Biology: Cell Systems, Homeostasis, and Respiration Key Concepts
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
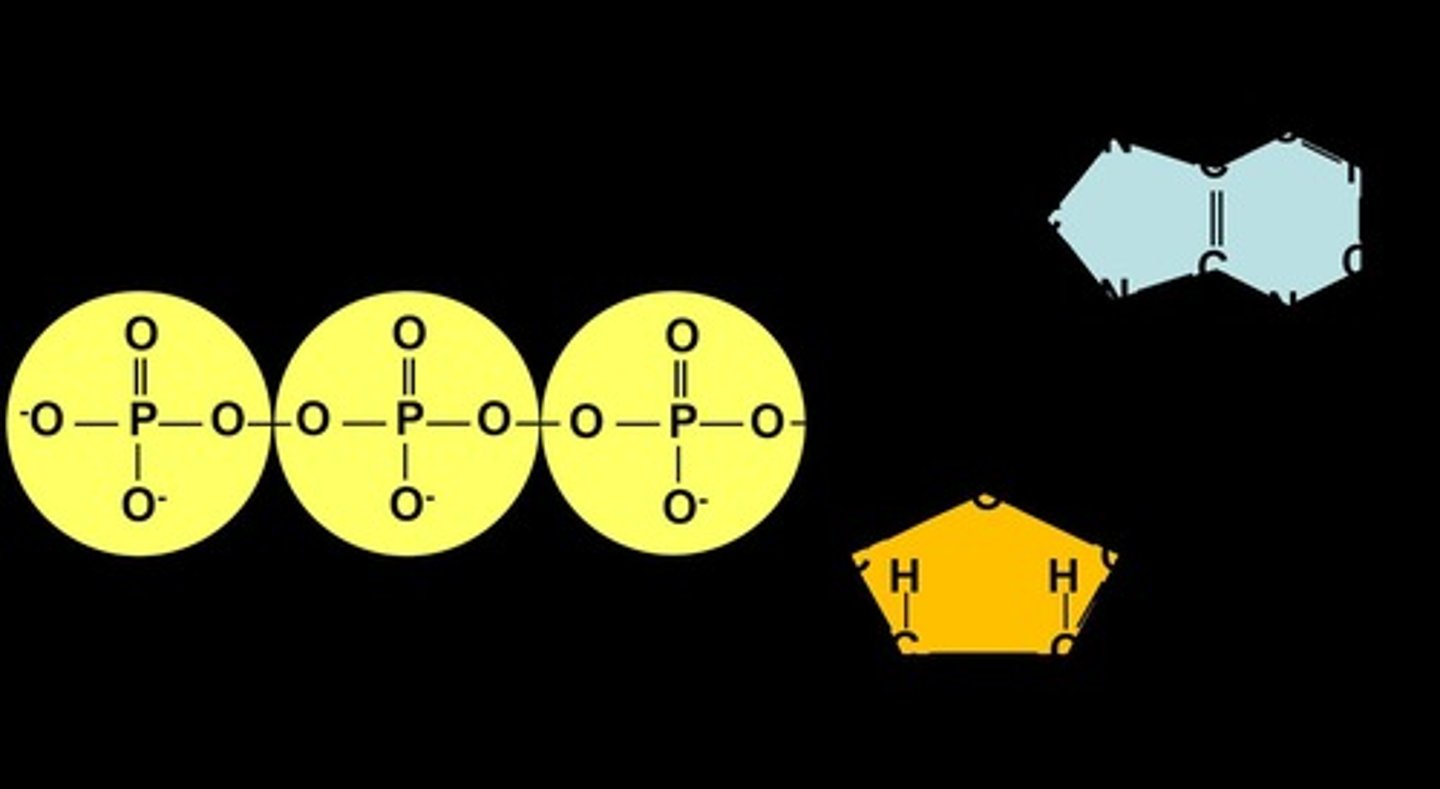
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate
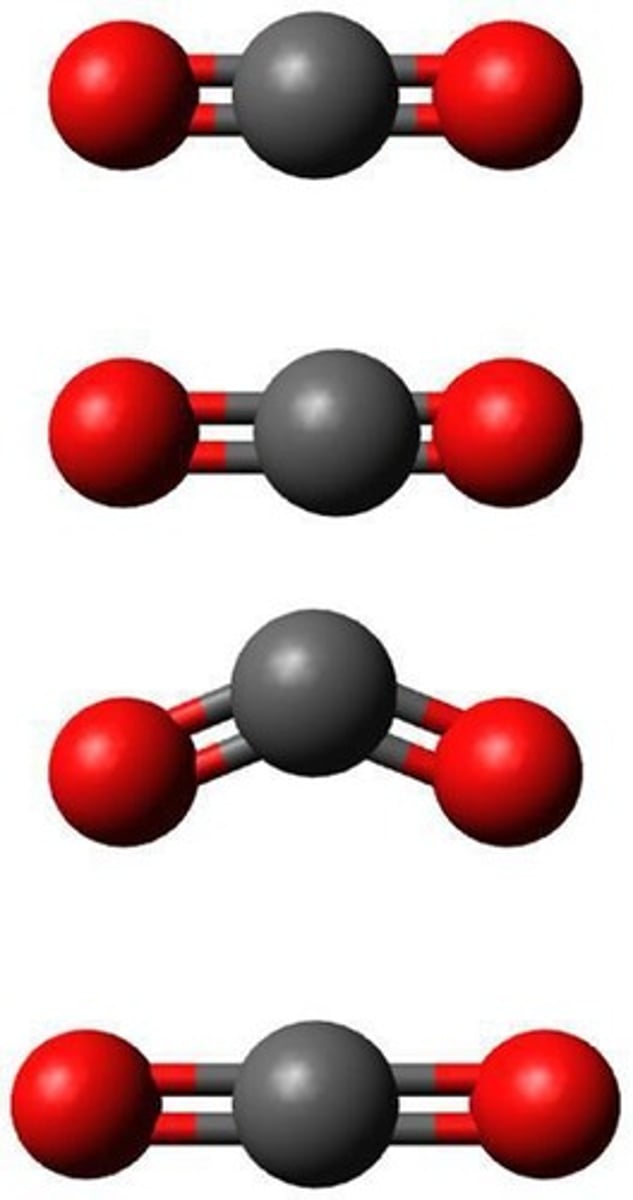
Carbon Dioxide
Gas molecule containing one carbon and two oxygens
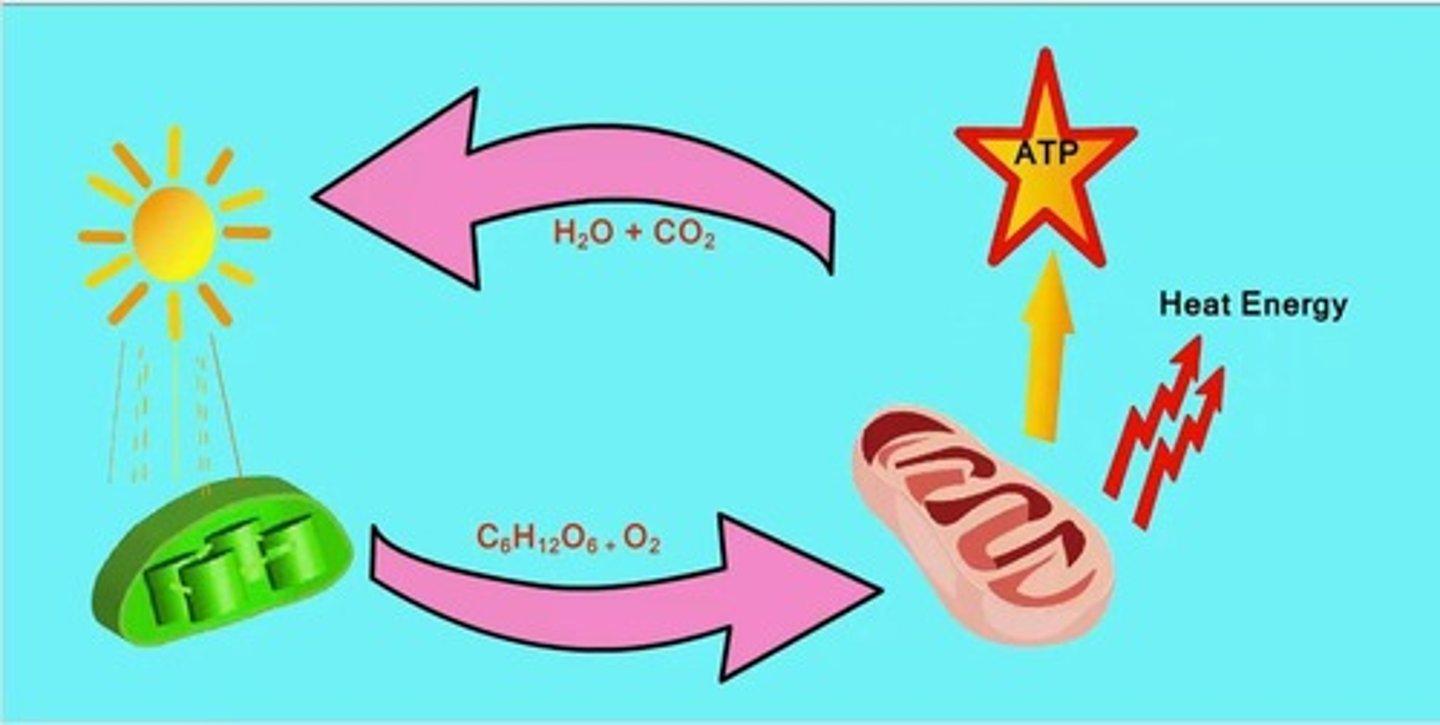
Cellular Respiration
Process of converting glucose into ATP
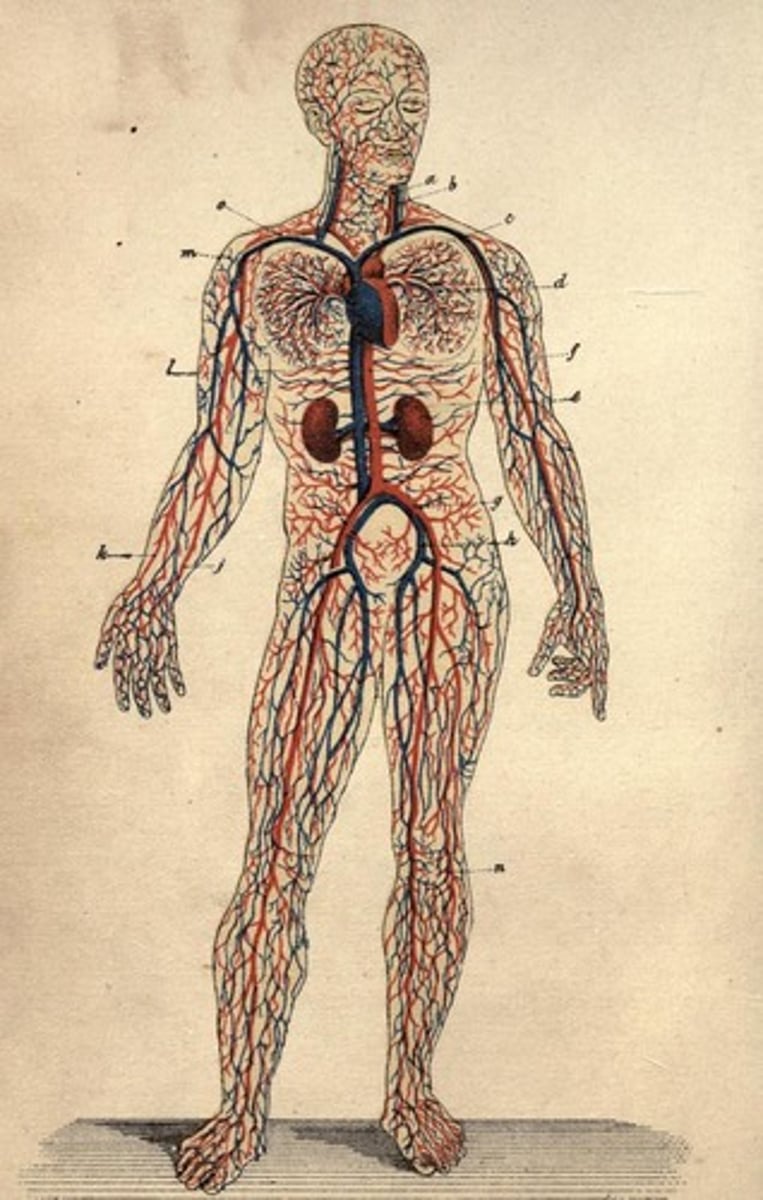
Circulatory System
Body system responsible for transport of nutrients and waste
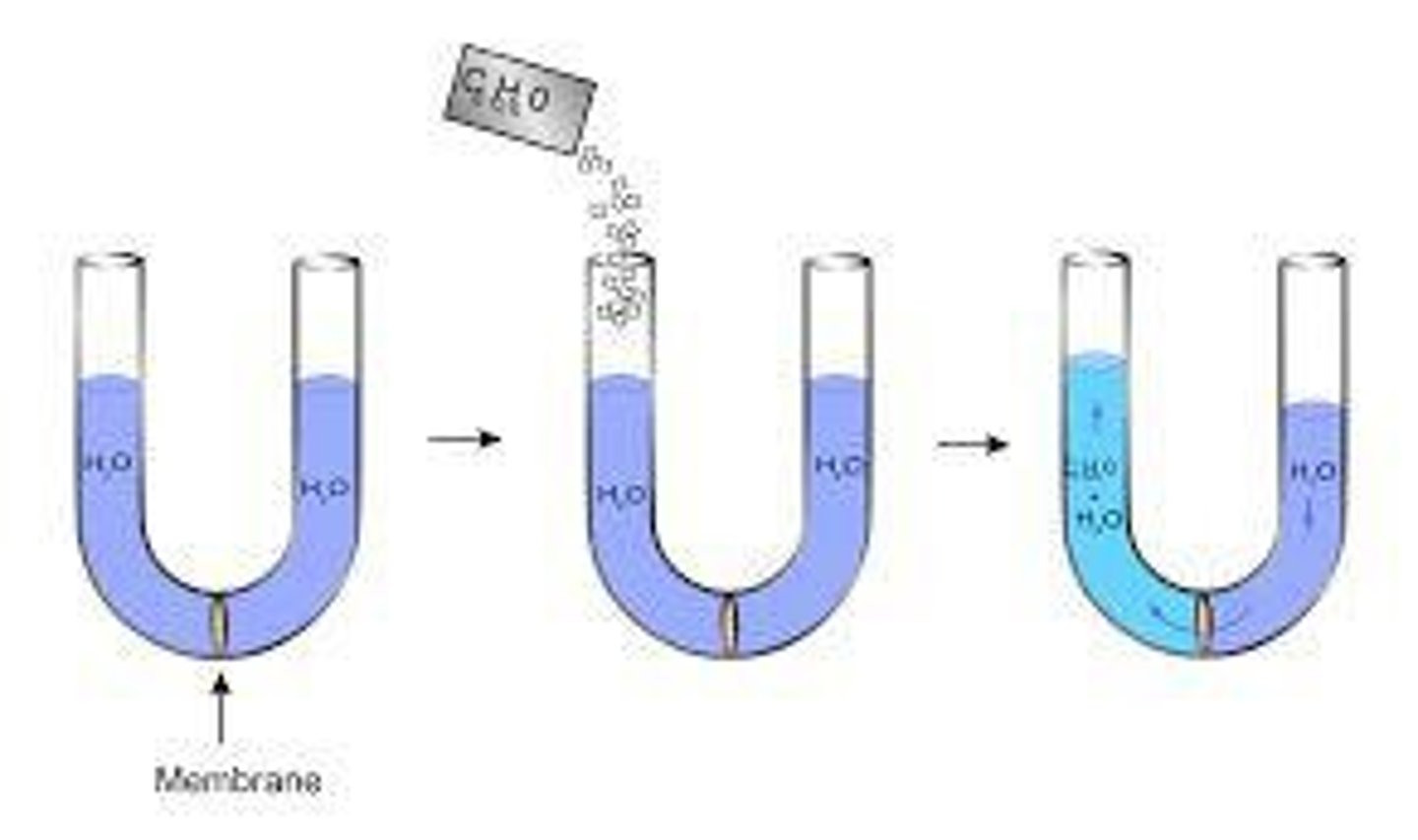
Diffusion
Movement of substances based on concentration
Dynamic Equilibrium
Maintaining overall balance
Excretory System
System responsible for water balance
Feedback Loop
Response to a stimulus that attempts to return a system to normal
Gas Exchange
Inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide
Glucose
Sugar
Homeostasis
The maintenance of stable internal conditions
Hypertonic
A solution with a higher concentration of solutes compared to another solution
Hypotonic
A solution with a lower concentration of solutes compared to another solution
Isotonic
A solution with an equal concentration of solutes compared to another solution
Metabolic Process
Biochemical reactions that occur within a living organism
Mitochondria
Organelles that produce ATP through cellular respiration
Nervous System
System responsible for transmitting signals between different parts of the body
Osmoregulation
The process of maintaining water balance in the body
Osmosis
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
Oxygen
A gas essential for cellular respiration
Respiratory System
System responsible for the exchange of gases in the body

Thermoregulation
The process of maintaining an optimal body temperature
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
A chemical process whereby the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and the bonds in new compounds are formed resulting in a net transfer of energy.
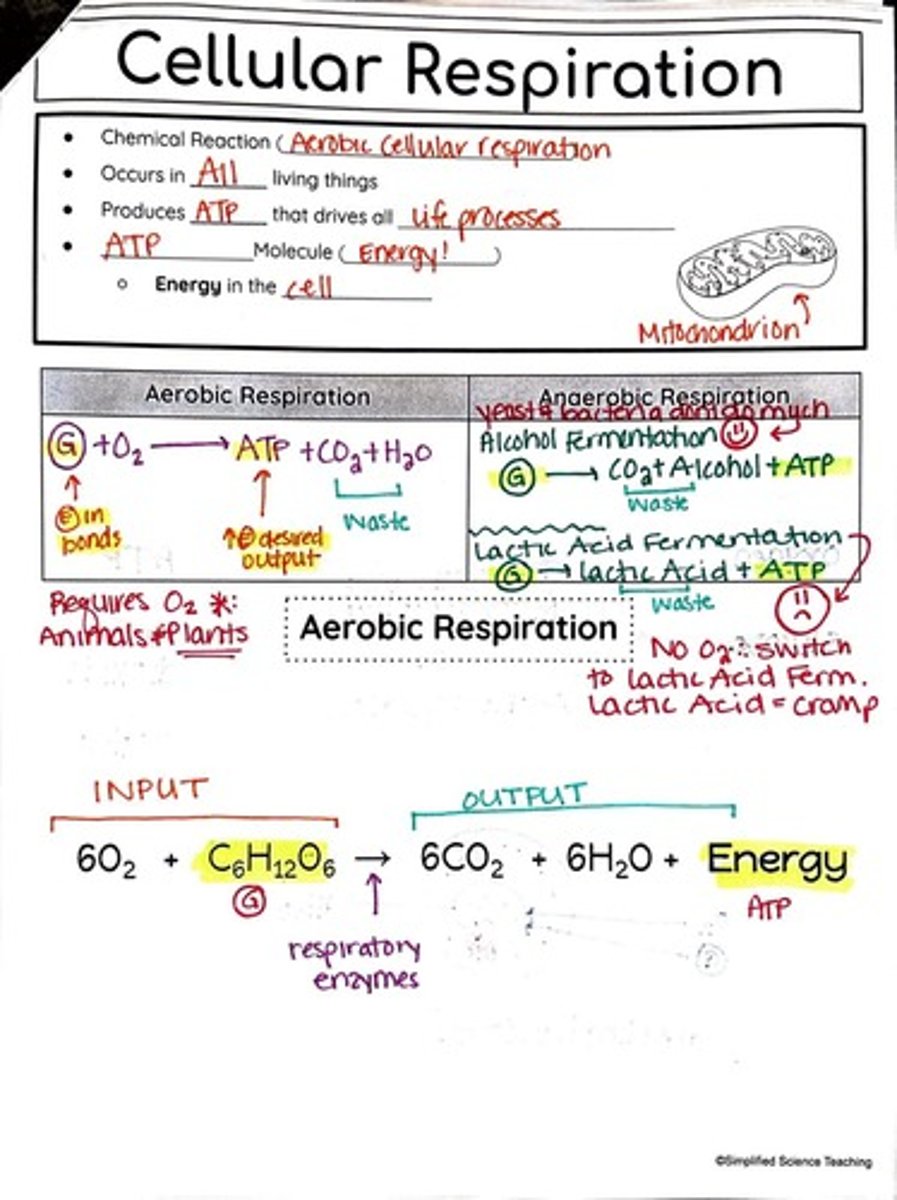
Anaerobic Respiration
A type of respiration that occurs without oxygen, often resulting in fermentation.
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food through processes like photosynthesis.
Heterotroph
An organism that obtains food by ingestion and absorption, such as animals and fungi.
Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods with the help of chlorophyll.
Excretion
The process of removing metabolic wastes from the body, such as sweat, urine, and exhaled gases.
Metabolism
The set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms that includes both anabolism and catabolism.
Mitosis
A process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells.
Assimilation
The process by which nutrients are incorporated into the living organism's tissues.
Growth
An increase in size or number of cells in an organism.
Regulation
The process of coordinating and controlling all life processes within an organism.
Reproduction
The biological process by which new individual organisms are produced.
Asexual Reproduction
A type of reproduction involving one parent, resulting in genetically identical offspring.
Sexual Reproduction
A type of reproduction involving two parents, resulting in genetically varied offspring.
Transport
The movement of substances around the cell and organism.
Nucleus
The part of the cell that contains DNA and controls cell activities.
Cytoplasm
The site of chemical reactions within the cell.
Cell Membrane
A semipermeable barrier that regulates what enters and leaves the cell.
Cell Wall
A structure that provides support and protection to plant cells.
Organelle
A specialized structure within a cell that performs a specific function.
Model Organism
An organism suitable for studying a specific trait, disease, or phenomenon.
Requirements for Model Organism
1) Observable traits; 2) Manageable in a laboratory setting.
Aerobic Respiration
A type of cellular respiration that requires oxygen and produces ATP.
Alcohol Fermentation
A process where yeast converts sugars into alcohol and ATP in the absence of oxygen.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
A process where glucose is converted into lactic acid and ATP without oxygen.
Inputs of Cellular Respiration
Oxygen and glucose are the main inputs for cellular respiration.
Outputs of Cellular Respiration
ATP, carbon dioxide, and water are the main outputs of cellular respiration.
Metabolic Wastes
Products of metabolism that need to be removed from the body, such as carbon dioxide and urea.
Urinary System
The system that filters blood to remove wastes and maintain osmotic pressure.
Exhalation
The process of breathing out carbon dioxide and water vapor.
Vasoconstriction
The narrowing of blood vessels to reduce blood flow.
Vasodilation
The widening of blood vessels to increase blood flow.
Osmotic Pressure
The pressure required to prevent the flow of water across a semipermeable membrane.
Mitochondrion
An organelle in cells where aerobic respiration occurs.
Research Question
A question that guides scientific investigation, such as how sugar affects yeast respiration.