Exam 3 - Chapter 30
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Epidemiology
Study of the occurrence, distribution, and determinants of health and disease in a population
Incidence
Number of new cases of the disease in a given period of time
Prevalence
Total number of new and existing cases in a population in a given time
Endemic disease
Disease that is constantly present, usually at low number in a population
Epidemic
Occurrence of a disease in unusually high numbers in a localized population
Pandemic
A widespread, usually worldwide epidemic
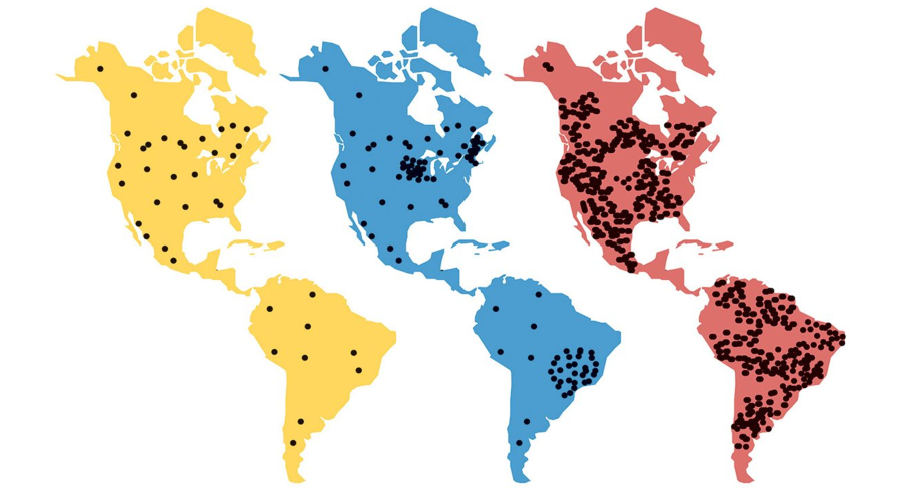
What does the yellow image represent?
Endemic disease
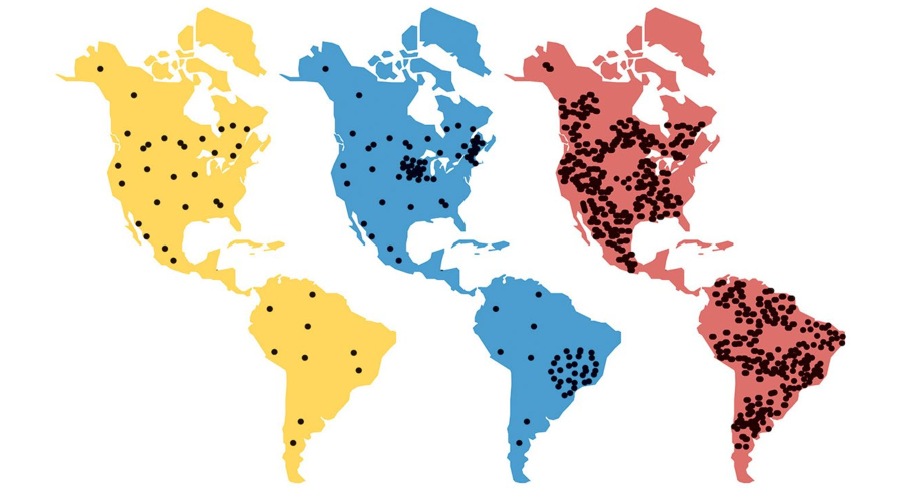
What does the blue image represent?
Epidemic disease
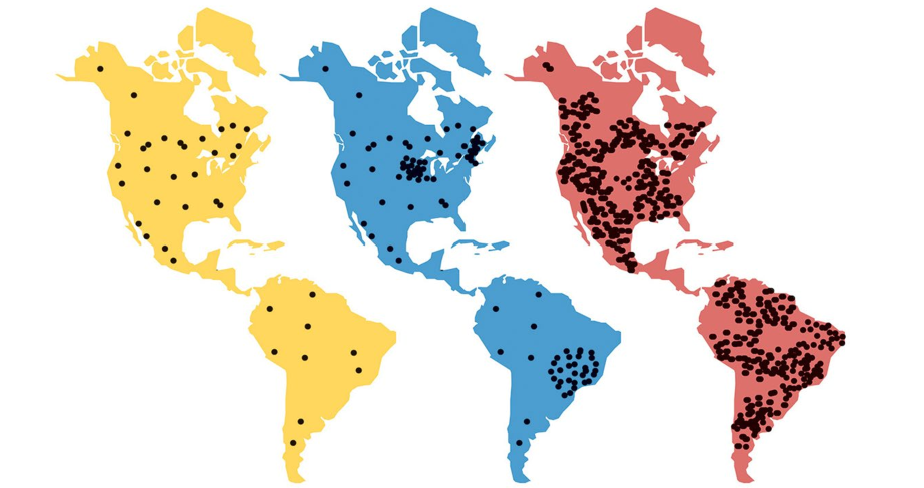
What does the pink image represent?
Pandemic disease
Mortality
Incidence of death in a population
Morbidity
Incidence of disease, including fatal and non fatal diseases
Disability-Adjusted Life Year (DALY)
Quantitatively measures disease burden in terms of lost years due to the disease, disability due to disease, and premature death
Direct host-to-host transmission
Infected individual transmits a disease directly to a susceptible host without the assistance of an intermediary
Examples of directly transmitted diseases
Flu
Common cold
STDs
Ringworm
Indirect host-to-host transmission
Occurs when transmission is facilitated by a living or nonliving agent
Vectors
Living agents that can transmit disease
Fomites
Nonliving agents that can transmit disease
Reservoirs
Sites in which infectious agents remain viable and from which individuals can become infected
Carriers
Pathogen-infected individuals showing no signs of clinical disease
Zoonosis
Disease that primarily infects animals but is occasionally transmitted to humans
R0
The average number of people who will contract a contagious disease from one person with that disease
What affect does herd immunity have on disease transmission
Decreases the R0 of the disease in that population (blocks transmission to immune people)
Pathogen eradication
Remove all of a pathogen from any reservoir
Examples of pathgoen eradication
Smallpox
Polio
Leprosy (potentially)
What impact did the introduction of a measles vaccine have?
Eliminated measles as a common childhood infection
Emergent
Diseases that suddenly become prevalent
Reemerging diseases
Diseases that have become prevalent after having been under control
Worldwide distribution of diseases…
changes rapidly
Emergence factors
Human demographics and behavior
Technology and industry
Economic development and land use
International travel and commerce
Microbial adaptation and change
Breakdown of public health measures
Abnormal natural occurrences
Biological weapons
Organisms or toxins that are:
easy to produce and deliver
safe for use by the offensive soldiers
able to incapacitate or kill individuals under attack in a consistent and reproducible manner