BHD Oncology- Week 3 Combined
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
Hodgkin's lymphoma

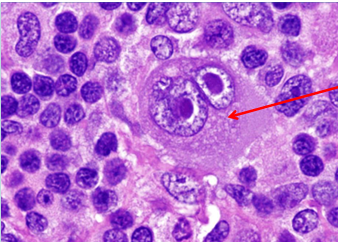
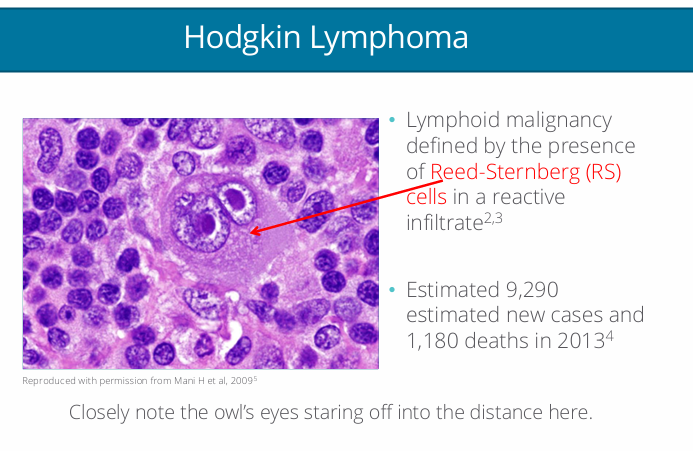
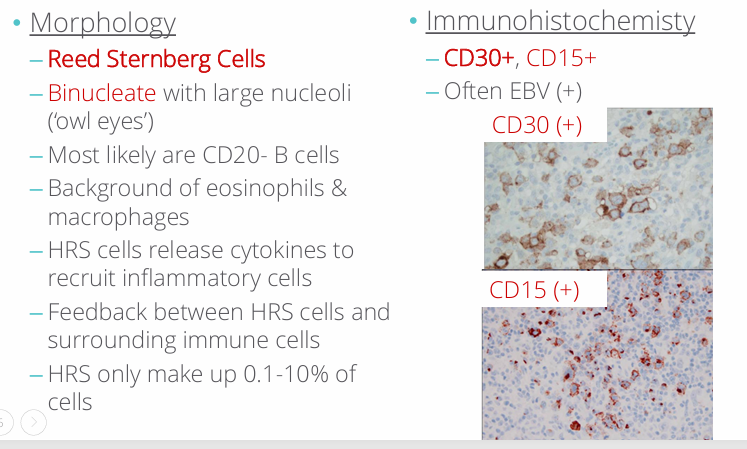
HL morphology and IHC
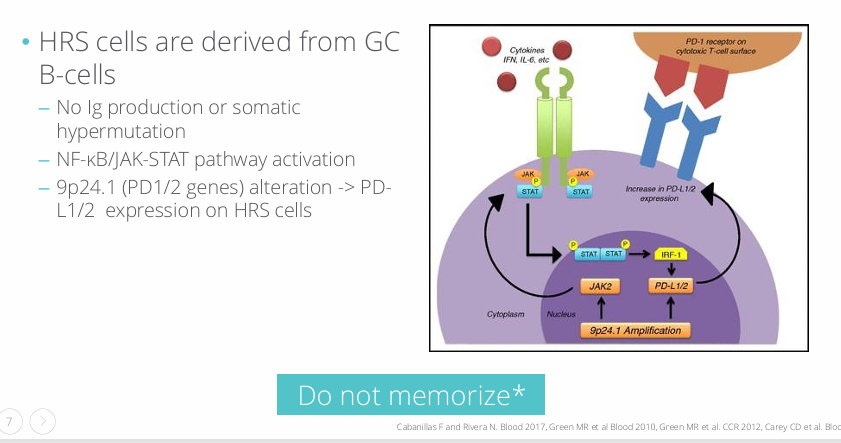
HL pathogenesis
classical HL

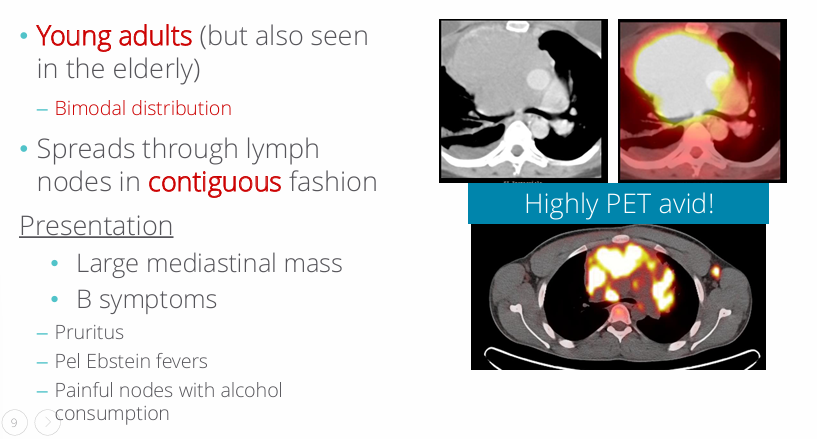
classical HL presentation
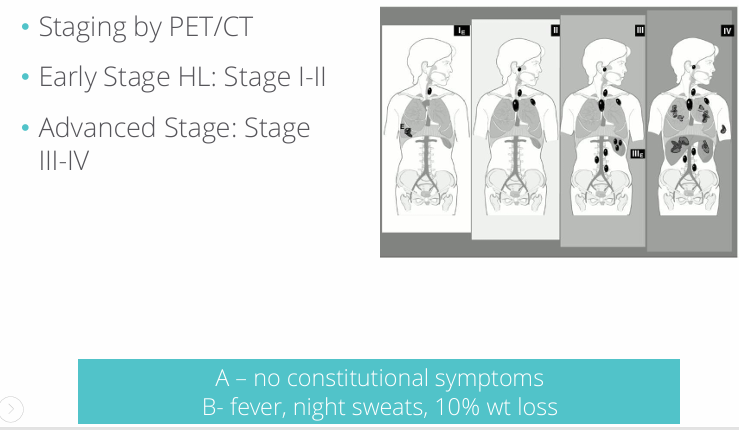
HL staging
prognostic markers in HL

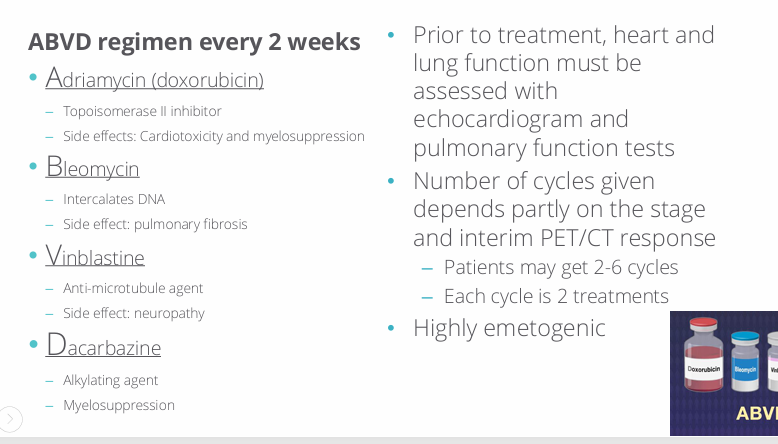
HL treatment
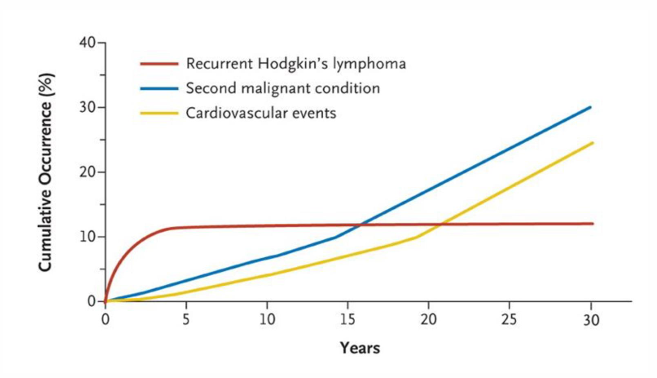
long term complications of early stage HL
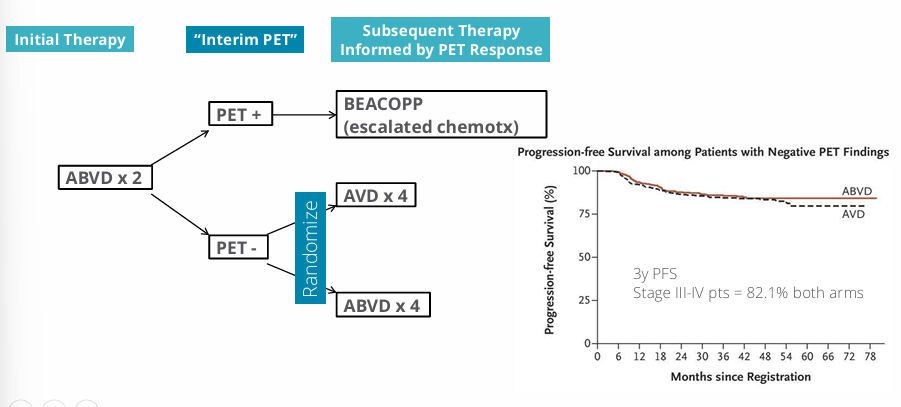
“PET-adapted” treatment- advanced stage HL

PET adapted treatment
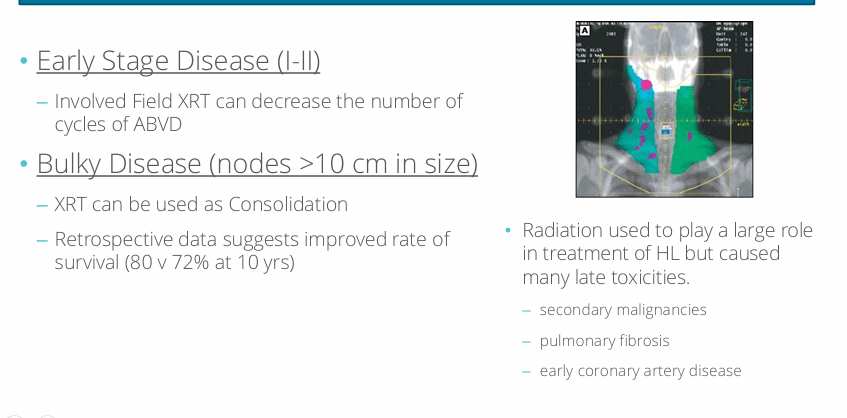
role of radiation (XRT) in HL
relapsed HL

hematologic malignancies expressing CD30

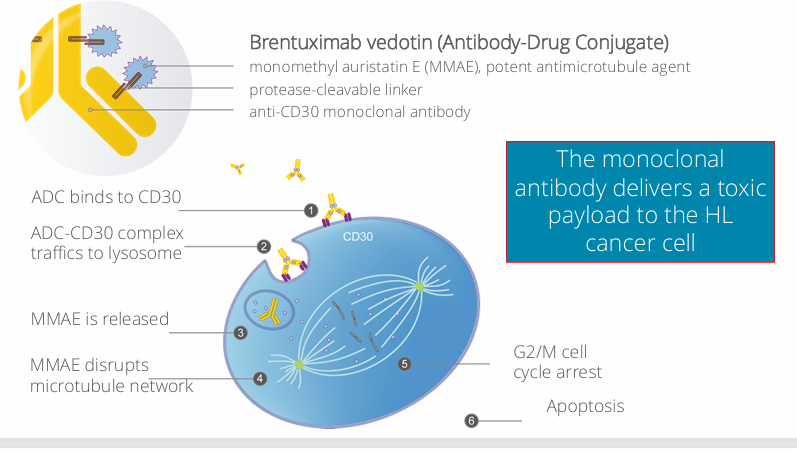
brentuximab vedotin- MOA
ECHELON-1: BV+AVD in advanced stage HL
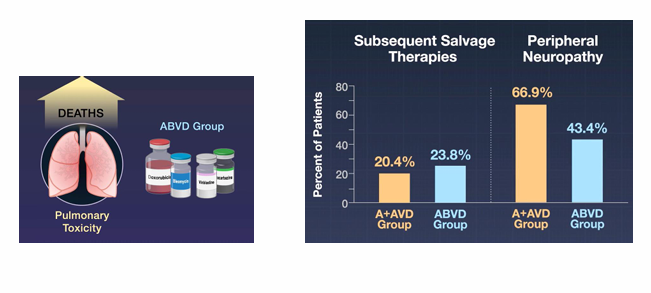
challenges of treating elderly pts with HL

refractory HL: targeting PD-1
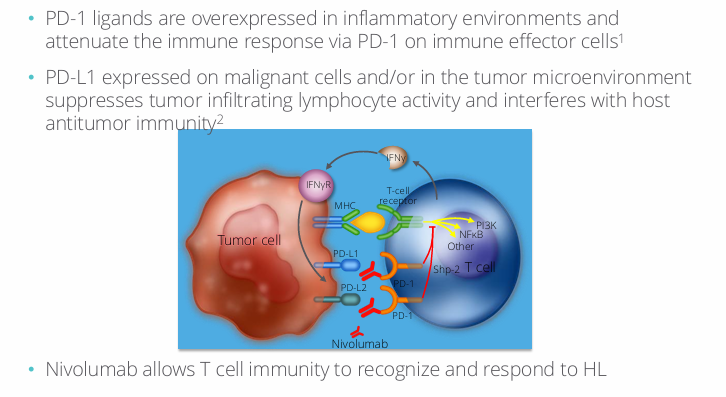
nivolumab in advanced HL
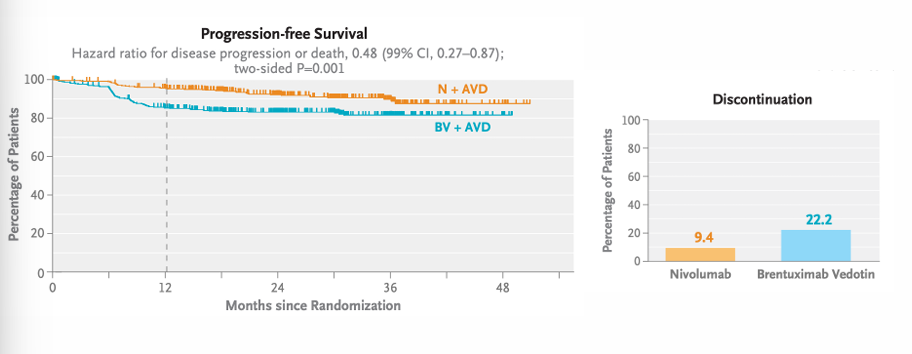
nivolumab in advanced HL conclusions
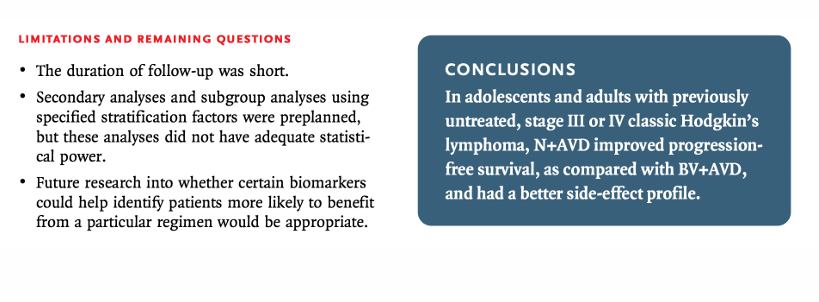
HL summary

T cell lymphomas

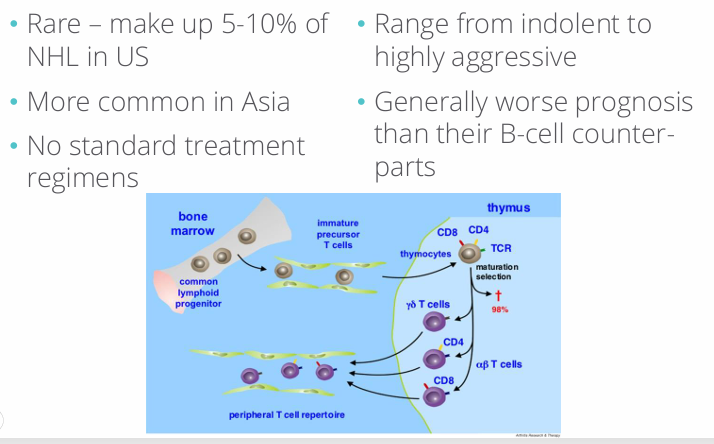
T cell lymphomas introduction
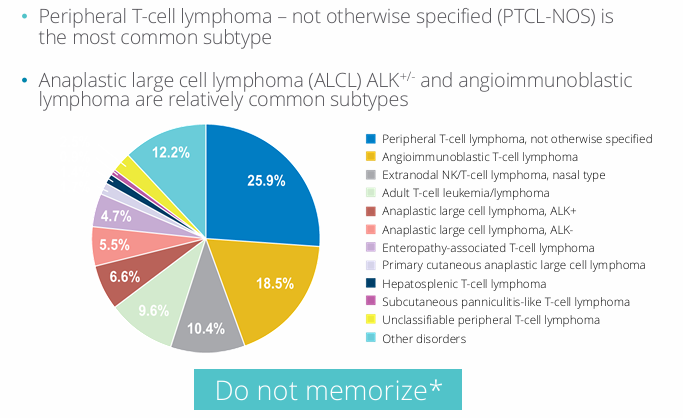
most common TCL subtypes
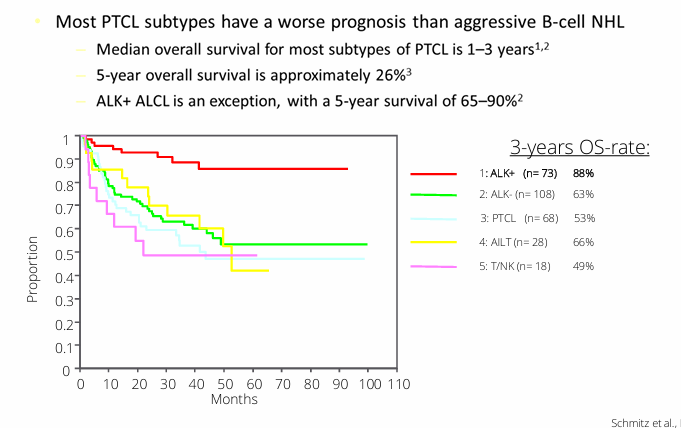
T-cell lymphoma survival
peripheral T cell lymphoma: PTCL-NOS

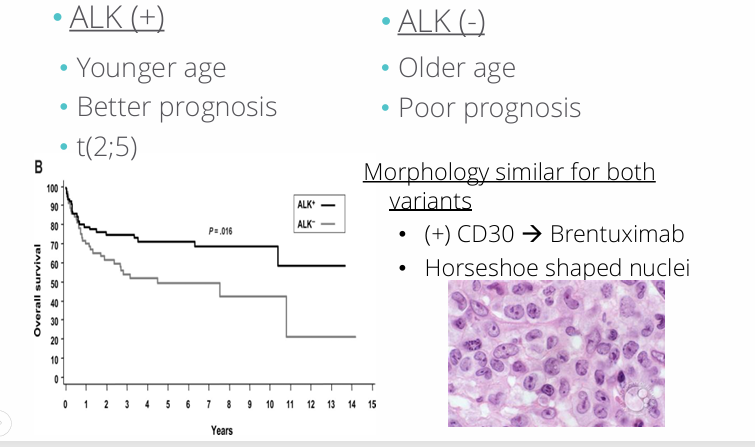
anaplastic large T cell lymphoma
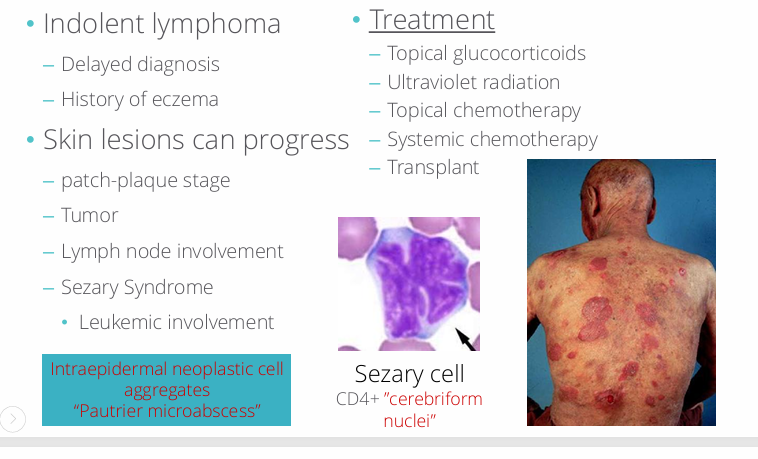
mycosis fungoides- cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
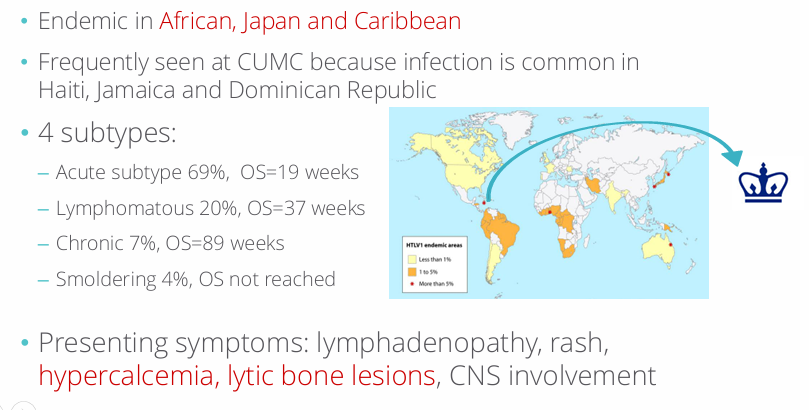
adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL)
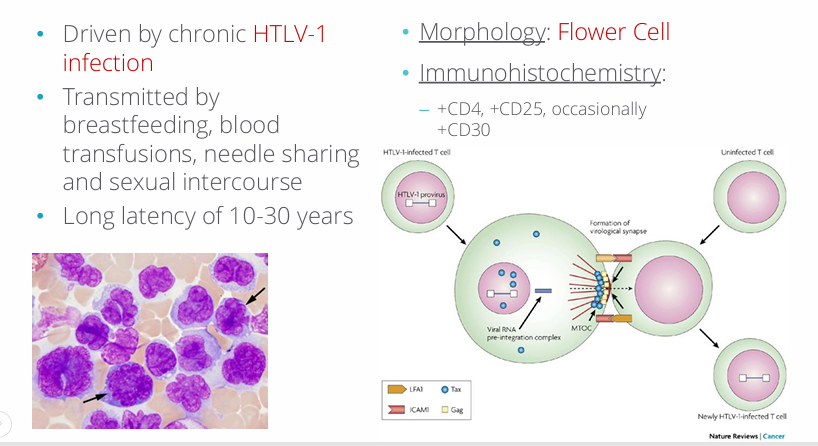
HTLV-1 and adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL)
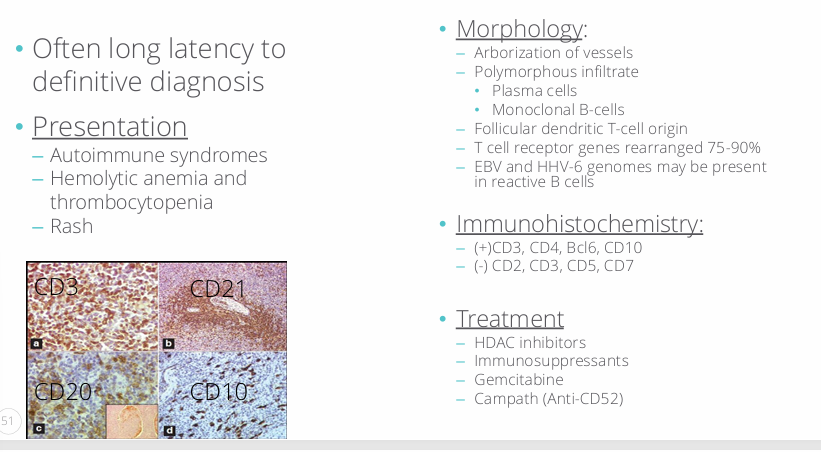
angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma
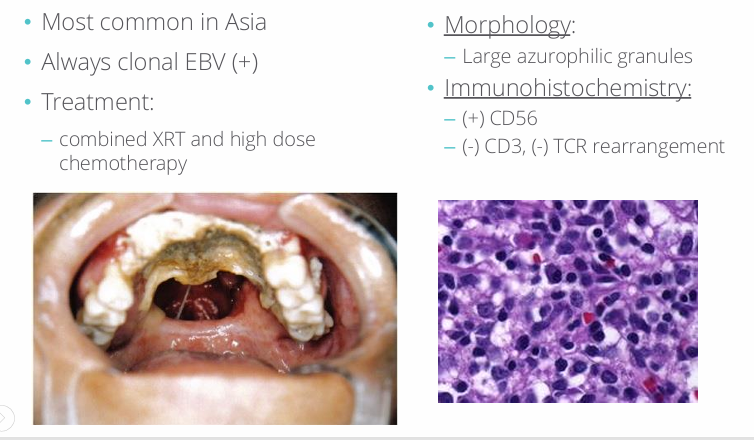
extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma- nasal type
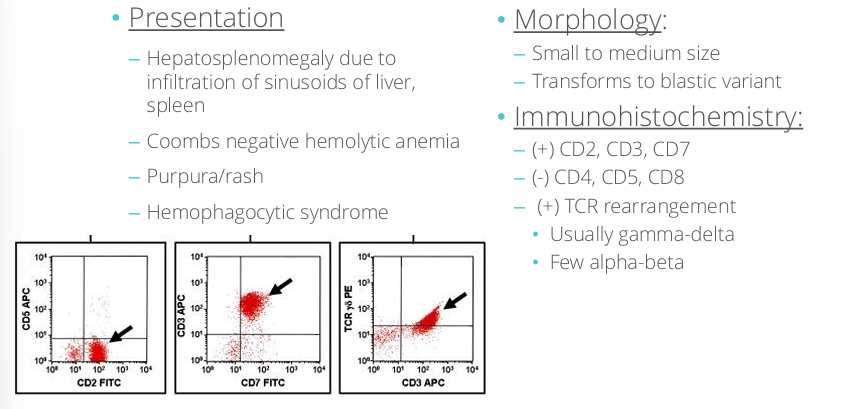
hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma
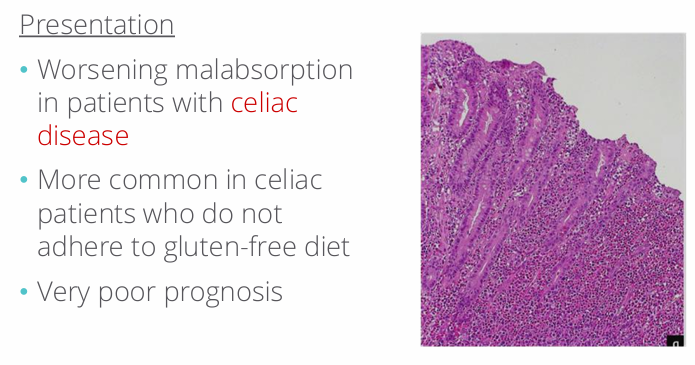
enteropathy associated T-cell lymphoma presentation
myeloma epidemiology

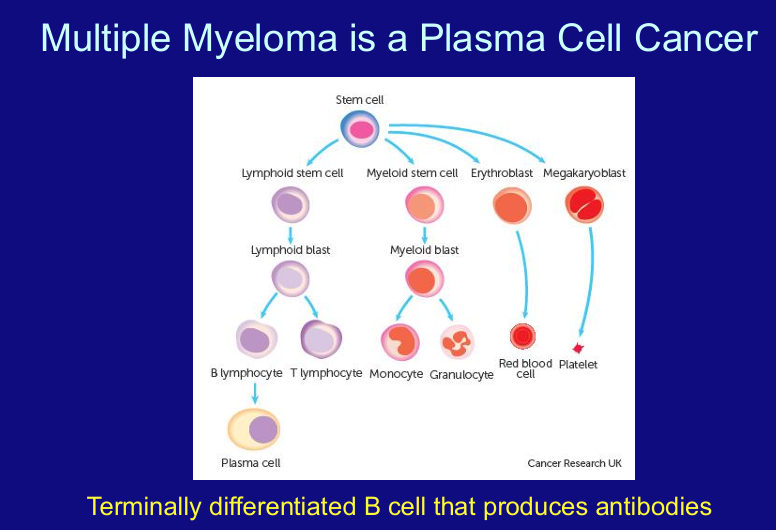
multiple myeloma is a ____ cancer
spectrum of plasma cell disorders
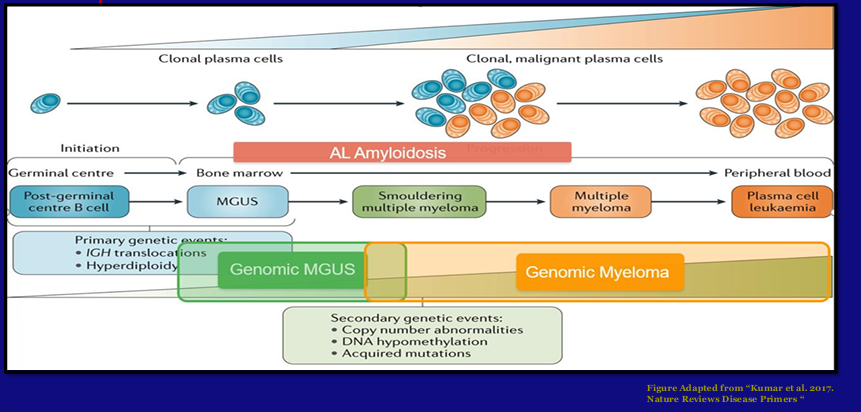
plasma cell disorders
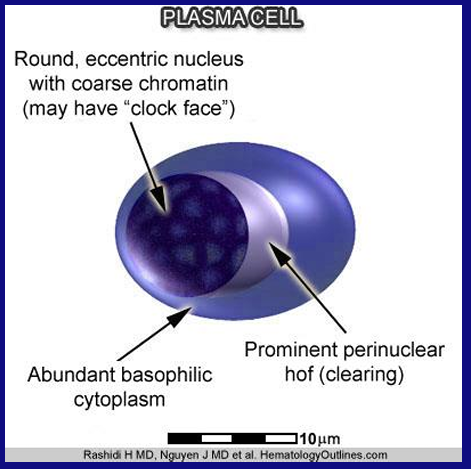
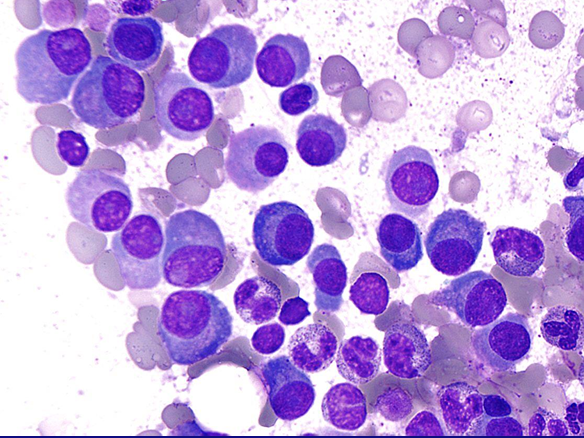
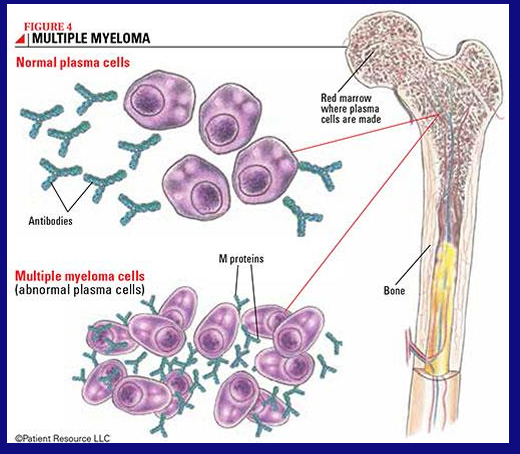
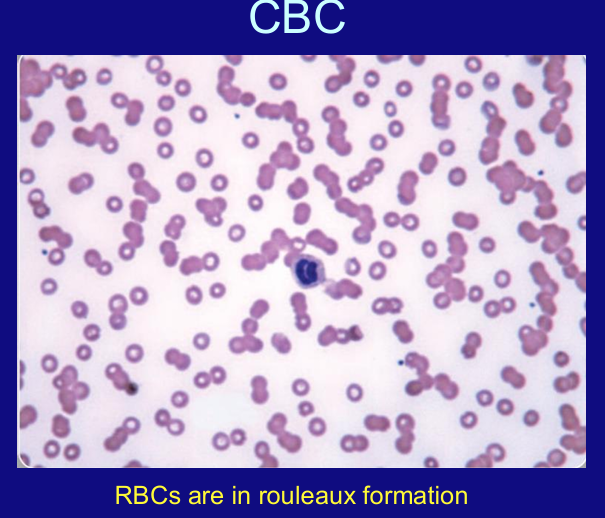
morphology of MM cell
MM is a blood cancer found primarily in the
-bone marrow
MM cells secrete
-monoclonal immunoglobulins
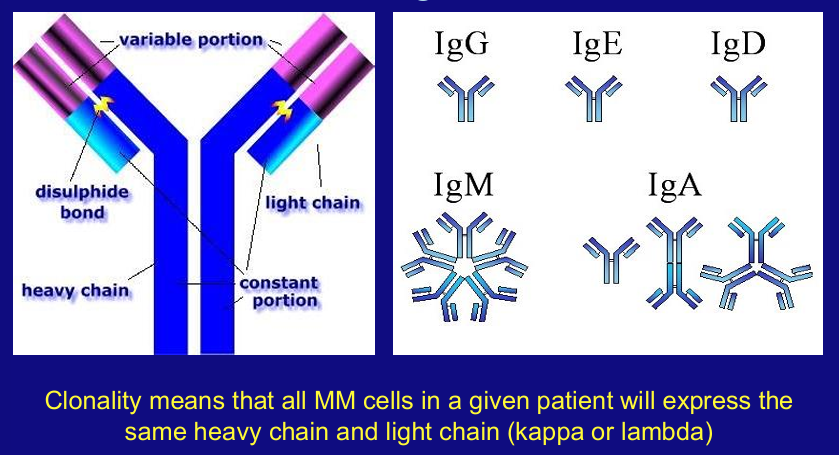
in MM, an increased number of _____ oversecrete _____
-malignant plasma cells; an abnormal antibody called an “M protein”
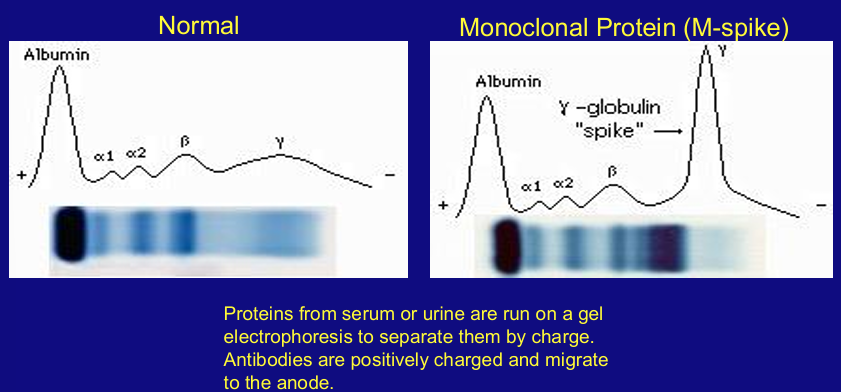
serum and urine protein electrophoresis (SPEP and UPEP) quantify
-monoclonal Ab secretion
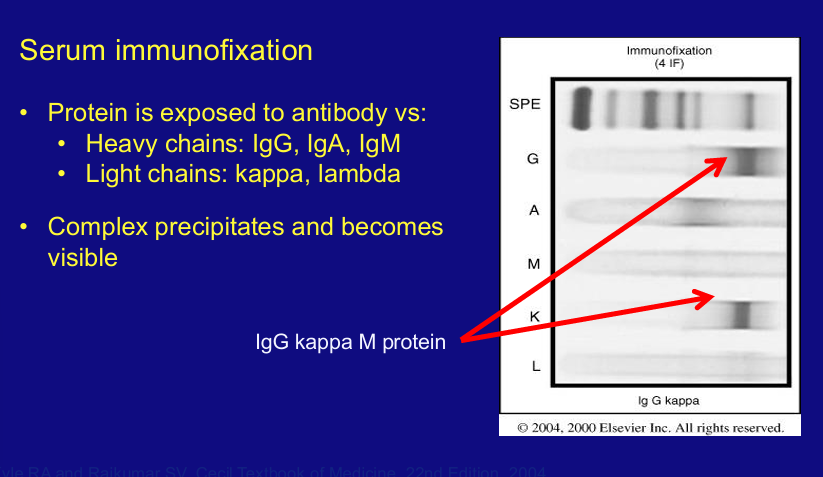
SIFE
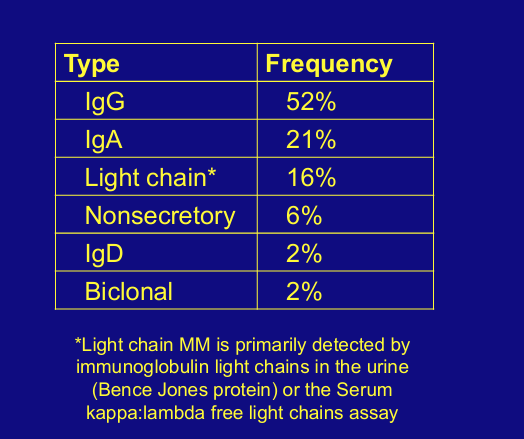
MM by immunoglobulin type
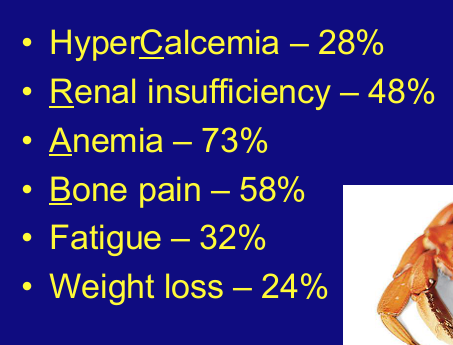
MM clinical presentation
MM diagnostic criteria

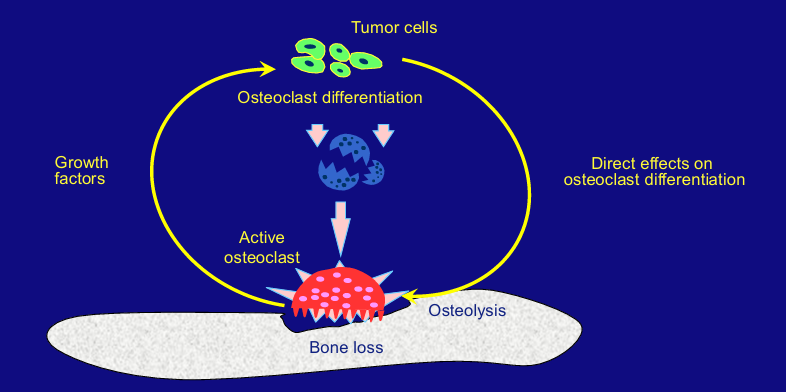
myeloma alters
-bone metabolism
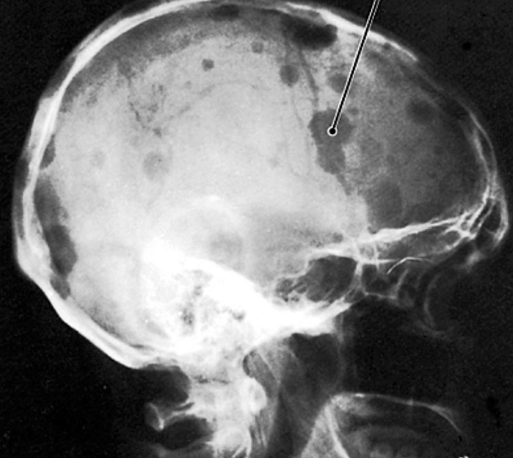
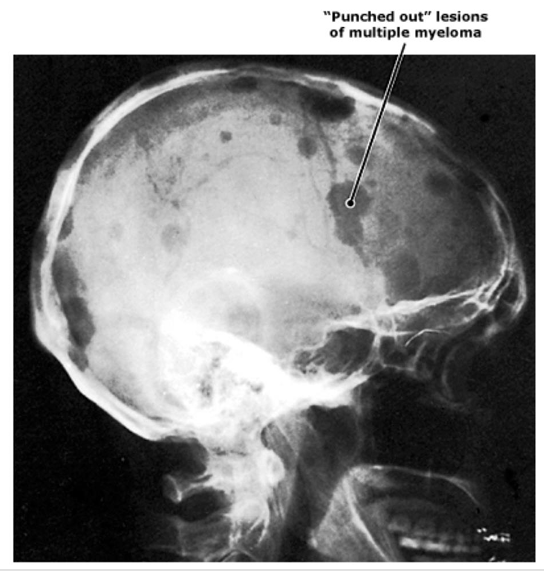
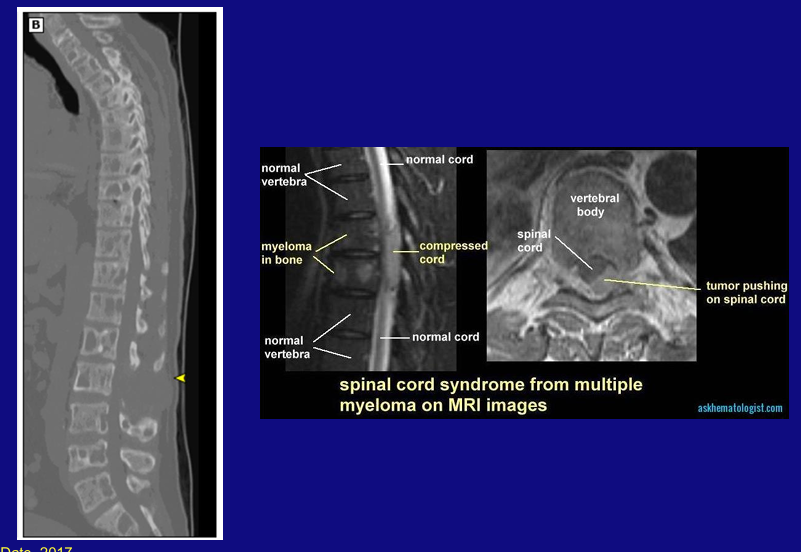
spinal cord syndrome
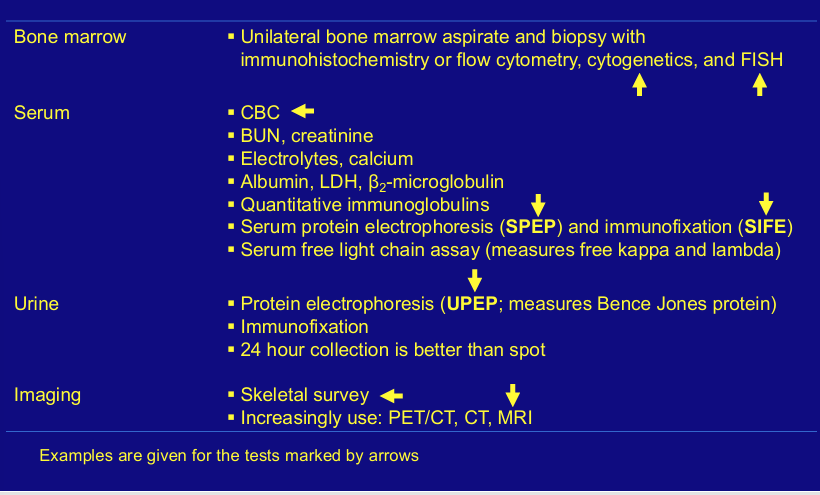
diagnostic tests
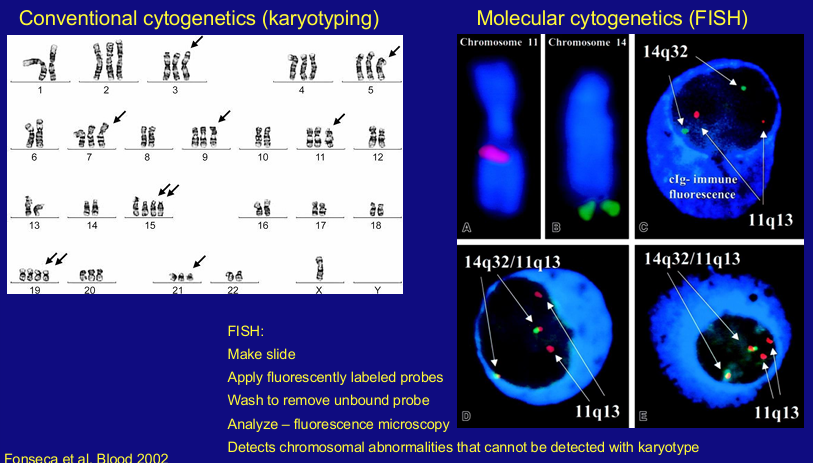
MM prognosis- karyotype and FISH
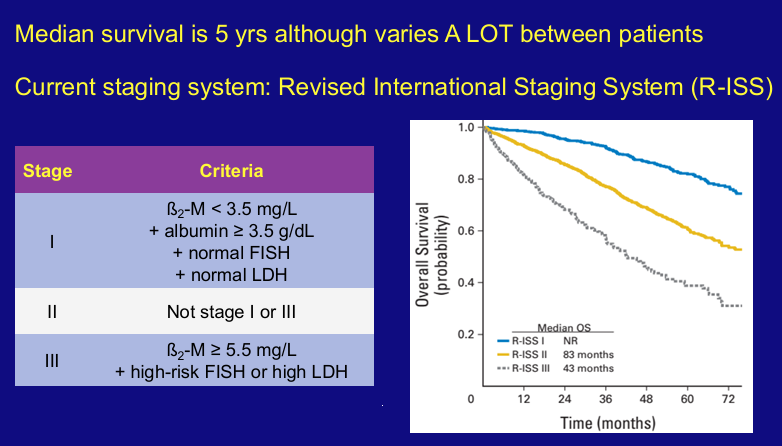
prognosis of myeloma
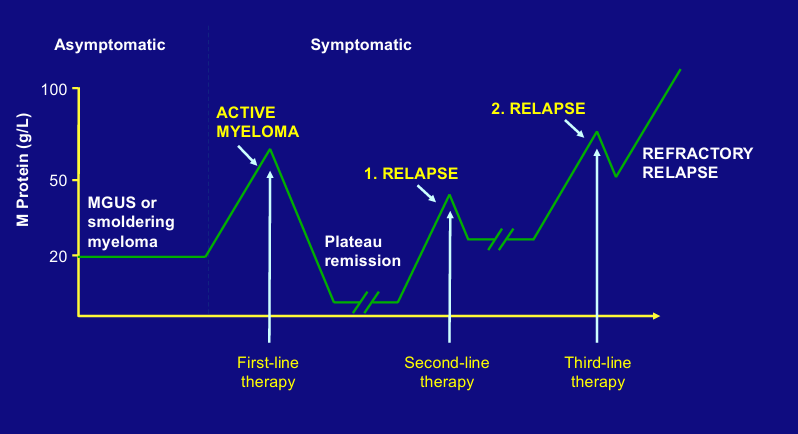
natural history of myeloma
myeloma treatments

myeloma chemo principles

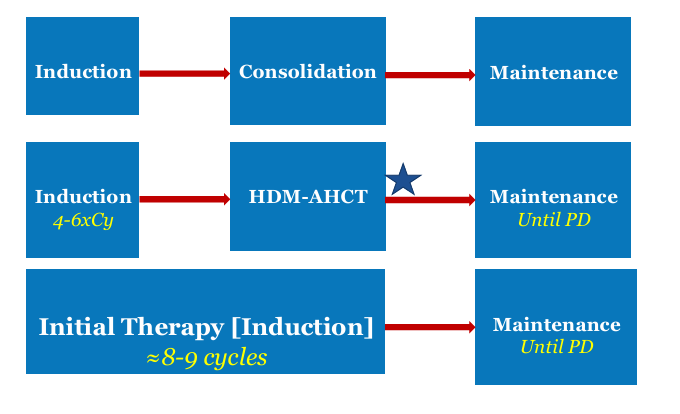
treatment paradigm
MM treatments by class

commonly used MM regimens

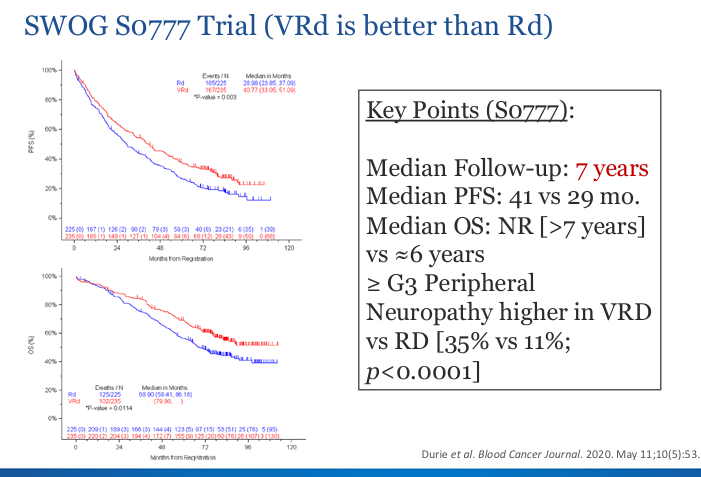
SWOG S0777 trial
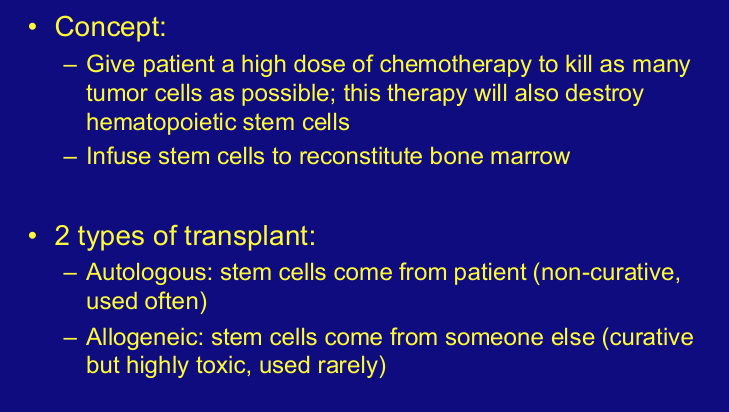
bone marrow transplant
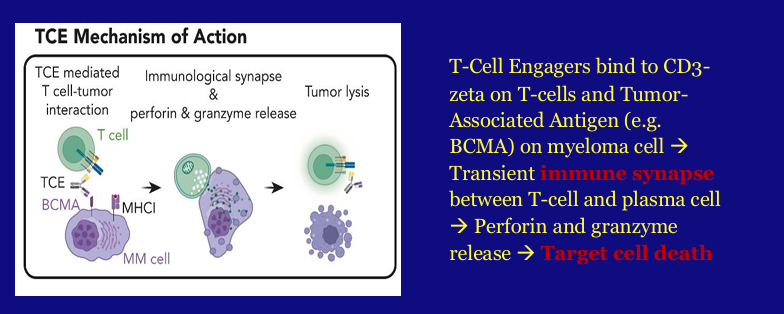
bispecific antibodies in relapsed/refractory plasma cell disorders
myeloma complications- infections

myeloma complications- thrombosis

myeloma complications- bone

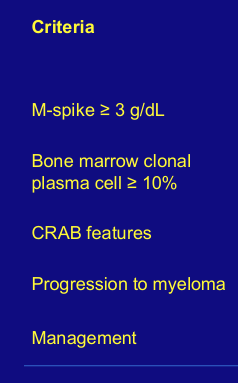
MGUS v. SMM v. MM
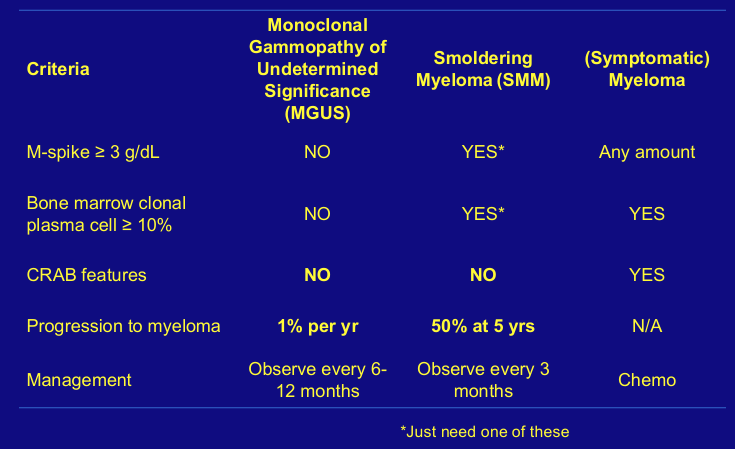
MGUS and SMM- progression to MM
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia

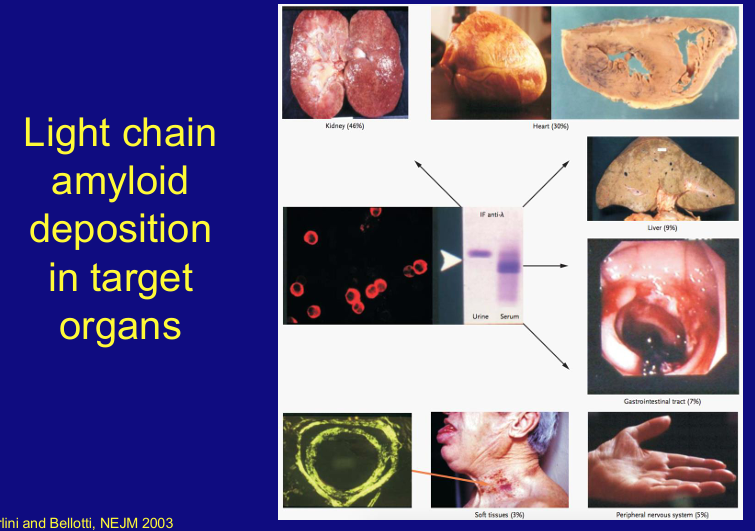
AL amyloidosis

light chain amyloid deposition in target organs
key points

cellular therapy, HCT/HSCT/SCT/BMT, adoptive cell therapy definitions
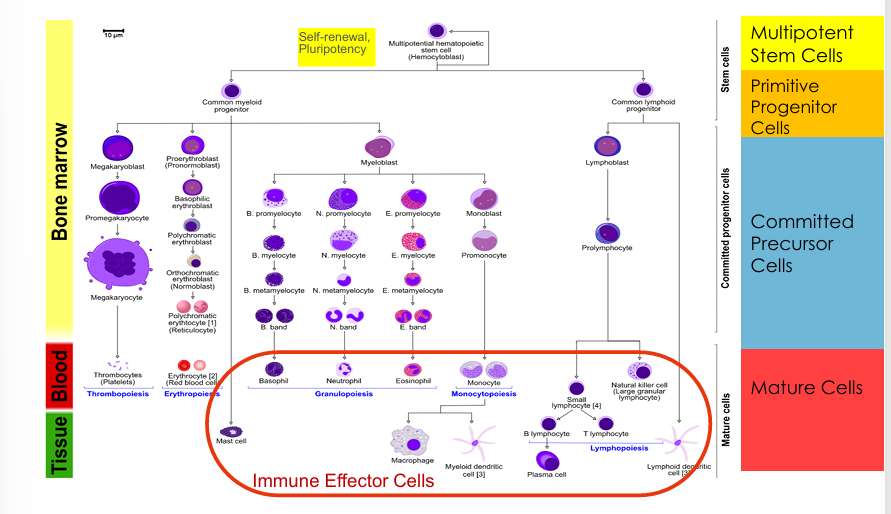
normal hematopoiesis
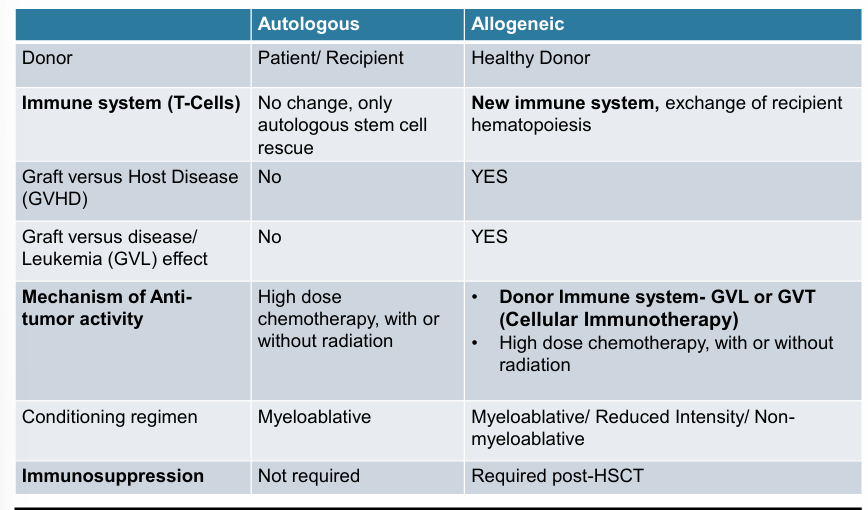
types of HCT


auto- v. allo-HCT
auto HCT steps
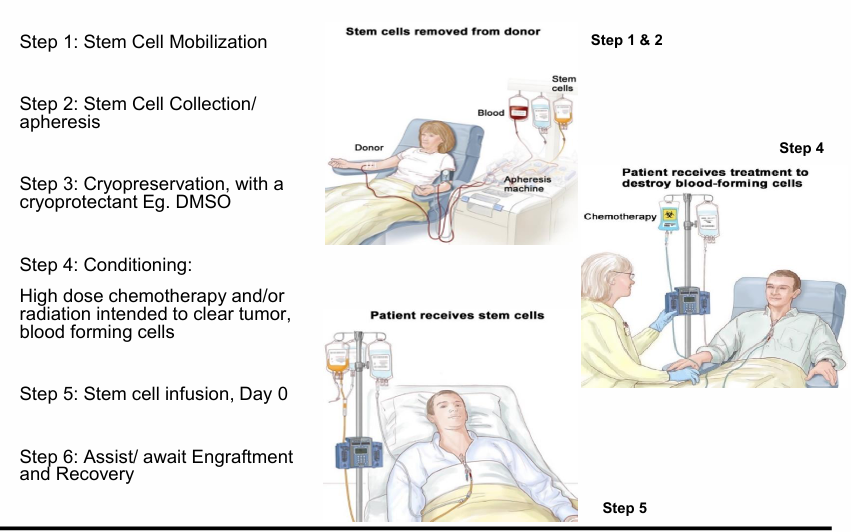
allo HCT steps
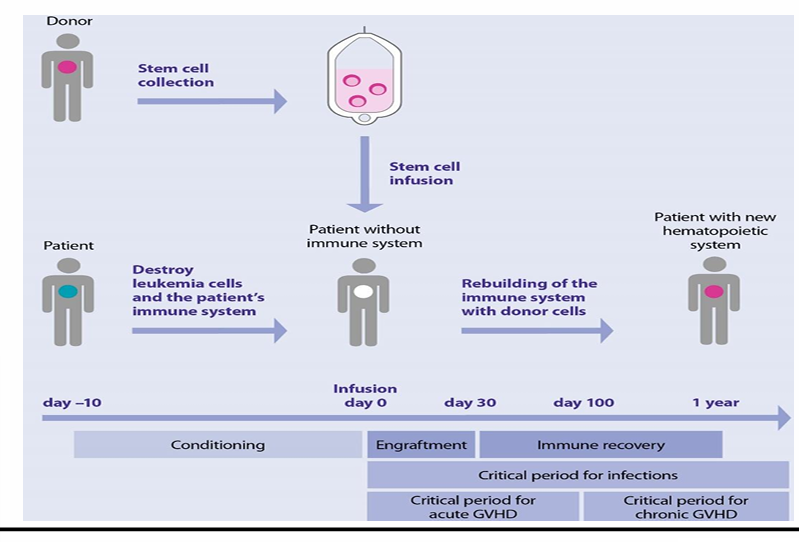
auto HCT common indications- malignant, non-malignant

allo HCT common indications

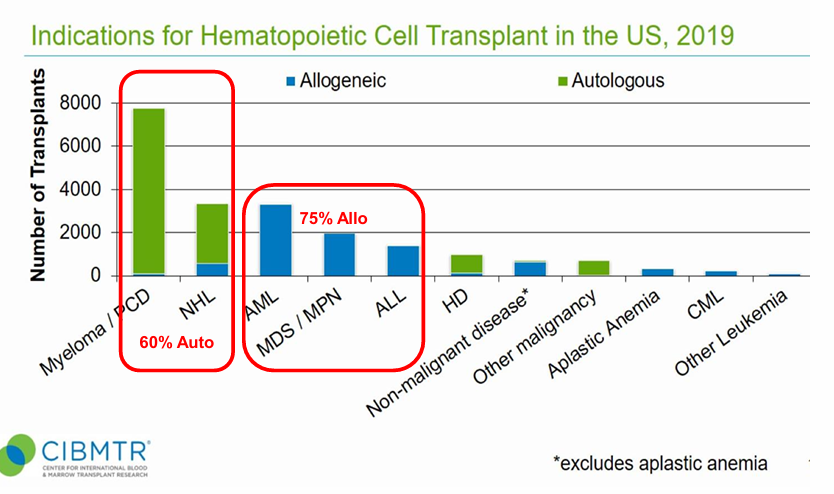
indications for HCT
pre-HCT assessment

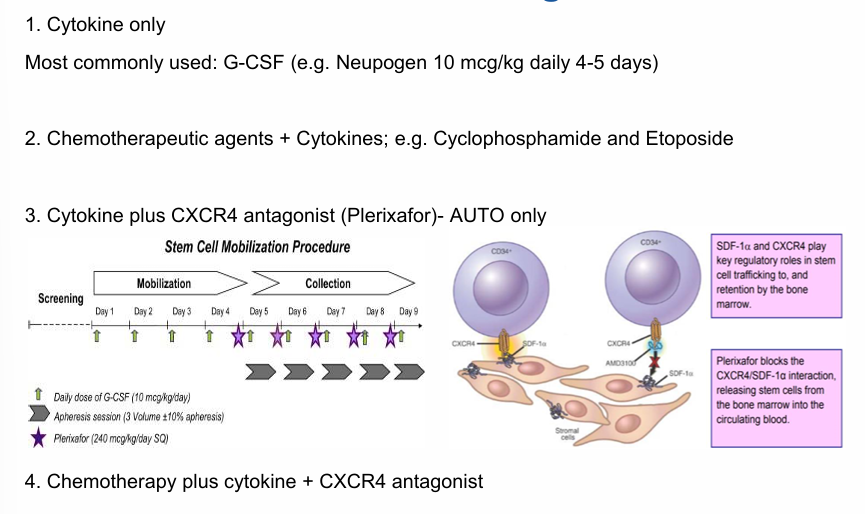
mobilization strategies
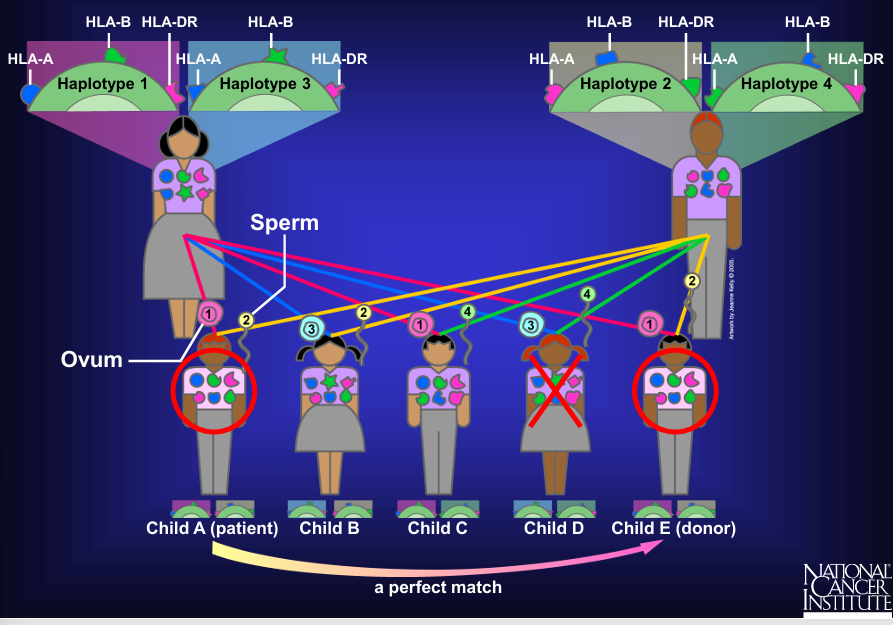
donor selection- HLA matching
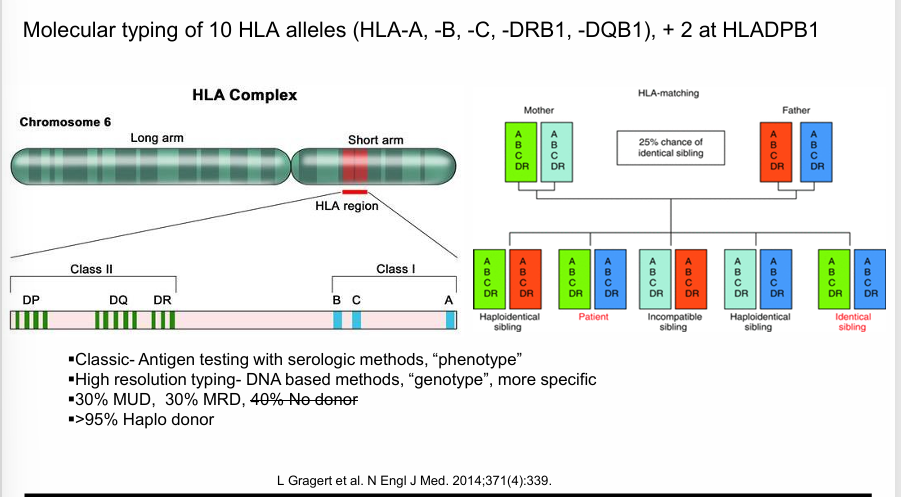
a “clinical match”
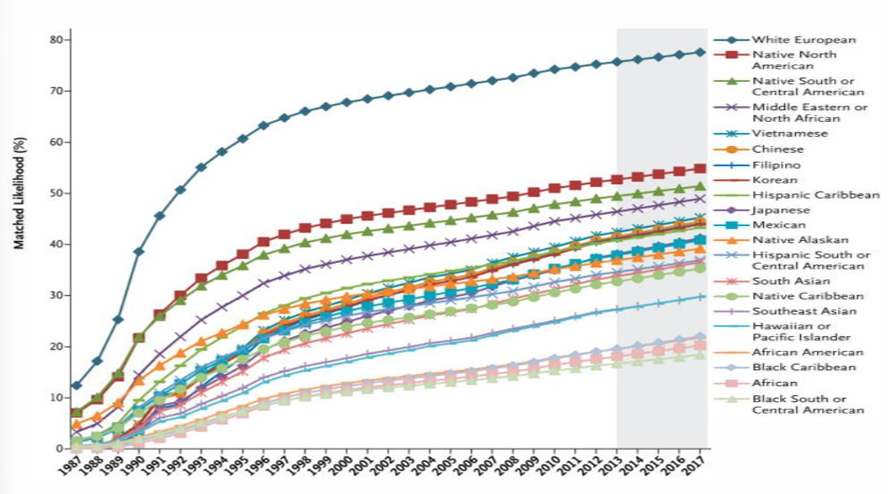
likelihood of finding 8/8 HLA match donor
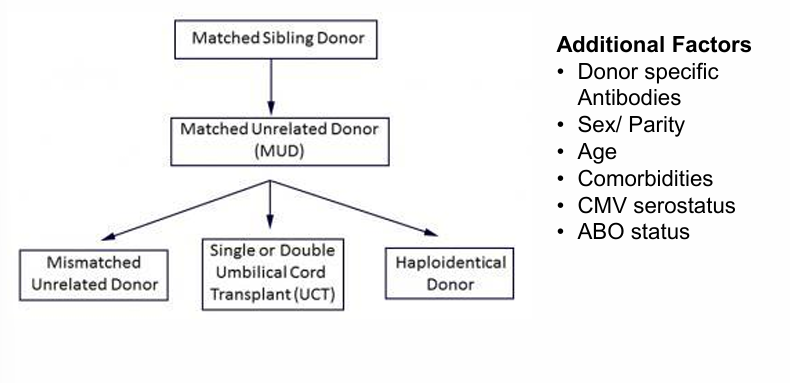
donor selection algorithm for allogeneic HCT
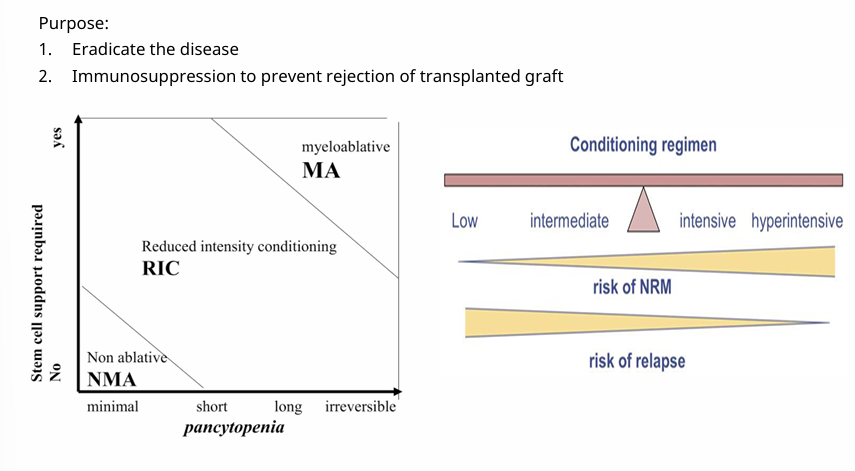
conditioning/preparative regimens
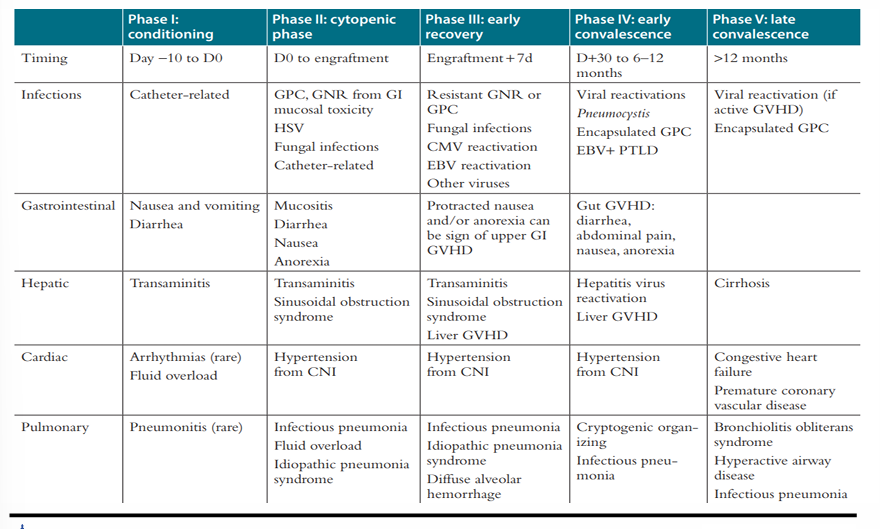
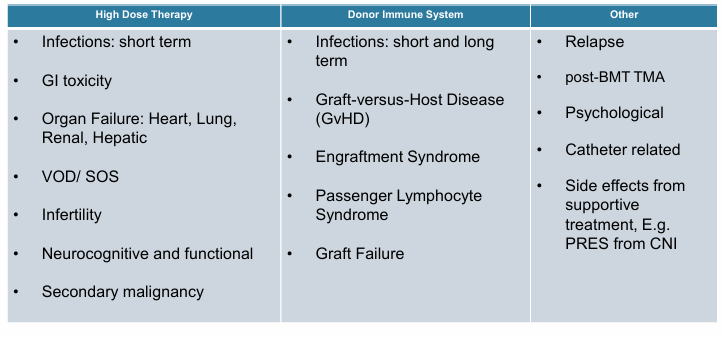
complications post-HCT

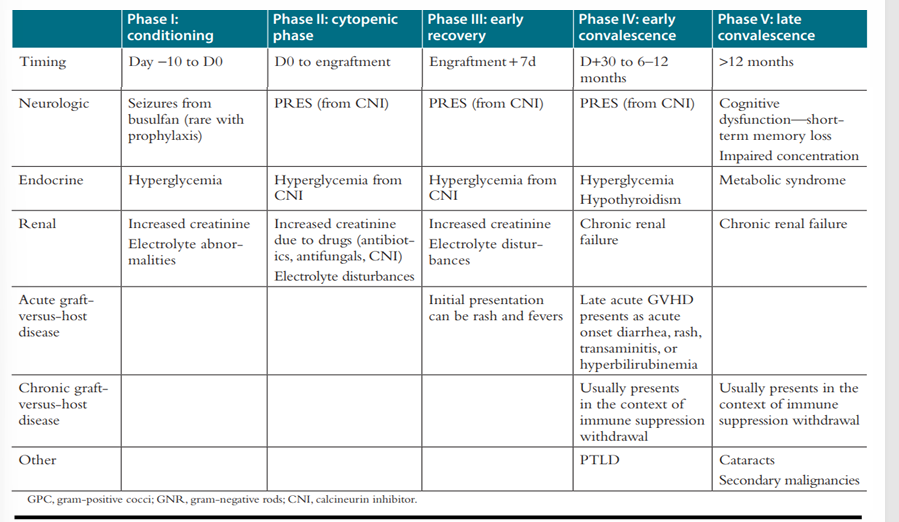
complications post-HCT
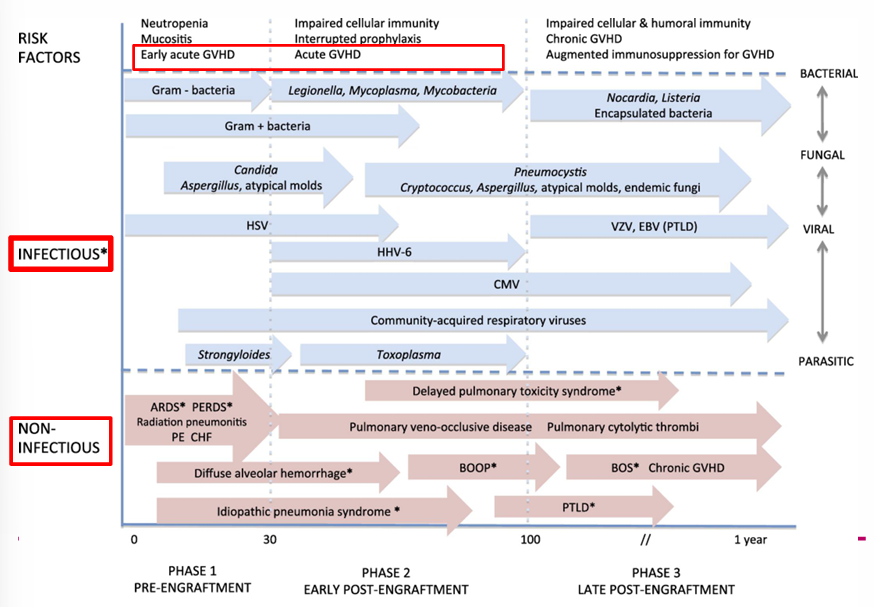
risk factors, infectious, non-infectious
supportive care- anti-microbial prophylaxis
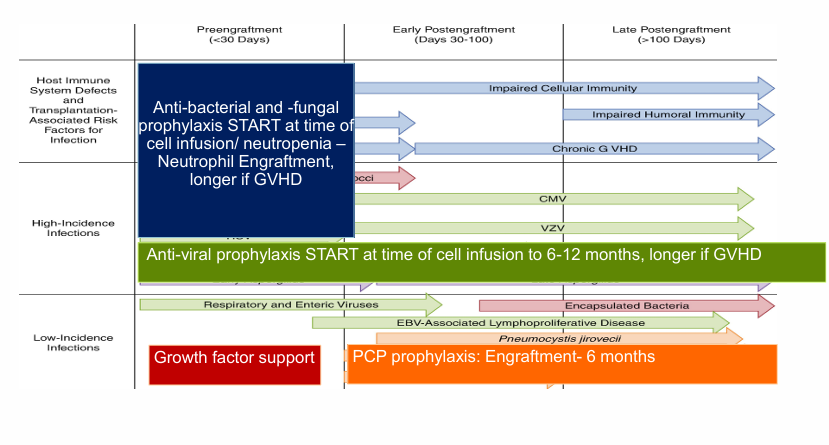
supportive care

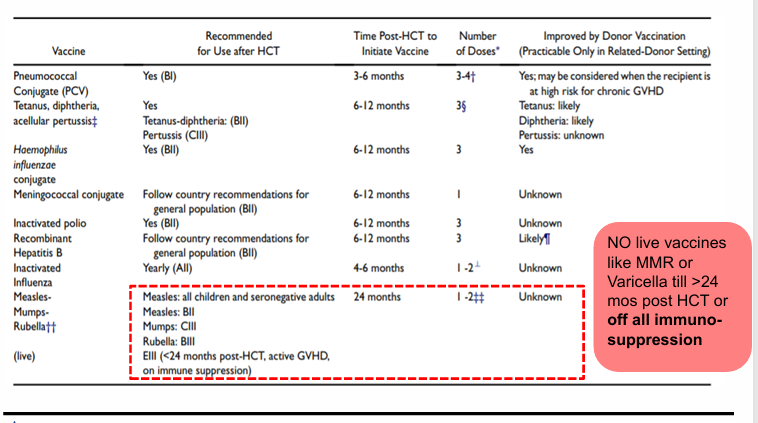
immunizations
allogeneic HCT- specific complications
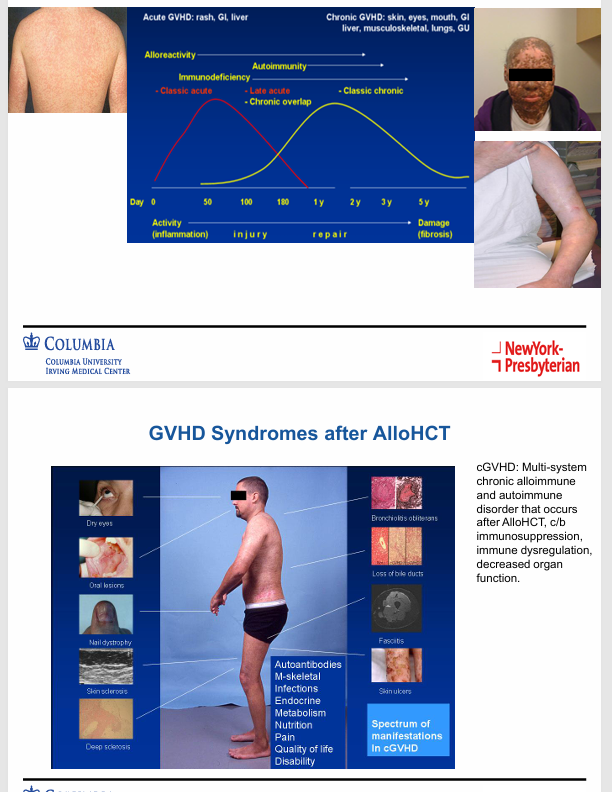
GvHD and GvT responses
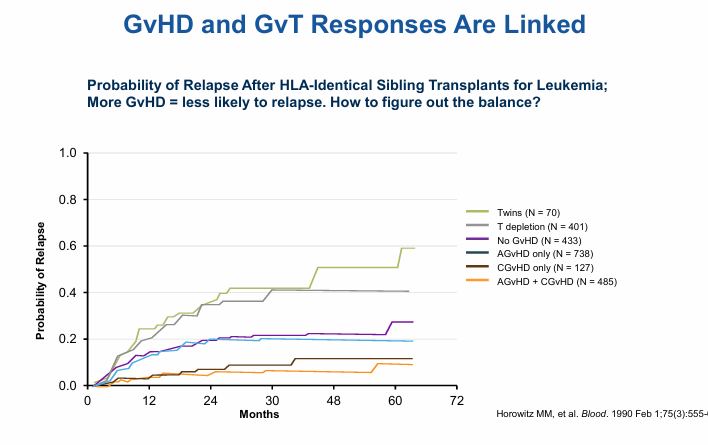
GvHD

pathogenesis of GvHD
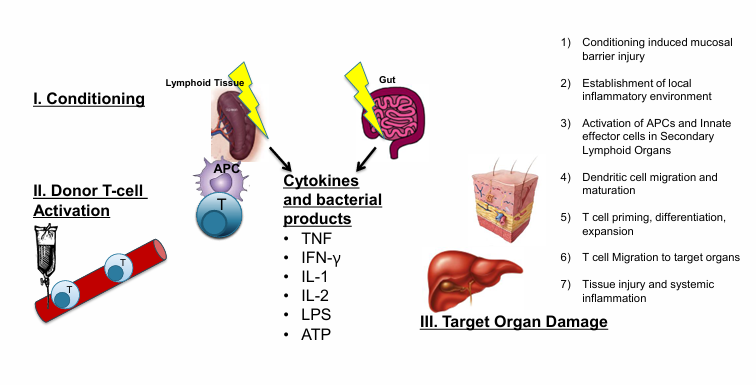
GvHD syndromes after alloHCT