Cheat sheets: 11/12 Biological Diversity: Taxonomy and Microbial Life
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What are obligate aerobes and their role in the microbiome?
Obligate aerobes are microorganisms that need O2 to survive and make up the microbiome, which includes both good and bad bacteria in the digestive tract.
What infections can bad bacteria in the body lead to?
Bad bacteria can lead to infections such as gonorrhea, tuberculosis, leprosy, and pneumonia.
How do good bacteria benefit the human body?
Good bacteria help synthesize vitamins and enhance metabolism.
What is a consequence of extended antibiotic use?
Extended use of antibiotics can result in vitamin deficiency due to depletion of vitamin-metabolizing bacteria.
What are obligate anaerobes?
Obligate anaerobes are organisms that cannot survive in the presence of O2.
What are facultative anaerobes?
Facultative anaerobes can grow in the presence of O2 but can utilize anaerobic metabolism when O2 is absent.
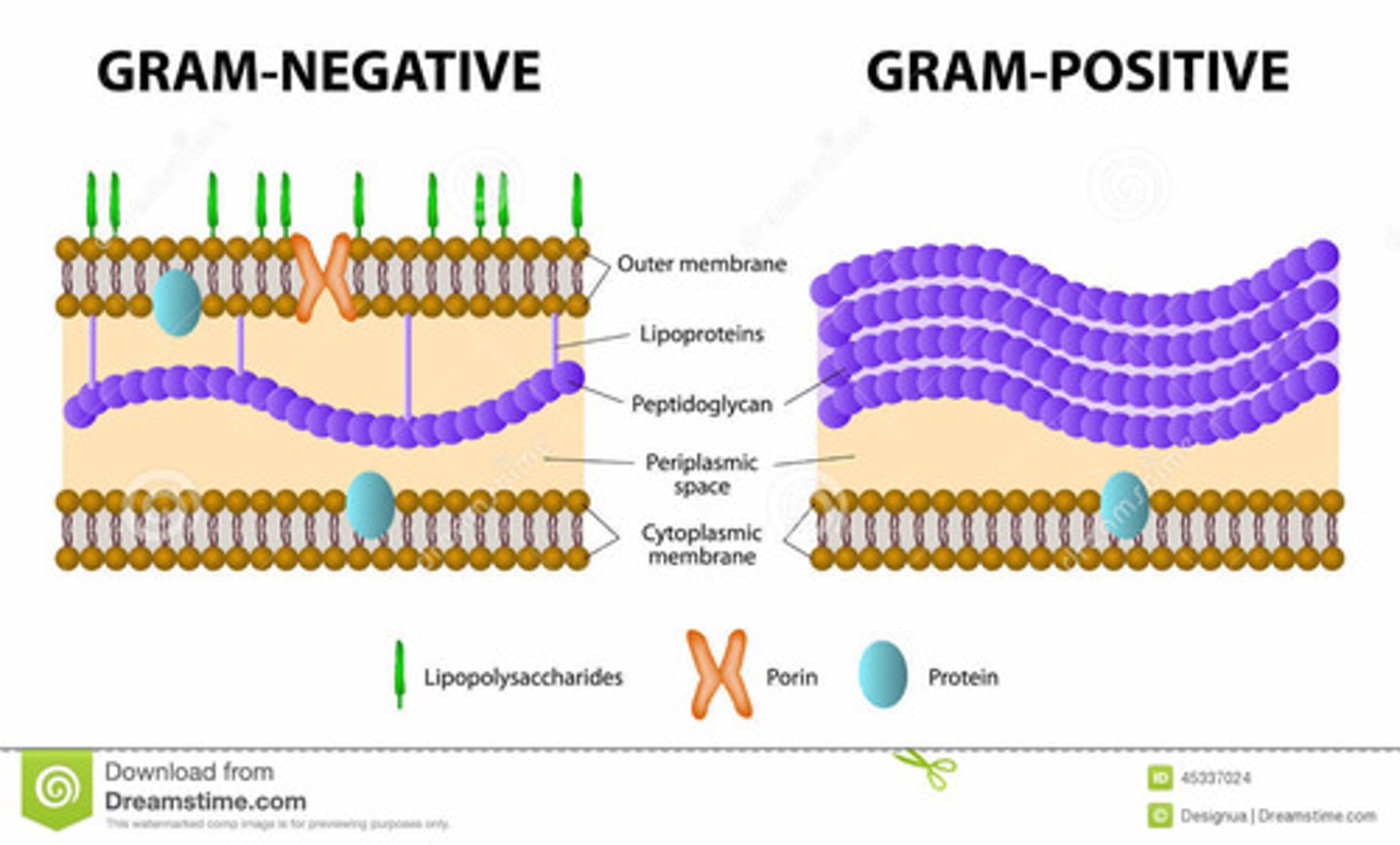
What are characteristics of Gram-Positive Bacteria?
• Stain purple
• Thick peptidoglycan layer in cell wall
• No outer membrane
• Does not produce endotoxins
• Teichoic acids increase cell wall flexibility
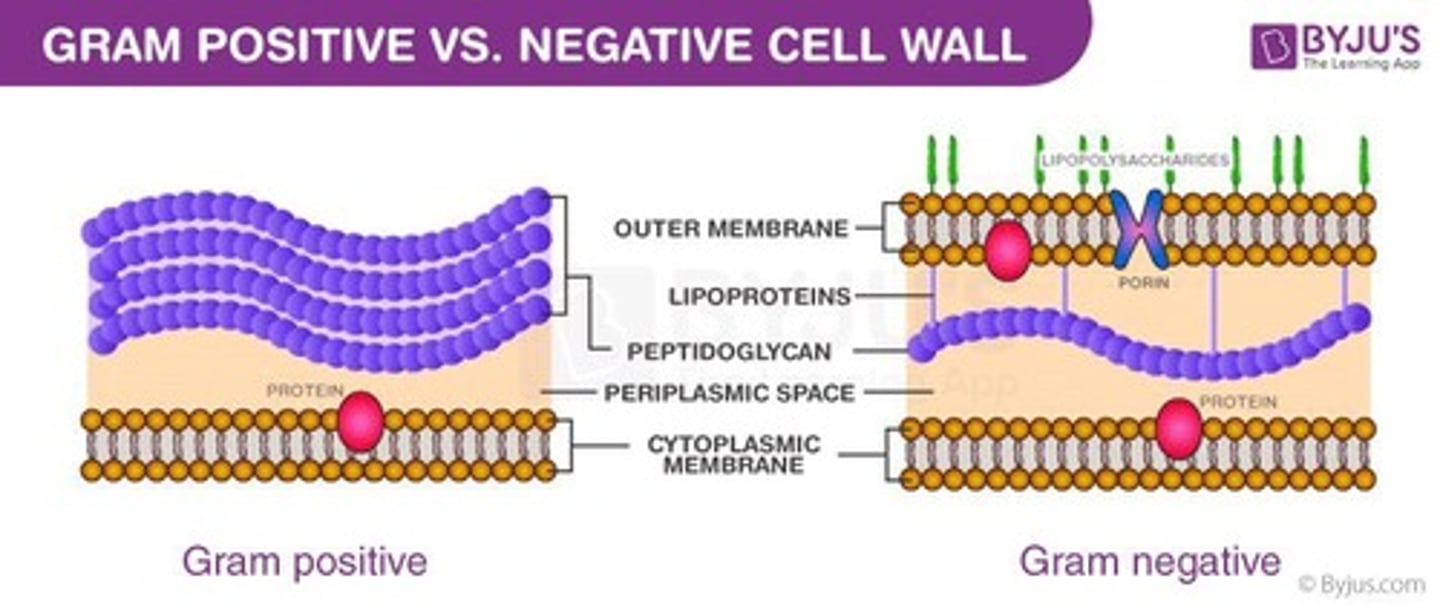
What are characteristics of Gram-Negative Bacteria?
• Stain pink
• Thin peptidoglycan layer in cell wall
• Contains an outer membrane
• Produces endotoxins when broken down
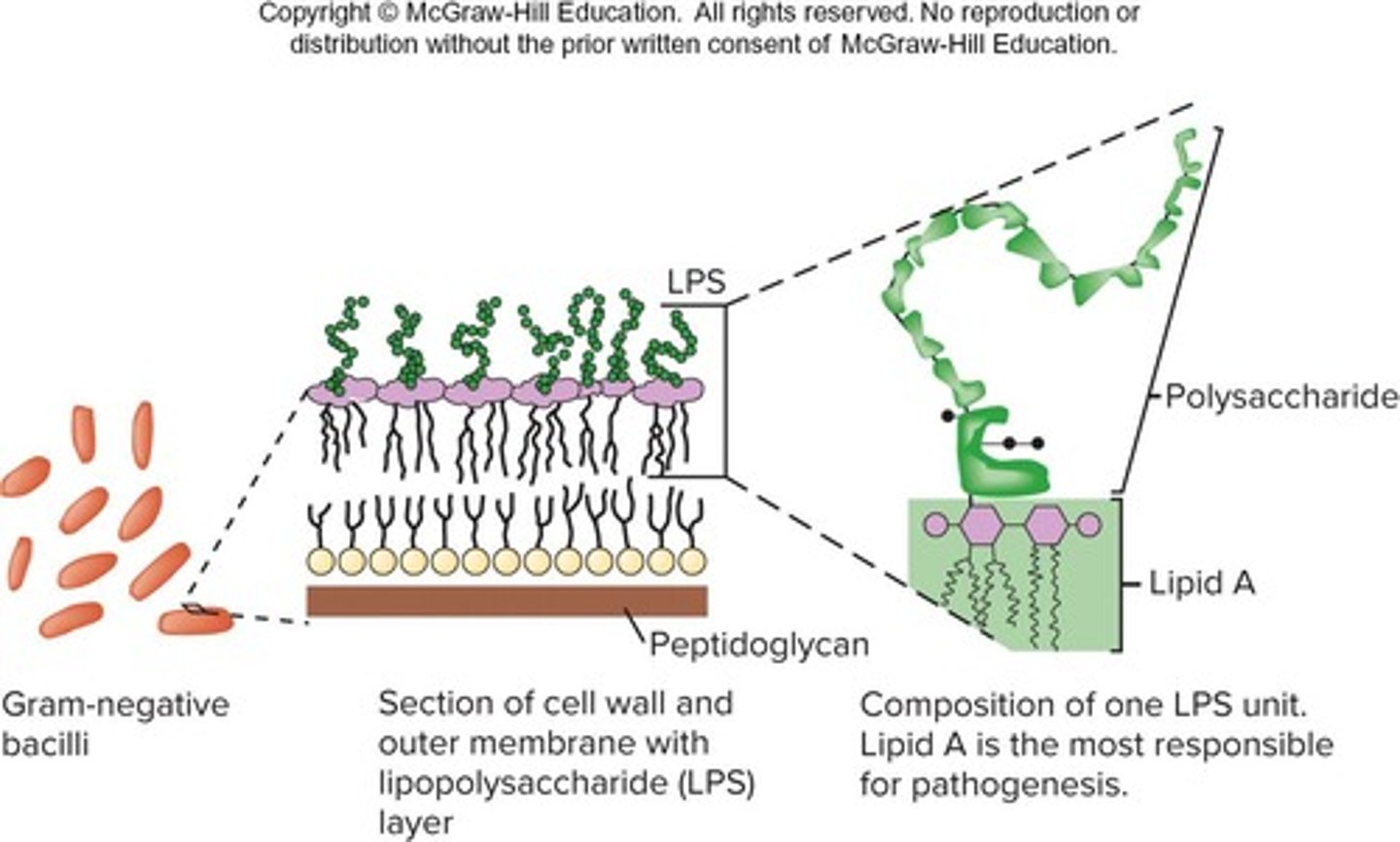
What is the significance of LPS in gram-negative bacteria?
LPS (lipopolysaccharides) in gram-negative bacterial membranes enhance integrity and protect the membrane from chemical attack.
How are humans classified in biological taxonomy?
Humans are classified as Homo (genus) sapiens (species).
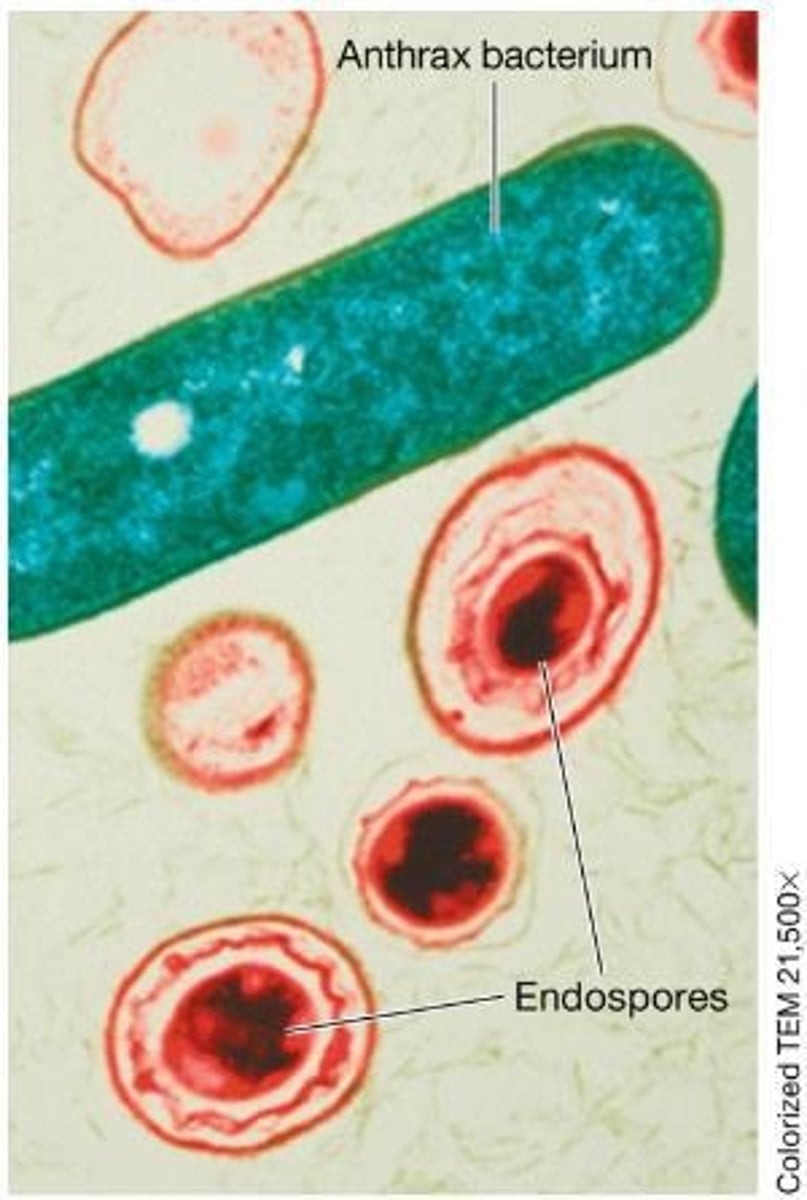
What are endospores and their function?
Endospores are durable structures produced by some bacteria that help them survive in extreme environmental conditions.
What are the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells have single, short, circular DNA in the nucleoid region and lack organelles
eukaryotic cells have multiple, long linear chromosomes in a nucleus and contain organelles.
What are heterotrophs and autotrophs?
Heterotrophs are consumers of organic substances produced by autotrophs, which are producers of organic substances.
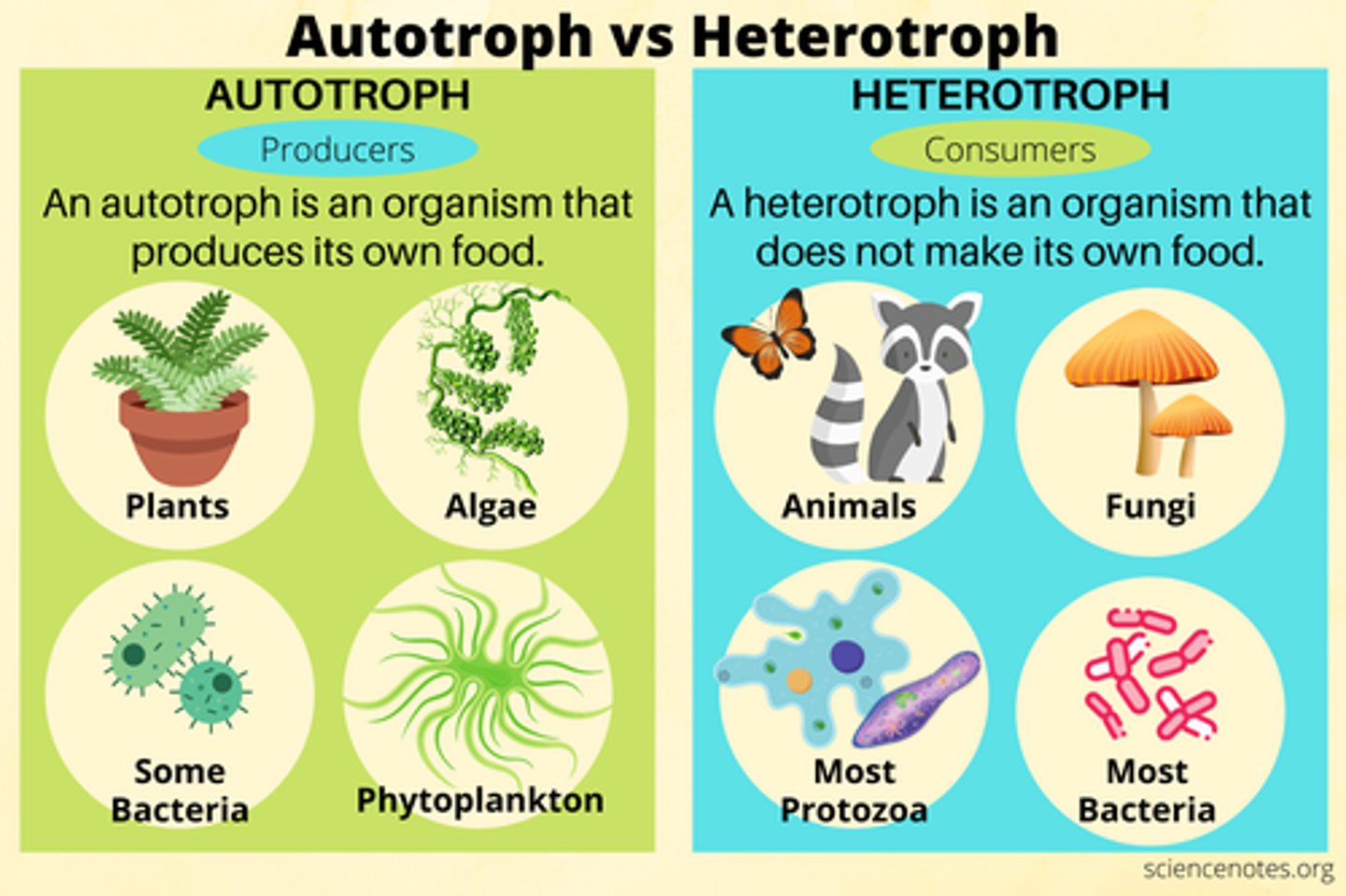
What are the energy acquisition methods of chemoheterotrophs and chemoautotrophs?
Chemoheterotrophs use organic compounds as their energy source, while chemoautotrophs use inorganic chemicals in reactions.
Where does transcription occur in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
Transcription occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells.
Where does Translation occur in eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
Cytoplasm
What organisms have histones and which do NOT?
Eukaryotes and Archaea have histones. Bacteria DO NOT
What organisms have introns and which DO NOT?
Eukaryotes and Archaea have histones. Bacteria DO NOT
What is the cell wall composition of Eukaroyic Plants and Fungi?
Plants: Cellulose
Fungi: Chitin
What is the cell wall composition of prokaryotic archaea?
Pseudomurein
What is the cell wall composition of prokaryotic bacteria?
Peptidoglycan
What are Photoheterotrophs?
• Use light for energy
• Obtain carbon for metabolism through
consuming organic materials

What are Photoautotrophs
• Use light for energy
• Make organic substances/carbohydrates via
photosynthesis
• Obtain carbon for metabolism through
consuming inorganic carbon sources (CO2, HCO3)
• E.g., Bacteria found at the top of a pond

What are Decomposers?
Consume the remains of organisms & non –
living organic material
What is the function of ribosomes in cells?
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis and are present in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
What are the two prokaryotic domains?
1. Archaea
2. Bacteria
What are protists?
A taxonomic group that consists of eukaryotic organisms
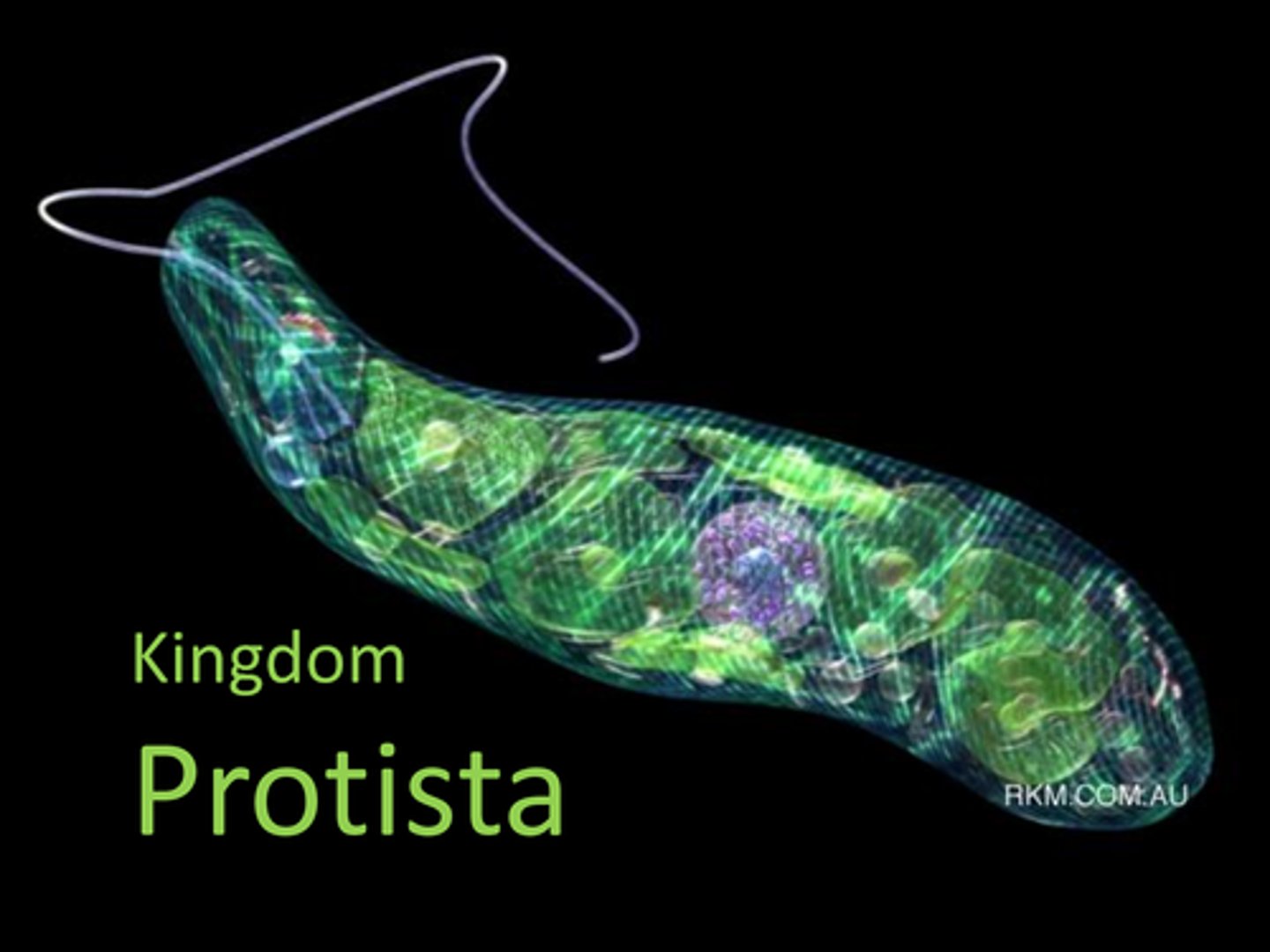
What are the three categories of protists?
The three categories of protists are
1. plant-like
2. fungus-like
3. animal-like (protozoa).
What are plant-like protists and their characteristics?
• Are photosynthetic autotrophs found in
water
• Contain chloroplasts
• Use photosynthesis as food source
• E.g., Red algae, euglenoids

What are fungus like protist?
• Referred to as “slime molds” or “water molds”
• Not the same as fungi molds
Heterotrophic – includes decomposers &
saprobes that feed on non-living organic matter
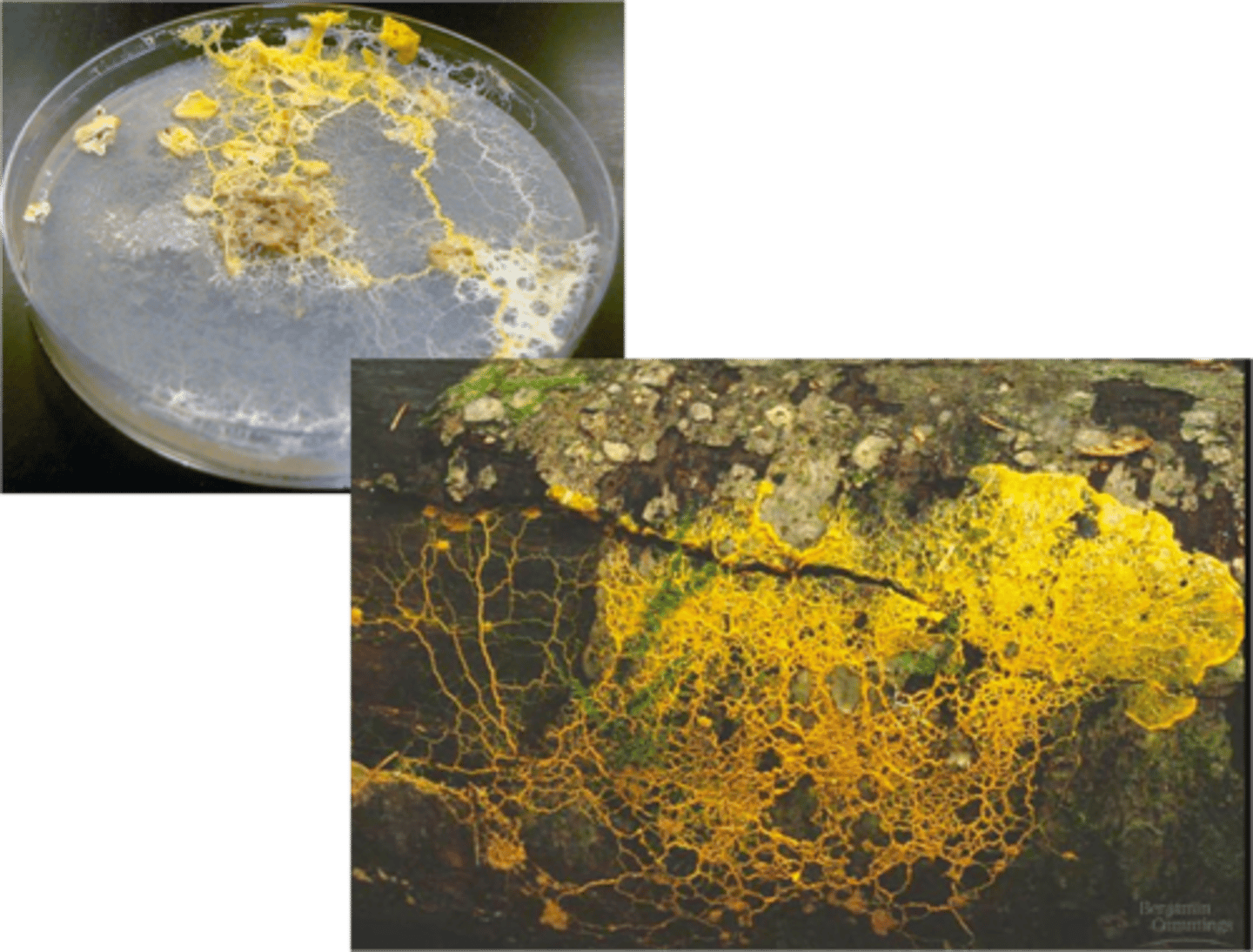
How do fungus like protist reproduce?
reproduce via spores
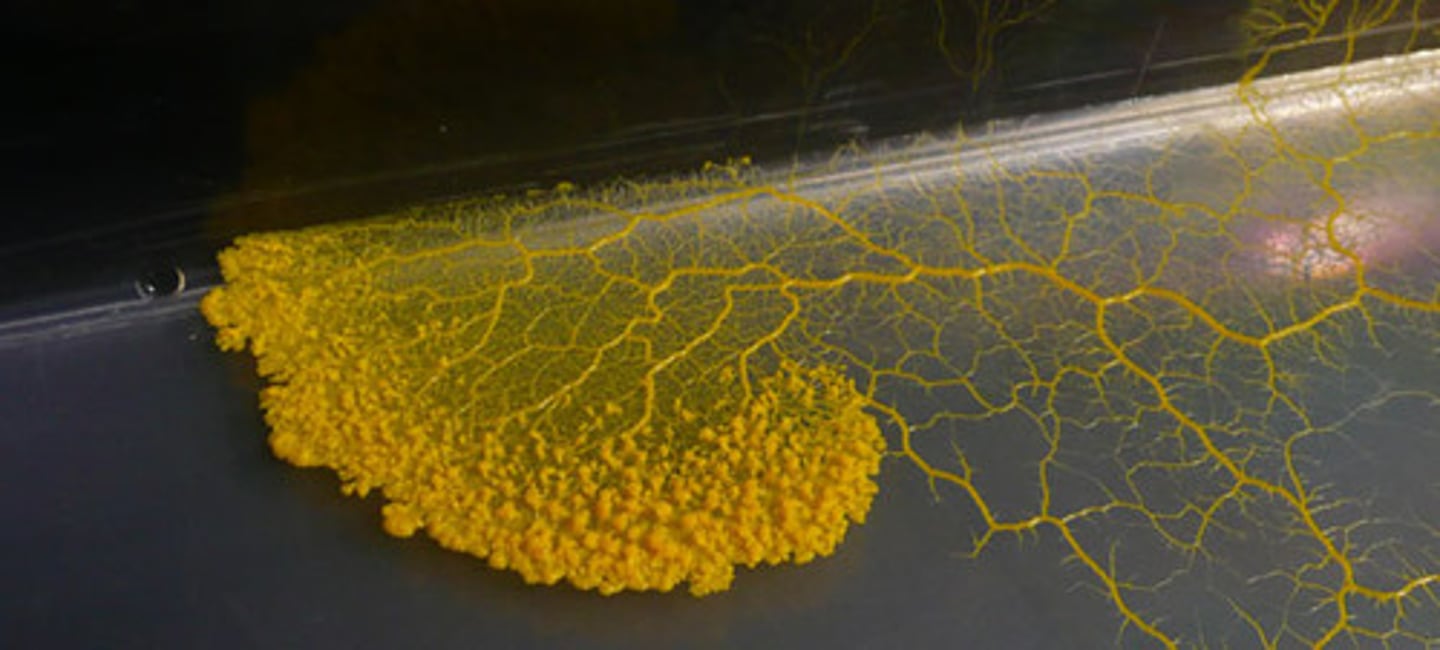
What distinguishes fungus-like protists from true fungi?
Fungus-like protists, such as slime molds, are not the same as fungi and do not contain chitin.
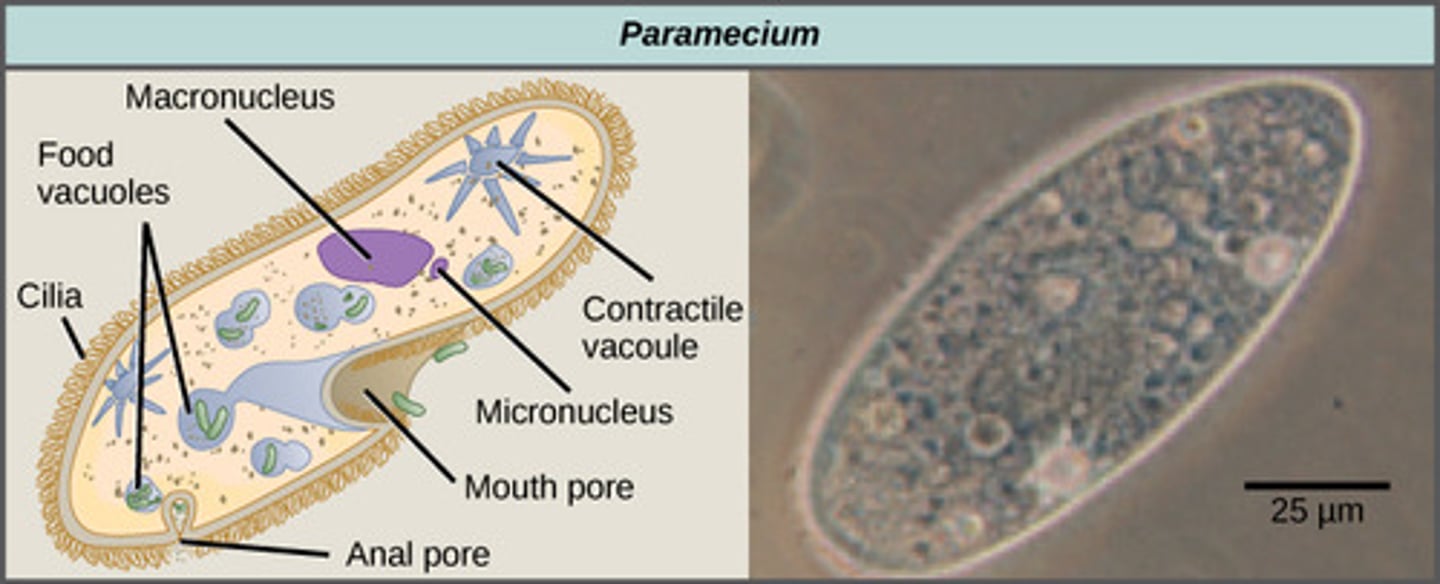
What are animal like protist?
Are categorized based
on motility
• Have cilia or flagella
• Referred to as animal-
like protists because
they are capable of
movement
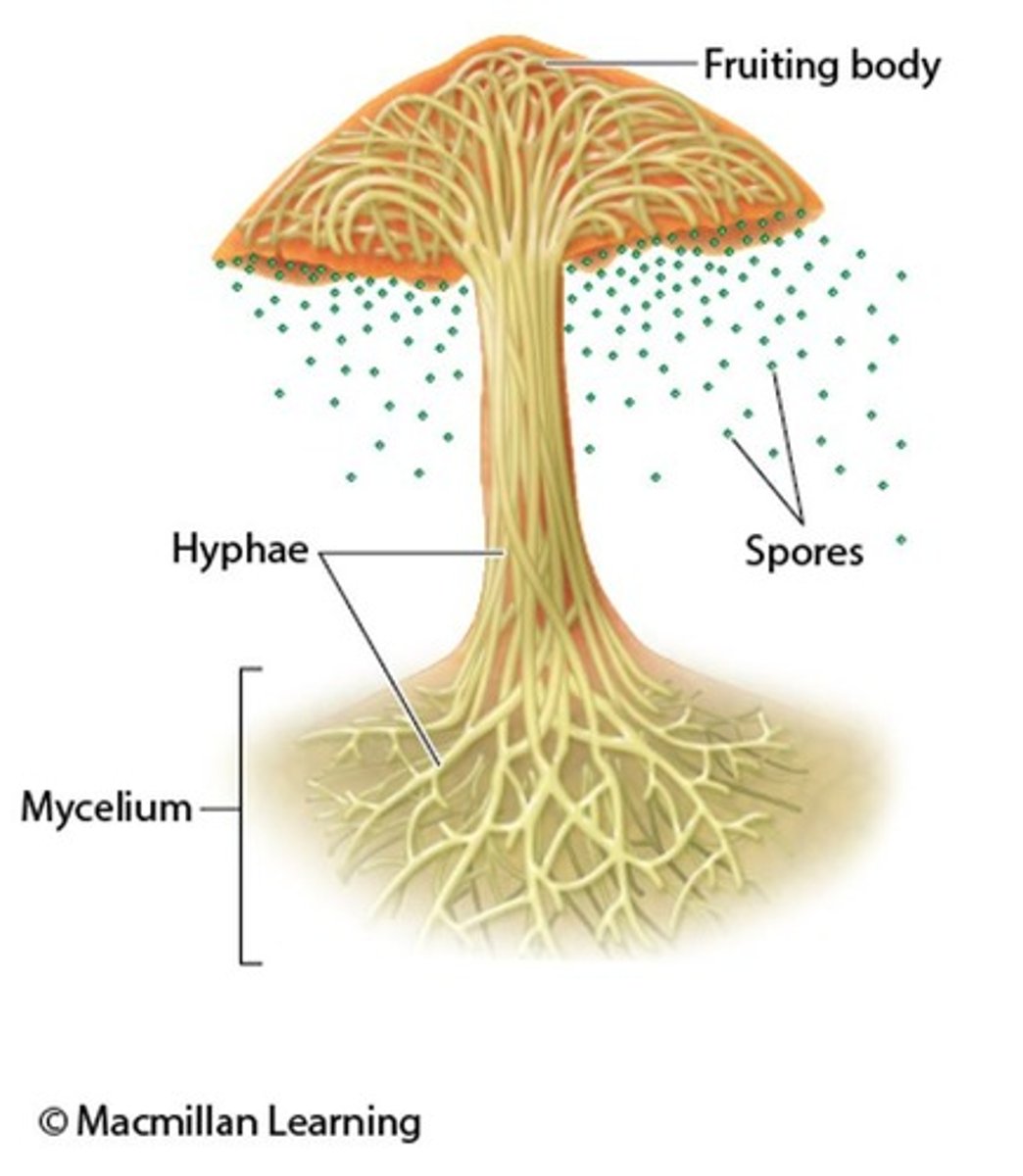
What is mycelium in fungi?
Mycelium is a network of fungal filaments (hyphae) that connect fungi together.
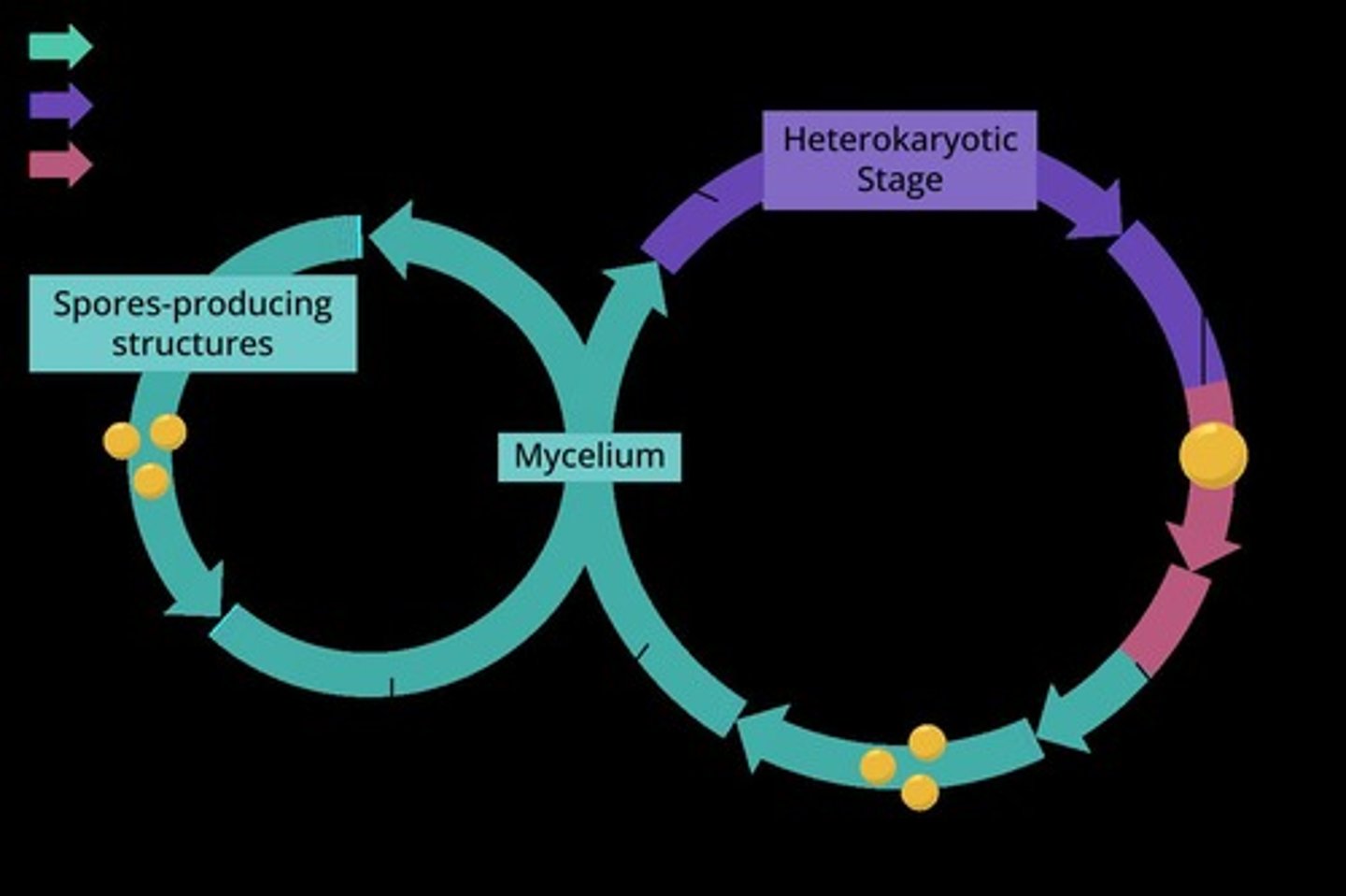
How do fungi reproduce?
Fungi can reproduce sexually, asexually, or both, and are typically haploid for most of their life cycle.
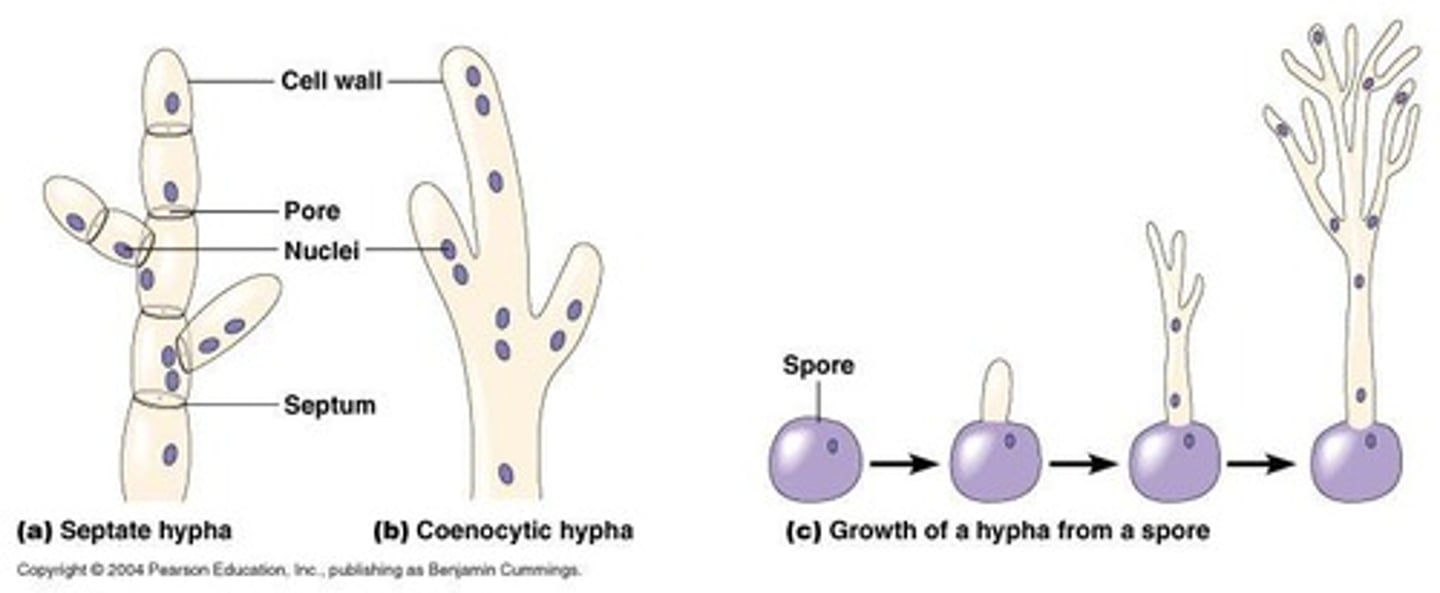
What are the types of hyphae in fungi?
Hyphae can be septate (with cell walls that separate hyphae) or coenocytic (without division of hyphae during cell division).
What is the role of rhizoids in fungi?
Rhizoids are small branching hyphae that anchor fungal structures to the ground.
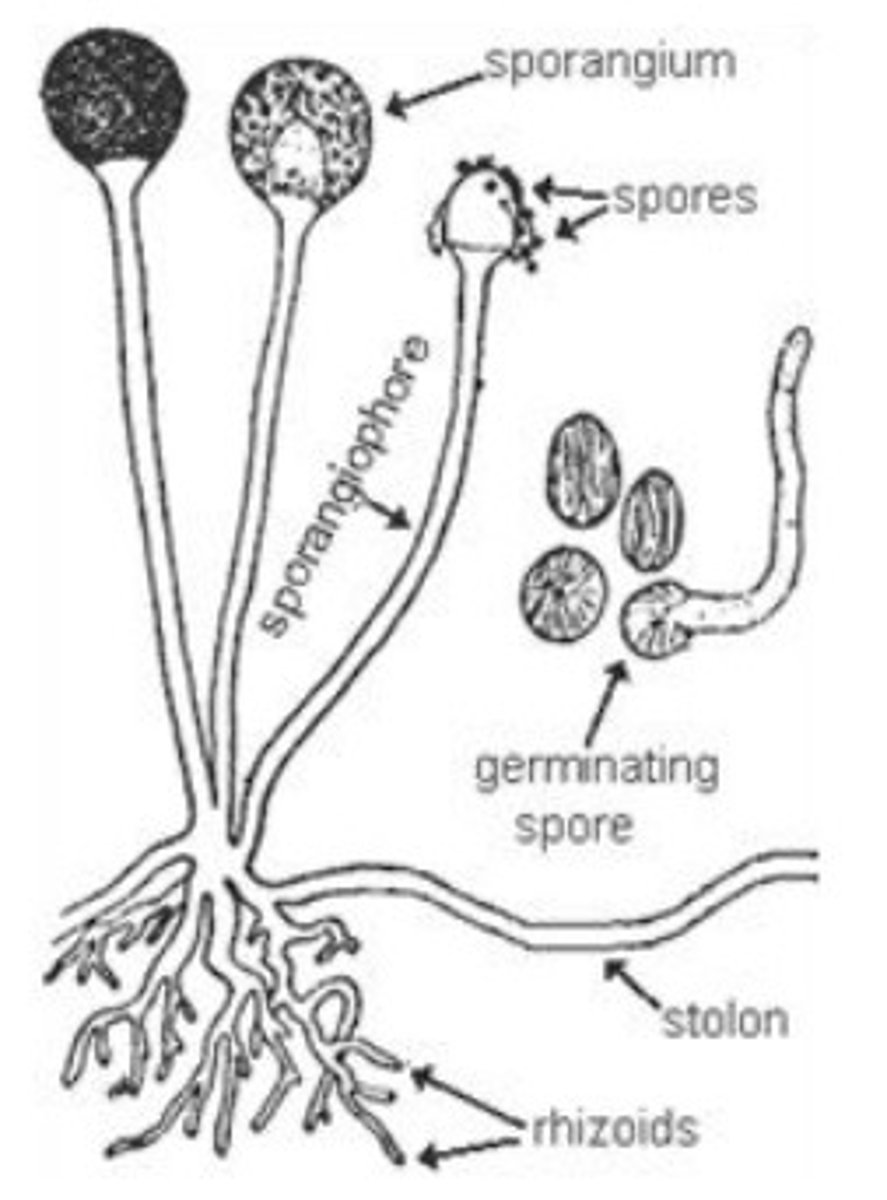
What are the differences between unicellular and multicellular fungi?
Unicellular fungi include yeasts that reproduce asexually by budding
multicellular fungi include molds and mushrooms that can reproduce sexually or asexually.
What is the significance of chitin in fungal cell walls?
Chitin provides structural support in fungal cell walls, differentiating them from plant cell walls, which contain cellulose.
What are the functions of enzymes secreted by fungi?
Fungi secrete enzymes that break down organic matter, releasing nutrients for absorption by hyphae, making them effective decomposers.
What are characteristics of Non-filamentous fungi
• Unicellular
• Includes yeasts
• Asexual reproduction by budding via mitosis
• Replicate genetic material and pinch off a
portion of cytoplasm and cell membrane to
form a new cell

What are characteristics of Filamentous fungi?
• Multicellular
• Includes molds & mushrooms
• Sexual or asexual reproduction
• Mushrooms grow outward from
mycelium
