The Biological Resources & The Biodiversity Crisis
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts and facts from the lecture on biodiversity and extinction.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is the estimated number of species on Earth according to the lecture?
Estimated 5 million to 100 million species, with approximately 1.5 million species formally described.
What is the current mass extinction event referred to in the lecture?
The Biodiversity Crisis, which is identified as the 6th mass extinction event.
the rapid decline of biodiversity, with species going extinct at a rate far exceeding the natural background extinction rate.
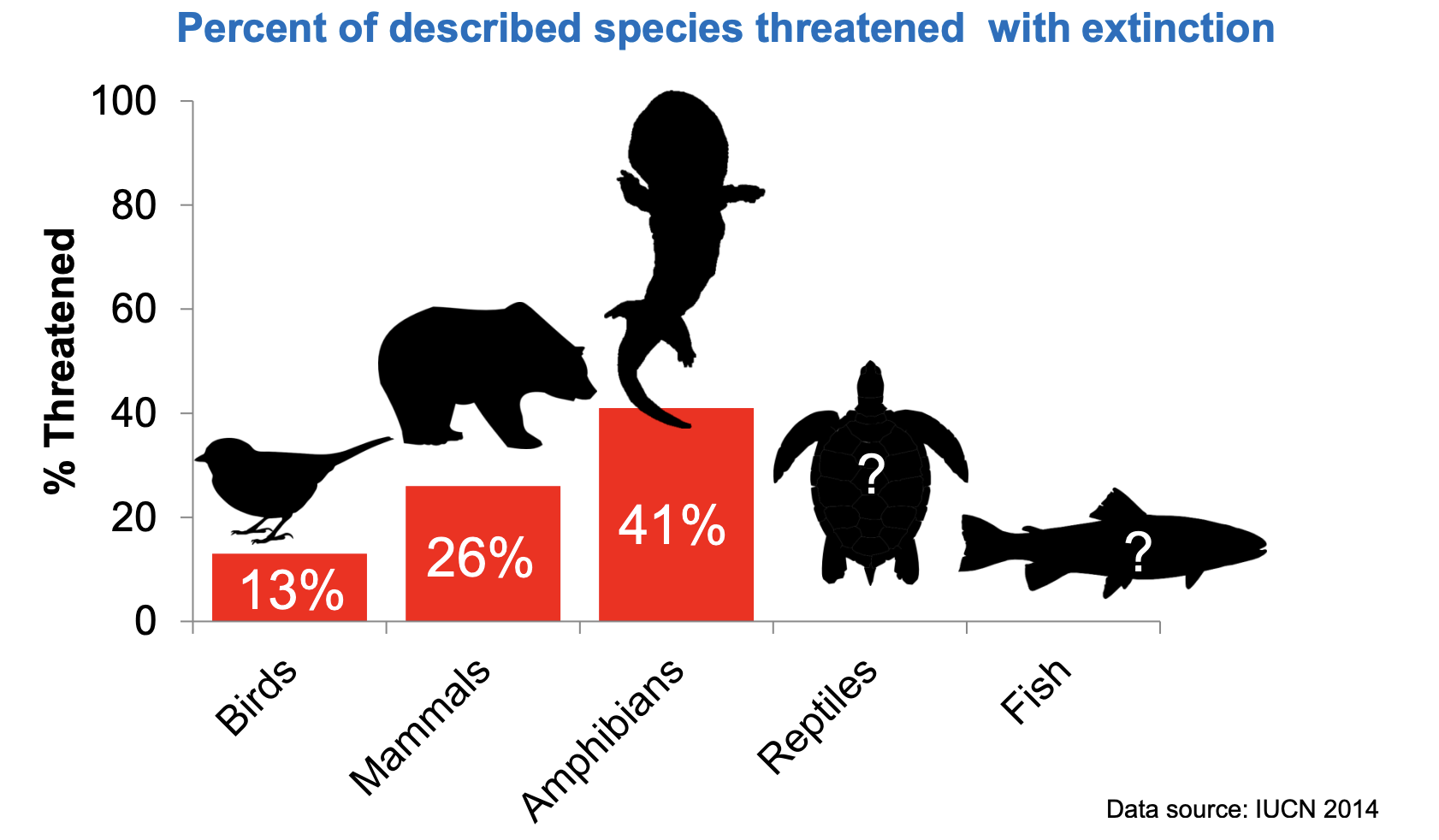
What is the percentage of described species threatened with extinction?
Between 13% and 41% of described species are threatened.
What has been the average decline of animal populations over the last 40 years?
Animal populations have declined by an average of 60%.
-99% of current extinctions are caused directly or indirectly by people
-Species extinction rates >>1000 times background rate
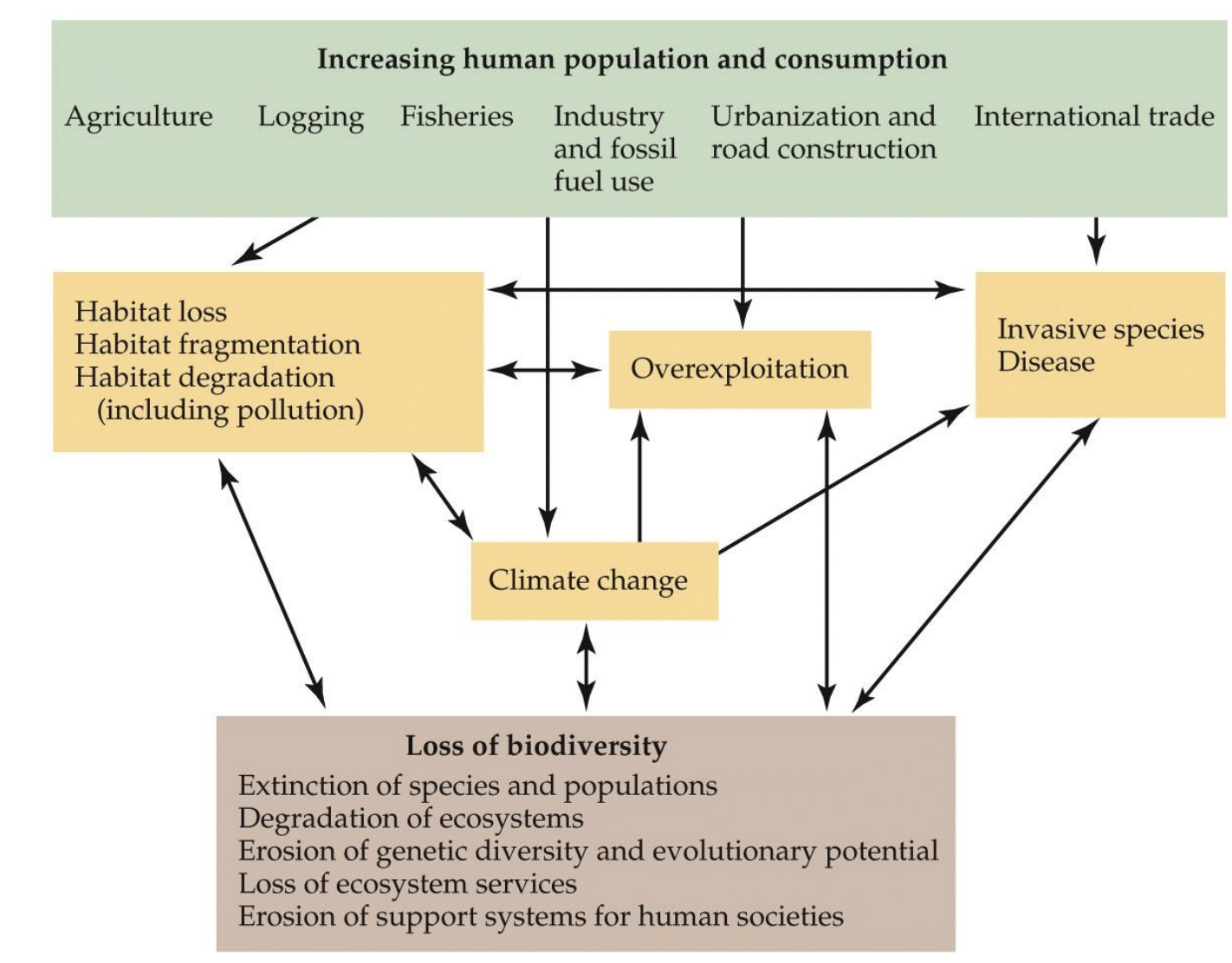
What are some human activities contributing to the loss of biodiversity?
Agriculture, logging, industrialization, urbanization, habitat loss, and climate change.
More people = More resource consumption = Loss of biodiversity
What type of extinction includes species that only exist in captivity?
Extinct in the wild.
-Only living individuals of a species are in captivity; the species is no longer found in the wild
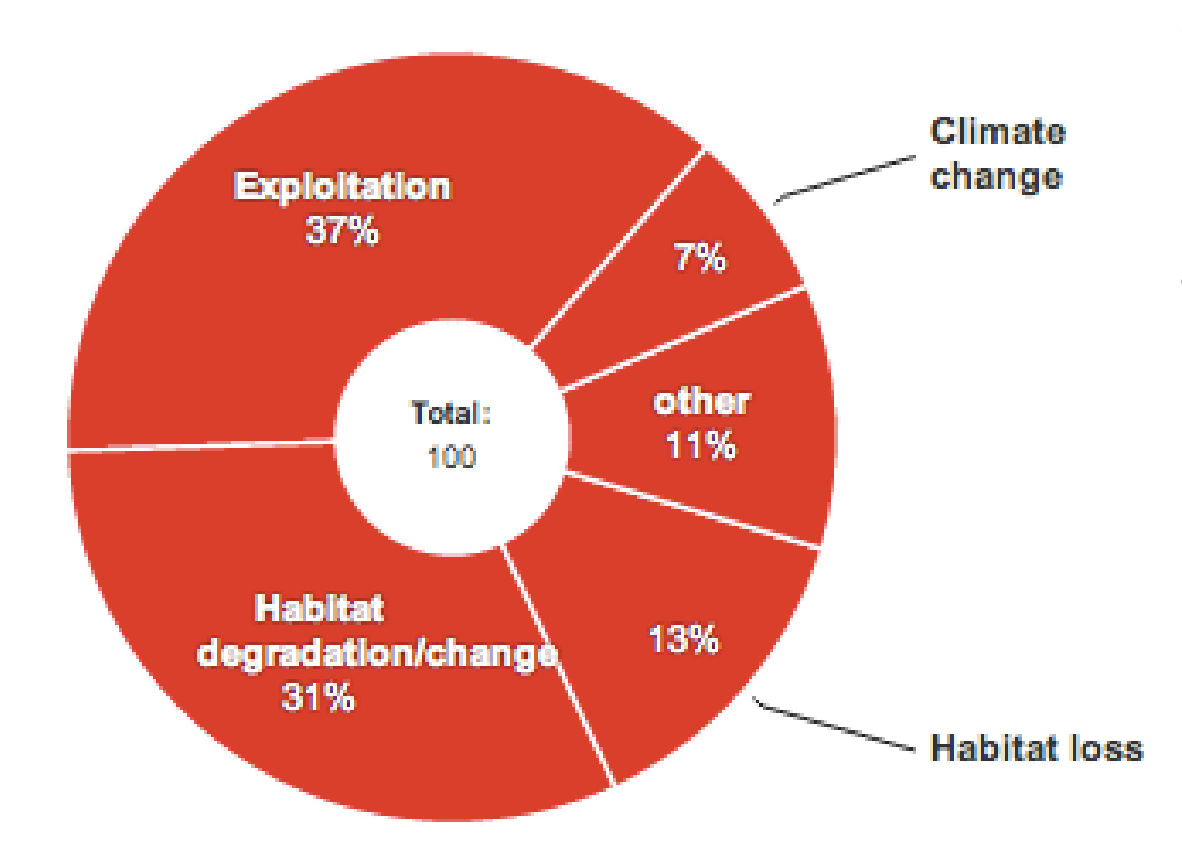
What has been identified as a major factor in wildlife declines globally?
Exploitation, accounting for 37% of wildlife declines according to WWF's Living Planet Index.
Types of extinction
Extinction – Loss of a species, genus, family, or other higher taxonomic group
• Extinct – No living individuals remain; i.e., Globally extinct
Ecologically extinct
Remaining population is so small that the species does not contribute to ecological interactions or ecosystem function
Pygmy tarsier (Tarsius pumilus) Native to Indonesia Cause of decline: Habitat loss & degradation; collection for pet trade
Extirpation
Loss of a population; i.e., local extinction; regional extinction
• Extirpated – No living individuals remain in a population; i.e., locally extinct; regionally extinct
Gray wolf (Canis lupus) Cause of decline: Overhunted
Patterns of extinction
Limited range areas
• Small population sizes
• Few populations
• Evolved under conditions of few competitors, predators, and diseases
• Many endemic species (species that only occur in one place)
extinction on islands
• European colonization was particularly destructive
• Extensive land clearing
• Introduced nonnative species
Extinction rates are greater on islands than on the mainland
Many early extinctions were on islands
ex:Hawaii O’o (Moho nobilis) Declared extinct: 1934 Cause: Habitat destruction, introduced disease, hunting for feathers
Extinctions in aquatic environments
• Extinction rates are greater in aquatic (freshwater) ecosystems than in marine environments
Extinctions in freshwater & marine ecosystems are underestimated
• Marine species may have greater resiliency, but…
• 49% decline of marine vertebrates since 1970
• Many whale and large fish species have declined by >90% due to overharvesting
• Small fish are declining rapidly due to new overharvesting pressures
Current environmental conditions associated with extinction vulnerability
Deforestation
• Urban, suburban, and rural development
• Degraded water quality
• Climate change
What traits make species more vulnerable to extinction under current conditions?
Require stable environments
Specialized niche requirements
Habitat specialists
Dietary specialists
Specialized species interactions/relationships
Form permanent or temporary aggregations
Limited mobility
Large body size
Long lived
Delayed sexual maturation & low birth rate
Low genetic variability
Naïve to people & other predators
Hunted or harvested by people
warning signs of extinction vulnerability
Closely related to a species that is endangered or extinct
ex: Eastern Black Rhino Critically endangered (Black rhino is extinct)
Ranking from Greatest to Least Extinction Risk
Bornean Orangutan
• Ploughshare Tortoise
• Chinese Giant Salamander
• Eastern Black Rhinoceros
• Philippine Eagle
• Rhondo Dwarf Galago
• Sunda pangolin
• Bog turtle
Habitat destruction/loss
– destruction of an ecosystem so that it no longer exists, nor can it provide habitat for the native species that existed in the original ecosystem • The habitat no longer exists • Populations of native species are extirpated • All ecosystem function is lost
Habitat fragmentation –
the breaking up of habitat into smaller, unconnected pieces
• A side effect of habitat destruction/loss
• Results in edge effects
• Small fragments may not be able to support minimum viable populations
• High isolation lowers migration rate
• Increases mortality rates of wildlife
• Human-wildlife interactions increase → conflict
Habitat degradation –
the alteration of a habitat so that it is negatively impacted through forces such as pollution or introduced species
• Ecosystem functions break down
• Populations of native species decline or are extirpated
• Ecosystem transitions into a different state that does not provide the same ecosystem functions or habitats
• Leads to habitat loss
edge effects
Microclimate changes
• Increased fire
• Increased invasive species
• Increased disease due to crowding & stress
• Core habitat decreased or lost
• Loss of core habitat species
• Exploitation
the unsustainable killing, collection, or use of organisms and resources
• Also known as “Overharvesting”
• People often try to justify exploitation for economic, religious, or educational purposes
• Leads to collapse and loss of populations, species, & ecosystems
• Technological advances have increased the efficiency of exploitation
Environmental Economics
A subfield of economics focused on the environment, recognizing that ecosystem services and natural resources hold economic value. It applies money and economic principles to inform most policy decisions.
Market Value
What people are willing to pay for a resource; includes harvest value and represents direct use value.
Value of Unharvested Resources
Economic benefit from resources left in nature, such as tourism value; considered a form of indirect use value
Future Value of Resources
Includes option value (potential future use), ecosystem service value, and the costs associated with protecting or replacing species, services, or resources, as well as fixing environmental problems.
Externalities
Hidden costs or benefits that affect others who did not choose to incur them, such as pollution impacting public health.
Market Failure
Occurs when externalities cause a misallocation of resources, where a few benefit while society bears the cost.
Tragedy of the Commons
The overuse and depletion of shared, open-access resources due to individuals acting in their own short-term interest.
Short-Term Focus
Economic valuations often prioritize immediate benefits while ignoring long-term environmental impacts.
Government Subsidies
Financial support from taxpayers to industries, often not factored into environmental costs and benefits.
Indirect Benefits and Impacts
Non-obvious effects, such as ecosystem support or future resilience, are frequently excluded in economic evaluations.