Equilibrium
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Closed system
allows energy, but not matter to be exchanged with surroundings
Open systems
Allows matter and energy to be exchanged with surroundings
What is the difference between chemical and physical change
Physical: No change to the chemical composition e.g change in state, dissolving
Chemical change: involves a rearranging of chemical bonds, reactants → products
Reversible reactions
it does not go to completion
reactants combine to form products, the products regenerate the reactants
eventually the rate of forward and reverse reactions will be the same and chemical equilibrium is established
if conditions change to favour either reaction then it will proceed at a greater rate
Activation energy
the minimum energy that is required for a collision to result in a reaction
the difference in enthalpy between reactants and the activated complex
Activation energy indicates how easily the reaction will be reversed
At equilibrium in a closed system at a constant temperature there is:
constancy of macroscopic properties - all observable properties (composition, density, colour) remain constant
a dynamic condition - equal but opposing rates of reaction - forward and reverse reaction occur but at equal rates
dynamic equilibrium
chemical equilibrium is dynamic: a state in a closed system where the rates of the forward and reverse processes are equal, resulting in no net change in the system's properties.
the equilibrium constant (K)
a numerical value of relative concentrations of products to reactants at equilibrium
A and B are reactants and C and D are products
a,b,c and d are the coefficients in the equation
only aqueous and gaseous substances are included
PRODUCTS IN NUMERATOR AND REACTANTS IN THE DENOMINATOR

what does the size of the equilibrium constant mean?
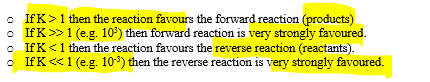
changes in value of K
K changes if temperature changes
K gives no indication of RoR
solids and liquids are NOT included in the K expression
K does not change if you alter concentration, pressure or volume
K only refers to the equilibrium position
Reaction quotient
the ratio between products and reactants under any conditions
Q>K therefore the concentrations of reactants must increase and products decrease to reach equilibrium
Q=K therefore system is at equilibrium
Q<K therefore the concentrations of reactants must decrease and products increase to reach equilibrium
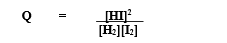
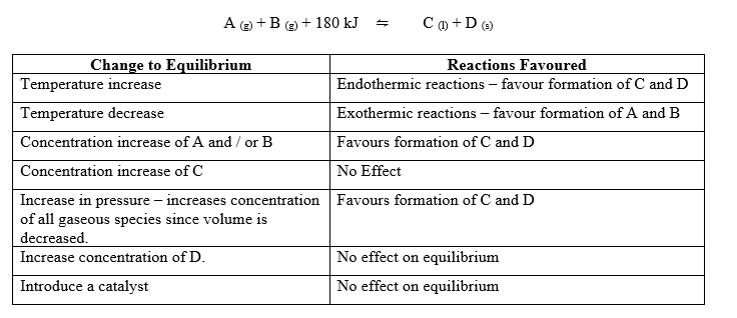
Changes imposed to an equilibrium system
changes to temp
adding or removing reactant or product (changing concentrations or in gases, partial pressure)
changing pressure by changing volume
Diluting
how do we predict vs how to we explain changes
Explaining changes: collision theory and reaction rates
Predicting these changes: using Le Chatelier’s Principle
Factors which effect equilibrium position
changing temperature
changing concentration
changing the pressure of a gas
factors which do not affect the equilibrium position
presence of a catalyst
adding an inert gas (or any gas not changing the partial pressure of the gases in the system)
LCP
if a chemical system at equilibrium is subjected to a change in conditions, the system will behave in such a way as to partially counteract the imposed change
Changing temperature
Predicting via LCP
if the temperature is increased the system will favour the endothermic reaction which absorbs heat
if the temperature of the system is lowered the exothermic reaction will be favoured which raises the temperature through creation of energy
Explaining via collision theory and reaction rates
if temp is increased, both reactions speed up, but endothermic reaction speeds up more because the activation energy is higher in the endothermic therefore and increase will affect the percentage of particles able to react in an endothermic reaction than an exothermic
decreasing the temp decreases the average kinetic energy of the system. Both reaction decrease: endothermic slows to a greater extent due to its larger energy requirement.
How does the enthalpy convey if the reaction is exothermic or endothermic
(-) enthalpy = exothermic
(+) enthalpy = endothermic
Adding or removing reactant or product (changing concerntrations)
Predicting:
Increasing the conc of reactants favours formation of products
decreasing the conc of reactants favours the formation of reactants
increasing the conc of products favours formation of reactants
decreasing the conc of products favours the formation of products
if the partial pressure of a gaseous species increases, LCP predicts the net reaction will occur in the direction which tends to lower the partial pressure of said species
Explaining;
increasing conc increases the frequency of collisions
sentence used to describe the effect of a product/reactant when it’s conc is increased
partially reduced, but higher than original value
what is the rule for water in equilibrium reactions
it does not exist
Changing the pressure by changing the volume
Predicting:
if volume of system is reduced the system will oppose this change by favouring the reaction which produces the lease number of molecules
decreasing the pressure favours the reaction which will produce more molecules
addition or removal of products which are solids or liquids will have no effect on equilibrium concentrations in gaseous specied
diluting

summary table
what is a homogeneous system
a system that contains reactants and products in the same phase (e.g. all gaseous)
what is a heterogeneous system
contain reactants and products in different phases
solubility equilibrium
if a reaction with reactants in a solid state and products in an aqueous state has a high K value we can determine that the reactant is very soluble in water. And if it has a low K value we can the determine that the reactant is insoluble in water.