201K: To Alkenes, Arenes and Beyond - Olefinations
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Conjugated molecule
When 2 (or more) double bonds are separated by a single bond → uninterrupted chain of p-orbs on adjacent C atoms
What’s an ylide?
Ylides are compounds that are often depicted with a positive charge on one atom and a negative charge on the next atom.
They are examples of zwitterions, compounds that contain both positive and negative charges within the same molecule. They differ from other zwitterions due to proximity of the charges.
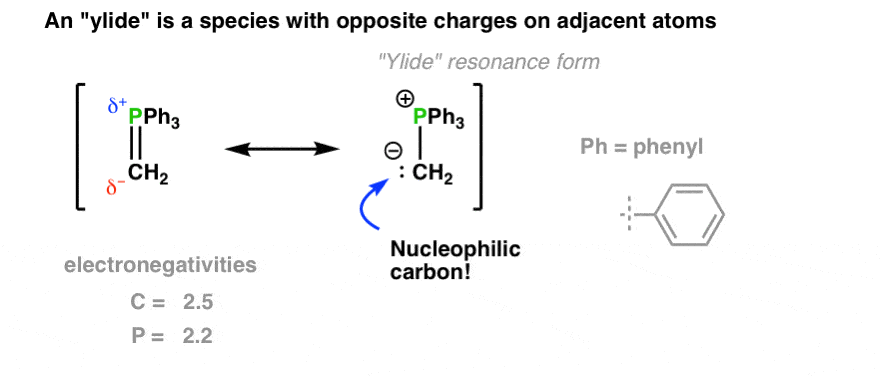
Stereospecific reaction
When stereoisomers of a compound react under identical conditions to give different products.
e.g. Sn2, E2, Diels-Alder, hydroboration of alkenes and alkynesDraw
Stereoselective reaction
When a substrate is non-stereoisomeric but its reaction leads to different stereoisomers in unequal amounts.
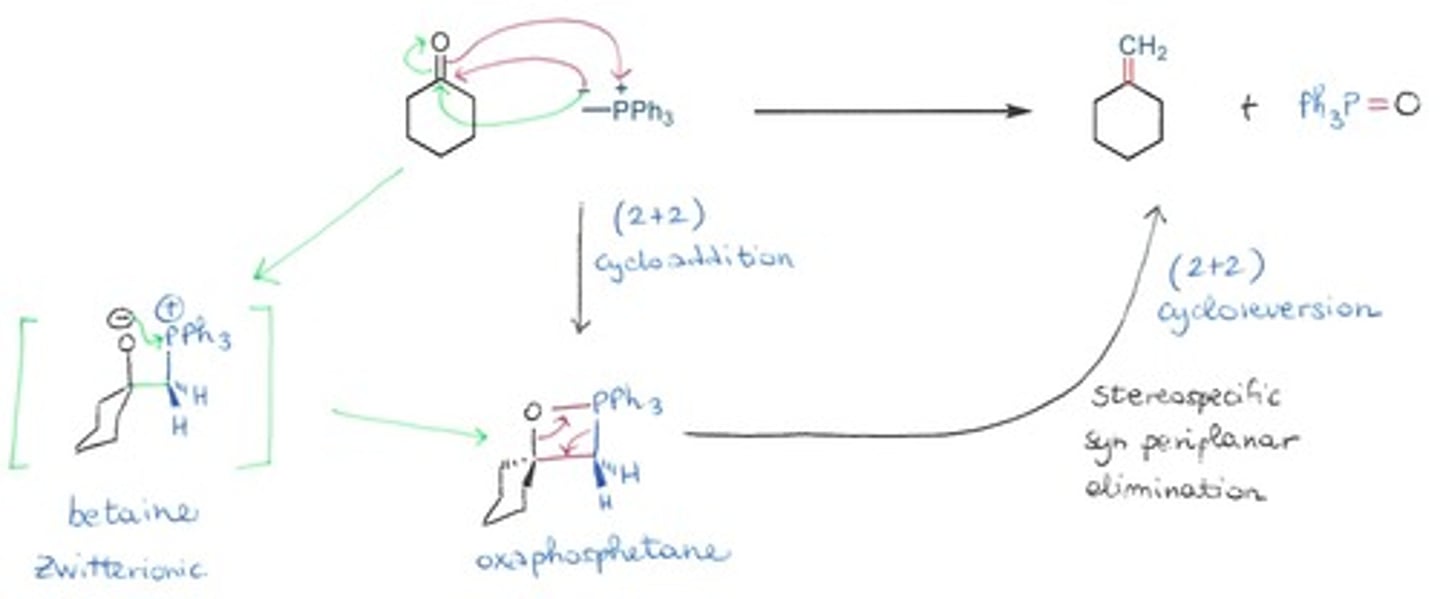
Draw the Wittig reaction
Olefination (turning something into an alkene) mediated by an alpha-phosphorus carbanion.
Put these bases in order of strongest to weakest:
ⁿBuLi
tBuOK
NaH
PhLi
NaNh₂
NaOMe/NaOCl

When do we need a strong base in Wittig reaction (+ modifications)?
When R₃ is an alkyl group
When do we need a weak base in Wittig reaction (+ modifications)?
When R₃ is something that stabilised the -ve charge (definitely not an alkyl group)
What's an unstabilised ylide?
Which product does it stereoselectively give?
- Has an alkyl group next to -ve charge.
- Gives predominantly or only Z-alkenes.
What's an stabilised ylide?
Which product does it stereoselectively give?
- Has an EWG next to -ve charge - stabilises anion via resonance (-M)
- Gives E alkenes as major product
4 examples of EWGs
CO₂R (ester)
COH
COR
CN
Why are unstabilised ylides Z selective?
Irreversible formation of cis oxaphosphetane
- no steric clashes

Why are stabilised ylides E selective? (1st explanation)
Reversible formation of cis and trans oxaphosphetane; → minor trans oxaphosphetane closes faster + irreversibly to the E alkene
(The 2 groups are trans in the TS - don't have to become eclipsed → lower barrier of elimination so forms faster + irreversibly.)
i.e. Equilibration of oxaphosphetanes to more stable trans diastereomer → eliminates more rapidly than cis isomer
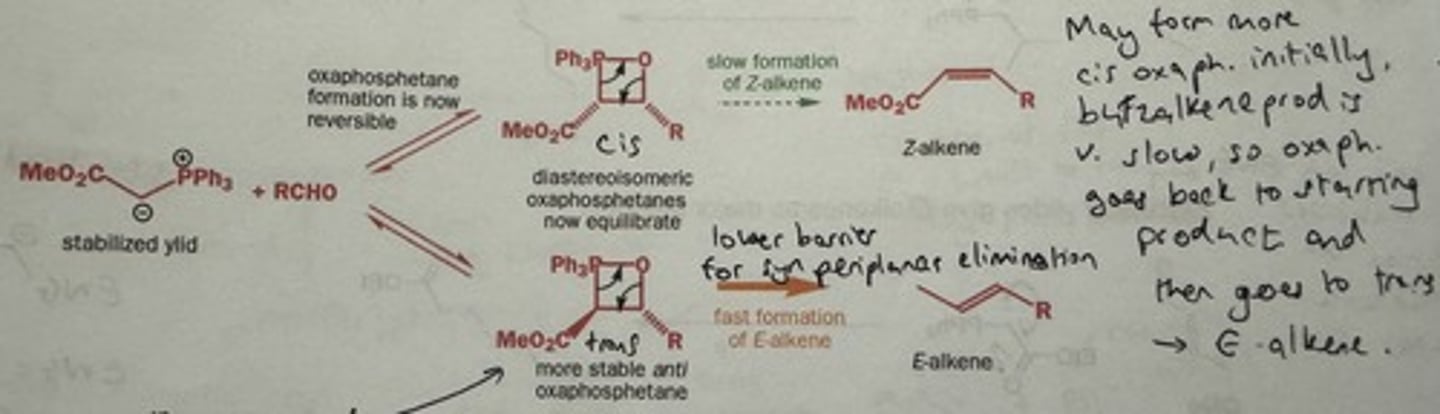
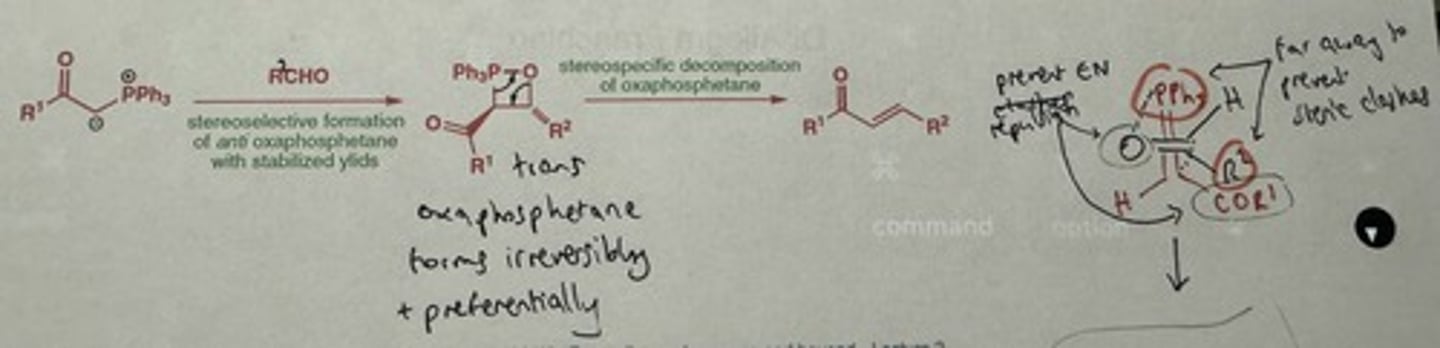
Why are stabilised ylides E selective? (2nd explanation)
Preferential irreversible stereoselective formation of trans oxaphosphetane, via perpendicular approach between. aldehyde + ylides
→ minimises steric clashes AND repulsion between electroneg. groups
Stabilised ylides are so stable that they're sluggish to react with ketones. How can we overcome this limitation?
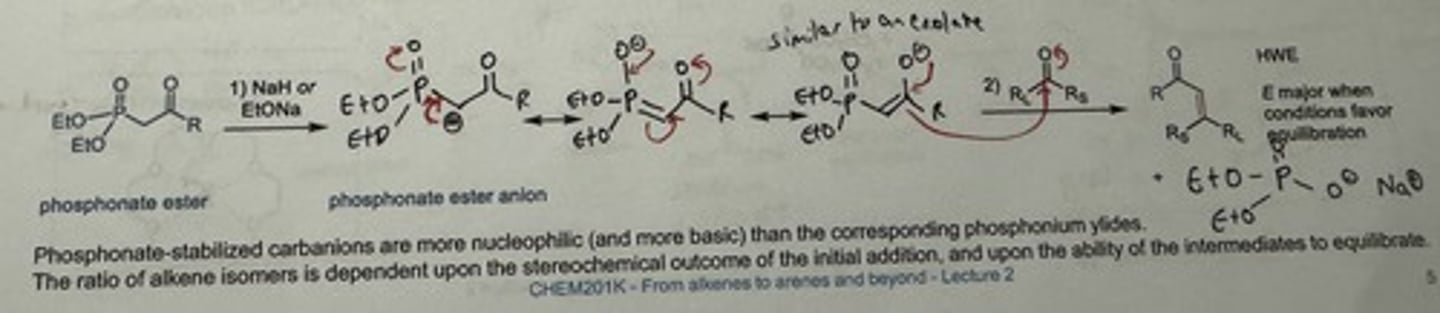
Use the HWE reaction: phosphonate ester used instead of phosphonium ylide.
→ phosphonate-stabilised carbanions are more nucleophilic (+ more basic) than p. ylides
→ ester group lowers pKa
→ major E alkene (when conditions favour equilibration)
Mechanism + reagents for Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons Reaction
1) NaH or EtONa (base), DME (aprotic solvent)
2) Ketone or formaldehyde?
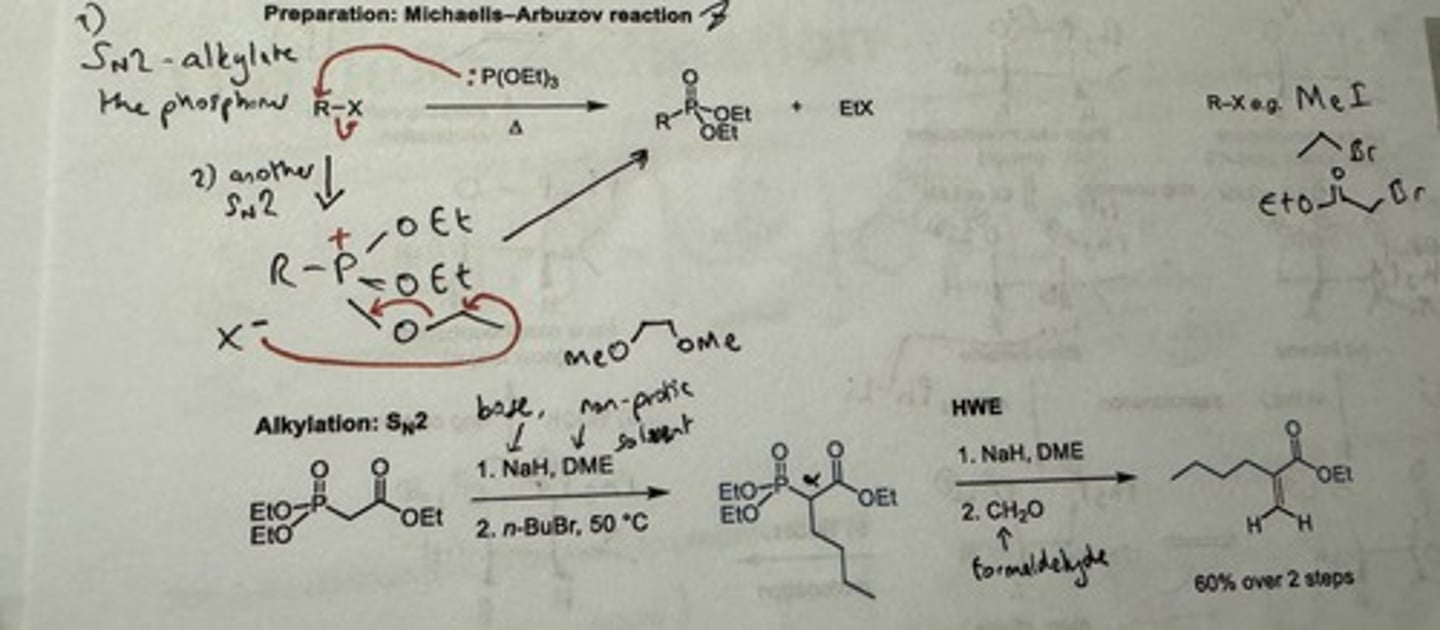
Show mechanism + reagents for preparation of phosphonates for HWE
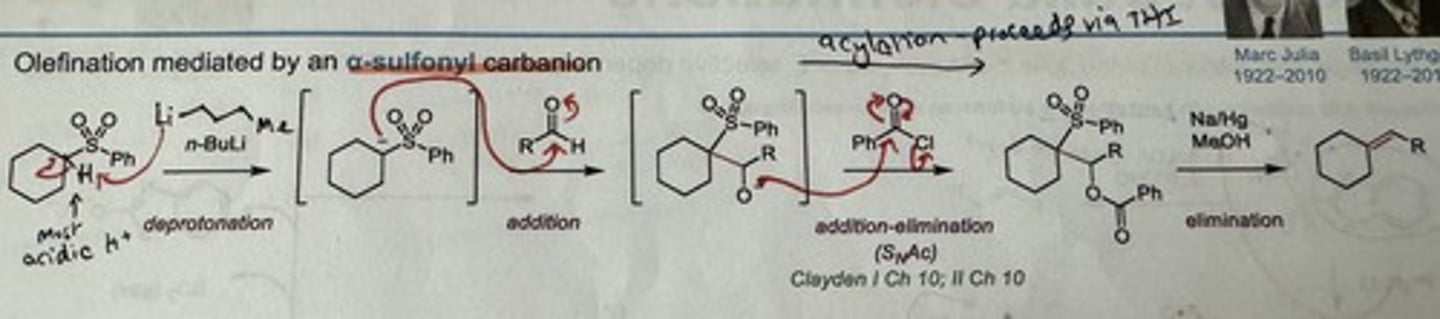
What is the Julia olefination?
State 3 steps + reagents
Olefination mediated by alpha-sulfonyl carbanion (SO₂Ph).
→ Forms E alkenes.
3 steps:
1) Deprotonation at the α carbon by n-BuLi or EtMgBr
2) Acylation to add a LG (RCHO)
3) Elimination using Na/Hg + MeOH
Show mechanism + reagents for the Julia olefination.
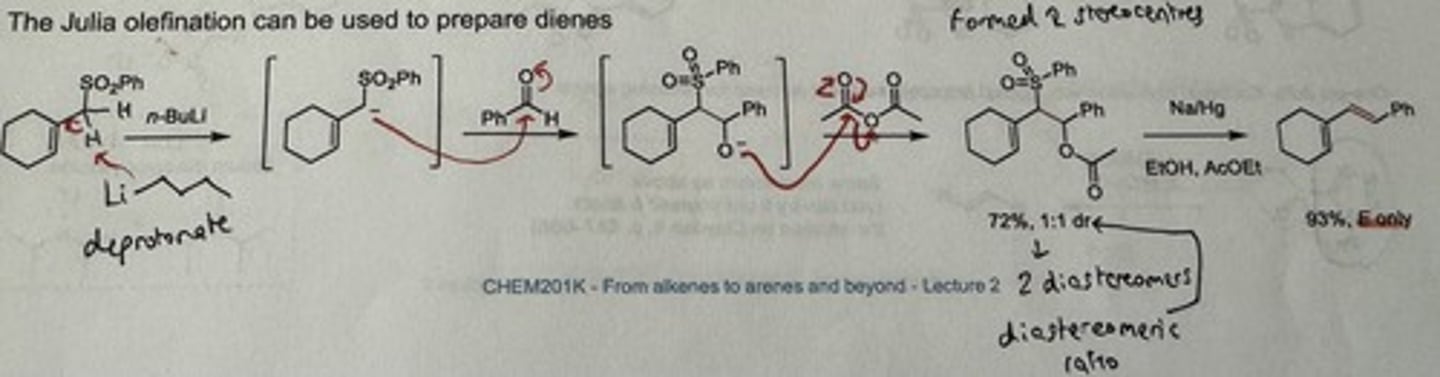
What can the Julia olefination be used to prepare? Show the mechanism for it.
Dienes!! (diene = an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing two double bonds between carbon atoms)
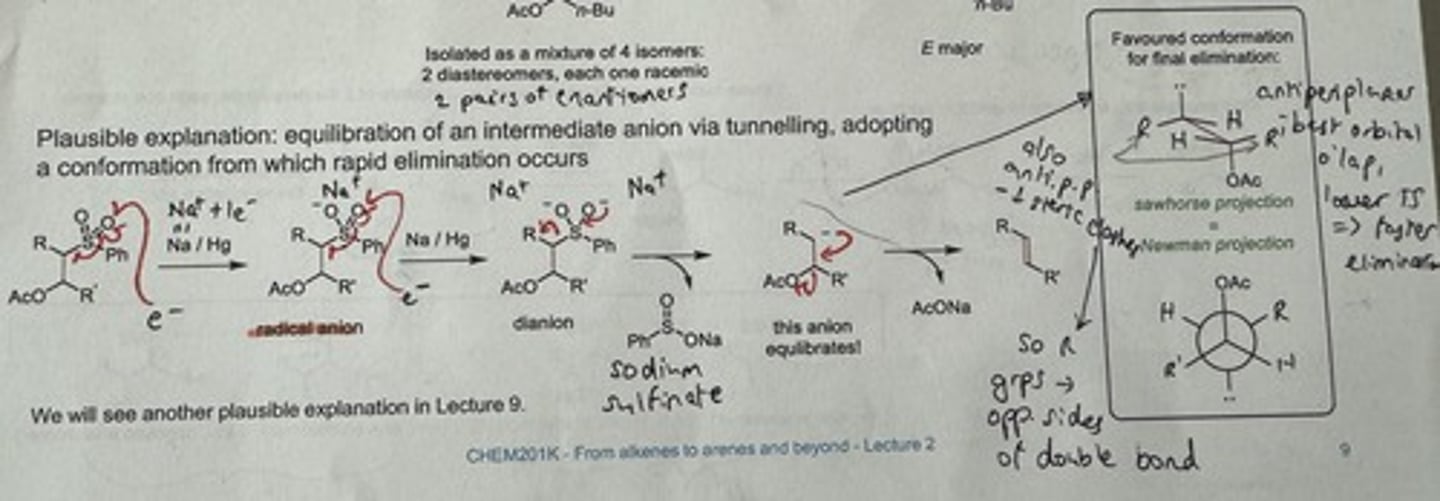
Is the Julia olefination stereospecific or stereoselective for a certain alkene? Give a plausible explanation for your answer.
Stereoselective for E alkene.
→ Equilibration of an intermediate anion via tunnelling
→ adopts a conformation from which rapid elimination occurs (antiperiplanar - best orb overlap, lower TS = faster elimⁿ)
What are the two single-step variants of the Julia olefination which eliminate the need for reducing agents? Show reagents.
1) J.olefination w/ benzothiazole sulfone
→ 1) LDA (base to deprotonate), 2) R'CHO
2) Julia-Kocienski olefination w/ phenyl tetrazole sulfone
→ 1) KHMDS, 2) R'CHO
Show mechanism for J.olefination w/ benzothiazole sulfone
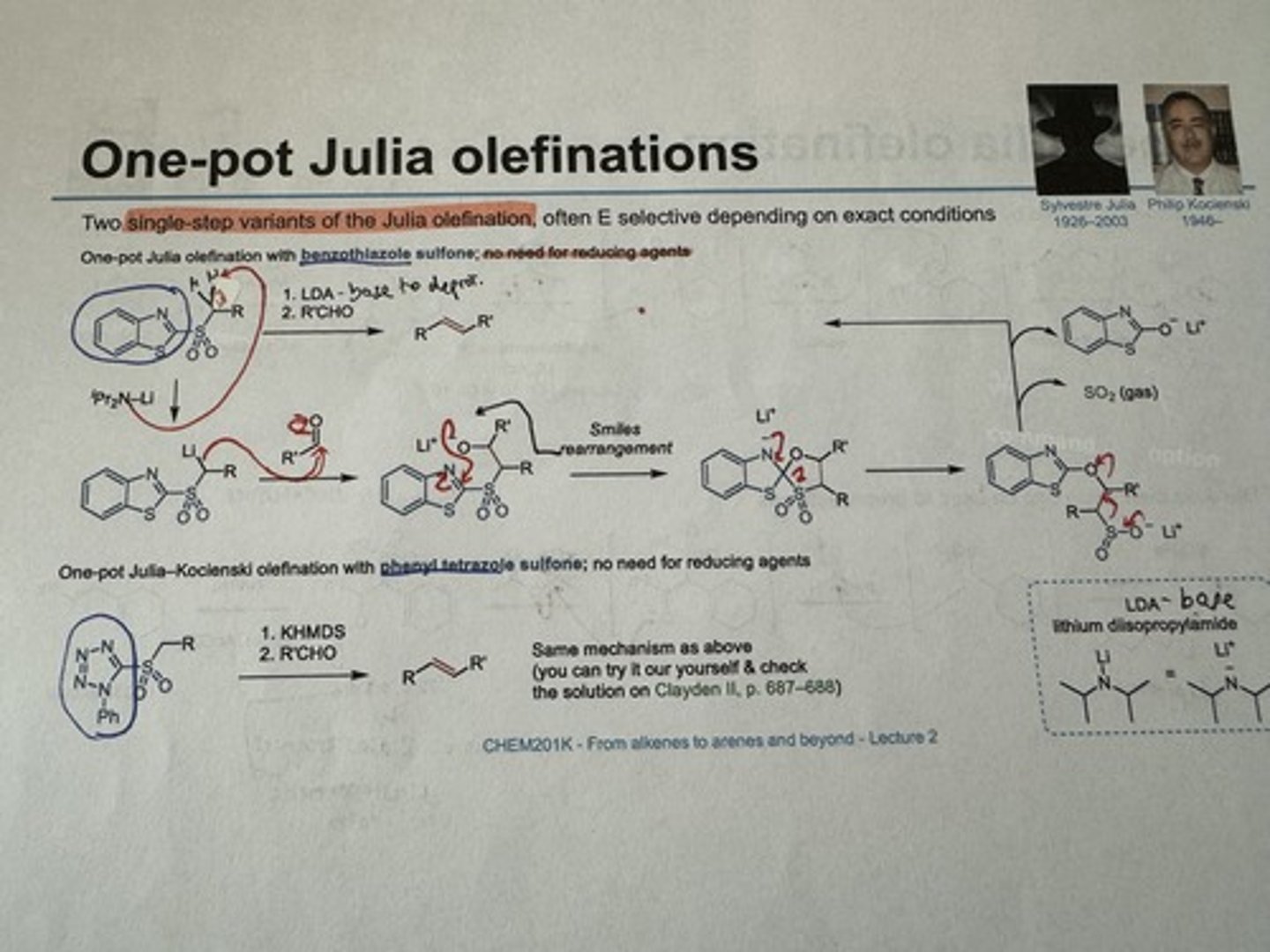
Show mechanism for Julia-Kocienski olefination w/ phenyl tetrazole sulfone
(Add from pg 897 of Clayden)
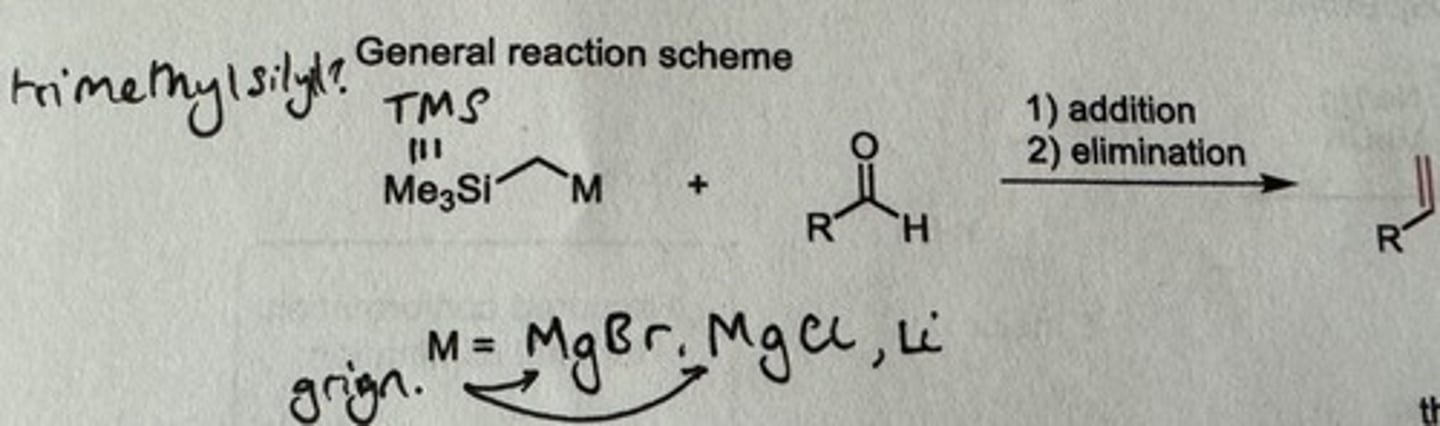
What is the Peterson olefination? (Silly!!!)
Show general reaction scheme
Olefination mediated by an alpha-silyl carbanion
1) addition - requires addition of Grignard reagent first
2) elimination
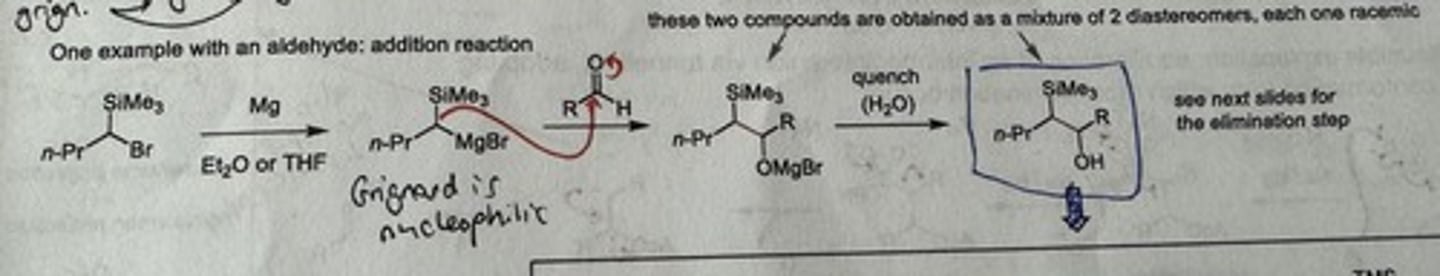
Show mechanism + reagents of Peterson olefination addition step with an aldehyde.
Reagents: Mg, Et₂O or THF → aldehyde → quench w/ H₂O
What determines the stereochemical outcome of the Peterson elimination?
STEREOSPECIFIC: produces specific alkenes based on stereochemistry of the Beta-silyl alcohol undergoing elimination
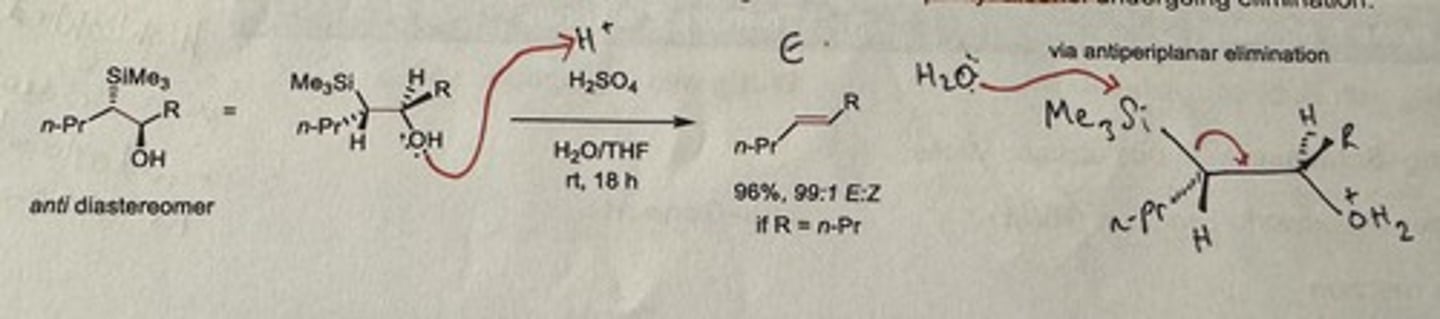
Show Peterson olefination elimination step in acid-mediated conditions for the anti diastereomer.
H₂SO₄, H₂O/THF, rt is 18h
Gives major E alkene if R = n-Pr
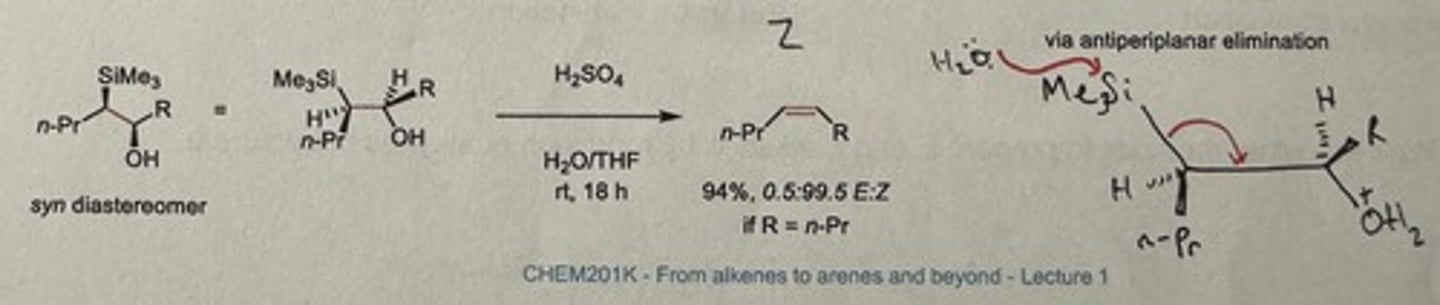
Show Peterson olefination elimination step in acid-mediated conditions for the syn diastereomer.
H₂SO₄, H₂O/THF, rt is 18h
Gives major Z alkene if R = n-Pr
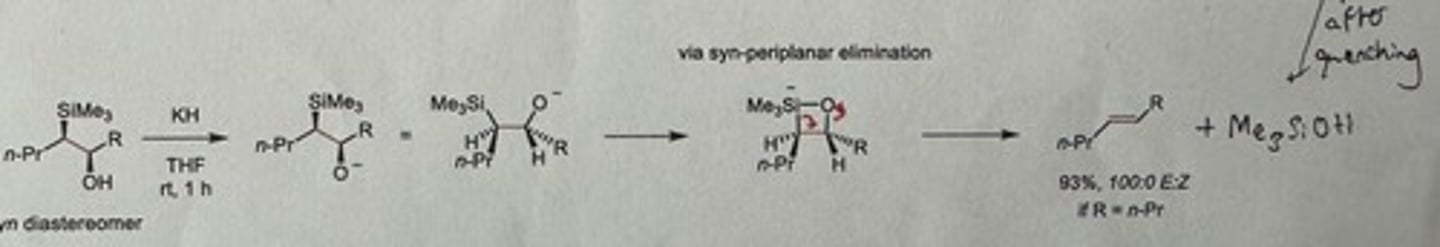
Show Peterson olefination elimination step in base-mediated conditions for the anti diastereomer.
KH (v. reactive base), THF, rt is 1h
Gives major Z alkene if R = n-Pr

Show Peterson olefination elimination step in base-mediated conditions for the syn diastereomer.
KH (v. reactive base), THF, rt is 1h
Gives major E alkene if R = n-Pr
Which olefinations can be used to make E alkenes?
- Wittig w/ stabilised ylides
- HWE reaction
- Julia reaction
- Peterson elimination
Which olefinations can be used to make Z alkenes?
- Wittig w/ unstabilised ylides
- Peterson elimination