Absorption Versus Variable Costing
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards on Absorption and Variable Costing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Product Costs
Costs that are a necessary and integral part of producing the finished product; they do not become expenses until the company sells the finished goods inventory.
Period Costs
Costs that are matched with the revenue of a specific time period rather than included as part of the cost of a salable product; includes selling and administrative expenses and companies deduct them from revenues in the period in which they are incurred
Absorption Costing
A costing method that includes all manufacturing costs (direct materials, direct labor, and both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead) in the cost of a unit of product; also called Full Costing and Conventional Costing. Treats fixed manufacturing overhead as a product cost.
When units produced exceed units sold, net income under this costing method will show a higher net income than variable costing. Companies must report financial information using GAAP, which requires this for the costing of inventory for external reporting purposes.
Variable Costing
A costing method that includes only variable manufacturing costs (direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead) in the cost of a unit of product; also called Direct Costing. Treats fixed manufacturing overhead as a period cost.
Net income computed under this costing method is unaffected by changes in production levels; is consistent with cost-volume-profit analysis and incremental analysis. Net income computed under variable costing is closely tied to changes in sales and provides a more realistic assessment of the company’s success or failure. The presentation of fixed and variabe cost components on the variable costing income statement makes it easier to identify these costs and understand their effect on the company’s results.
Selling and Administrative Expenses
Under both absorption and variable costing, these are period costs.
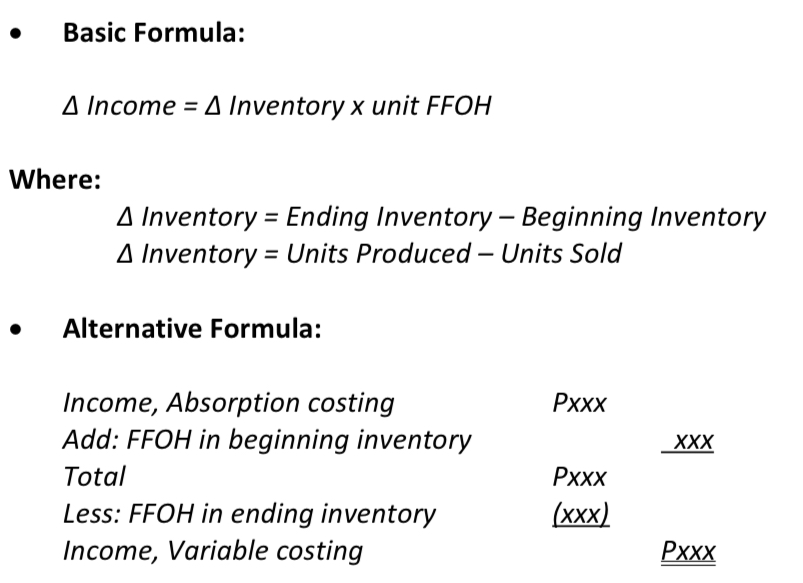
∆ Inventory
Ending Inventory - Beginning Inventory or Units Produced - Units Sold
∆ Income
∆ Inventory x unit FFOH or Income, Absorption costing + FFOH Beginning inventory - FFOH ending inventory