Chapter 22
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
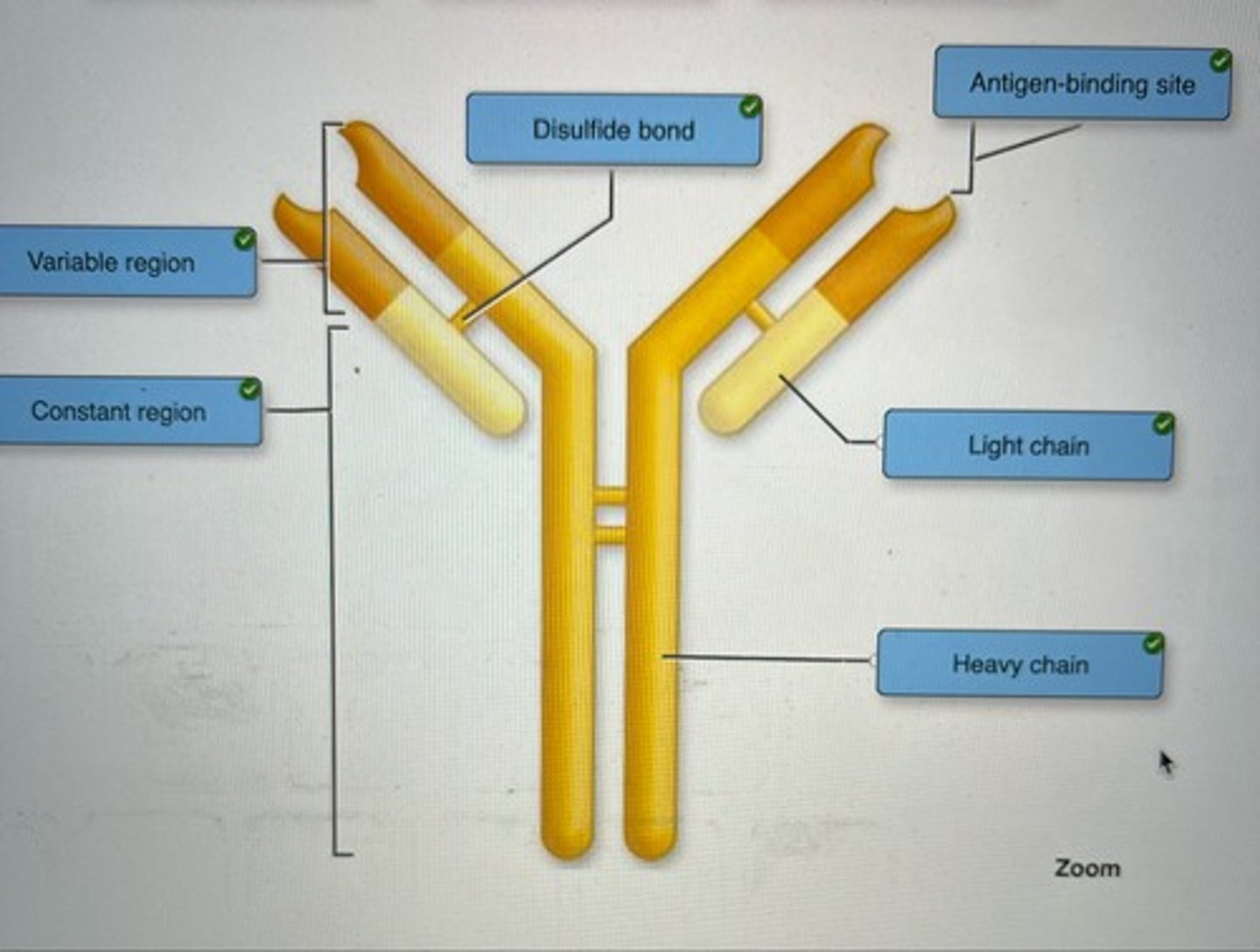
Correctly label the structure of an antibody.
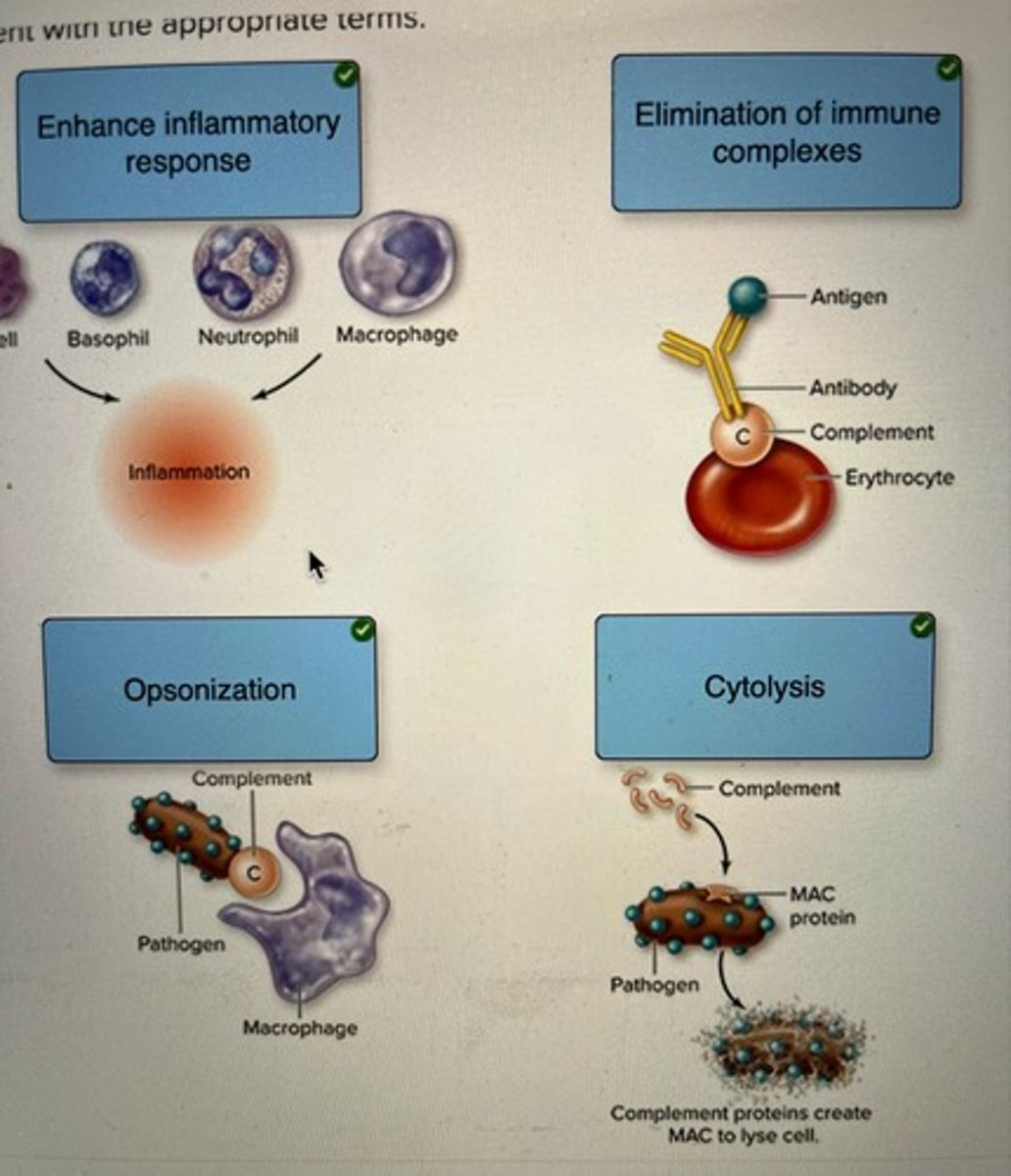
Label the effector functions of complement with the appropriate terms.
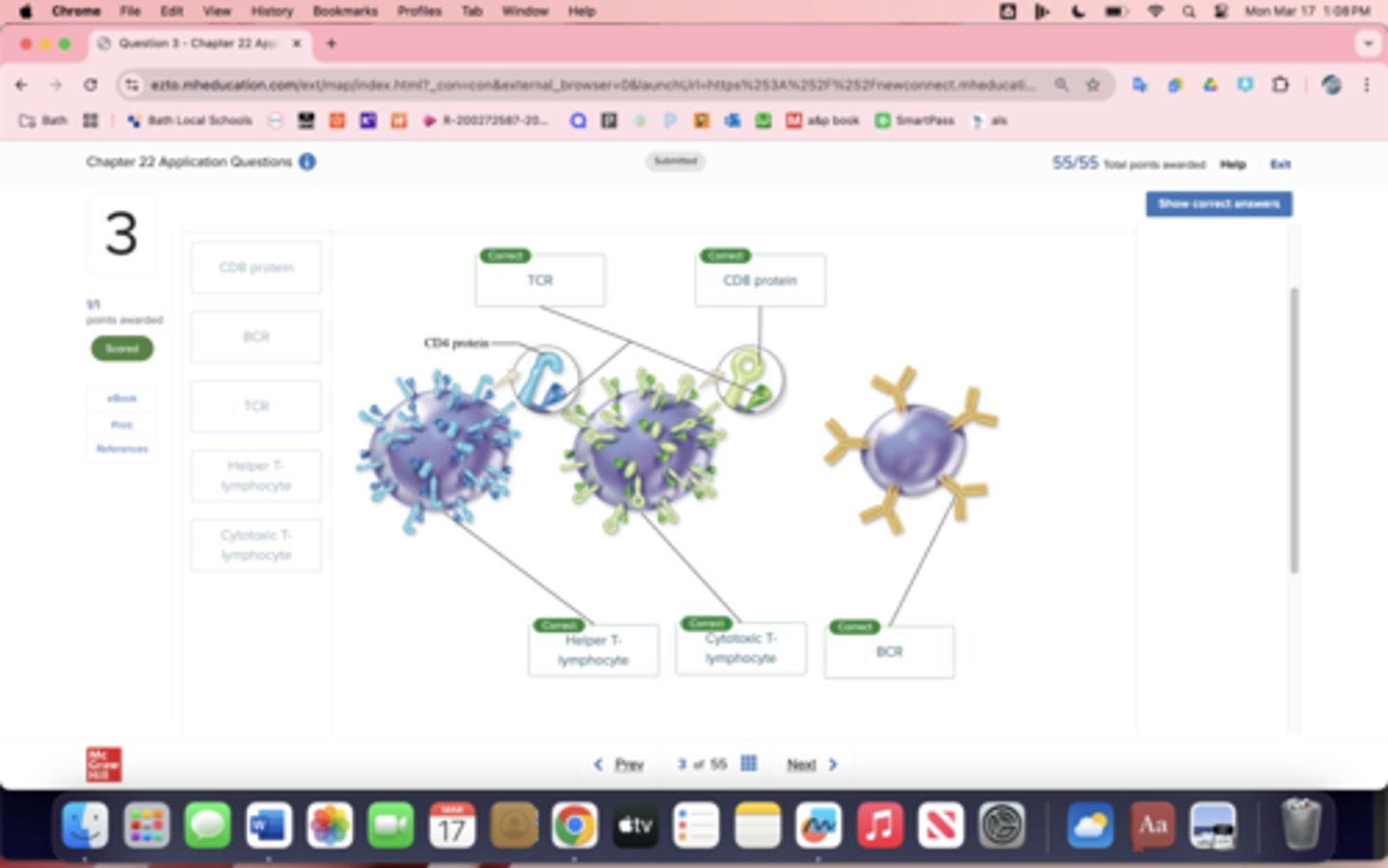
Label the figure with the items provided.
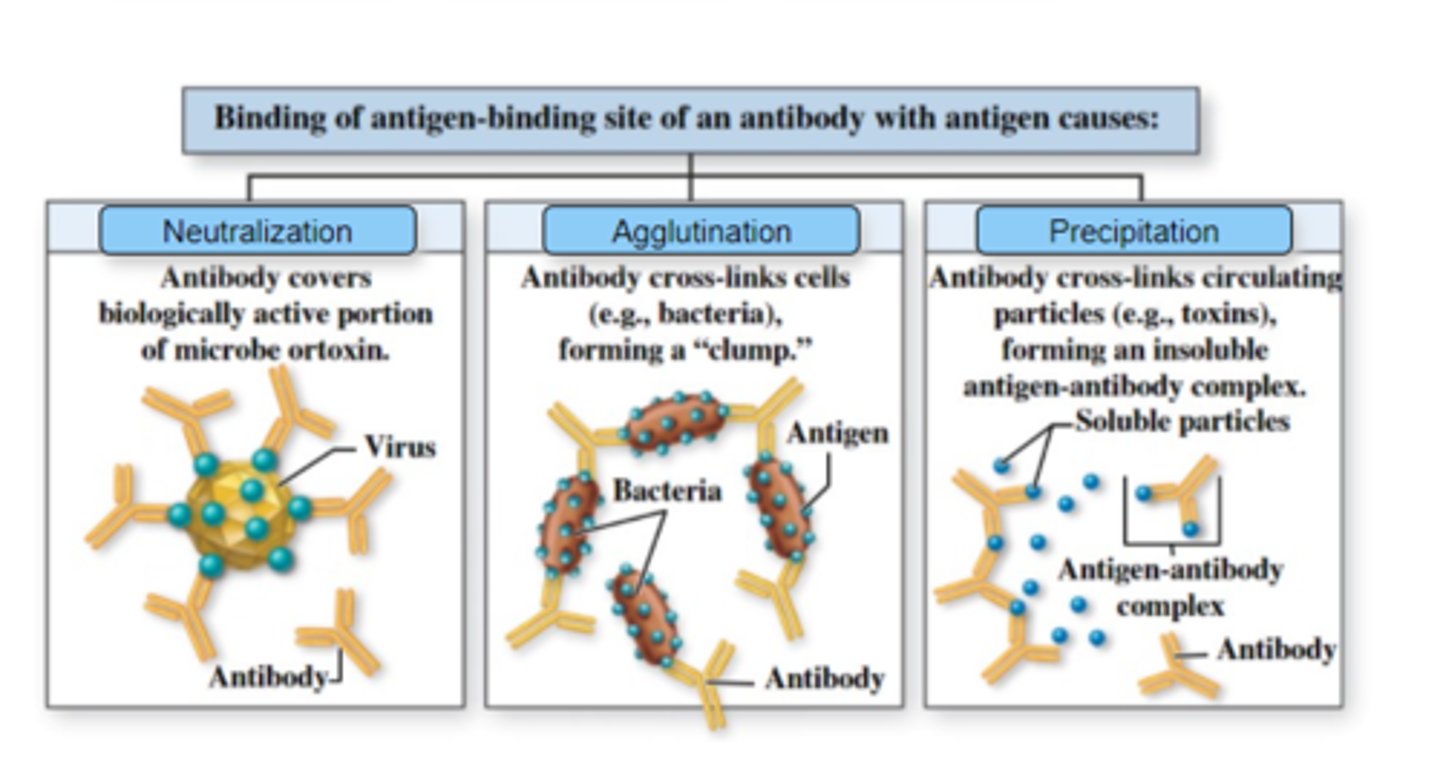
Label the effector functions of antibodies with the appropriate terms.
1. T-lymphocytes mature and differentiate in the ---.
2. Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes --- secrete antibodies.
3. Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes ---in direct contact with an infected cell in order to kill it.
4. Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes secrete ---, which cause a hole in the target cell's plasma membrane.
1. thymus
2. do not
3. need to be
4. perforins
1 A ---is an abnormal elevation of the body temperature.
2. A low to moderate fever, when allowed to run its course, can be --.
3. Fever can ---interferon activity.
Fever can also --- tissue repair.
Lastly, fever will inhibit the --- of bacteria and viruses.
1, Fever
2. Beneficial
3. Promote
4. accelerate
r. reproduction
1. Four cardinal signs of --- are recognized.
2. Erythrocytes arriving at the site and perfusing the dermis are visible through the skin which produces ---.
3. The increase in blood flow to an area of injury or infection brings ---from the axial regions of the body.
4. With increased blood flow and leakiness of capillaries, fluids are delivered to the tissue faster than they are removed resulting in ---.
5. Swelling increases the pressure of fluids and mechanical structures on adjacent structures and thus activating receptors for ---
1. inflammation
2. redness
3. heat
4. swelling (edema)
5. Pain
1. The --- Correctdefense system is what we are born with and it is nonspecific; all antigens are attacked pretty much equally.
2. It is ---based and we pass it on to our offspring.
3. Parts of immunity, or --- resistance, are changeable and can adapt to better attack the invading antigen.
4. There are two fundamental adaptive mechanisms: cell-mediated immunity and ---immunity.
1. innate
2. genetically
3. specific
4. antibody-mediated
1. Skin is an important part of the immune system. It acts as a ---boundary between germs and your body.
2.Skin is tough and generally impermeable to bacteria and viruses. The skin also secretes--- substances
3. Tears and mucus contain--- Correctthat breaks down the cell wall of many bacteria.
4. Saliva is also antibacterial. Because the nasal passage and lungs are coated in--- many germs are trapped in this substance and soon--- down the esophagus.
1. primary
2. antibacterial
3. lysozyme
4. mucus, swallowed
1 Activating complement triggers ---of the infected cell.
2. Precipitation and --- result from antigen-antibody complexes that make substances aggregate.
3. During --- bacterial surfaces are covered to prevent effective movement and release of toxins.
4. Production of antibodies is referred to as the --- immune response.
5. Each antibody recognizes a specific ---unique to its target.
6. An antibody is a --- used by the immune system to identify and otherwise block or kill foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses.
7. When antibodies are bound to ---cells they function as an ---, which enhances phagocytosis.
1. Lysis
2. agglutination
3. neutralization
4. antibody-mediated
5. Antigen
6. Protein
7. Target, opsonin
Basophils and ---are both proinflammatory chemical secreting cells. Recall that ---circulate in the blood, and --- reside in connective tissue of the skin, mucosal linings, and various internal organs. These cells release granules during the inflammatory response. These cellular granules contain various substances including ---, which increases both vasodilation and capillary permeability, and ---, an anticoagulant. They also release ---from their plasma membrane which increase(s) inflammation.
mast cells, basophils, mast cells, histamine, heparin, eicosanoids
Interferons (IFNs) are a class of --- released from a variety of cells, including T-lymphocytes and --- IFN serves as a --- defense mechanism against the spread of any --- infection.
cytokines, NK cells, nonspecific, viral
Which of the following is not an example of nonspecific (innate) immunity?
Antigens
The ability to ward off a specific infection or disease, usually as a result of prior exposure and the body's production of antibodies or lymphocytes against one pathogen, is called
specific immunity.
Which of the following statements accurately describes the difference between cellular and antibody-mediated immunity?
Cellular immunity directly attacks pathogens and infected cells, while antibody-mediated immunity releases antibodies to do so.
In _________blank immunity, the body's reaction to foreign substances is the same regardless of the pathogen, but in _________blank immunity, the body's reaction to foreign substances is specific to the particular pathogen present
innate; adaptive
Antigen presentation requires the physical attachment of antigen to a specialized transmembrane _________blank called MHC.
protein
Antibodies are _________blank produced in response to an antigen.
proteins
When interferon attaches to a cell,
virus can enter the cell but cannot replicate.
When interferon from one cell attaches to a second cell
the recipient cell makes enzymes that degrade viral RNA and DNA.
A normal, healthy cell only displays self-antigens with the MHC class I molecules.
true
Histamine released by mast cells leads to all of the following symptoms except
high fever.
Activated helper T-lymphocytes produce cytokines, which may stimulate B-lymphocytes to proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells capable of producing antibodies
True
The inflammation response triggers all of the following except
inhibition of mucus.
Foreign substances that elicit an immune response are termed
antigens
Which of the following describes the correct sequence of endogenous antigen presentation?
Proteins are broken into fragments, transported to the rough endoplasmic reticulum and combined with class I MHCs, move to the Golgi apparatus, and then to the plasma membrane.
Which of the following describes the correct sequence of exogenous antigen presentation?
Proteins are broken into fragments within a vesicle, which fuses with a vesicle containing class II MHCs in the Golgi apparatus, and this complex is transported to the plasma membrane.
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes produce a substance called _________blank, which creates holes in the cell membranes of target cells.
perforin
Which of the following is not an antigen-presenting cell?
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes
Helper T-lymphocytes interact with APCs by recognizing
antigen−MHC protein complexes.
Helper T-lymphocytes secrete _________blank to stimulate the proliferation of B-lymphocytes.
cytokines
Arrange the following in the sequence in which they occur during the inflammatory response, prior to diapedesis.
1.Neutrophils roll along endothelium
2.Expression of cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs)
3. Margination
1,2,3
Which of the following terms describes the migration of neutrophils from blood vessels
Diapedesis
A helper T-lymphocyte becomes activated by a(n)
antigen presenting cell.
An antigen presenting cell presents antigen to a helper T-lymphocyte
on its surface on a class II MHC.
The CD8 protein binds
MHC class I molecules.
If negative selection of T-lymphoctyes in the thymus never occurred, what would likely happen?
T-lymphocytes would bind self-antigens.
Once activated, helper T-lymphocytes
continue to release cytokines such as IL-2.
Because they come in direct contact with infected cells, the effector response of _________blank is referred to as cell-mediated immunity.
T-lymphocytes
In the blood, the antibody in most abundance is
igG
The process of antibody production after initial exposure to an antigen is known as the _________blank response.
primary
If someone is infected with a virus, resulting in activated and memory B-lymphoctes and T-lymphoctes, they are exhibiting _________blank immunity.
active
Receiving antivenom to treat a snake bite is an example of _________blank immunity.
artificially acquired passive
All of the following processes can be activated by complement except
(VIDEO)
antibody production.
Opsonization is (VIDEO)
enhancing phagocytosis.
Complement proteins C5-C9 can form a membrane attack complex that results in
(VIDEO)
cytolysis
Complement factors are named in the order in which they function.(video)
False
In the classical pathway of complement activation, complement attaches to an antigen-antibody complex.(VIDEO)
true
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes produce(VIDEO)
perforin, which makes holes in cell membrane of infected cells.
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes recognize
antigens and MHC class I.
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes produce cytotoxins, which cause apoptosis of infected cells.
true
Which leukocyte is most prevalent in blood?
Neutrophils
Identify the leukocyte that secretes cytotoxic chemicals (i.e. perforin).
Natural killer cells
(ARTICLE)
1. Fluids known to transmit HIV include all the following except
2.The underlying cause for Jack's initial confusion, disorientation and inability to remember things was
3. Since HIV infection and fully developed AIDS are not the same thing, AIDS is defined as
1. saliva
2.his low blood oxygen levels due to decreased lung function resulting from his Pneumocystis pneumonia.
3. Both choices
(ARTICLE)
1. Although Jack was infected with HIV and later developed AIDS, his initial screening test for HIV was negative because
2.The current group of HAART medications includes
1.the test was most likely done too early in the course of his infection, and he had not yet developed high enough levels of the antibodies to be detected.
2. all of these are correct