Anatomy of Long Bones and Muscle Tissue
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Long Bone
Has distinct areas: diaphysis, metaphysis, epiphysis.
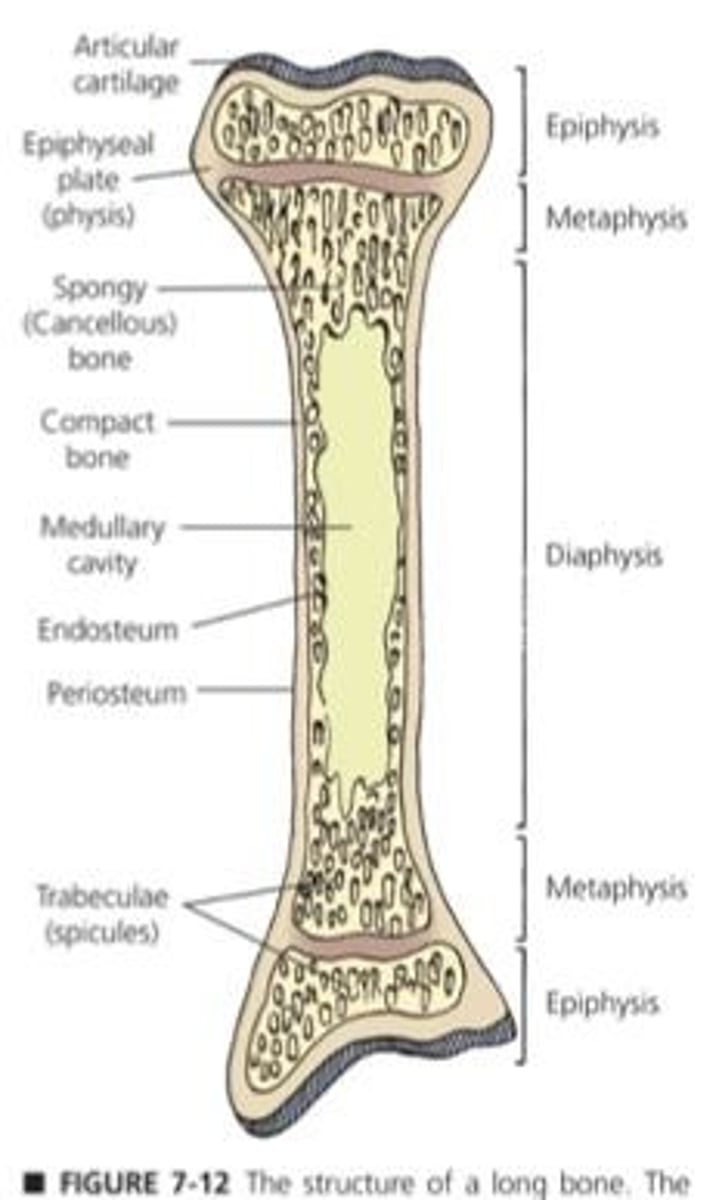
Spongy Bone
Porous bone found at ends and tops.
Compact Bone
Solid bone structure, lines the outer surface.
Trabeculae
Structural units of spongy bone, hole-like appearance.
Diaphysis
Long shaft of bone containing medullary cavity.
Metaphysis
Transition area between diaphysis and epiphysis.
Epiphysis
Widened ends of long bones.
Physis
Growth plate, also known as epiphyseal plate.
Endosteum
Membrane lining the medullary cavity.
Periosteum
Outer membrane covering the bone.
Bone Composition
Contains water, minerals, and organic matter.
Wet Weight Ratio
Bone: 25% water, 45% minerals, 30% organic.
Dry Weight Ratio
Bone: 0% water, 70% minerals, 30% organic.
Calcium in Bone
Ca2+ constitutes 37% of bone minerals.
Phosphorus in Bone
P constitutes 18.5% of bone minerals.
Osteoprogenitor Cells
Stem cells that differentiate into bone cells.
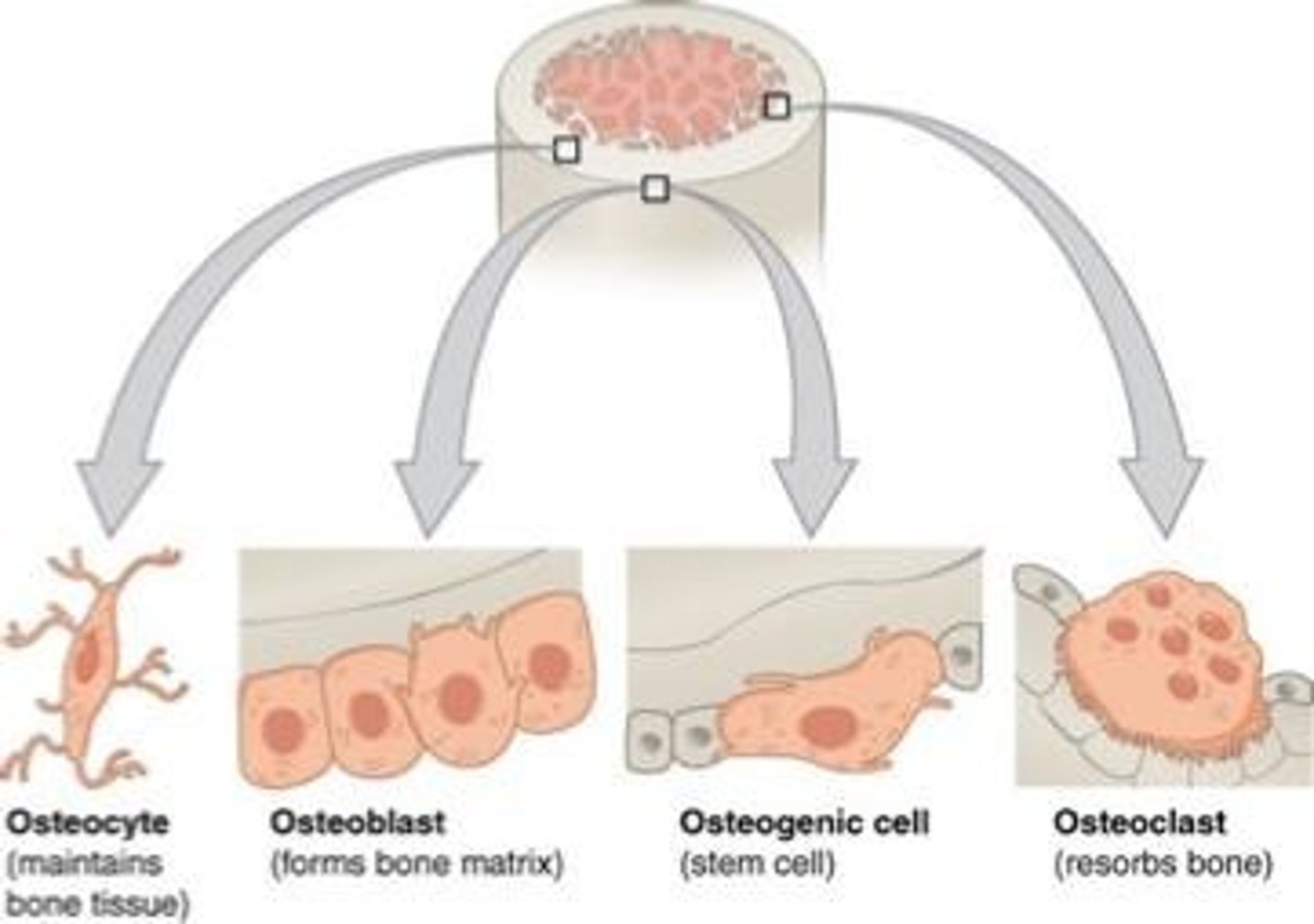
Osteoblasts
Cells responsible for building bone matrix.
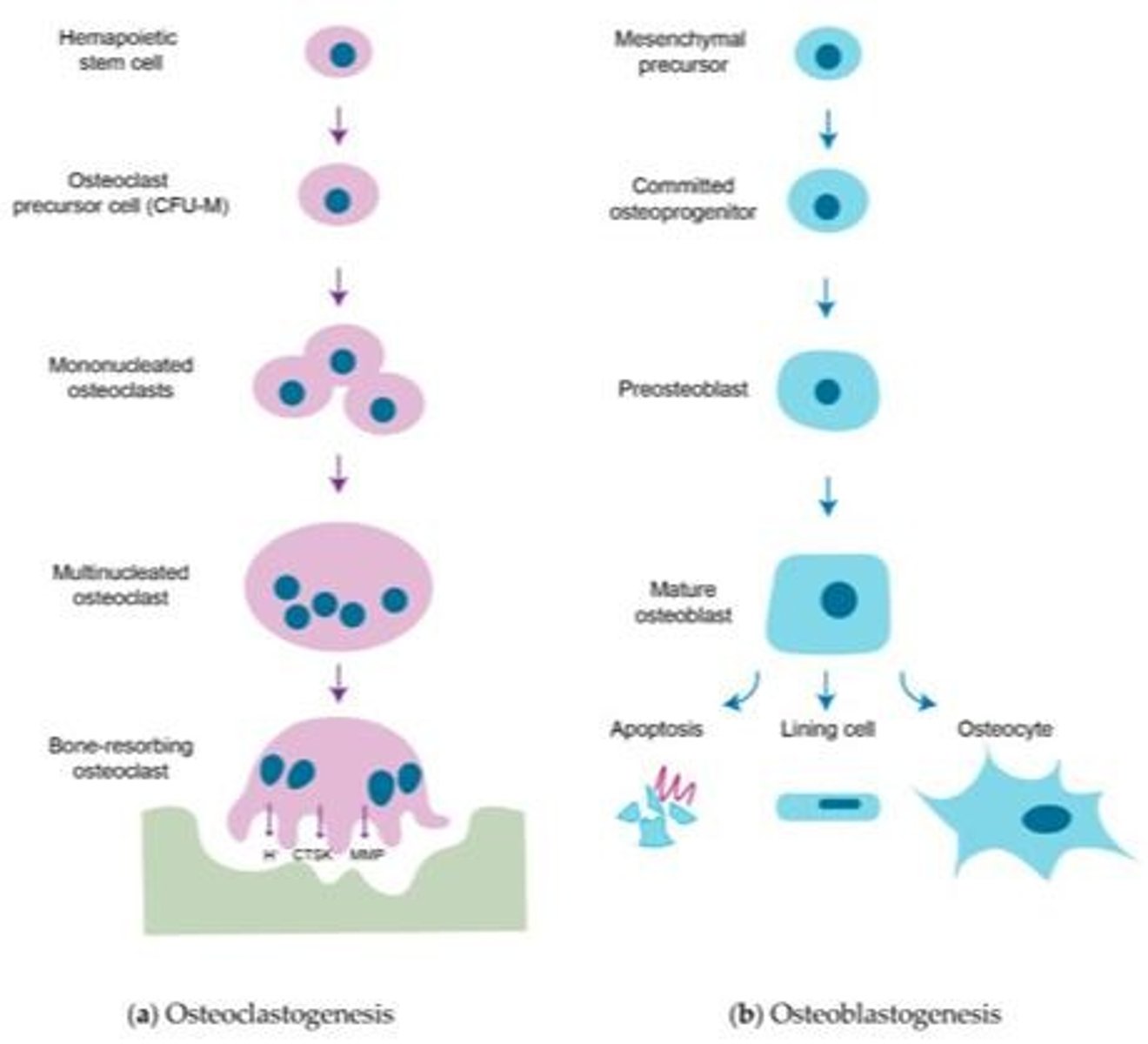
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells maintaining tissue and communication.
Osteoclasts
Cells that resorb and break down bone.
Haversian System
Canal system in compact bone for blood vessels.
Haversian Canals
Horizontal canals containing blood vessels.
Volkmann Canals
Vertical canals connecting Haversian systems.
Canaliculi
Small channels for osteocyte communication.
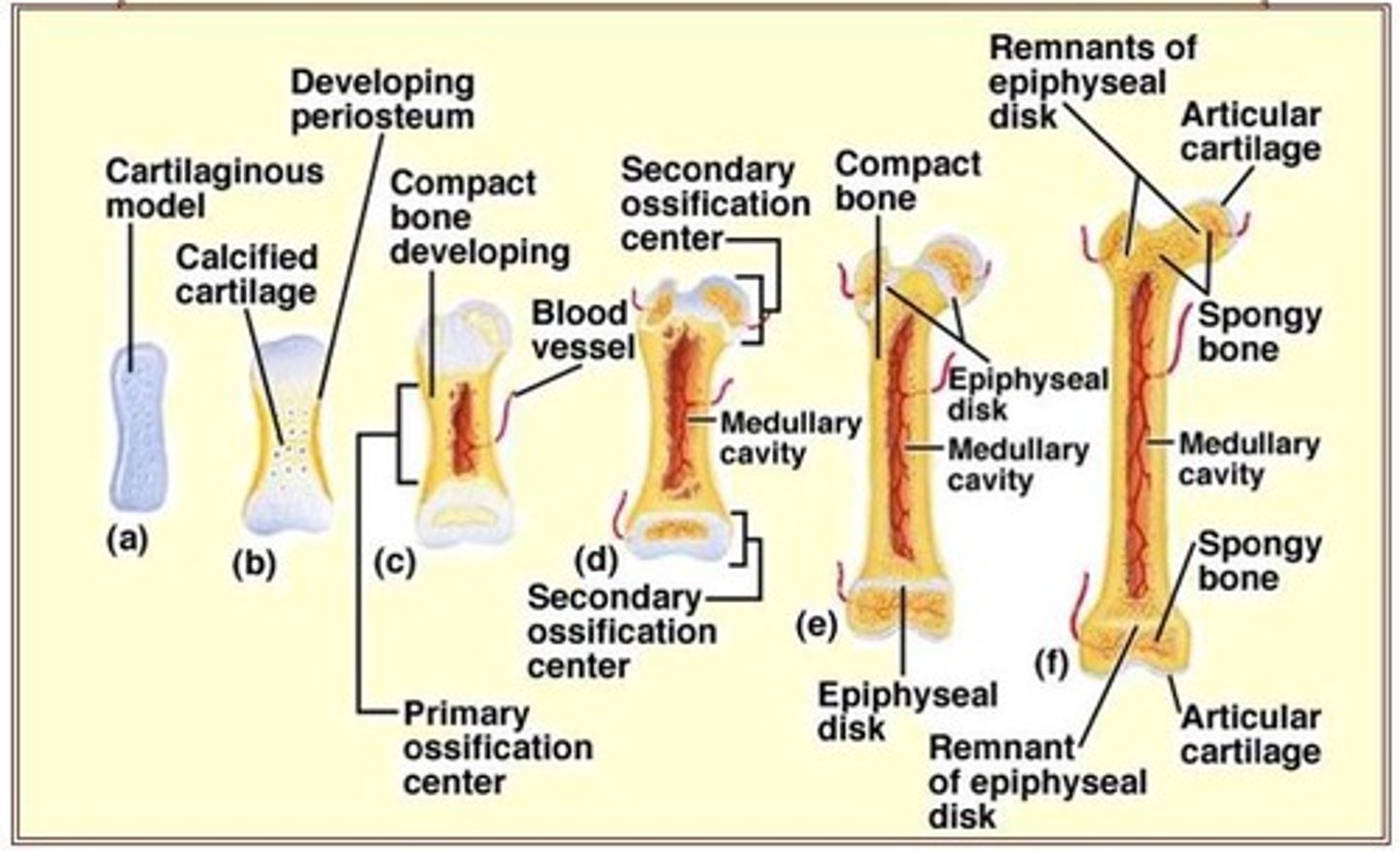
Ossification
Process of bone formation, includes endochondral and intramembranous.
Synovial Joints
Freely movable joints with synovial fluid.
Joint Capsule
Two-layered structure enclosing synovial joints.
Ligaments
Connective tissue stabilizing joints.
Skeletal Muscle
Contractible tissue responsible for voluntary movement.
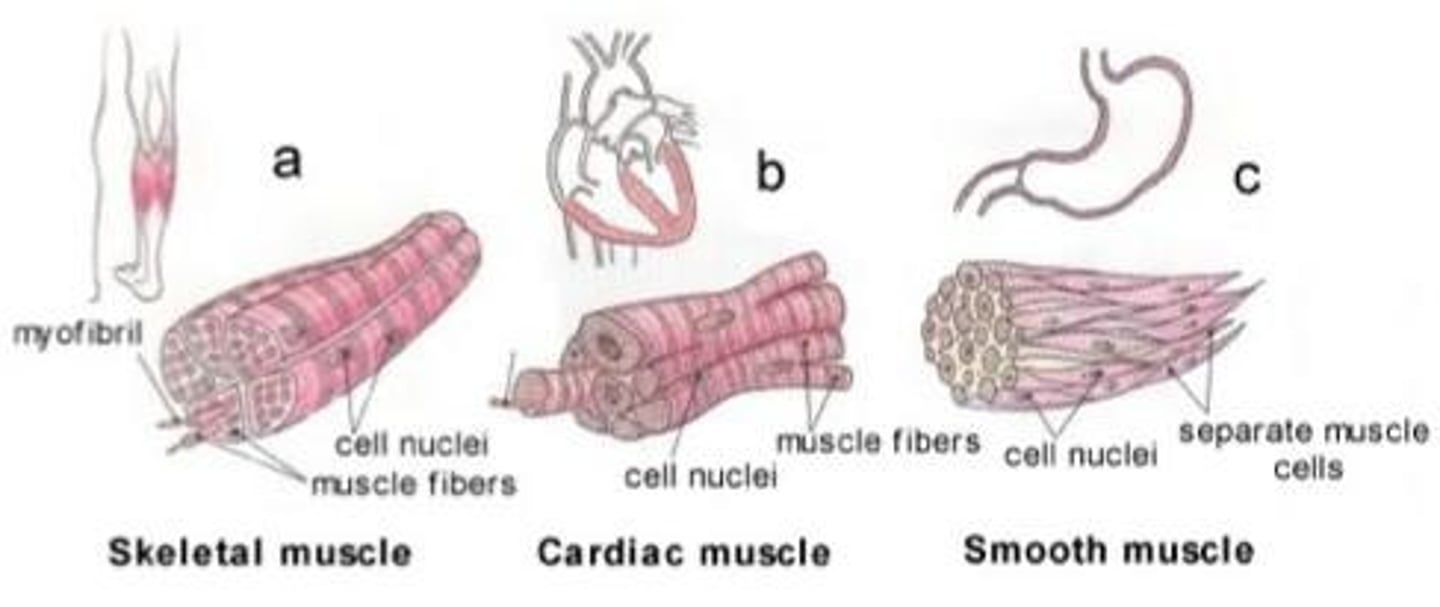
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary muscle with branched cells and intercalated discs.
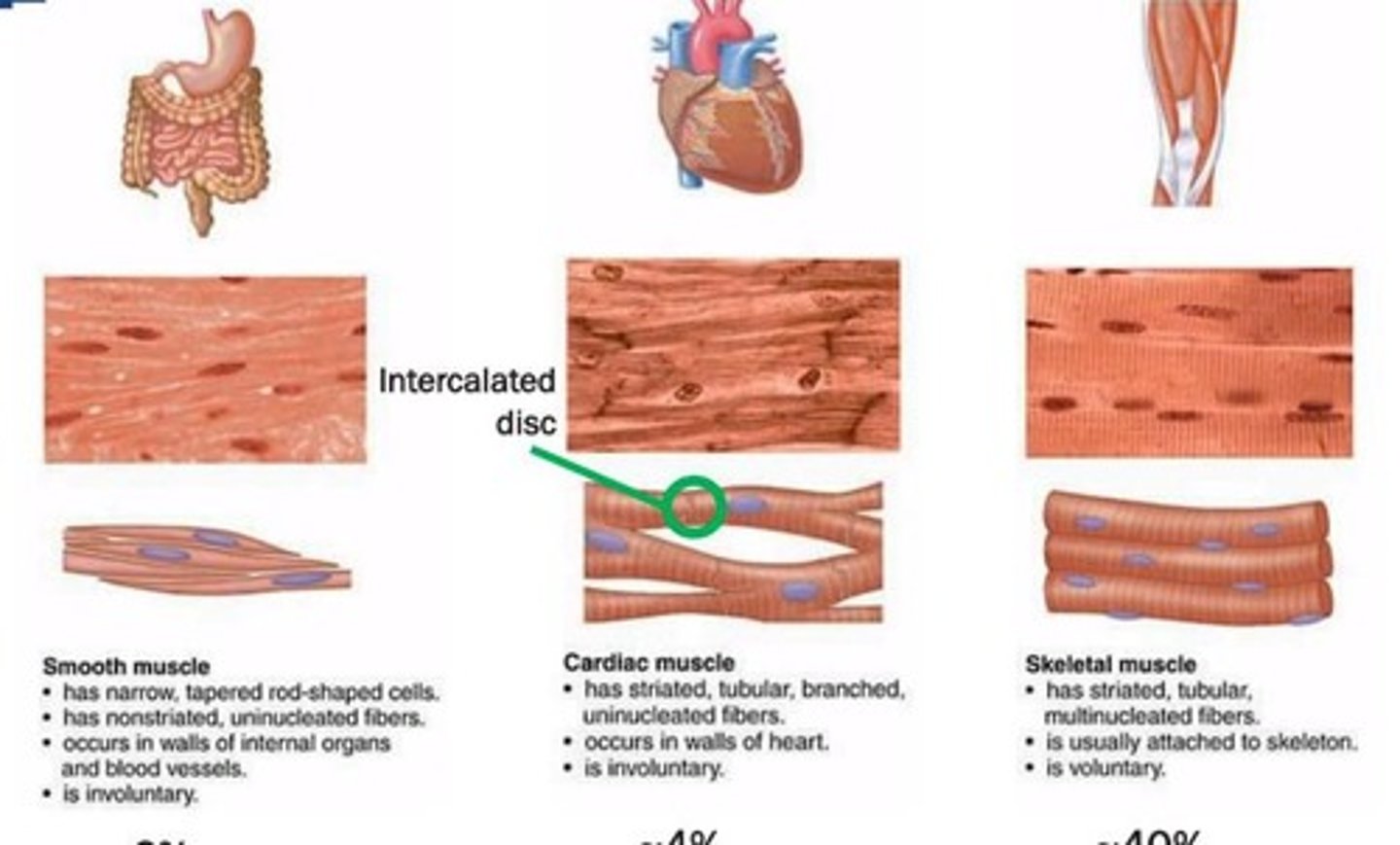
Smooth Muscle
Involuntary muscle, non-striated, found in organs.
Muscle Origin
End attached to stationary bone.
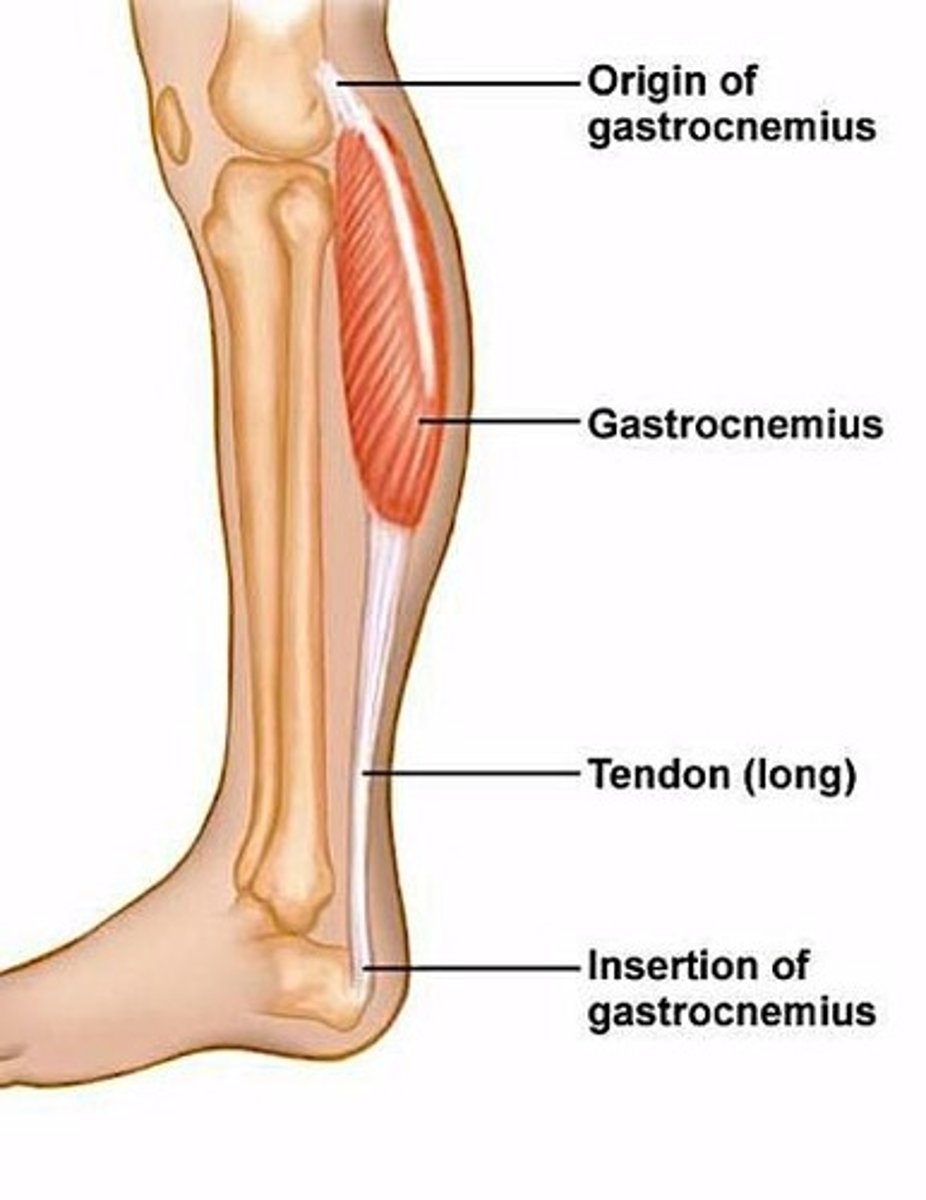
Muscle Insertion
End attached to movable bone.
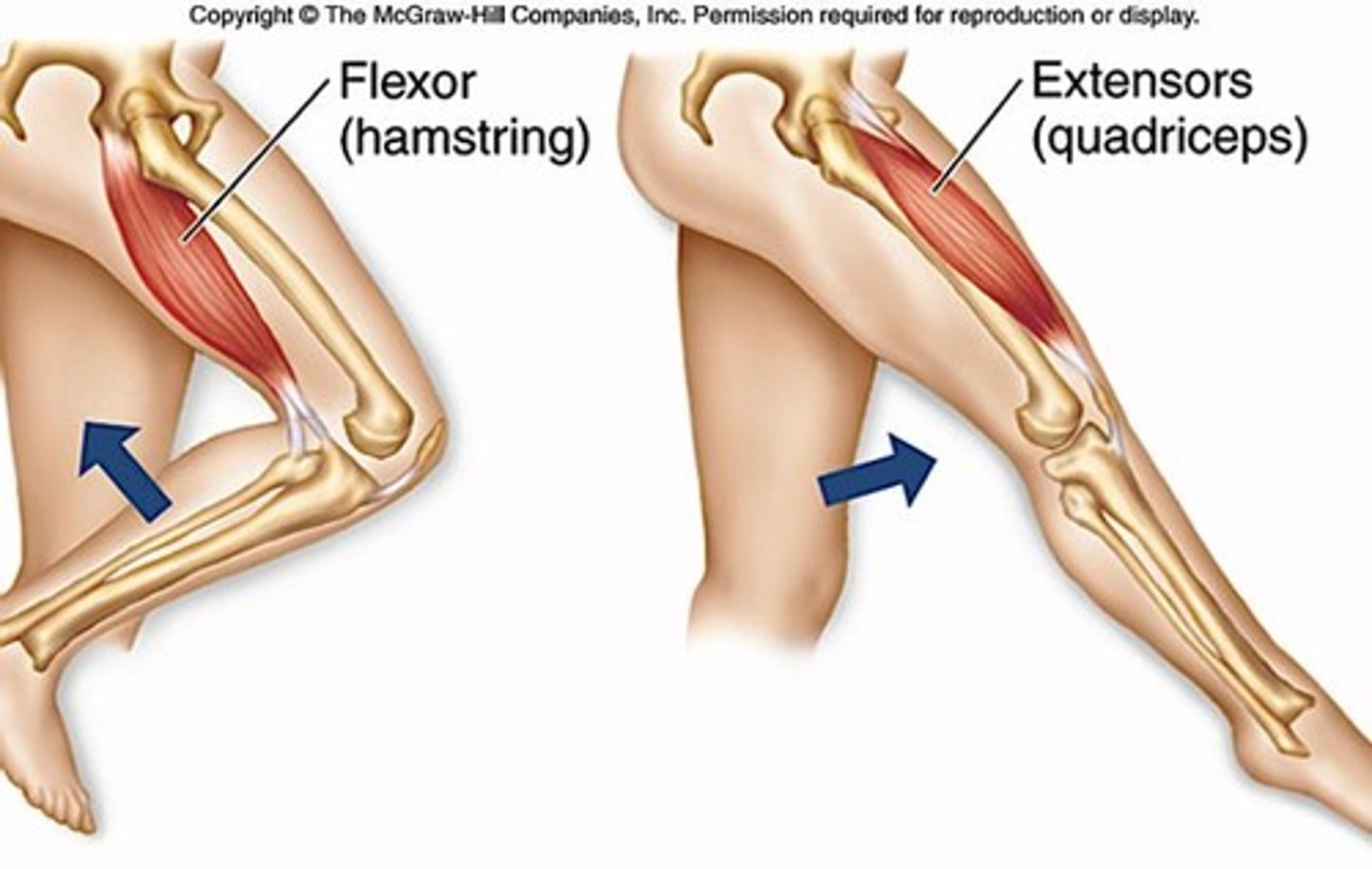
Flexor Muscle
Brings bones closer together.
Extensor Muscle
Moves bones away from each other.
Antagonistic Muscle Groups
Pairs of muscles opposing each other's actions.
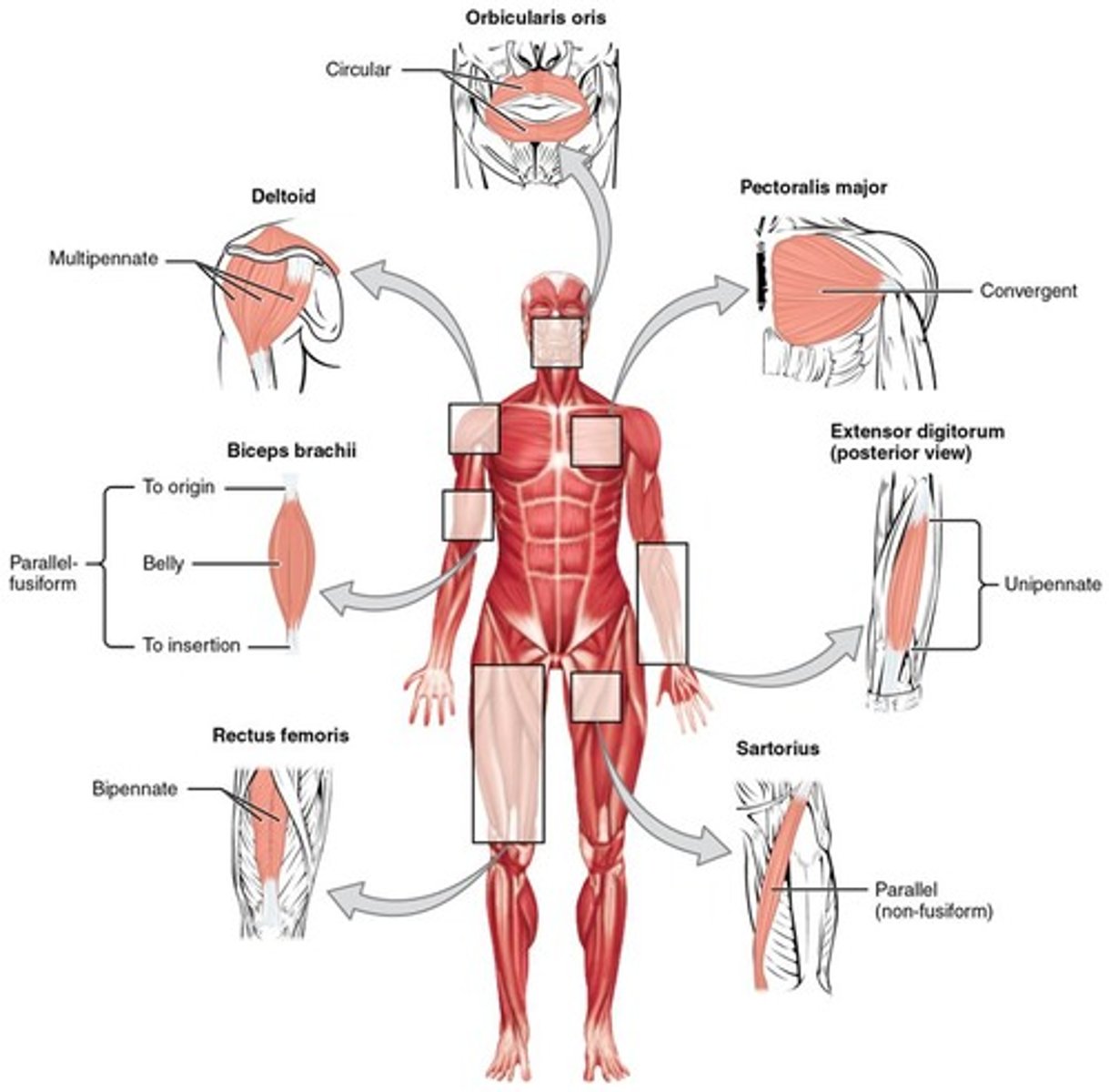
Muscle Architecture
Classified as parallel or pennate arrangements.
Epimysium
Outer layer of connective tissue around muscles.
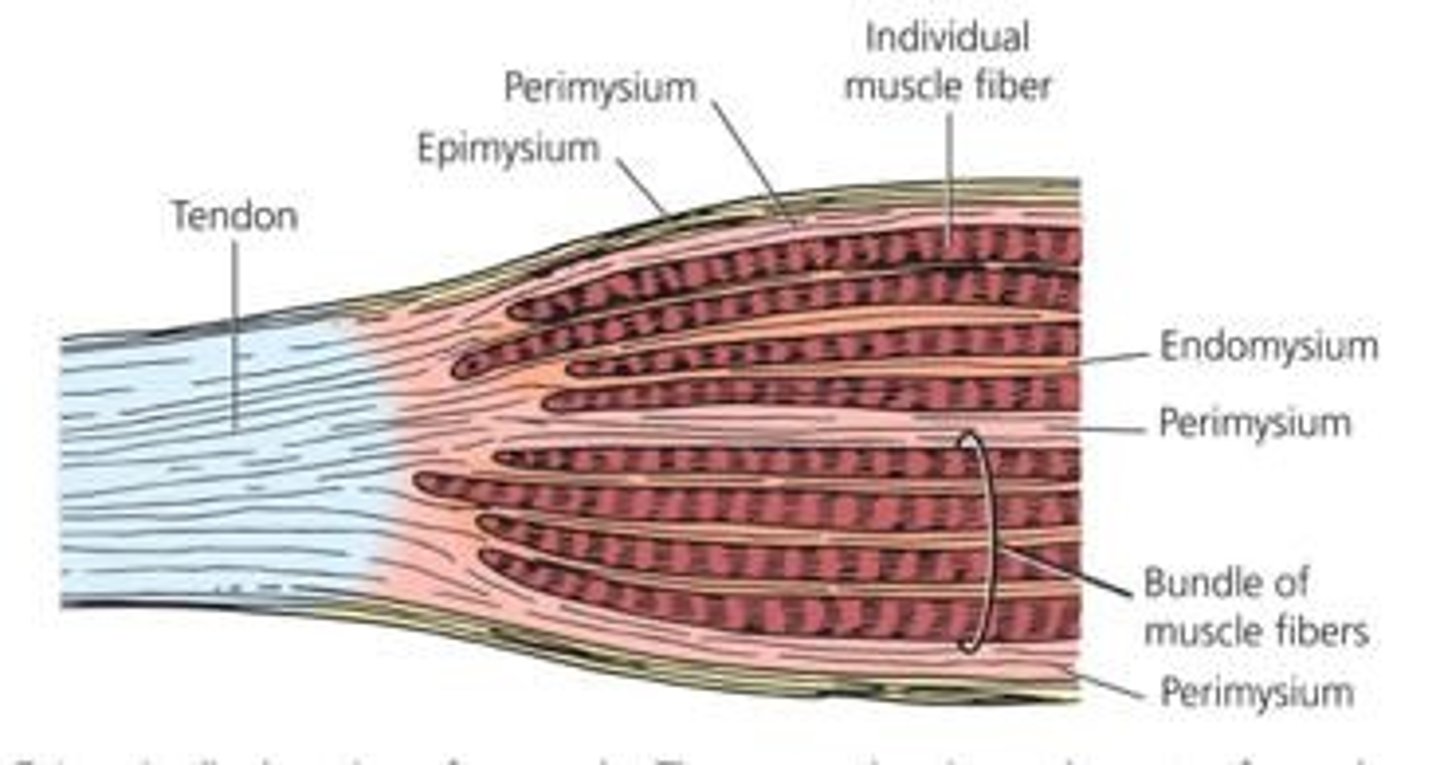
Perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding muscle fiber bundles.
Endomysium
Connective tissue between individual muscle fibers.
Myofibril
Intracellular bundles of contractile proteins.
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Releases Ca2+ for muscle contraction.
T-tubules
Transmits electrical signals into muscle fibers.
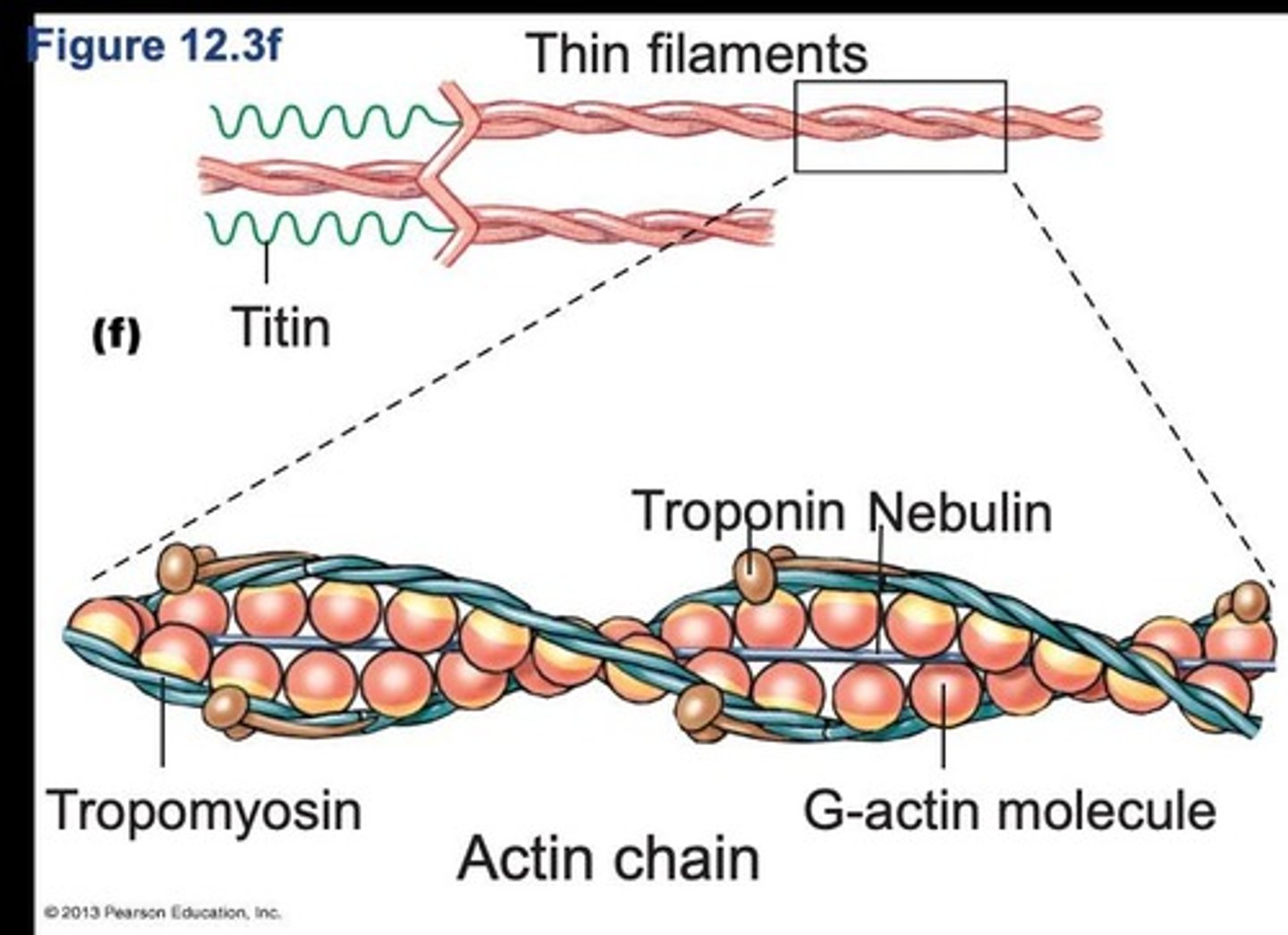
Actin
Thin filament protein involved in muscle contraction.
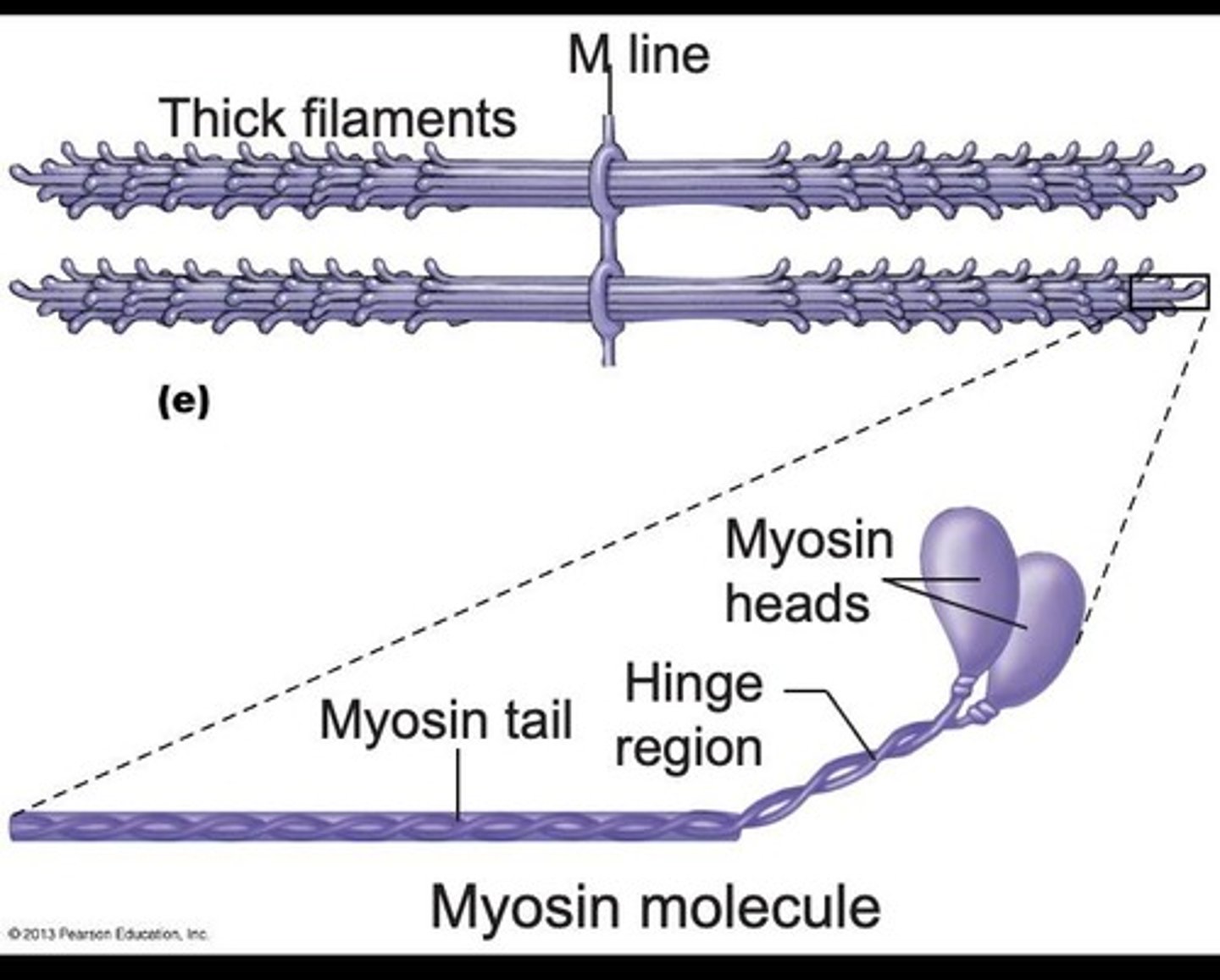
Myosin
Thick filament protein forming muscle contractions.
Tropomyosin
Regulatory protein that blocks actin binding sites.
Troponin
Regulatory protein that binds calcium to initiate contraction.
Titin
Giant accessory protein providing structural support.
Nebulin
Accessory protein stabilizing actin filaments.