Histology: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What layer of skin?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium; derived from ectoderm; attached to the basement membrane; avascular
epidermis
What layer of skin?
dense connective tissue; derived from mesoderm, vascular
dermis
What layer of the skin?
subcutaneous fascia composed of septta and adipose; vascular
hypodermis
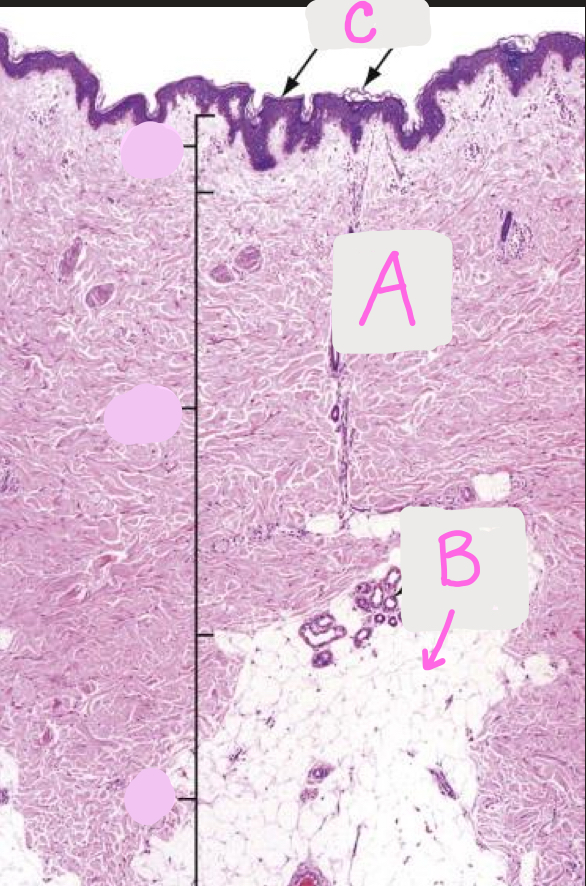
Identify each layer of the skin (A-C)
A. Dermis
B. Hypodermis
C. Epidermis
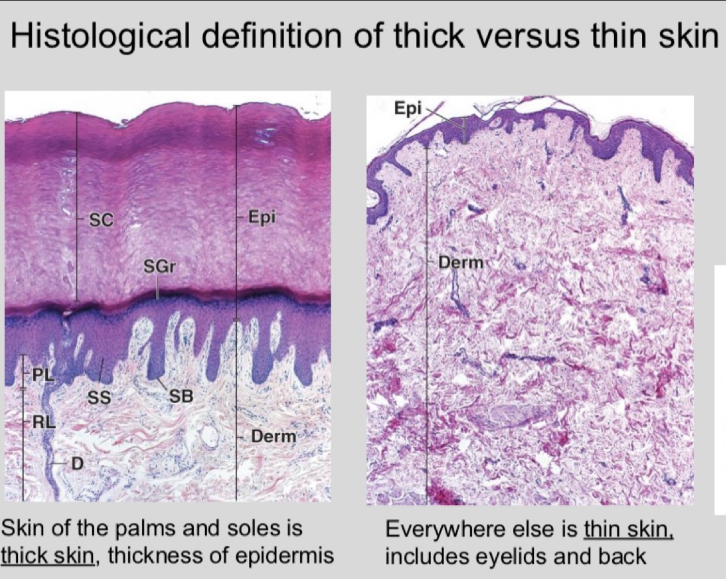
What is thick versus thin skin? Where is it found, what makes the difference, and what layer is affected?
thick versus thin is based on the epidermis
thick is found on the palms and soles; thin is everywhere else
thick skin has stratum lucidum
glabrous versus non-glabrous skin
glabrous: hairless skin
non-glabrous: hairy skin
think being hairless is more glamorous
What is the predominant cell type of the epidermis?
they originate in the deepest layer of the epidermis and grow outward
keratonocytes (produce keratin)
What are the layers of the epidermis?
“can lauren get some bitches?”
strutum corneum, stratun lucidum (thick skin), stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
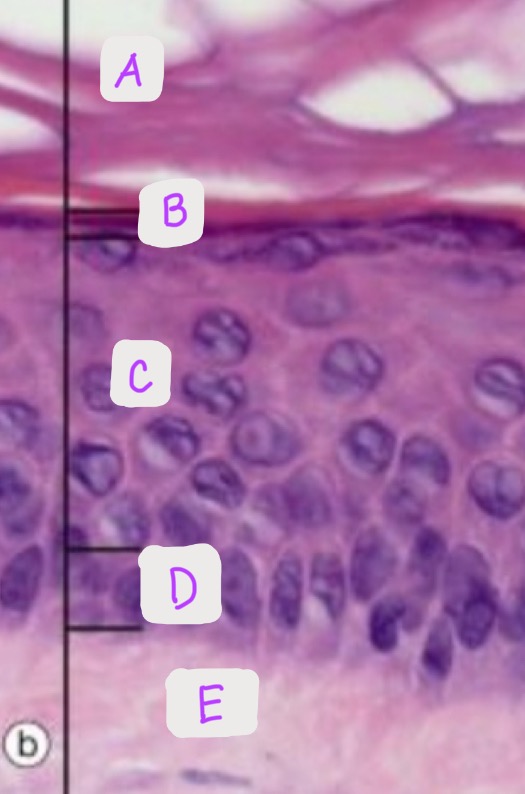
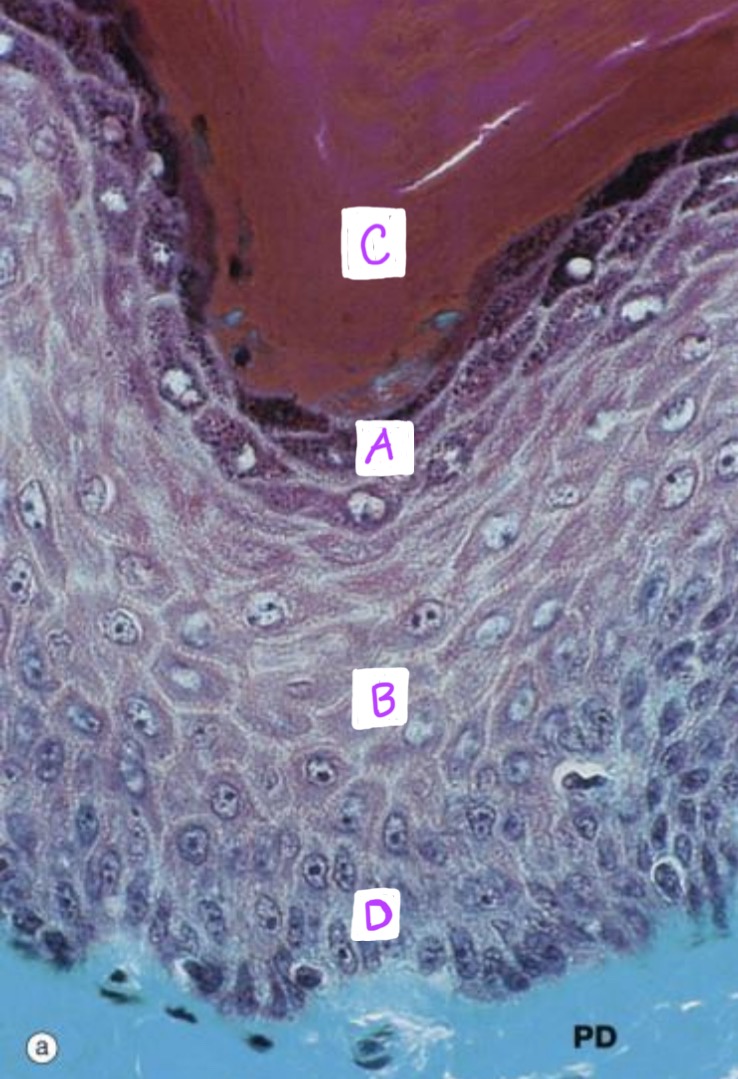
Identify each layer of the epidermis: (A-D)
-Bonus: Is this thick or thin epidermis, why?
A: Stratum granulosum
B: Stratum spinosum
C: Stratum corneum
D: Stratum basale
This is thin epidermis because there is no stratum lucidum pictured
What layer and what sublayer?
outermost layer; made up of keratin-filled dead keratinocytes termed squames, layer that varies the most in thickness
epidermis: stratum corneum
What layer and sublayer?
thin layer of cells that is only evident in thick skin
epidermis: stratum lucidum
what layer and sublayer?
diamond shaped keratinocytes, contain keratohyalin granules
epidermis: stratum granulosum
What layer and sublayer?
irregular, polyhedral keratinocytes with desmosomes that link neighboring cells
epidermis: stratum spinosum
What layer and sublayer?
deepest layer, separated from the dermis by the basement membrane and attached by the hemidesmosomes/ cells are cuboidal to columnar and are mostly keratinocytes
epidermis: stratum basale
explain the role of the basement membrane and the hemidesmosomes
basement membrane: separates the stratum basale (deepest layer of epidermis) to the dermis
hemidesmosomes: attaches the stratum basale to the dermis
explain the development and migration of keratinocytes (include tonofilaments, keratohyalin granules, lamellar bodies, and tonofibrils)
they start at the deepest layer of the epidermis (basale) and go out to the stratum corneum
basal: the KC make tonofilaments that are bundles together to make tonofibrils
spinosum: they start to produce the keratohyalin granules and produce lamellar bodies
granulosum: they flatten some and accumulate the keratohyalin granules
corneum: lose the lamellar bodeis and nuclei. The keratohyalin granules turn tonofibrils into a homogenous keratin matrix
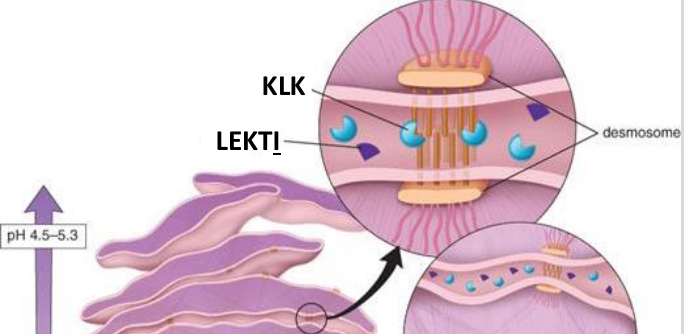
Explain the keratinocytes being desquamated. How is it triggered
the enzyme KLK (kallikrein-related serine peptidase) is triggered to break-down the desmosomes
the lymphoepithelial kazal-type inhibitors are what inhibit the KLK from breaking it down too early (not at the top)
the KLK are triggered to do the breakdown at the top because the pH is lower near the surface
Explain psoriasis and epidermal hyperplasia. Why is it happening, what layer is most affected, what do we see?
when there is accelerated maturation of the keratinocytes then they do not form properly (8-10 days) and there is insufficient development of tonofibrils and keratohyaline.
This causes the granular layer to not form properly
the skin surface has white flakes over a thick red epidermis
Explain the epidermia cell and lipid envelope. What is their purpose?
water barrier
cell envelope: insoluble proteins on the inner surface of the plasma membrane (loricrin)
lipid envelope: layer attached to the outer surface of the plasma membrane, lamellar bodies that contain a mixture of oils that get exocytized
What are the 3 major cell types in the epidermis?
keratinocytes, melanocytes, and langherhan’s cells
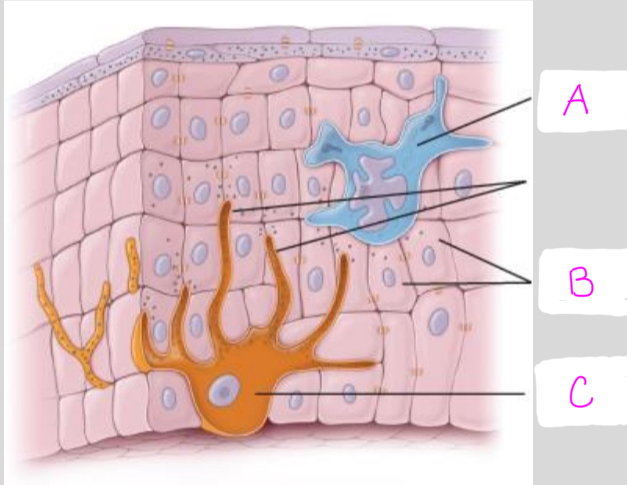
Identify each cell type (A-C)
A: Langerhan’s cell
B: Keratinocyte
C: Melanocyte
What type of cells are depicted on this histology slide?
Melanocytes
Where are the melanocytes located?
in the epidermis, specifically in the stratum basale
What is the condition where we have melanocytes but they do not produce melanin?
albinism
What is the condition where the melanocytes are targeted by the immune system and die? (autoimmune)
vitiligo
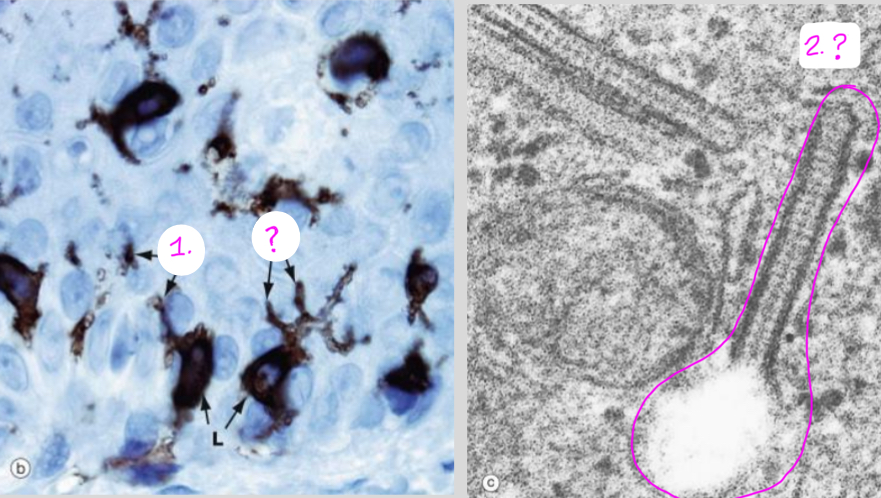
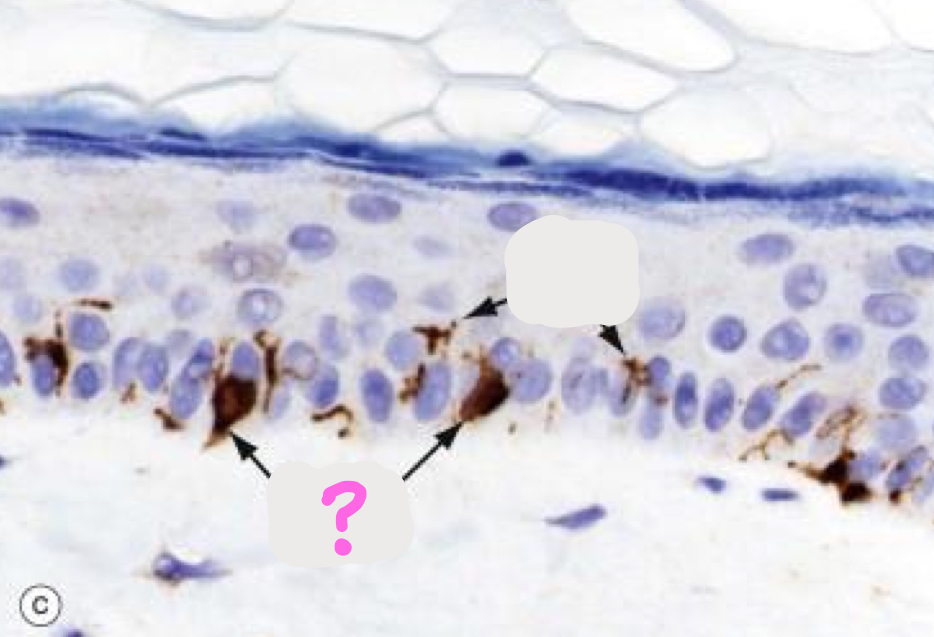
What type of cell is depicted on this histology slide?
What is the cellular component circled in pink? (and where is this located)
Langerhan’s cells
Birdeck’s granules (located in the Langerhan cell cytoplasm)
What cells serve as both APCs and macrophages? where are they located?
Langerhan’s cells
in the epidermis, specifically the stratum spinosum mostly
What is within the cytoplasm of the Langerhan cells and encloses the pathogens?
birdeck granules
What cells are involved in delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions like contact dermatitis?
langerhan’s cells
at the dermal-epidermal junction, ____ anchor cells to the hemidesmosome
____ bind the hemidesmosomes to the papillary dermis
tonofibrils go to hemidesmosome
loops of collagen go to papillary dermis
What layer houses the epidermal appendages and sensory neurons?
dermis
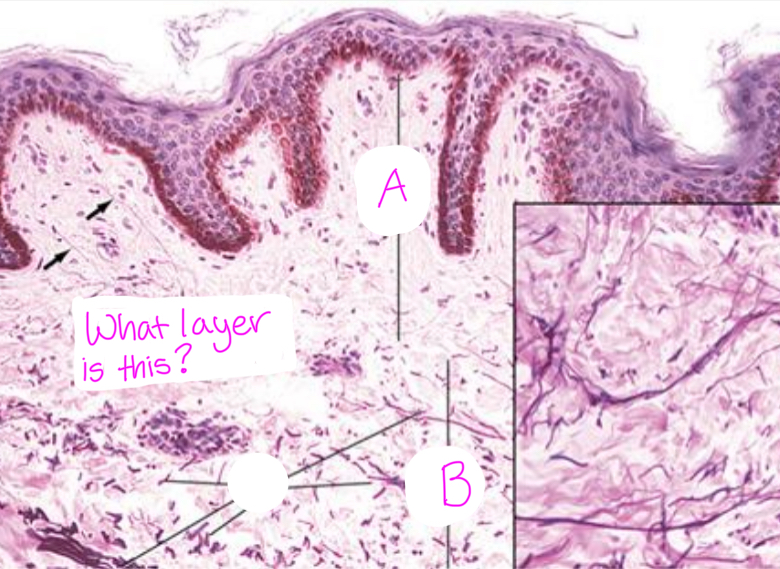
Identify each sublayer of the_______ (layer shown). (A,B)
The layer is the dermis.
A. Papillary dermis
B. Reticular dermis
What is the layer and sublayer?
outer layer connected to the basement membrane, composed of loose connective tissue (areolar), plentiful ground substance, type I and III collagen
dermis: papillary layer (top layer)
what layer and sublayer?
deeper and thicker layer, less cellular, consists of dense irregular connective tissue, bundles of type I collagen fibers and course elastic fibers
dermis: reticular layer (inner/bottom layer)
In addition to blood vessels (being vascularized) what is another component of the dermis that runs along near the vasculature?
lymphatics
what layer of the dermis has langer lines? what are they?
the reticular layer
the collagen and elastic fibers have a consistent orientation and form regular lines of tension. If incisions are made along these lines then there is less scarring
What layer?
also called the subcutaneous fascia, contains adipose lobules, skin appendages (hair follicles), sensory neurons, and lood vessels. is important for energy storage and delivering injections
hypodermis