smoking notes packet BSC2010 EXAM 1
1/461
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
462 Terms
biology
study of life
metabolism
-the set of processes by which organisms convert molecules from the environment into new biology molecules
-all of the reactions and energy conversions within the cell
-all of the reactions and energy conversions within the cell to harvest energy which is used to do work
evolution
change in the genetic makeup of a population overtime
adaptation
process of becoming better-suited to a particular environment
cell theory
-cells are fundamental units of life
-all organisms are made up of cells
-all cells come from pre-existing cells
population
organisms of the same species living together
communitites
populations that live together
ecosystem
consists of communities and the abiotic elements in the area
biosphere
highest level of organization (because it is not a closed system) of life consisting of all parts of the Earth and its atmosphere that support life
entropy
-second law of thermodynamics
-natural tendency for closed systems become more disordered overtime
In what environment did the first living things evolve?
underwater
photosynthesis
-set of chemical reactions that transfers the sun's energy to energy stored in chemical bonds of sugars
-anabolic
-uses light energy and carbon dioxide to produce glucose
-photons of light energy are converted into chemical energy
primary productivity
organic biomass produced from carbon dioxide
what process creates atmospheric oxygenic
photosynthesis
photosynthesis reaction
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy ---> C6H12O6 + 6 O2
When life was first created on earth, what allowed the shift from anaerobic respiration to aerobic respiration?
Great Oxidation Event--> increase in atmosphere oxygen
What facilitated the formation of the ozone layer?
increase in atmospheric oxygen
What is the function of the ozone layer?
protect organisms from harmful radiation from the sun and trap heat
What is the key distinction between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
the nucleus within eukaryotes
endosymbiosis
early eukaryotic cell engulfed but did not digest a prokaryotic cell leading to a symbiotic relationship
At the start of Earth, how were more complex organisms created?
through the process of aerobic metabolism
hypothesis
potential answer to a specific question (must lead to a testable prediction)
experiments
test hypotheses
When evaluating a hypothesis, what conclusions can experimental tests lead to?
-rule out hypothesis
-falsify hypothesis
-cannot prove a hypothesis
scientific theory
a well-tested concept that explains a wide range of observations
homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment (example: body temperature)
matter
-has a mass
-takes up space
element
basic unit of matter that cannot be subdivided into simpler substances through ordinary chemical means
6 most prominent elements
-carbon
-hydrogen
-oxygen
-nitrogen
-phosphorus
-sulfur
molecule
substance composed of more than one atom bonded together
compound
substance composed of more than one kind of element
atom
smallest subdivision of an element that retains the properties of an element
components of an atom:
-dense nucleus composed of neutrons and protons
-electrons orbit
inverse square law
the strength of the electromagnetic attraction between positive and negative charges is inversely related to the square of the distance between them
octet rule
atoms aspire to have a full valence electron shell
atomic number
number of protons an atom has
mass number
the number of protons and neutrons an atom has
isotope
two or more forms of an element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
valence electrons
-electrons in the outermost shell
-determines whether a chemical bond will form and what shape the bond will have
ionic bonds
-attractions of opposite charges
-electrons are transferred
-large differences in electronegativity
-strong bond
ion
has fewer or more electrons than its neutral state
cation
positively charged ions
anion
negatively charged ions
covalent bonds
-involve sharing of electron pairs
-between different elements or the same element
-strong bond
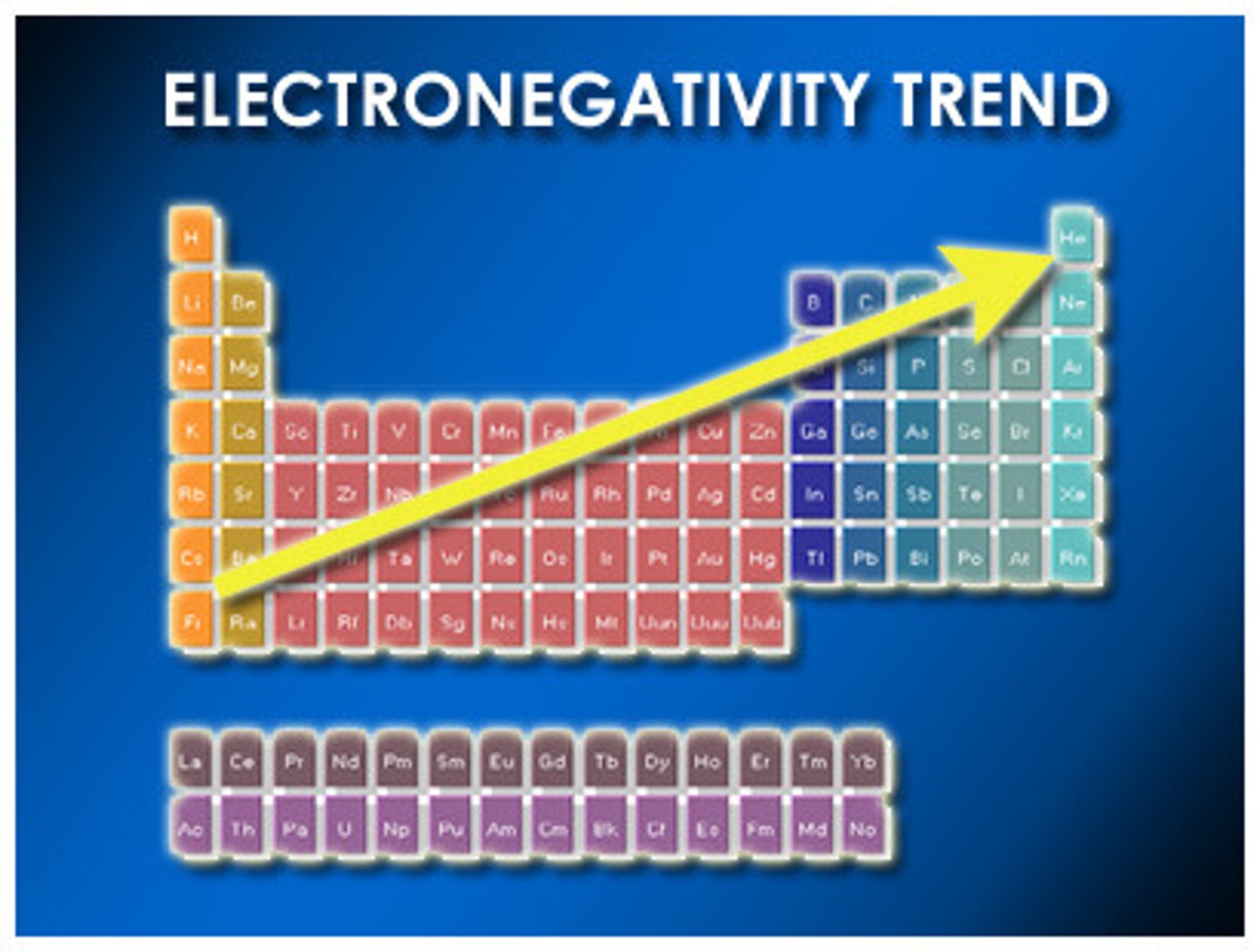
electronegativity
measure of an atom's attraction for electrons
polar covalent bond
-electrons are not equally shared between two atoms
-partial charges (dipole)
nonpolar covalent bonds
-electrons are equally shared between two atoms because of similar electronegatvities
hydrogen bonds
-positively charged hydrogen atom is attracted to an electronegative oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine
-weak individually but strong collectively strong
-can happen within a molecule or between molecules
van der waals interactions
-induced electrical interactions that create partial dipoles when atoms are very close to each other (random movement of electron cloud)
-nonpolar substances
functional group: hydroxyl group
-OH
-polar
-alcohol
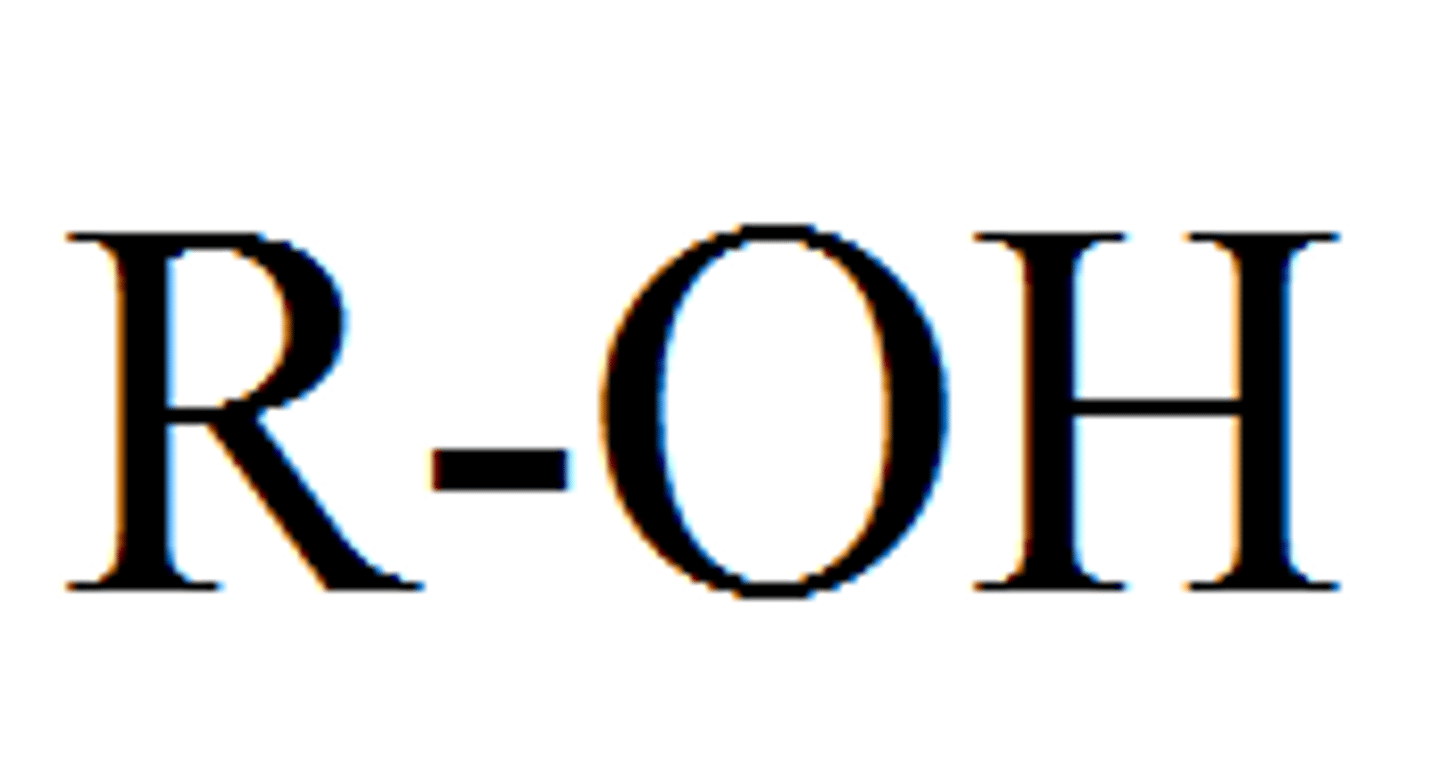
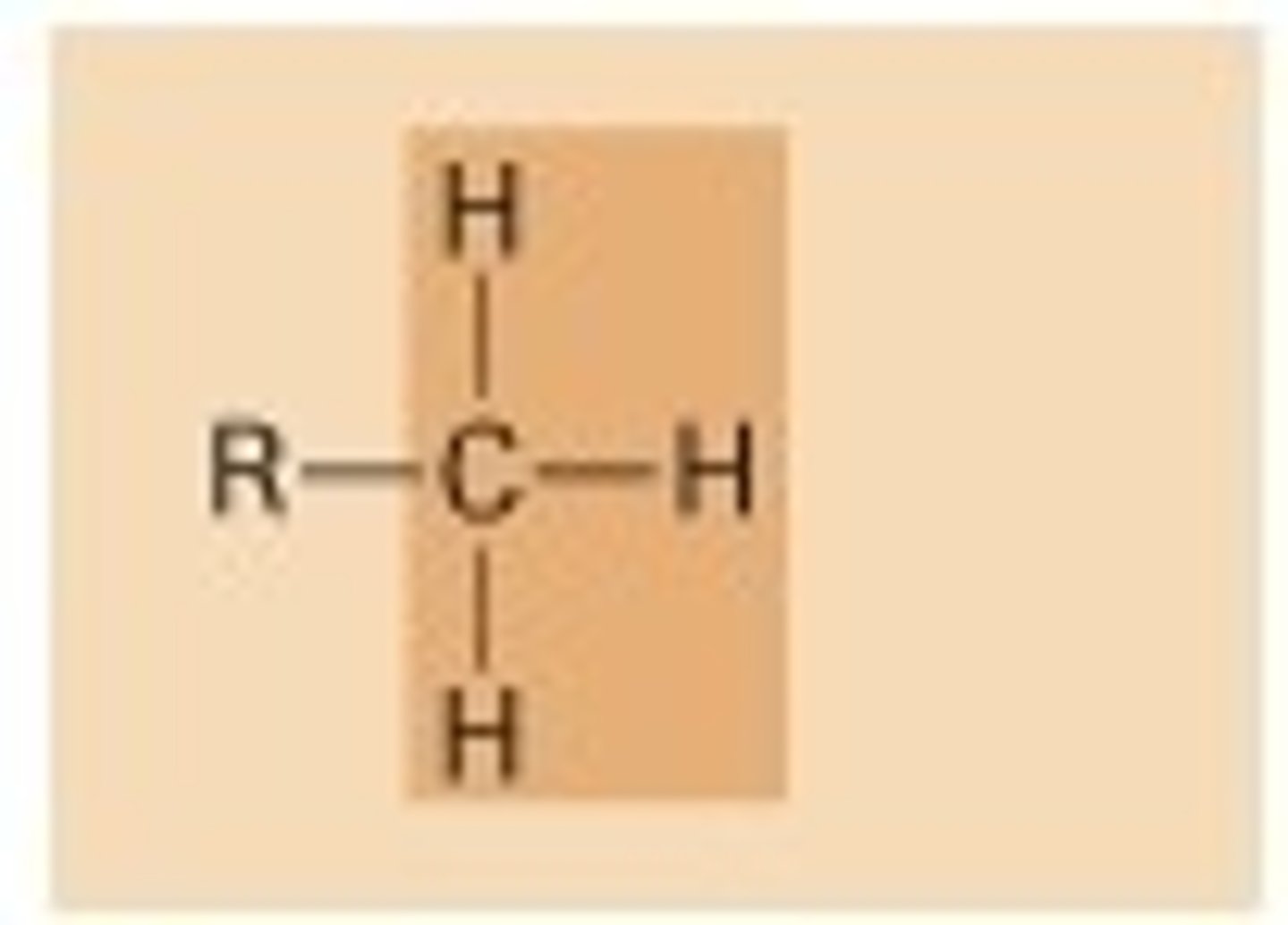
functional group: methyl group
-carbon bonded to three hydrogens
-alkyls
-nonpolar
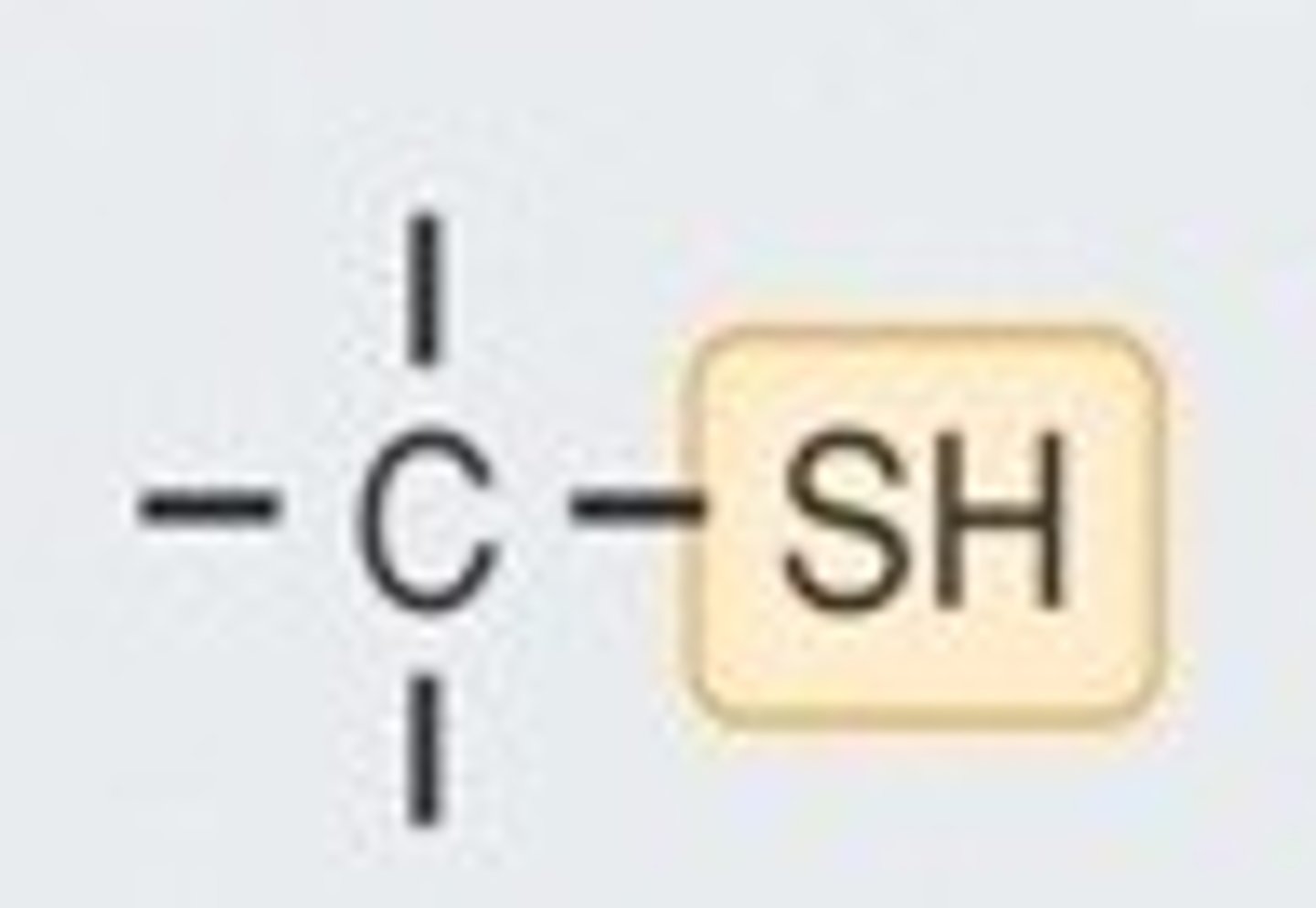
functional group: sulfhydryl group
-thiols
-sulfur
-polar
-two sulfhydryls interacting forms a disulfide bridge
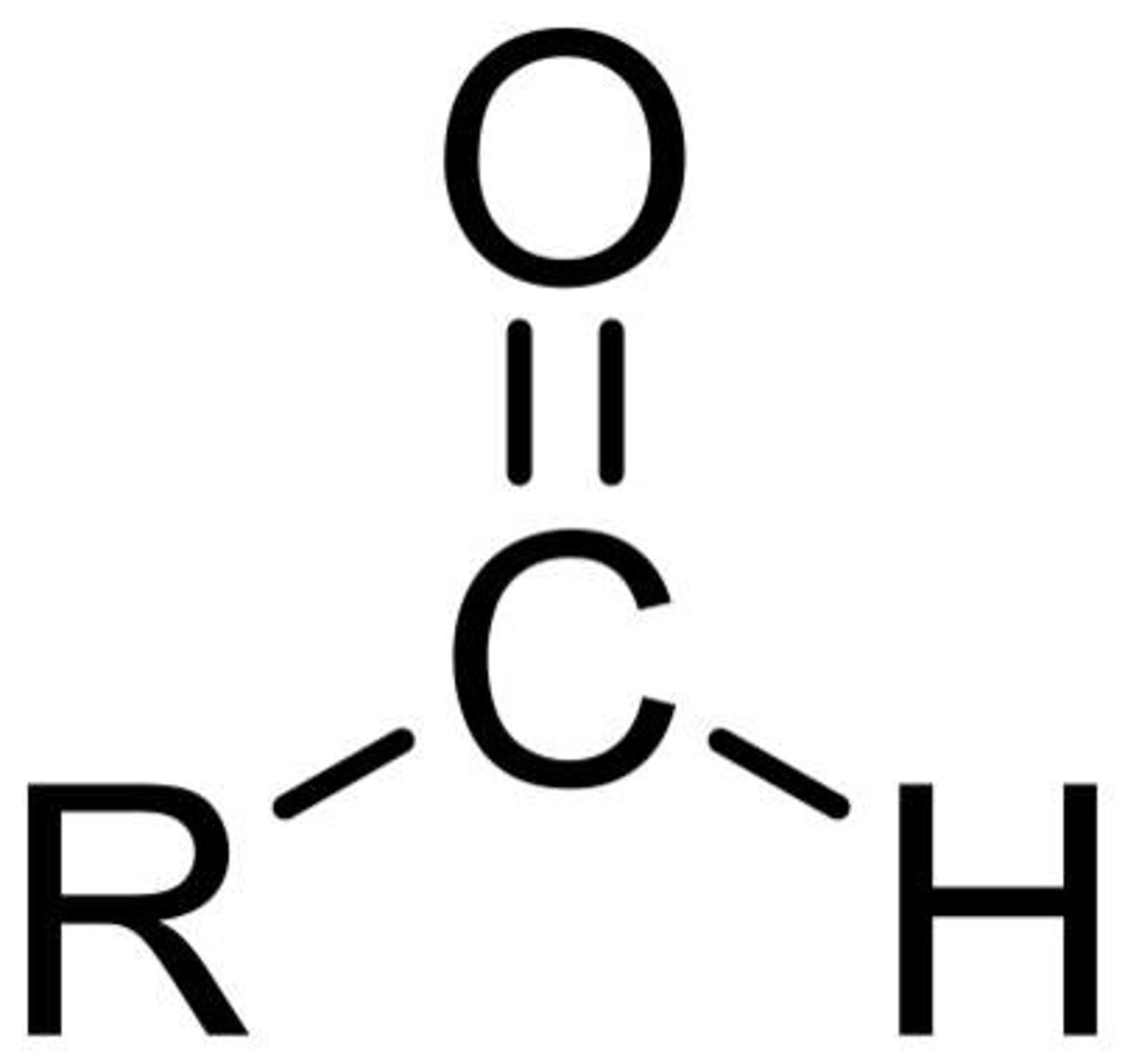
functional group: aldehyde group
-carbonyl group
-highly reactive
-polar
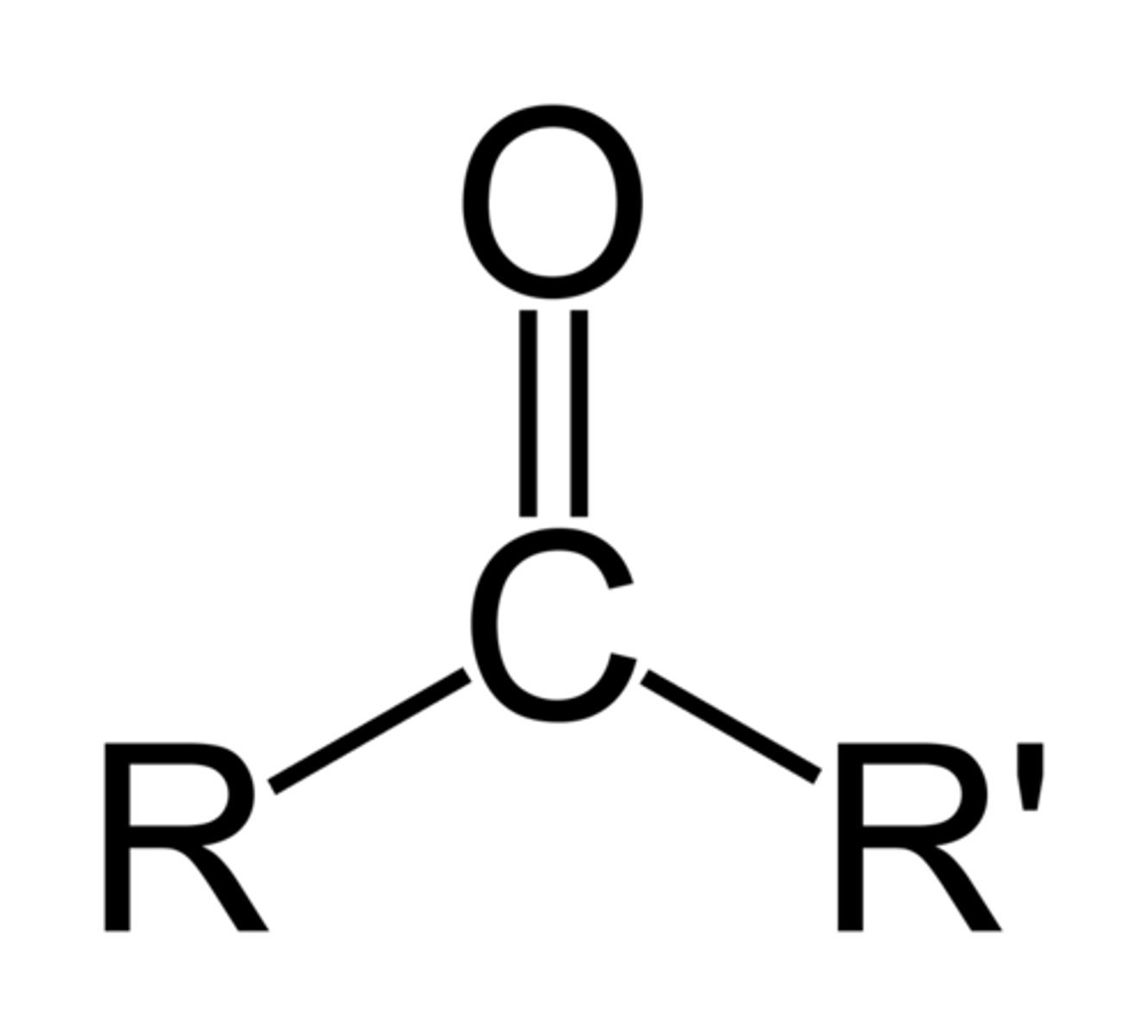
functional group: keto groups
-ketones
-carbonyl group in middle of carbon chain
-polar
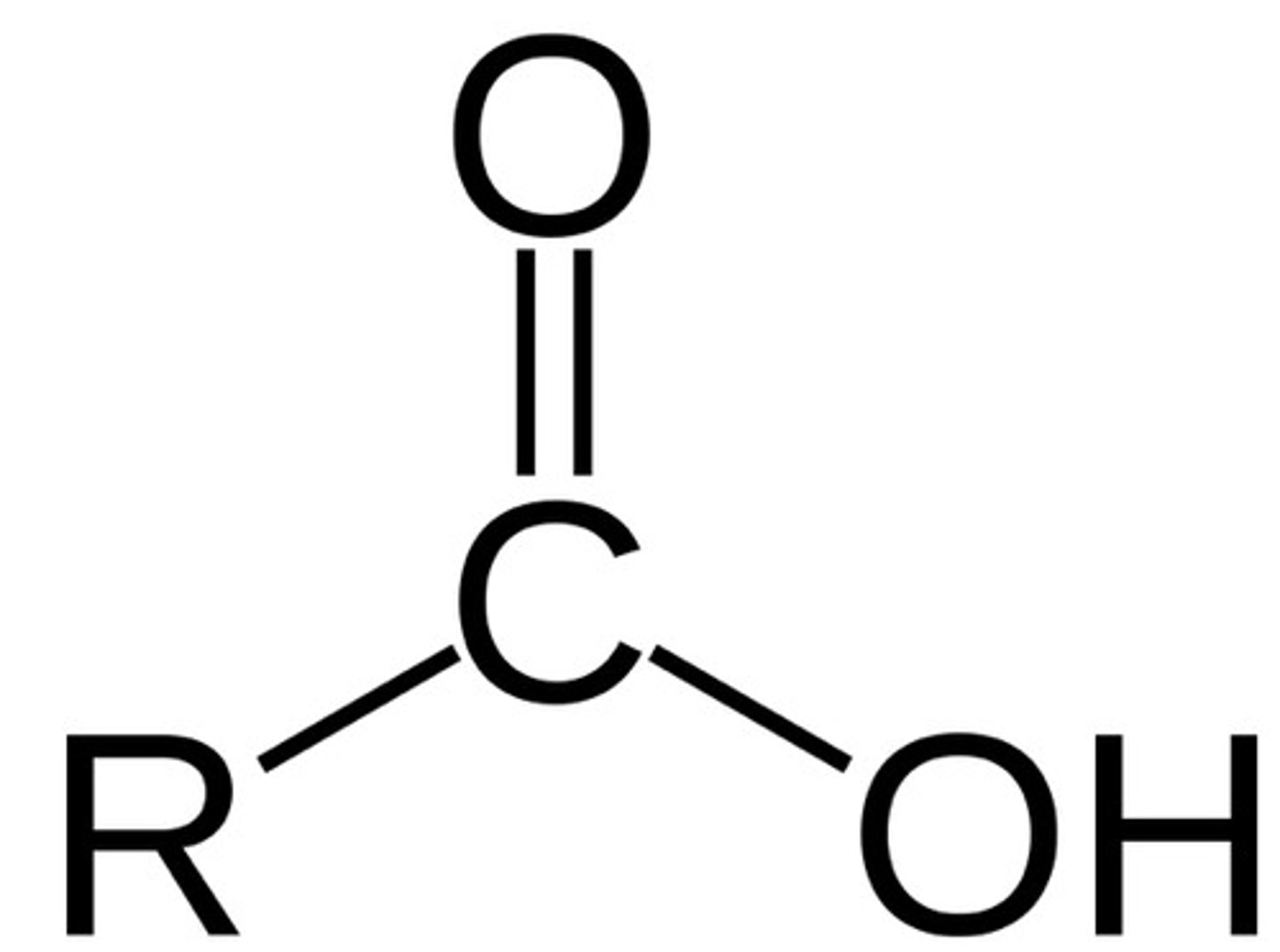
functional group: carboxyl groups
-end of molecules
-carbon double bonded to an oxygen and single bonded to a hydroxyl group (hydrogen is easily removed)
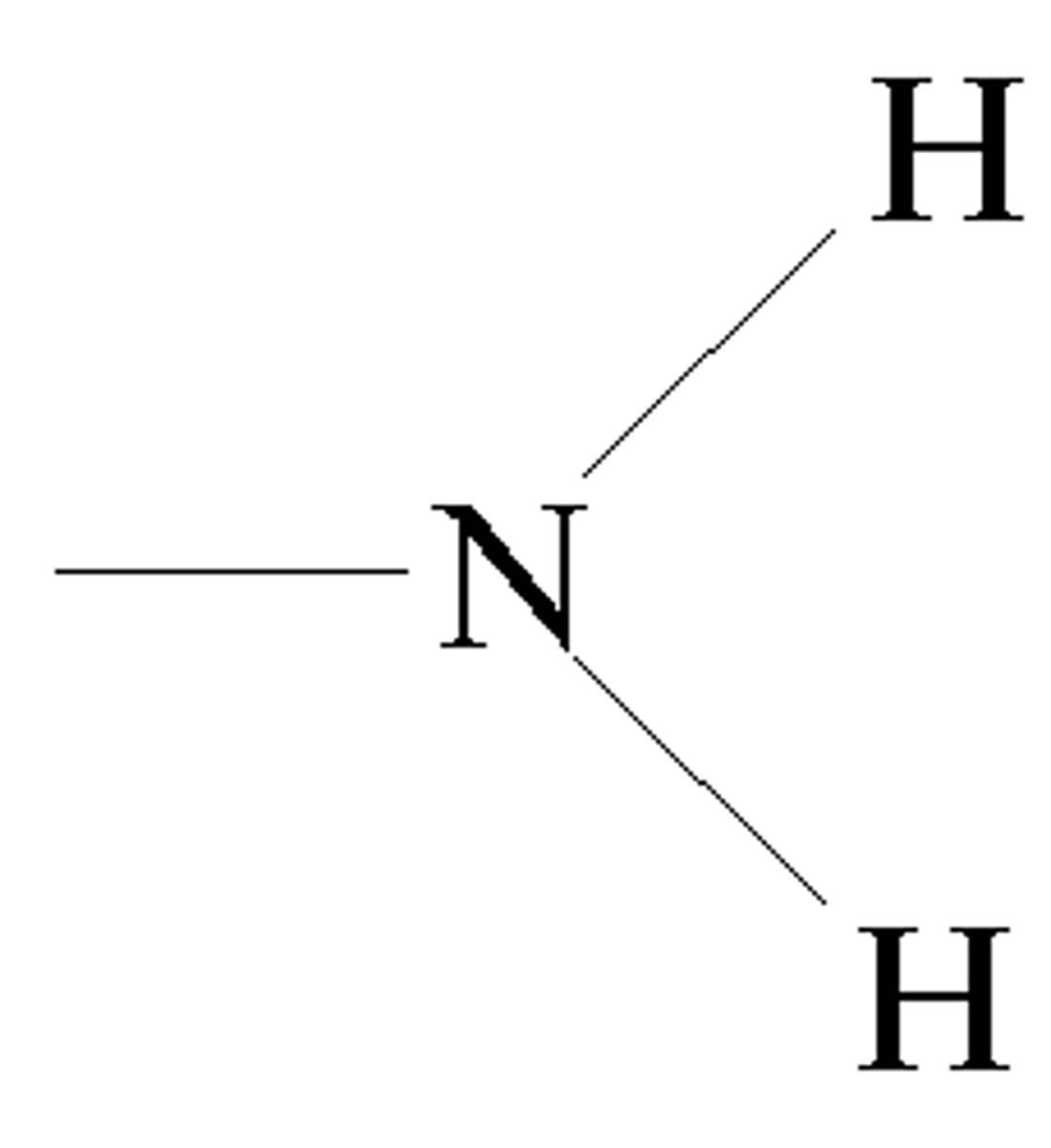
functional group: amino groups
-nitrogen bonded to two hydrogens
-easily accept proton (act like base)
-charged
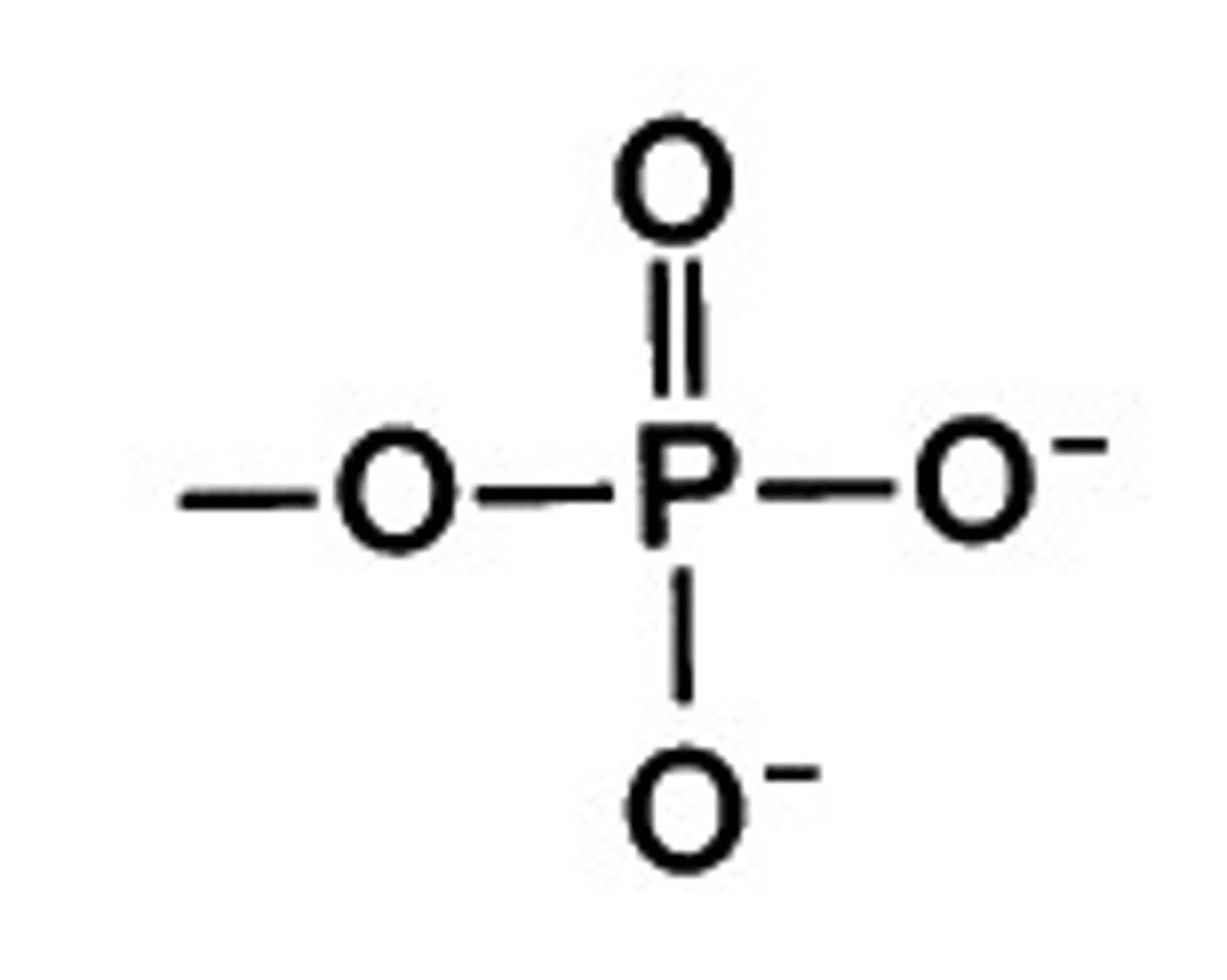
functional group: phosphate groups
-functions-->energy transfer reactions, protein structure, and cell membranes
-ATP
What percent of your body does water make up?
70%
properties of water:
-polar
-high specific heat (takes a lot of energy to change temperature)
-homeostasis
-high heat of vaporization
-cohesion & adhesion
-solvent
cohesion
tendency of water molecules to stick together
adhesion
tendency of water molecules to stick to other polar substances
evapotranspiration
pulls water molecules from the bottom of the plant closer to the top (capillary action)
hydrophilic substances
-love water
-easily dissolve in it
-polar molecules & ions
hydrophobic substances
-afraid of water
-do not dissolve in it
-nonpolar molecules
chemical reaction
atoms combine or change bonding partners because they have enough energy
energy
capacity to do work
kinetic energy
-energy of motion
-higher temperature=greater KE
potential energy
-stored energy that has the potential to become KE
-exists in bonds of atoms
thermodynamics
study of energy transformation
first law of thermodynamics
energy can be transferred or transformed, but it can neither be created nor destroyed
second law of thermodynamics
entropy (disorder) in the universe is always increasing
bond enthalpy
amount of energy required to break a bond
enthalpy of reaction
difference between the PE of the products and the PE of the reactant bonds
entropy (S)
-degree of disorder or randomness in a system
-negative entropy=increased order
-positive entropy=decreased order
Gibbs Free Energy
-amount of energy available to initiate a chemical process under constant pressure and temperature
-BASED ON entropy and enthalpy
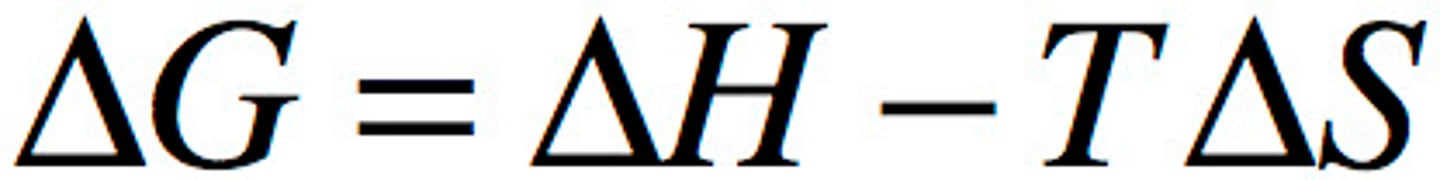
exergonic
-release energy
-decrease in delta G (negative)
-spontaneous (occur without addition of energy)
-negative delta H
-positive delta S
endergonic
-require energy
-increase in delta G (positive)
-positive delta H
-negative delta S
What determines whether a reaction is endergonic or exergonic?
delta G (free energy)
metabolic pathway
-enzyme mediated process by which a precursor molecule is converted into a final product
-product of one reaction feeds into the next
anabolic pathway
-construction of complex molecules from simpler ones
-require energy
-photosynthesis
catabolic pathway
-involve the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler subunits
-release energy
-cellular respiration
Does breaking bonds require or release energy?
require
Does forming bonds require or release energy?
release
Do complex molecules have weaker or stronger bonds?
weaker
Do simple molecules have weaker or stronger bonds?
strong
polymers
long molecules that consist of repeated monomers
monomers
building blocks of macromolecules
condensation reactions/dehydration synthesis
-water molecule is released and a covalent bond forms in order to build a polymer
-endergonic
-anabolic
hydrolysis reaction
a water molecule is added in order to break the bond between monomers
macromolecules
larger molecules made up of smaller molecules
four major carbon-based macromolecules necessary for life:
-carbohydrates
-lipids
-proteins
-nucleic acids
main components of macromolecules:
-carbon
-hydrogen
-nitrogen
-phosphorus
What is the most abundant macromolecule in the body?
proteins
Main components of proteins:
-carbon
-nitrogen
main components of carbohydrates and lipids:
-carbon
-phospholipids have a small amount of phosphorus
main components of nucleic acids:
-carbon
-nitrogen
-phosphorus
How are polymers built?
condensation reactions
with the exception of lipids what are all macromolecules?
polymers
carbohydrates: monomer and bond
-monosaccharides
-glycosidic linkages
proteins: monomer and bond
-amino acids
-peptide bonds