Liver pt 2 + SG
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
what are the causes of hepatocellular disease (6)
alcohol and dietary excesses
drugs and toxins
infections → especially viral
autoimmune disorders
genetic metabolic defects
impairment of hepatic circulation and/or oxygenation
what are abnormal liver functions seen in hepatocellular disease (6)
decreased:
synthesis
detoxification
excretion
extraction
storage
removal
what liver function tests reflect hepatocellular disease
elevated AST and ALT levels → damaged hepatocytes
elevated alkaline phosphatase → damaged cholangiocytes
what antibody can be seen in ACUTE viral hepatitis
IgM
what antibody can be seen in CHRONIC viral hepatitis
IgG: will be present if pt has cleared the infection OR if they currently have the chronic infection and they cannot clear it
what antigens are present in viral hepatitis
viral RNA/DNA and/or viral antigen/active
what is ALD
alcohol associated liver disease
triggered by toxic effects of alcohol and its oxidative metabolites-acetaldehyde and acetate
what is MetALD
someone who is taking in too many calories and too much alcohol
is a combo of metabolic risk factors: obesity and excessive alcohol intake
what is Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
metabolic syndrome → obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, prediabetes or diabetes
basically- the liver has an excess amount of fat in it
what is Metabolic Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH)
liver inflammation due to excess amount of fat in the liver → from MASLD
will have hepatocyte death w or w/o fibrosis of liver
can lead to cirrhosis/liver cancer
etiology of ALD
alcohol is converted to acetaldehyde → acetate → building block for LFAC → buildup in storage w excess intake → trigger the release of TNF-alpha from Kupffer cells → TNF-alpha start immune cascade
etiology of MASLD
inc calories → convert to TG → there is always a balance between TG and LCFA, so as TG inc → LCFA will inc → kpuffer cells release TNF-alpha → immune cascade
what is the immune cascade caused by the release of TNF-alpha
progressive fibrosis
insulin resistance
immune inflammatory damage
what is the common factor/etiology of ALD vs MASLD
excess long chain fatty acids
what do stellate cells make in the presence of TNF-alpha
will lay down collagen → fibrose liver
what are the leading liver diseases in the US in 2024
ALD
MASLD
hepatitis C
what are the two type of Drug Induced Liver Injuries (DILI)
reproducible
idiosyncratic
what is reproducible DILI
hepatic metabolism of parent compound to toxic metabolite
is a dose-related injury
what is idiosyncratic DILI
uncommon and unpredictable; such a rare thing it isn’t even spotted in drug trials bc there aren’t that many participants
what do you give for an acetaminophen overdose, why
acetylcysteine → can limit formation of protein and DNA adducts adn generally improve survival
in a person w longer standing alcohol use disorder, is the toxic dose of acetaminophen smaller/the same as/larger compared to a person who does not drink at all
a smaller dose would be toxic for the alcoholic disorder person
what are the 3 patterns of idiosyncratic drug rxns
hepatocellular
cholestatic
mixed
what do the hepatocellular and cholestatic idiosyncratic drug rxn have in common
delayed onset
disproportionate elevation of alkaline phosphatase
unique features of hepatocellular idiosyncratic drug rxn
presents like acute viral hepatitis
can be asymptomatic
high mortality rate
rapid recovery
risk w re-challenge
unique features of cholestatic idiosyncratic drug rxn
slow recovery
low mortality
drugs interfere w bile salt excretory protein
why can nutritional supplements cause and idiosyncratic drug rxn
these are unregulated, there are various herbs blended together, and the potency is not standardized → DILI
what injuries are associated w zone 1
viral inflammation → Hep B/C, autoimmune
what injuries are associated w zone 3
vascular → congestive hepatopathy
toxins→ acetaminophen, alcohol
metabolic → bile canaliculi, hepatocytes
what are hepatic responses to injuries
necrosis, apoptosis
steatosis
cholestasis
ballooning degeneration w Mallory inclusions
what is steatosis
abnormal accumulation of fat (TG) within the cytoplasm of parenchymal cells in the liver
what is cholestasis
reduced or obstructed bile flow leading to accumulation of bile components in the liver and the bloodstream
what causes chronic passive congestion of the liver
right sided heart failure: back pressure from IVC leads to retrograde sinusoidal congestion
what zone is most affected by chronic passive congestion of the liver
zone 3- due to location by central vien
what is the website: Livertox.gov.
you can put in a name of a drug and it will give you effects and management of the drug
what are the various classes of substances that are toxic to the liver
meds
herbal products
dietary supplements
poisonous plants and fungi
household and industrial products
ointments, perfumes, shampoo, cleaning solvents, pesticides
in the US, what is the most common cause of liver failure necessitating transplant
acetaminophen toxicity
how can ALD lead to cancer
steatosis → hepatitis → cirrhosis → hepatocellular carcinoma
___% of adults in the US are affected by ALD
18%
ALD is resonsible for >__% of chronic liver disease and ~___% of deaths from alcohol-associated cirrhosis
>60% chronic liver disease; ~50% of deaths
what are the histological features of ALD
steatosis→ fat droplets in hepatocytes
usually in zone 3
steatohepatitis → steatosis and inflammation
ballooning degradation
mallory-denk bodies
clumps of cytoskeletal filaments
what are non-hepatitis viruses that affect the liver
EBV
CMV
dengue
yellow fever
what viruses can lead to chronic hepatitis
HBV< HDV < HCV
HEV in immunocompromised pts
NEVER HAV
what is the route of transmission in Hep A
fecal-oral route, highly contagious
who is commonly affected by Hep A
happens as outbreaks in US, restaurants, institutions
Hep A risk of development
no carrier state so it cannot lead to chronic infection of cirrhosis/cancer
what is the route of transmission of Hep B
mother child, sex/IVDA
who is commonly affected by Hep B
unvaccinated people in the US
adult prognosis of Hep B compared to babies
adult: will more than likely undergo slow, complete recovery from illness, <1% progress to chronic
babies: 95% who are infected perinatally become chronic carriers, and 30% of them develop chronic active hepatitis
people w chronic hepatitis are _____________ for the rest of their life
infectious-carriers
many cases of chronic hepatitis will develop cirrhosis, there is a high risk of…
hepatocellular carcinoma
progression of HBV infection
(5-10% of the time) HBV → acute infection → chronic hepatitis → cirrhosis → hepatocellular carcinoma
what is the route of transmission of Hep C
bloodborne
who is commonly affected by Hep C
high incidence in boomers, but new cases are in younger
what hepatitis virus in the #1 cause of cirrhosis in the US
Hep C
Hep C risk of progression
80-90% will result in chronic hepatitis; higher risk for cirrhosis and carcinoma
incubation period of hep A
2-6 week
initial signs of Hep A
abdominal pain, pale stool, dark urine, jaundice, pruritis, RUQ tenderness
incubation period of hep B
1-4 months
incubation period of hep C
2-6 weeks
what is autoimmune hepatitis
chronic, progressive disorder w features that include a genetic predisposition, an association w other autoimmune diseases, and the presence of autoantibodies
what is the predominate cell type in autoimmune hepatitis
plasma cells
what is Hemochromatosis
is an autosomal recessive disorder w a defect in the HFE gene, leading to excessive intestinal absorption of iron
what is the normal role of hepcidin
a peptide hormone that helps iron exit the enterocyte from the intestines
what is happening w hepcidin in hemochromatosis
there is a lot less hepcidin which will result in more iron being secreted into the blood
what organs are affected in hemochromatosis
liver
pancreas
heart
joints
endocrine organs
skin pigmentation: “BRONZE DIABETES”
what is wilson’s disease
autosomal recessive disorder or copper metabolism that results in accumulation of copper in organs
what organs are affected in wilsons disease
liver
brain
eye
what is the function of ceruloplasmin
will regulate body’s copper levels
what is happening w ceruloplasmin in wilson’s disease
there is decreased serum ceruloplasmin so there is not regulation of copper → buildup of copper in certain organs/tissues
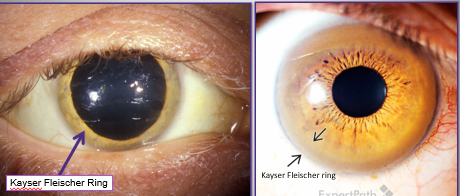
what is Kayser-Fleisher ring
later manifestation of Wilson’s disease
ring at the periphery of the cornea
what is alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency
autosomal co-dominant disorder that has a defect in the SERPINA1 gene, characterized by a reduction in serum A1AT levels
what does A1AT normally do
usually protects the lungs from damage
what is happening to A1AT during alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency
there is a dec in A1AT that will lead to excessive protease activity → will destroy alveolar walls
what organs are affected by alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency
liver
lung
LFT in alcohol vs hepatitis B
alcohol: very slightly elevated AST > ALT (2:1 ratio)
Hep B: very elevated ALT > AST
what is Ag testing for in serology
testing for an antigen on the viral surface
if you test positive for an Ag, this means…
you are infectious UNLESS you have anti-ag
what is “anti-X” test for
antibodies against an antigen
if you test positive for “Anti-X” this means…
you are immune
HBsAg +
infectious
anti-HBc IgM +
early immune response so recent infection, and STILL infectious
anti-HAV IgG +
immune to Hep A (+ means they have been exposed)
anti-HCV -
not immune to Hep C → not exposed in the past → does NOT mean they have Hep C now
anti-HEV IgM and IgG -
not exposed to hep E
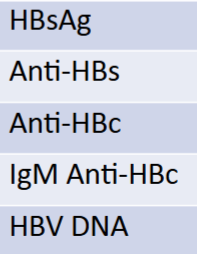
serology report if pt was immune due to natural infection
HBsAG: -
Anti-HBs: +
Anti-HBc: +
IgM anti-HBc: -
HBV DNA: -
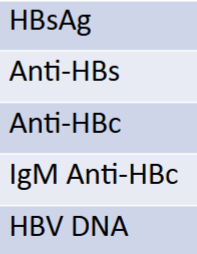
serology report if pt was immune due to Hep B vaccine
HBsAG: -
Anti-HBs: +
Anti-HBc: -
IgM anti-HBc: -
HBV DNA: -
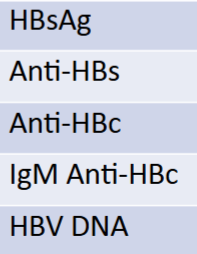
serology report if pt had an acute infection
HBsAG: +
Anti-HBs: -
Anti-HBc: -
IgM anti-HBc: +
HBV DNA: +
serology report if pt had a chronic infection
HBsAG: +
Anti-HBs: -
Anti-HBc: ±
IgM anti-HBc: -
HBV DNA: +
what is happening biologically in acute acetaminophen toxicity
glutathione is used to detoxify many chemicals → if it is used up by one substance (alcohol), it cannot detoxify other substances (acetaminophen) → tylenol can get converted to quinone substance and causes liver failure