Unit 1: Research Methodology
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Hypothesis
predictions on how factors may be related
Operational Definition
specific procedure used to determine the presence of a variable
Independent Variable
the factor that is being manipulated
Dependent Variable
behavior or mental process that is being measured
Random Sample
every member of the sample has an equal chance of being selected
Stratified Sample
grouping a population into relatively homogeneous subgroups
Validity
extent to which an instrument measures or predicts what it is supposed to
Reliability
consistency or repeatability
Correlation Research
looks at the relationship between two variables without establishing a cause and effect relationship
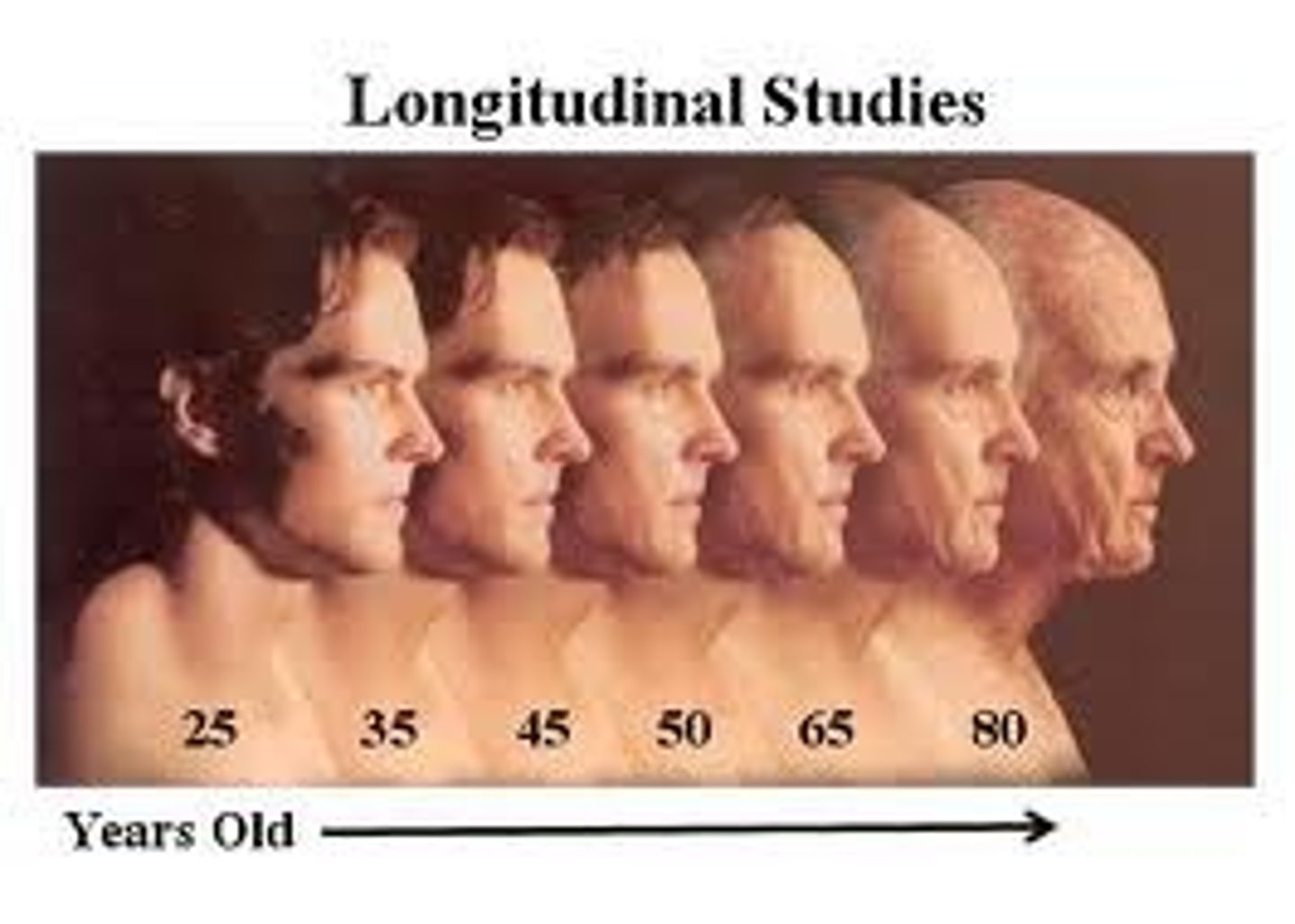
Longitudinal Studies
conducting a study over time
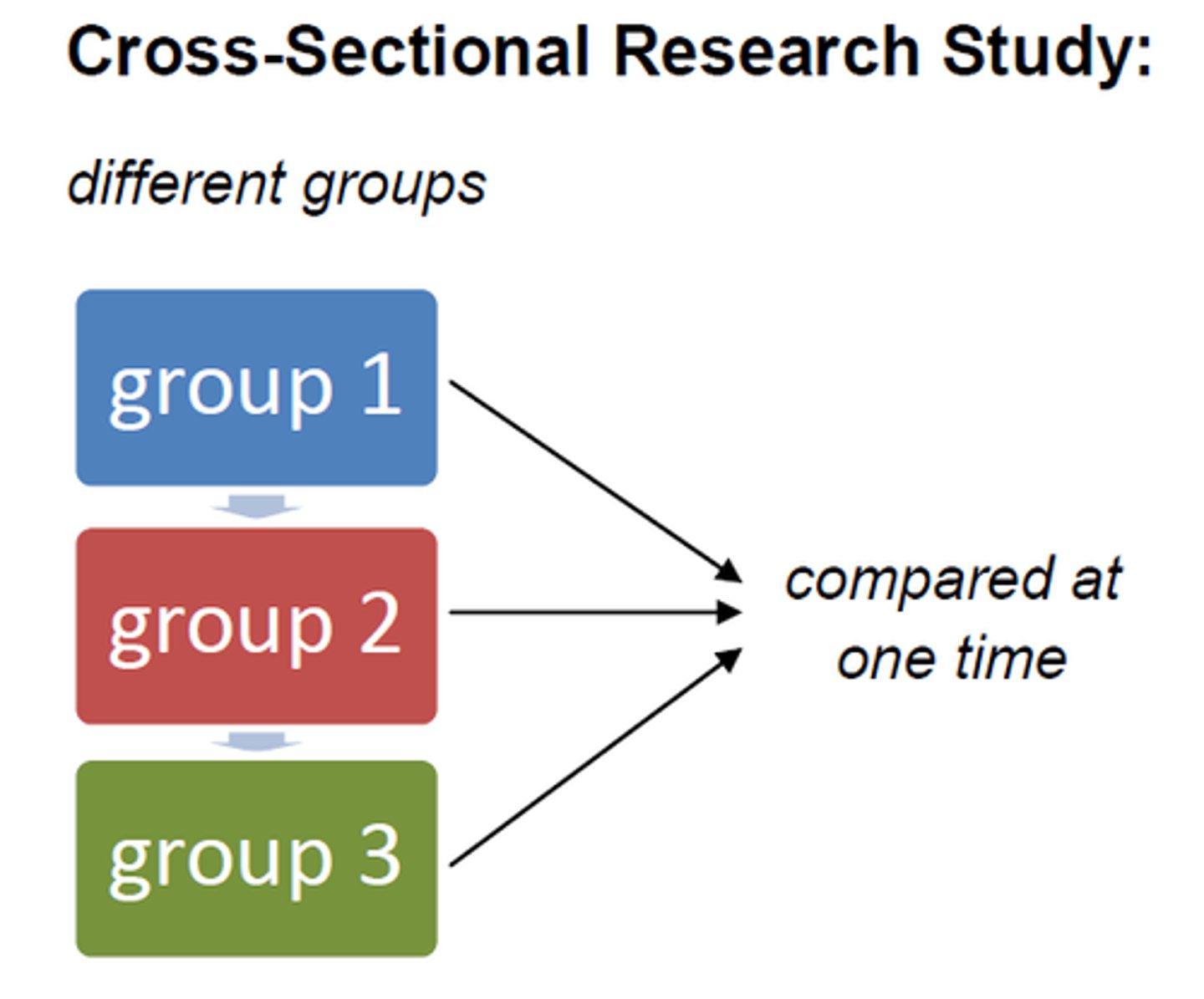
Cross-Sectional Studies
observing at a single point in time a subset of a population
Case Study
an in depth examination of a specific group or single person that typically includes interviews, observations, and test scores
Controlled Study
An experiment or clinical trial in which two groups are used for comparison purpose
Quasi Experiment
similar to controlled experiment, except participants are not randomly selected
Experimental Group
receives treatment
Control Group
part of the experiment but doesn't receive treatment
Double Blind Experiment
the experimenter and the participants don't know of group placement
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
a prediction that directly or indirectly comes true
Field Experiment
conducted out in the environment not in a lab
Surveys
use of questionnaires or interviews to ask a large number of people about behaviors, thoughts, and attitudes
Confounding Variables
differences between the experimental and the control group(s) other than those that result from the independent variable
Measures of Central Tendency
average or most typical scores for a set of research data or distribution
Mean
arithmetic average of a set of scores
Mode
most frequently occurring number
Median
middle score in a distribution
Normal Distribution
a normal or "bell curve"
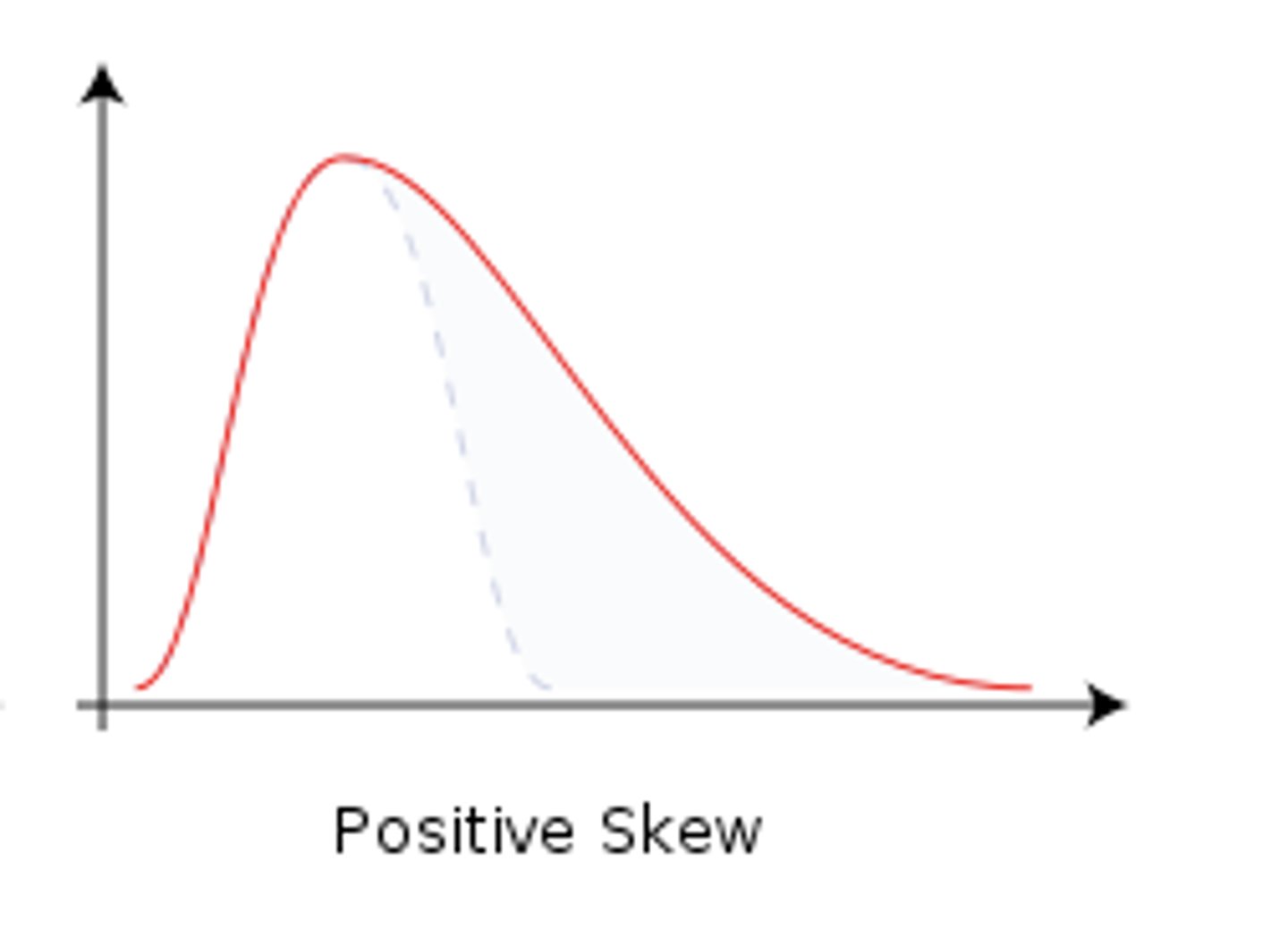
Positively Skewed
scores that are skewed to the right
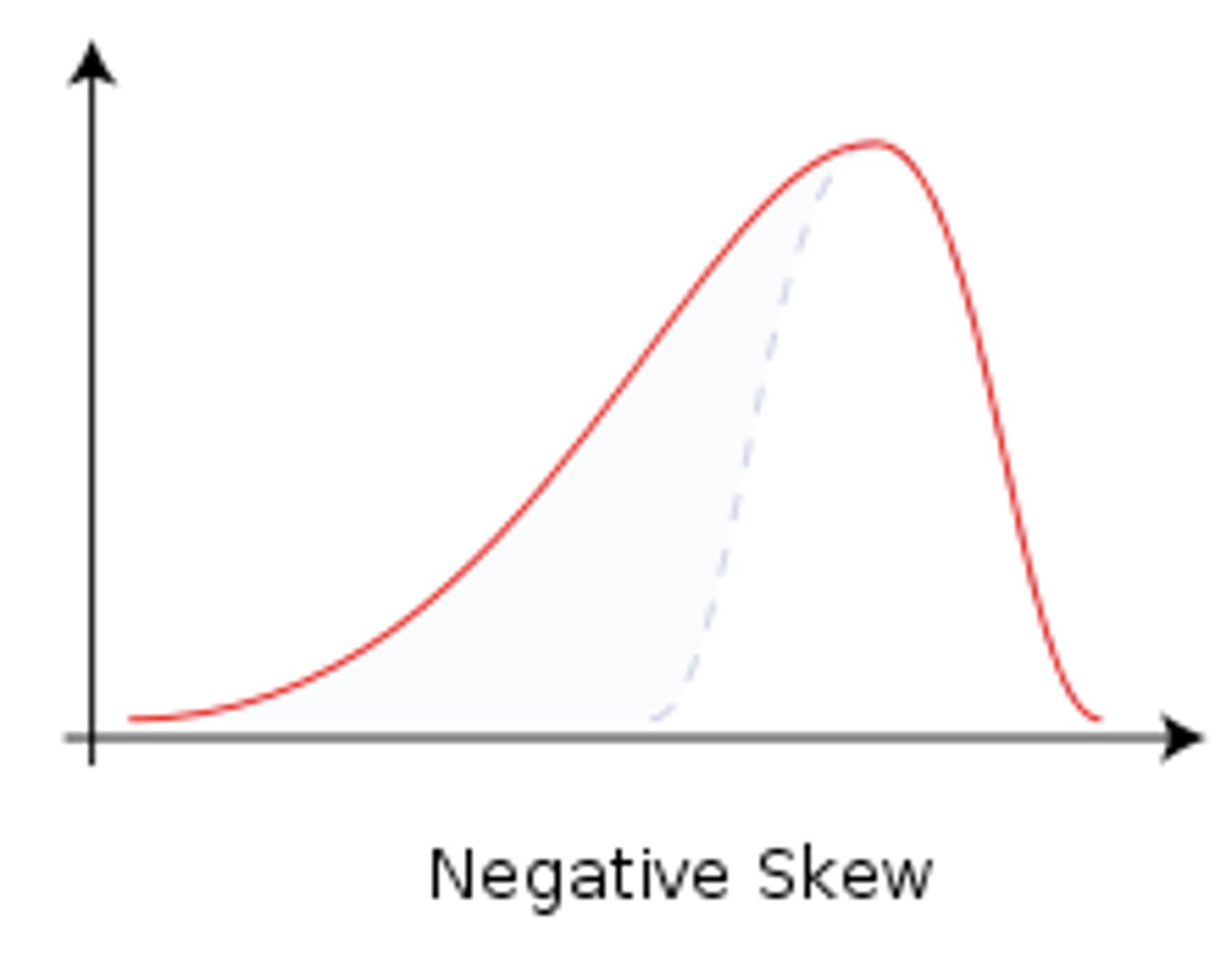
Negatively Skewed
scores that are skewed to the left
APA Ethical Guidelines
-informed consent
-no harm or discomfort
-confidentiality
-disclosure of results
Range
largest score minus the smallest score
Measures of Variability
is used to describe the amount of variability or spread in a set of data. Common ones are IQR and range
Standard Deviation
compare scores that are on a different scale
Statistical Significance
it is when data is within the designated p value. Didn't happen by chance or luck
Experimenter Bias
when the researcher's expectations or preferences about the outcome of the study influence the result
Placebo and Placebo Effect
Placebo- subjects are given an imitation of the treatment
Placebo effect- subjects believe they are feeling the effects of treatment
Percentile Score
indicates percentage of scores at or below a particular score
Correlation Coefficient
statistical relationships between two or more random variables or observed data values
Hawthorne Effect
improvement of behavior when subject knows it is being watched, not due to manipulation of experiment
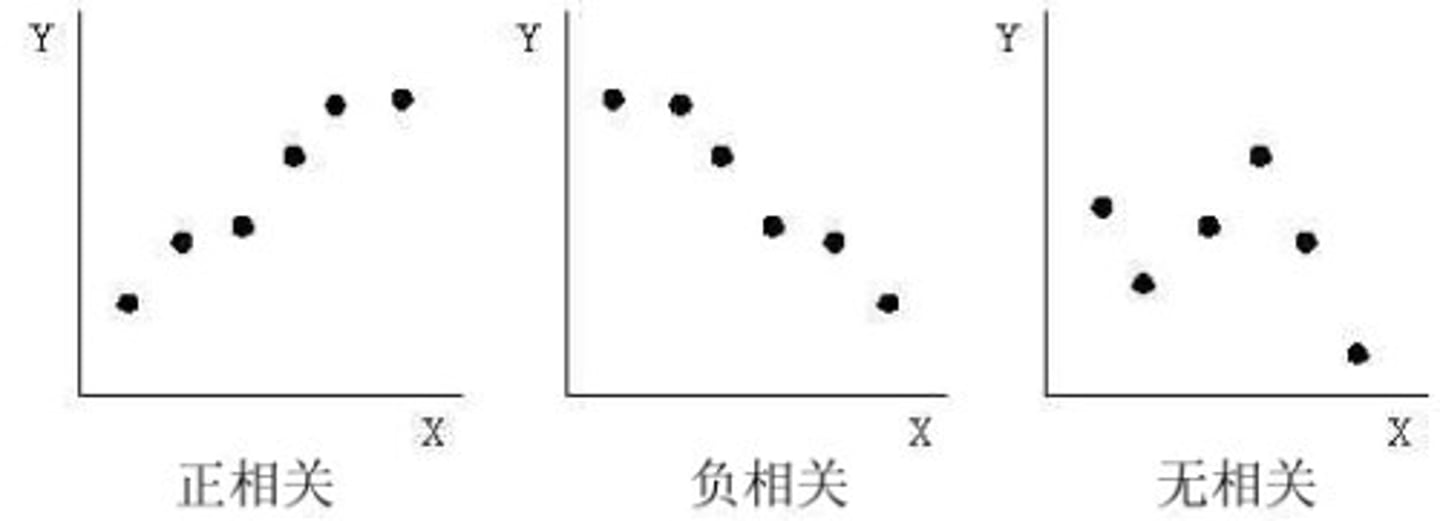
Scatter Diagram
paired X and Y scores for each subject are plotted as single points on a graph
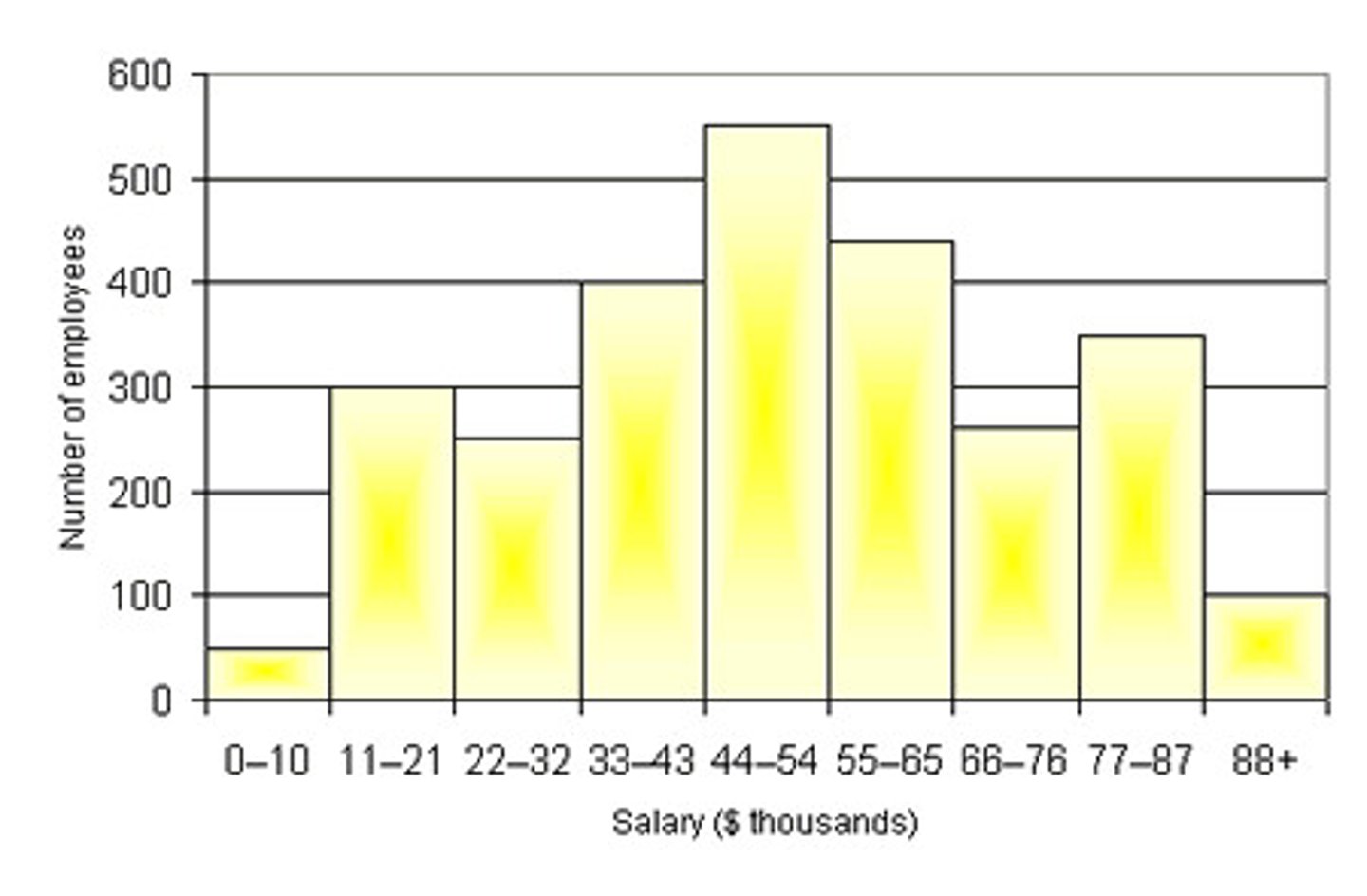
Histogram
a bar graph of frequency distribution
Frequency Distribution
line graph that uses a line to connect single points
Structuralism
understand the parts, to understand the whole (Edward Titchener)
Functionalism
How does the mind fulfill its purpose? (William James)
Pragmatism
testing truth by its practical consequences
Gestalt Psychology
perception based; how the parts and the whole are perceived and changed
Biological Approach
body and behavior
Behavioral Genetics
behaviors and the links to genetically based psychological characteristics
Behavioral Approach
observable behaviors (Skinner)
Cognitive Approach
encoding, processing, storing, and retrieving information
Humanist
free will and awareness of human condition (Maslov)
Psychoanalytic/Psychodynamic
levels of the mind (Froy)
-conscious
preconscious
-sub/unconscious
Socio-Cultural
the individual and environmental context
Neuroscience
brain and nervous system interaction with senses, memory, thoughts, and emotions
Trait
behavior and personality result from enduring psychological characteristics
Counseling Psychologist
advanced degrees; deals with less severe mental health issues
Psychoanalyst
Freudian methods, may or may not be Med. or Ph.d
Clinical or psychiatric social workers
earned Master's degree and are certified with state
Pastal counselors
clergy therapy training; typically family and marriage counseling
Experiment
systematic manipulation of variables under controlled conditions and observing the response
Codependent Variables
when 2 variables must be present together and could effect outcome
Demand Characteristics (subject bias)
clues participants discover about the experiment
Ex Post Facto
looks at an effect to seek the cause
Test Method
procedures used to measure attributes of individuals at a particular time and place
Descriptive Statistics
numbers that summarize a set of research data obtained from a sample
Inferential Statistics
used to interpret data and draw conclusions
Frequency Polygon
line graph that uses a line to connect single points
P-value
statistic that is equal or less than significance level (p less than or equal to .05%)
Archival Research
collecting data based on institutional records
Physiological Recording
using instruments to record various biological responses (brain waves, blood pressure, etc)