1.6: accessory structures: hair, nails, glands
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
composition of hair
row of keratinized squamous epithelial cells
-hair is found everywhere on the body except areas of thick skin
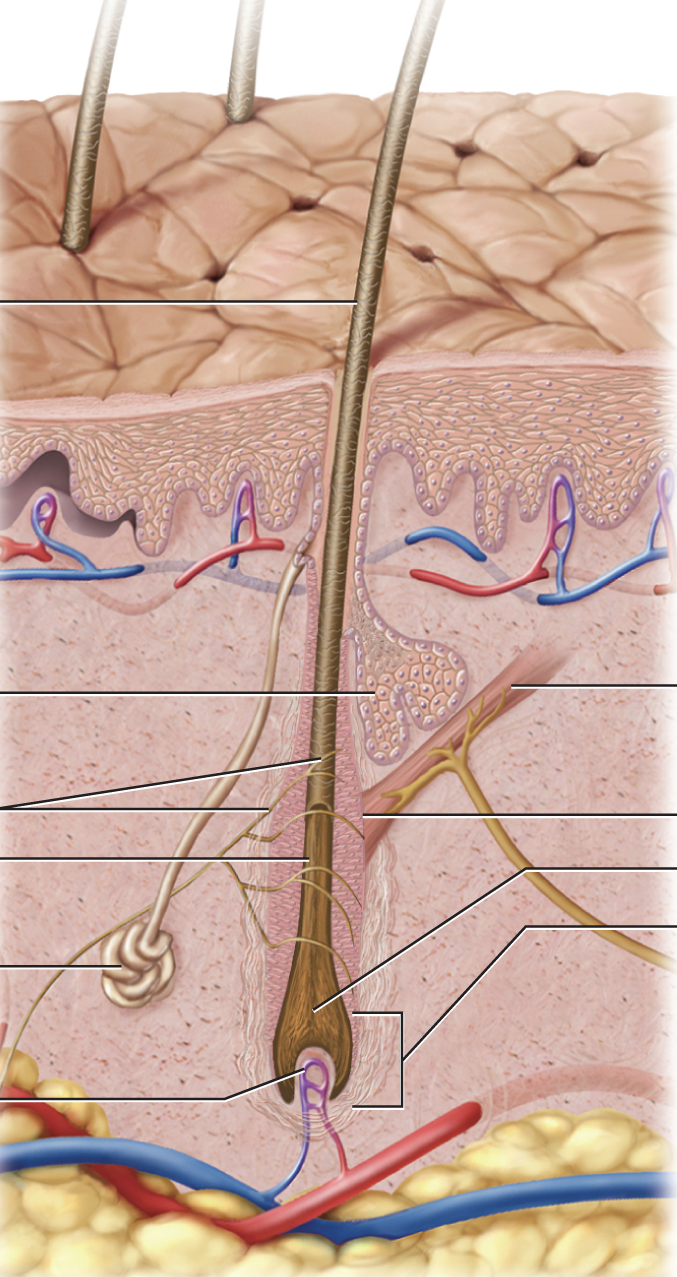
structure of hair
-shaft: exposed to external environment, contains dead cells
-root: internal
root of hair: hair follicle
layer of epidermal tissue anchoring root into dermis
root of hair: matrix
actively dividing stem cells above hair papilla (for blood supply)
root of hair: arrector pili
connected to hair follicle; smooth muscle, contract to cause piloerection
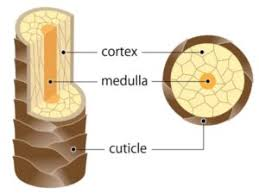
hair shaft composition
-medulla: core of loosely arranged cells made from soft keratin
-cortex: several layers of complex hard keratinocytes, site of pigmentation
-cuticle: single layer of overlapping cells, most highly keratinized region
split ends
damage to cuticle exposes underlying ayers
types of hair: lanugo
unpigmented hair in developing fetus, insulative purpose
types of hair: vellus
fin, thin body hair
types of hair: terminal
thicker hairr making up eyebrows, lashes, scalp
-after puberty, terminal hair grows in pubic region
-in males, facial, trunk, limbs
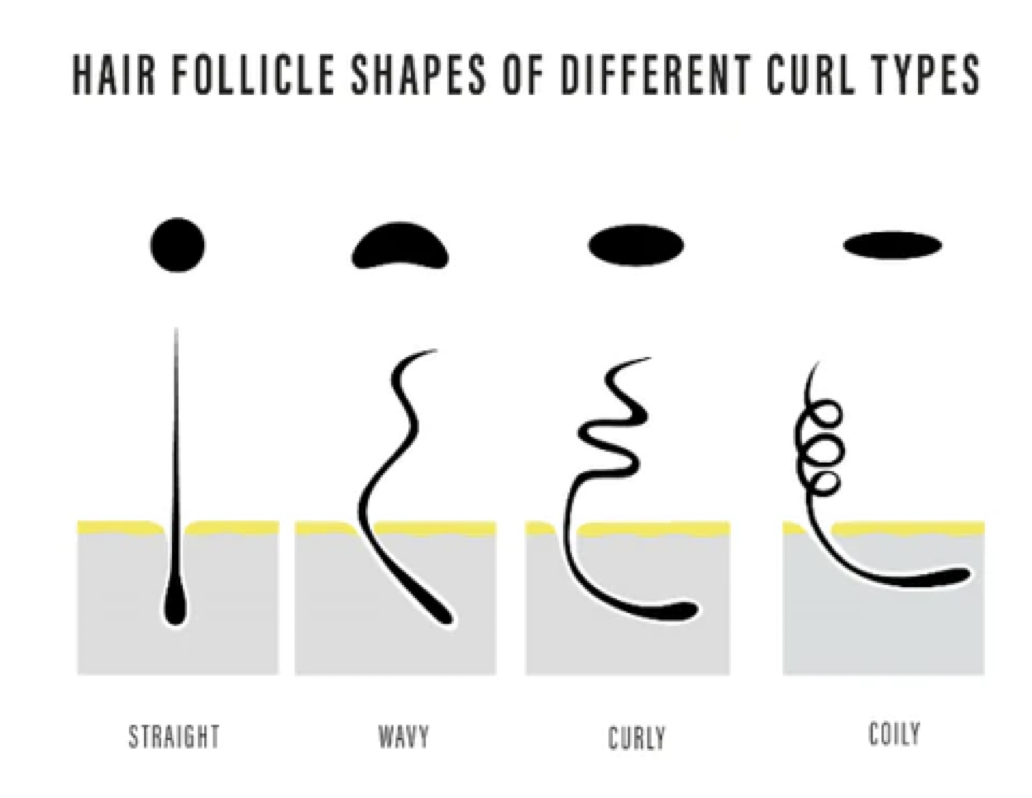
texture of hair is dictated by
shape of follicle
color of hair is dictated by
melanin pigment in hair shaft: eumelanin or pheomelanin
hair growth cycle: anagen
active cell division, utilize nourishing blood supply, get pushed superficially
hair growth cycle: catagen (transition phase)
stop cell division, detaches from nourishing blood supply
hair growth cycle: telagen (resting phase)
without nourishment, hair dies & falls outt
scalp hair: in anagen for __ years, high/ how mitotic rate
~6 years, higher mitotic rate
lashes & brows: in anagen for __ days, high/ how mitotic rate
~30 days, low mitotic rate
composition of nails
-hard keratin, no melanocytes
-external: nail plate
-nail bed: underlying nail plate
-nail matrix: site of nail growth
functions of nails
protection, object manipulation
glands
groups of modified epithelial cells located in dermis
exocrine glands & types of glands
release non-hormonal secretions secretions
-sweat
-sebaceous
*eccrine sweat glands
-abundant throughout body
-sweat secreted into skin surface via ducts
-99% water, solutes & bactericidal liquid
-thermoregulation
-emotional sweating begins on palms & spreads elsewhere
apocrine sweat glands
-only in genital regions
-nonfunctional until puberty
-sweat released through hair follicles
-bacterial activities on surface with sweat produce odor
ceruminous glands: modified sweat
-found in lining of ear canal
-secrete cerumen for lubrication & protection
mammary glands
-found in adipose tissue of breasts
-secrete milk: proteins, lipids, carbs
-present in males & females
-develop only during pregnancy & lactation
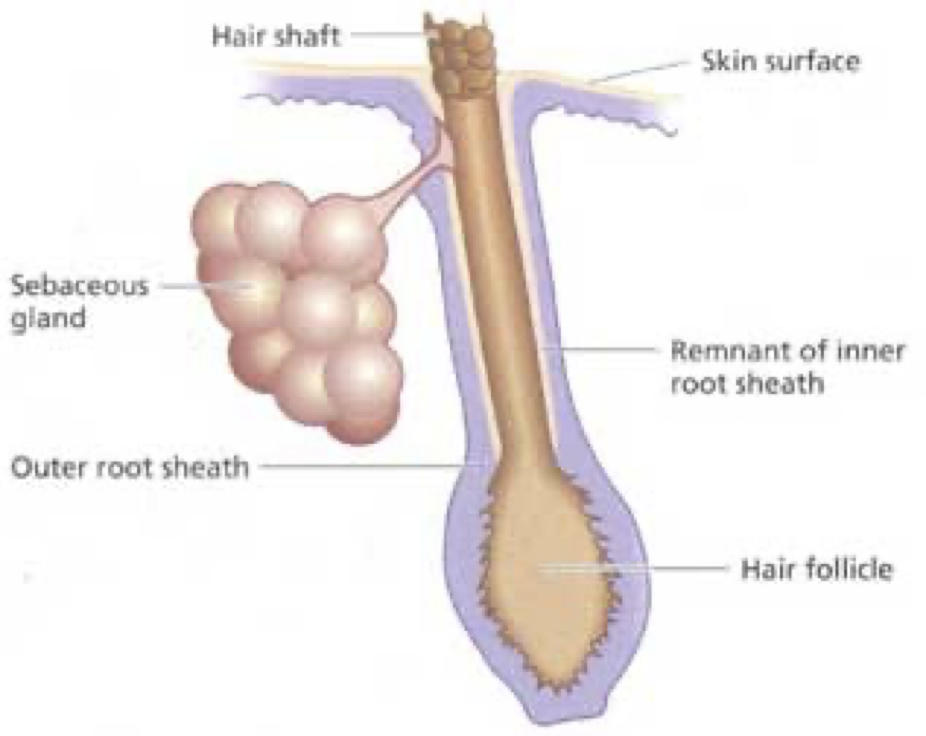
sebaceous glands (structurally different from other glands)
-most numerous on face & scalp
-secrete into hair follicle
-largely inactive until puberty
-secrete sebum: lubricates/ waterproofs skin & hair, bactericidal properties