IGCSE BIO 8. transport in plants
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
xylem vessel
role :
transport water & mineral ions
has lignin on cell wall, in spiral pattern
hollow vessel with no organelle & cytoplasm & no end walls --> to give low resistance to large volume of water flow
waterproof --> prevents water leaking out
bordered pits in the lignified walls --> allows lateral movement of water between vessels
role of lignin in xylem
- gives structure support
- makes xylem waterproof
- prevents inward collapse of plant
- allows flexibility & bending
- allows adhesion of water --> continuous flow of water as transpiration stream
phloem tissue
carries sucrose & amino acids, from source --> sink
contains different types of cell within it
vascular tissues in a dicot root
xylem --> star shape
phloem --> circular, surrounding xylem inside
endodermis / cortex / root hair...
vascular bundles in a stem
xylem inside, phloem outside
vascular bundles arranged in a ring near the outer edge
pith (inside the ring) / cortex (outside) / epidermis...
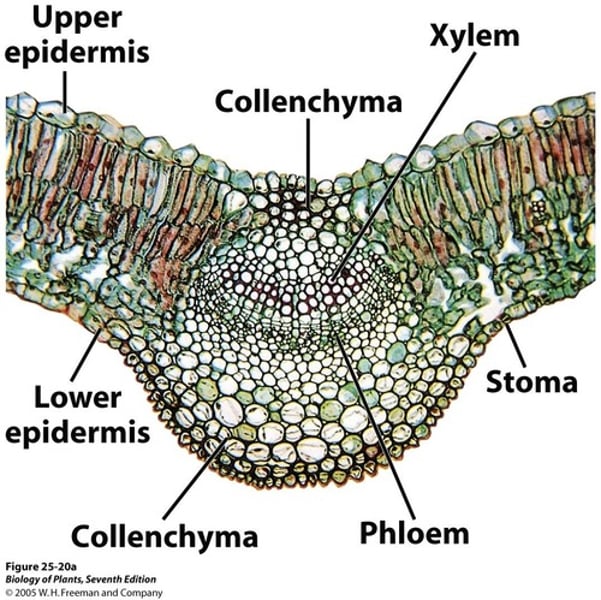
vascular bundles in a leaf
xylem above, phloem below
root hair cell
long cytoplasmic extension + vacuole extension along it --> large surface area --> increases the uptake of water & mineral ions
functions :
absorb water by osmosis & mineral by active transport
anchors the plant into the soil
water uptake process
enters root hair from soil (by osmosis) --> enters cortex cell by osmosis --> moves between adjacent cortex cells by osmosis & creating root cortical pressure --> the pressure pushes water into xylem through phloem --> rises through xylem due to capillary action & transpiration pull --> in leaves, move from xylem --> mesophyll cells by osmosis
water can also move through the permeable cortex cell walls only, without entering the cells
transpiration
loss of water from plant leaves by evaporation from the surface of the mesophyll cells into the air spaces, followed by loss of water vapour through the stomata
translocation
movement of sucrose and amino acids in the phloem, from sources to sinks
source
regions of production / site of photosynthesis / storage, if energy supply is low
sink
regions of storage (if excess present) & growth & utilisation for respiration & metabolism
what affects water loss by transpiration?
large internal surface area (interconnecting air spaces between spongy mesophyll cells)
size & number of stomata
capillary action
adhesion + cohesion
factors that help raise the water column
transpiration pull / capillary action / root (cortical) pressure
water movement in stems due to transpiration
loss of water from leaf by transpiration --> decrease in water potential in leaf --> water move into leaf from xylem --> water potential gradient is created with higher water potential in the xylem of roots --> creates transpiration pull --> water moves up the xylem by mass flow, due to cohesion (of water molecules) & adhesion (between lignin <-> water)
factors affecting transpiration
directly proportional :
- temperature : evaporates faster
- wind speed : sweeps away moist air and replace it with dry air (maintains the gradient)
- sunlight : stomata opens up
inversely proportional :
- humidity : diffusion gradient decreases
- water deprivation : stomata closes up
stomata
thick cell wall inside / thin outside
when short of water : guard cell becomes flaccid --> stomata remains closed
when plenty of water : guard cell becomes turgid (swells) --> as inner surface is very thick, it cannot stretch as much as outer surface --> guard cell bends outside --> opens up the stomata
in germination, source? sink?
source : seed / cotyledon (starch stored)
sink : emerging shoot & root (as seedling cannot photosynthesize yet)
in spring / summer (when light intensity is high), source? sink?
source : leaves (photosynthesize --> makes sucrose & amino acid)
sink : all other plant organs and storage organs
at the start of growing season (early spring), source? sink?
source : vegetative storage organs (roots, tubers...) (stores starch)
sinks : all growing parts of shoot (as it cannot photosynthesize yet till leaves develop)