refraction of light
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
refraction
The bending of a wave as it passes at an angle from one medium to another
some of the light ray will be reflected and some of it will be absorbed
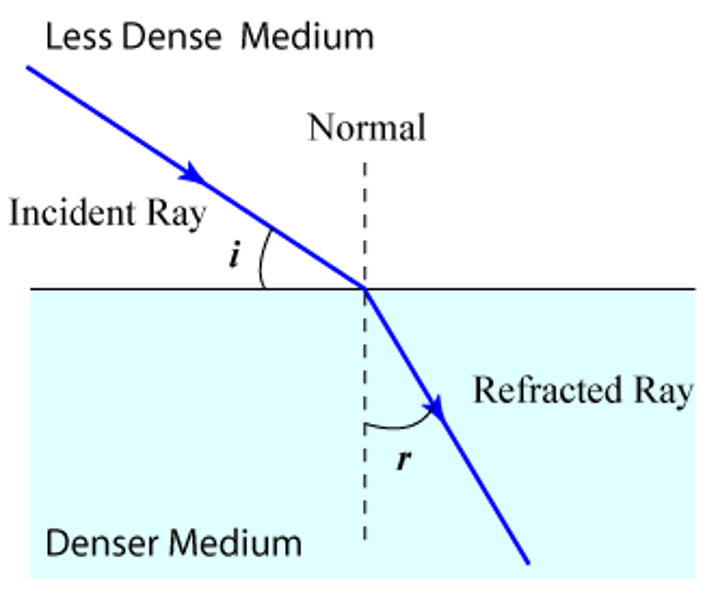
less dense to more dense medium
the angle of refraction will be smaller than the angle of incidence and bend towards the normal
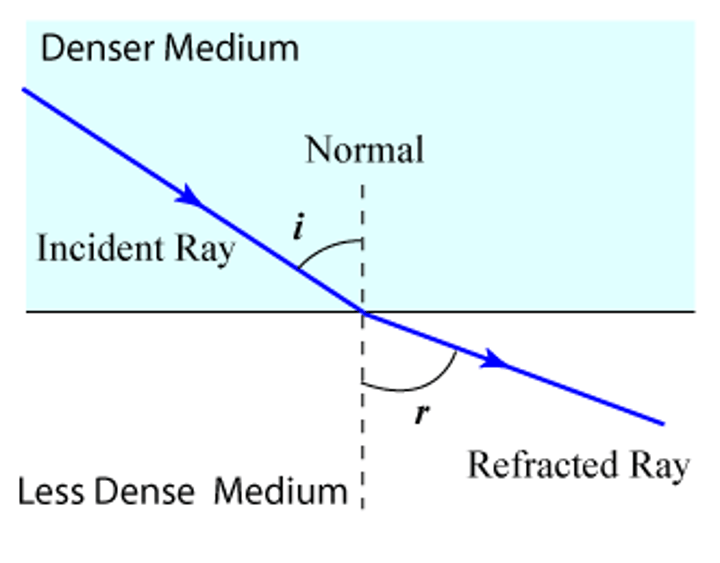
more dense to less dense medium
light ray will bend away from the normal and angle of refraction will be bigger than angle of incidence
Snell's law

refractive index
refractive index = v vacuum / v in a medium
speed of light in vacuum = 3 X 10 ^8 ms-1
Angles measured
clockwise
anticlockwise
clockwise direction -
anticlockwise direction +
apparent depth
The depth that an object appears to be at
due to the refraction of light in a transparent medium
Lateral displacement
s = d sin (i - i') / cos i'
incident ray and emergent ray are parallel
lateral displacement of light ray = its displacement sideways when going from 1 medium to the other
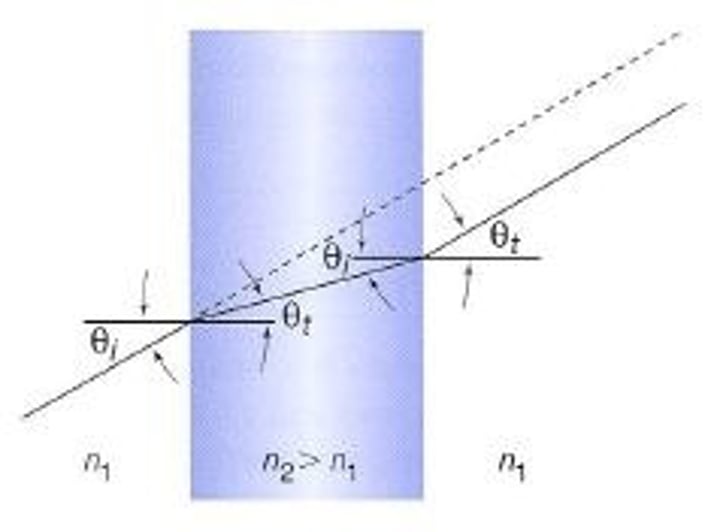
light ray entering a glass block
light ray will bend 10 degrees towards normal (air to glass)
when leaving the block the light ray will bend 10 away from the normal (glass to air)
the light doesn't have any overall bending
principal of resistibility
if light rays was travelling through glass block in the opposite direction
it would bend and move outward by the same amount as well
prism
the surfaces are not parallel
prism ocular health
use to relieve defects caused by extraocular muscle dysfunction
paraxial equation
L = n / l
n= refractive index
l = distance (m)
n' - n / r = n/l = n’/l'