Health Assesment Exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:08 PM on 10/26/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
1
New cards
function of respiratory system
- Supplies oxygen to the body for energy production
- Removes carbon dioxide as a waste product
- Maintains acid base balance in arterial blood
- Maintains heat exchange
- Removes carbon dioxide as a waste product
- Maintains acid base balance in arterial blood
- Maintains heat exchange
2
New cards
anatomical lanadmarks
- Going to hear more of the upper lobes when listening to the front side
- Going to hear more of the lower lobes when listening to the back
- Lobes sit on top of each other in a diagonal-ish way
- Going to hear more of the lower lobes when listening to the back
- Lobes sit on top of each other in a diagonal-ish way
3
New cards
developmental variation in children (thorax and lungs)
- smaller airway lumens
- asthma
- asthma
4
New cards
developmental variations in pregnant women (thorax and lungs)
- growing uterus displaces diaphragm
- increased oxygen demand
- increased oxygen demand
5
New cards
developmental variations in older adults (thorax and lungs)
- decreased ability to collapse and recoil
6
New cards
kyphosis
curvature of spine (hunchback)
7
New cards
subjective data for thorax and lungs
- Cough
- SOB
- Sputum and color
- Dyspnea
- Chest pain with breathing
- Edema
- Fatigue
- History of respiratory infections
- History of asthma
- Smoking
- Environmental exposures
- Vaccinations- pneumonia and influenza, COVID
- SOB
- Sputum and color
- Dyspnea
- Chest pain with breathing
- Edema
- Fatigue
- History of respiratory infections
- History of asthma
- Smoking
- Environmental exposures
- Vaccinations- pneumonia and influenza, COVID
8
New cards
edema
- Edema can be a sign of heart failure*
- Starts in lower extremities normally when assessing
- best place to check is behind the ankle (posterior tibial)
- Starts in lower extremities normally when assessing
- best place to check is behind the ankle (posterior tibial)
9
New cards
smoking
#1 risk factor for smoking
10
New cards
yellow/green sputum
- Likely related to a bacterial infection
- Can also mean allergies
- Can also mean allergies
11
New cards
pink/red/bloody sputum
- Could be related to an infection or cancer, in some cases
- Irritation in the respiratory system
- Irritation in the respiratory system
12
New cards
white
Allergies, asthma, or viral infections
13
New cards
charcoal gray
- Environmental, common in people who work in coal mines and factories, or heavy smokers
- Inhaling a lot of dust
- Inhaling a lot of dust
14
New cards
brown
Chronic lung disease, cystic fibrosis or bronchiectasis, TB, cystic fibrosis
15
New cards
respiratory quality
- Does it look automatic or that they are working hard to breathe > are they using accessory muscles to breathe (neck muscles)
- look for their posture to get more air in
- their skin color (blue=cyanosis)
- is the breathing regular (10-20 breaths), is their depth of breath okay
- look for their posture to get more air in
- their skin color (blue=cyanosis)
- is the breathing regular (10-20 breaths), is their depth of breath okay
16
New cards
inspect posterior and anterior chest
- Thoracic cage: shape, configuration, symmetry
- AP Lateral Ratio: COPD can have increased AP diameter
- AP Lateral Ratio: COPD can have increased AP diameter
17
New cards
adult respiratory pattern
- Rate: 10-20 breaths per min
- Air moving in and out with each respiration
- Even pattern, silent, automatic
- Air moving in and out with each respiration
- Even pattern, silent, automatic
18
New cards
tachypnea
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- Increased rate >24 breaths per min
- Response to pain fever, fear, exercise, infection
- Body goes into hypermetabolic state and needs more oxygen
- Increased rate >24 breaths per min
- Response to pain fever, fear, exercise, infection
- Body goes into hypermetabolic state and needs more oxygen
19
New cards
hyperventilation
- Increase in both rate and depth (fast, deep breaths)
- Response to exertion, fear, and anxiety
- Trying to take more oxygen than than Co2 coming out
- Response to exertion, fear, and anxiety
- Trying to take more oxygen than than Co2 coming out
20
New cards
bradypnea
- Slow breathing
- Decreased but regular rate
- Decreased but regular rate
21
New cards
hypoventilation
- Irregular shallow pattern
- Can be caused by narcotics or anesthetics and conscious splinting of the chest to avoid pain
- Can be caused by narcotics or anesthetics and conscious splinting of the chest to avoid pain
22
New cards
Cheyne-Stokes
- Periods of difficult breathing (dyspnea) followed by periods of no respirations (apnea)
- Cyclic episodes of apnea and hyperventilation
- Cyclic episodes of apnea and hyperventilation
23
New cards
biot's respirations
Variable in pattern, random apneas, clusters rapid short breaths
24
New cards
orthopnea
Difficulty breathing when supine
25
New cards
apnea
absence of breathing
26
New cards
dyspnea
Labored or difficult breathing
27
New cards
- Chest expansion
- Crackles (wrong)
- Fremitus
- Lumps and masses
- Crepitus
- Crackles (wrong)
- Fremitus
- Lumps and masses
- Crepitus
When palpating the chest what should the nurse look for? Select all that apply
28
New cards
fremitus
- tactile vibration
- can hear when the patient is breathing
- can hear when the patient is breathing
29
New cards
crepitus
- escaped air
-Rice krispies under the skin
- Can feel it not hear it
-Rice krispies under the skin
- Can feel it not hear it
30
New cards
resonance
- normal finding during percussion of the chest/lungs
31
New cards
auscultation of thorax and lungs
- Patient sitting
- Listen anterior and posterior
- Side by side comparison
- Listen for one full respiration in each location: inhalation and exhalation
- Monitor breathing: Offers times for the client to rest and breathe normally
- Listen anterior and posterior
- Side by side comparison
- Listen for one full respiration in each location: inhalation and exhalation
- Monitor breathing: Offers times for the client to rest and breathe normally
32
New cards
bronchial
- present over the large airways in the anterior chest near the second and third the anterior chest near the second and third intercostal spaces;
- these sounds are more intercostal spaces;
- more tubular and hollow-sounding than vesicular tubular and hollow-sounding than vesicular sounds
- these sounds are more intercostal spaces;
- more tubular and hollow-sounding than vesicular tubular and hollow-sounding than vesicular sounds
33
New cards
bronchialvesicular
- heard in the posterior chest between the scapulae and in the center chest between the scapulae and in the center part of the anterior chest.
- are softer than bronchial sounds, but sounds are softer than bronchial sounds, but have a tubular quality.
- are softer than bronchial sounds, but sounds are softer than bronchial sounds, but have a tubular quality.
34
New cards
vesicular
- Heard across the lungs surface. They are low pitched, rustling sounds with higher intensity during inspiration.
35
New cards
adventitious lung sounds
- crackles
- wheezing
- stridor
- pleural friction rub
- wheezing
- stridor
- pleural friction rub
36
New cards
crackles
- discontinuous popping sounds heard over inspiration
- Emphysema, bronchitis pulmonary edema, pneumonia
- Emphysema, bronchitis pulmonary edema, pneumonia
37
New cards
wheezes
- Continuous musical sounds
- constricted airway passage over expiration
- constricted airway, usually because of inflammation
- Acute Asthma, Chronic Emphysema, Bronchitis
- constricted airway passage over expiration
- constricted airway, usually because of inflammation
- Acute Asthma, Chronic Emphysema, Bronchitis
38
New cards
stridor
- high pitched crowing or seal like sound
- heard on inspiration on the upper airway;
- louder over neck
- needs to be treated very quickly
- Ex. croup, foreign body inhalation
- heard on inspiration on the upper airway;
- louder over neck
- needs to be treated very quickly
- Ex. croup, foreign body inhalation
39
New cards
pleural friction rub
- superficial sound that is coarse and low pitched.
- sounds like two pieces of leather or sandpaper being rubbed together
- Ex. pleuritis
- sounds like two pieces of leather or sandpaper being rubbed together
- Ex. pleuritis
40
New cards
lung cancer
the second most diagnosed cancer among men and women
41
New cards
asthma
the most common chronic disease in childhood
42
New cards
heart function
- Muscular Pump
- Located under sternum from the 2nd to 5th Intercostal space from right sternal border to midclavicular line
- Located under sternum from the 2nd to 5th Intercostal space from right sternal border to midclavicular line
43
New cards
blood vessels function
Provide pulmonary and systemic circulation
44
New cards
systole
heart contracts and pumps blood into the systemic and pulmonary system
45
New cards
diastole
ventricles relax and fill with blood
46
New cards
S1
- first heart sound
- Results from the closure of the *AV valve* (tricuspid and mitral)
- lub
- Results from the closure of the *AV valve* (tricuspid and mitral)
- lub
47
New cards
S2
- second heart sound
- Results from the closure of the *semilunar valve* (aortic and pulmonic)
- loudest at the base of the heart
- Results from the closure of the *semilunar valve* (aortic and pulmonic)
- loudest at the base of the heart
48
New cards
S3
- third heart sound
- abnormal
- Vibration of ventricles that resist filling
- abnormal
- Vibration of ventricles that resist filling
49
New cards
S4
- fourth hear sound
- abnormal
- Vibration of noncompliant ventricles when atria pushes blood
- abnormal
- Vibration of noncompliant ventricles when atria pushes blood
50
New cards
murmurs
- happen during the first and second heart sounds
- heard in the heart
- Gentle, blowing or swishing sound due to turbulent blood flow in the blood cycle
- Conditions that create turbulent blood flow and collision currents
- heard in the heart
- Gentle, blowing or swishing sound due to turbulent blood flow in the blood cycle
- Conditions that create turbulent blood flow and collision currents
51
New cards
jugular veins
give information regarding volume changes
52
New cards
developmental changes during pregnancy (heart and neck vessels)
- blood volume increases by 30-50%
- increases in stroke volume, cardiac output, and pulse rate
- increases in stroke volume, cardiac output, and pulse rate
53
New cards
developmental changes in older adults (heart and neck vessels)
- lifestyle, habit, and disease affect cardiac state.
- Increase in BP, increases in risk for dysrhythmia and ability to compensate with exercise decreases
- Increase in BP, increases in risk for dysrhythmia and ability to compensate with exercise decreases
54
New cards
nocturia
excessive urination at night
55
New cards
chest pain questions
- onset and location
- characteristics
- precipitating events
- associated symptoms
- relieved by or made worse by
- medication or treatments
- characteristics
- precipitating events
- associated symptoms
- relieved by or made worse by
- medication or treatments
56
New cards
physical assessment (neck vessels)
- Inspect: inspect jugular veins venous pulse
- Palpate: palpate each carotid artery separately
- Auscultate: Auscultate each carotid artery for bruit
--- Ask patient to hold their breath when auscultating to not confuse with breathing sounds
- Palpate: palpate each carotid artery separately
- Auscultate: Auscultate each carotid artery for bruit
--- Ask patient to hold their breath when auscultating to not confuse with breathing sounds
57
New cards
physical assessment (pericardium)
- Assess apical pulse
- patient needs to be laying down
- Detect heave or thrill
- patient needs to be laying down
- Detect heave or thrill
58
New cards
heart auscultatory areas
- all patients take medications
- aortic
- pulmonic
- erbs point
- tricuspid
- mitral
- aortic
- pulmonic
- erbs point
- tricuspid
- mitral
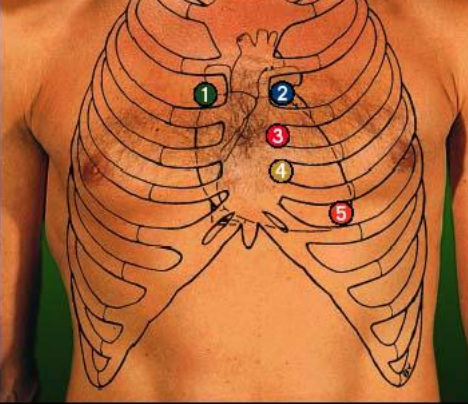
59
New cards
risk factors for heart disease and stroke
- High BP
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
- Physical inactivity
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
- Physical inactivity
60
New cards
health promotion/patient education for heart disease and stroke
- Preventative Aspirin Therapy
- BP and Cholesterol Control
- Smoking Cessation
- Lifestyle Modifications
- BP and Cholesterol Control
- Smoking Cessation
- Lifestyle Modifications
61
New cards
vascular system
Vessels of the body that carry blood or lymph
62
New cards
arteries
carry blood away from the heart to the extremities and organs
63
New cards
veins
- Drains deoxygenated blood and waste product from waste tissues and return to the heart
- If jugular veins are distended it shows if there are any fluid imbalance issues
- If jugular veins are distended it shows if there are any fluid imbalance issues
64
New cards
lymphatic system functions
- conserves fluid and plasma protein that leak out of capillaries and vascular system
--- removing lymph nodes can cause a lymphedema and cause swelling because there is no lymph nodes to drain the fluid and plasma
- immune system
- absorbs lipids from intestinal tract
--- removing lymph nodes can cause a lymphedema and cause swelling because there is no lymph nodes to drain the fluid and plasma
- immune system
- absorbs lipids from intestinal tract
65
New cards
components of the lymphatic system
- lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, thymus
- all contribute to draining and immune response
- can live without the spleen, tonsils, and thymus
- all contribute to draining and immune response
- can live without the spleen, tonsils, and thymus
66
New cards
developmental variations in children (lymphatic system)
- large lymph nodes
- immature immune system (get sick a lot)
- lymph nodes are bigger because they grow faster than their whole body
- immature immune system (get sick a lot)
- lymph nodes are bigger because they grow faster than their whole body
67
New cards
developmental variations during pregnancy (lymphatic/peripheral vascular)
- pitting edema
- venous disease
- venous disease
68
New cards
developmental variations in older adults (lymphatic/peripheral vascular)
arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
69
New cards
venous disease
- a weakening of the walls and valves of the veins, causing venous insufficiency, or problems returning your blood to your heart.
- Risk factors: standing, sitting, bed rest, hypercoagulation, vein wall trauma, varicose veins, obesity, pregnancy, and genetic predisposition
- venous stasis
- Risk factors: standing, sitting, bed rest, hypercoagulation, vein wall trauma, varicose veins, obesity, pregnancy, and genetic predisposition
- venous stasis
70
New cards
venous stasis
blood is not moving, it is just staying in one place can cause clots. It doesn't move to the heart
71
New cards
peripheral disease
- Caused by cigarette smoking, diabetes, and hypertension
- Caused by arteriosclerosis a lot of times
- Caused by arteriosclerosis a lot of times
72
New cards
subjective data for peripheral vascular
- Leg pain
---oxygen/blood is not traveling to the extremities
- Leg cramps
- Skin changes on arms or legs
--- No circulation can cause this (cyanosis)
- Swelling or edema
- Lymph node enlargement
- Medications
---Birth control can put women at risk for developing blood clots
- Smoking history
---oxygen/blood is not traveling to the extremities
- Leg cramps
- Skin changes on arms or legs
--- No circulation can cause this (cyanosis)
- Swelling or edema
- Lymph node enlargement
- Medications
---Birth control can put women at risk for developing blood clots
- Smoking history
73
New cards
inspection of upper extremities
Note:
- color
- edema lesions (no adequate circulation=at risk for developing lesions because the healing process is off so a small wound can turn into a nasty lesion)
- clubbing
- color
- edema lesions (no adequate circulation=at risk for developing lesions because the healing process is off so a small wound can turn into a nasty lesion)
- clubbing
74
New cards
inspection of lower extremities
- Note color, size, edema, hair distribution, varicosities
75
New cards
varicosities
- best assessed when the pt is standing
- can be benign or can cause patients a lot of pain
- can be surgically removed because of pain
- can be benign or can cause patients a lot of pain
- can be surgically removed because of pain
76
New cards
palpation of extremeties
- Cap Refill
- Temperature
- Size- Calf Circumference
- Edema
- Pulse Sites
- inguinal lymph nodes can be palpated
- Temperature
- Size- Calf Circumference
- Edema
- Pulse Sites
- inguinal lymph nodes can be palpated
77
New cards
capillary refill
- Pressing down on the fingernails to inspect for color return in less than 2 seconds or less
- Check on fingernails and toenails
- Check on fingernails and toenails
78
New cards
size-calf circumference
- Asses for edema using a tape measure
- Track size over time
- Track size over time
79
New cards
pulse force scale
3+ Full, bounding
2+ Normal
1+ Weak, thready
0 Absent
2+ Normal
1+ Weak, thready
0 Absent
80
New cards
pulse sites
temporal, carotid, apical, brachial, radial, ulnar, femoral, popliteal, posterior tibial, dorsalis pedis
81
New cards
doppler assesment
- device used to check for pulse in the case that the health care provider is unable to locate it.
82
New cards
allen test
- Used to evaluate collateral circulation before inserting a catheter into the radial artery
- 1. Press on ulnar and radial until color change begins,
- 2. Then release the radial to see if the blood returns quickly.
- That demonstrates how well the ulnar artery can deliver blood to the hand in the case the radial artery line is in to measure BP
- 1. Press on ulnar and radial until color change begins,
- 2. Then release the radial to see if the blood returns quickly.
- That demonstrates how well the ulnar artery can deliver blood to the hand in the case the radial artery line is in to measure BP
83
New cards
pitting edema 1+
mild pitting, slight indentation, no perceptible swelling of the leg
84
New cards
pitting edema 2+
moderate pitting, indentation subsides rapidly
85
New cards
pitting edema 3+
deep pitting indentation remains for a short time, leg looks swollen
86
New cards
pitting edema 4+
very deep pitting, indentation lasts a long time, leg is grossly swollen and distorted
87
New cards
foot care
- Checking feet everyday
- Keep blood flowing to the feet
- Wearing shoes that fit comfortably
- Keep skin soft and smooth
- Keep blood flowing to the feet
- Wearing shoes that fit comfortably
- Keep skin soft and smooth
88
New cards
left upper quadrant
- stomach
- spleen
- the left lobe of the liver
- body of the pancreas
- left kidney and adrenal gland
splenic flexure of the colon
- part of the transverse and descending colon
- spleen
- the left lobe of the liver
- body of the pancreas
- left kidney and adrenal gland
splenic flexure of the colon
- part of the transverse and descending colon
89
New cards
right upper quadrant
- liver
- gallbladder
- duodenum
- head of the pancreas
- right kidney, and adrenal gland
- the hepatic flexure of the colon
- part of the ascending and transverse colon
- gallbladder
- duodenum
- head of the pancreas
- right kidney, and adrenal gland
- the hepatic flexure of the colon
- part of the ascending and transverse colon
90
New cards
left lower quadrant
- a portion of the descending colon
- the sigmoid colon
- left ureter
- left ovary, and fallopian tube (women)
- left spermatic cord (men)
- the sigmoid colon
- left ureter
- left ovary, and fallopian tube (women)
- left spermatic cord (men)
91
New cards
right lower quadrant
- cecum
- appendix
- right ureter
- right ovary and fallopian tube
- right spermatic cord
- appendix
- right ureter
- right ovary and fallopian tube
- right spermatic cord
92
New cards
developmental variations in children (abdominal)
- abdominal wall is less muscular
- organs easily palpated
- organs easily palpated
93
New cards
developmental variations in pregnancy (abdominal)
- nausea acid indigestion
- constipation
- linea nigra
- striae/stretch marks
- constipation
- linea nigra
- striae/stretch marks
94
New cards
developmental variations in older adults (abdominal)
- fat deposits in abdominal areas
- salivation decreases (can impact taste and how easy it is to chew food)
- esophageal emptying delayed
- gastric acid increases
- gallstones
- liver size decreases
- salivation decreases (can impact taste and how easy it is to chew food)
- esophageal emptying delayed
- gastric acid increases
- gallstones
- liver size decreases
95
New cards
subjective data (abdominal)
- Appetite
- Dysphagia
- Food intolerance
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bowel habits
- Past surgical history
- Current medications
- Nutrition
- Dysphagia
- Food intolerance
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bowel habits
- Past surgical history
- Current medications
- Nutrition
96
New cards
dysphagia
- difficulty swallowing
- can put pts at risk for aspiration
- can put pts at risk for aspiration
97
New cards
physical assessment of abdomen
- abdominal wall relaxed
- empty bladder
- supine
- make sure to perform auscultation before palpation to prevent anything from falsely stirring up
- empty bladder
- supine
- make sure to perform auscultation before palpation to prevent anything from falsely stirring up
98
New cards
abdomen inspection
- Size, shape, symmetry
- Condition of skin: color, lesions, veins, hair distribution, hernias
- Movements: respirations, pulsations, and peristalsis
- Condition of skin: color, lesions, veins, hair distribution, hernias
- Movements: respirations, pulsations, and peristalsis
99
New cards
umbilicus inspection
Position, color, contour, and herniation
100
New cards
abdominal shapes
- Flat
- Rounded
- Scaphoid
- Protuberant (ascites)
- Rounded
- Scaphoid
- Protuberant (ascites)