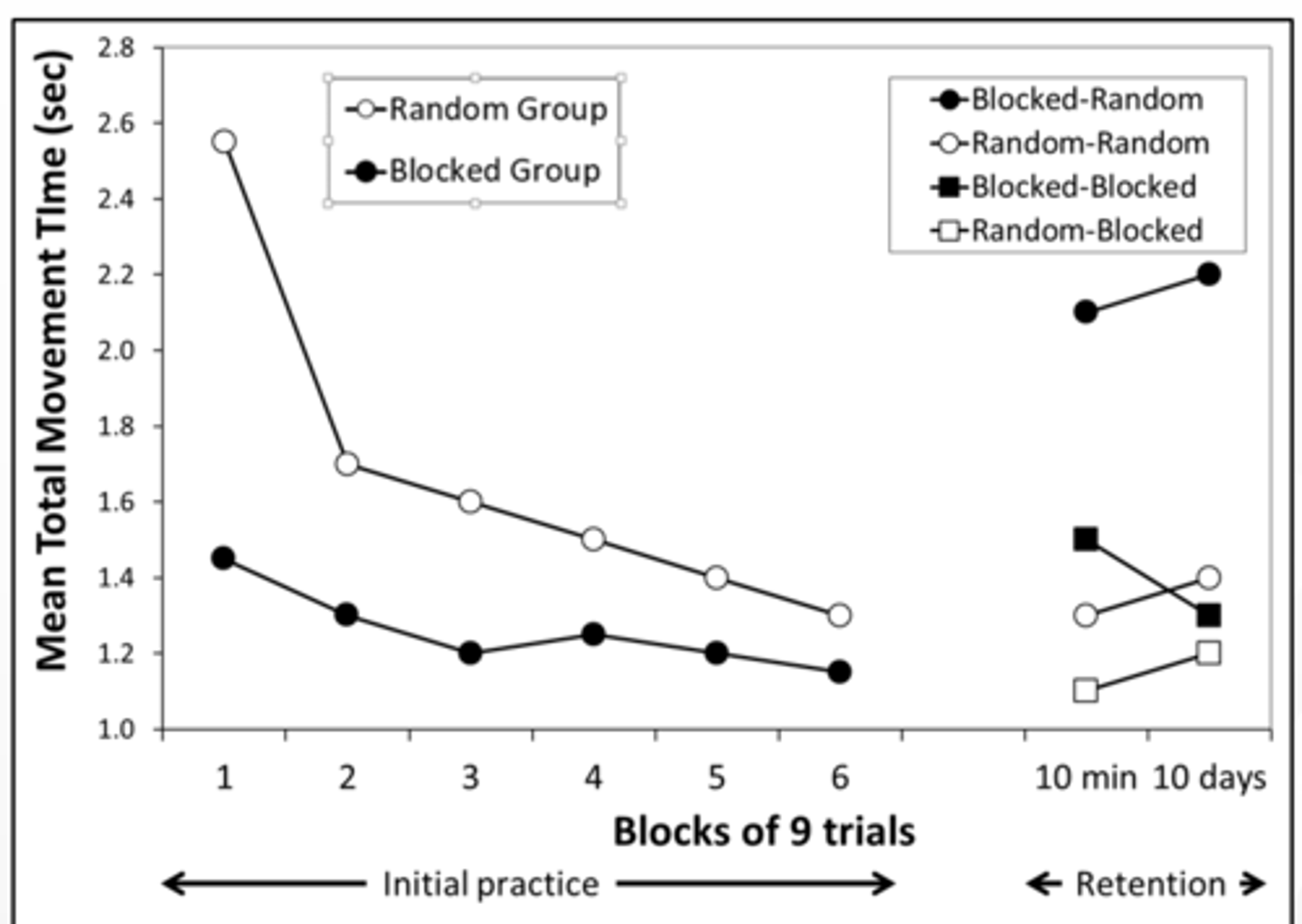
MOTOR LAB 8
3 types of practice and amt of interference
what is CI effect
blocked: low interference
AAAAAA, BBBBBB, CCCCCC
serial interference: medium interference
ABC, ABC, ABC, ABC, ABC
random practice: high interference
CBABACCABACBCBA
CI effect - blocked prac>random in acquisition
random prac> blocked prac in retention & transfer
MOTOR LAB 9
what is feedback
where does extrinsic feedback come from
feedback = sensory info to a movement
come from before (instructions), during(concurrent) or after(terminal) mvmt