Condensation polymerisation
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
how are condensation polymers formed?
condensation reaction, so a water molecule is removed
3 types of condensation polymers?
polyamides, polyesters, polypeptides
how are polyamides formed?
condensation reaction between dicarboxylic acid and a diamine,
water is removed leaving an amide linkage
what makes polyamides strong?
polyamides commonly formed from long chain molecules which provides them with strngth
by convention, the repeat unit isnt shorter than how many carbons?
2
(lots) diol + (lots) dicarboxylic acid -> ? + ?
polyester + water
ester functional group?
COO
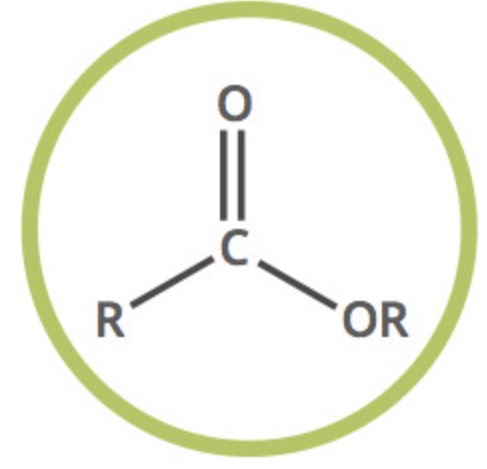
what are ester links?
the link produced when an ester is formed
from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol
what is a polyester?
condensation polymer in which monomers are joined with an ester linkage, contains more than 1 ester functional group
when are two monomer polyesters formed?
condensation reaction between 1 monomer of dicarboxylic acid and 1 diol
what does the repeat unit in a two monomer polyester contain?
2 oxygen atoms, 2 carbonyl groups, everything between the oxygens and carbonyl group
single monomer polyester?
polyester formed from a singular monomer (monomers containing an alcohol and carboxylic acid group react)
what does the repeat unit in a single monomer polyester contain?
1 oxygen atom, 1 carbonyl group, everything between oxygen and carbonyl group
carboxylic acid + amines -> ? + ?
amide + water
what type of reaction is carboxylic acid + amines?
condensation
lots diamine + lots dicarboxylic acid -> ? + ?
polyamide + water
(two monomer polyamide)
what is a polyamide?
condensation polymer in which the monomers are joined through amide linkages
what does a two monomer polyamide repeat unit contain?
two N-H groups, 2 carbonyl, everything between N-H and carbonyl groups
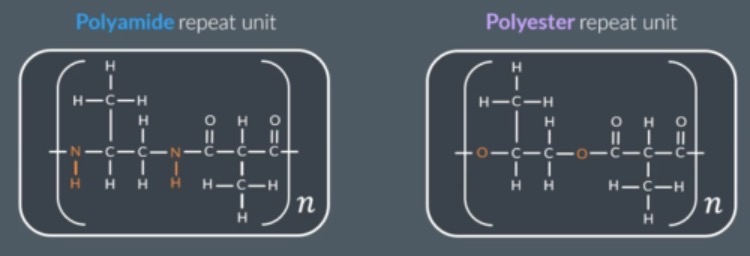
what single monomer forms a polyamide via condensation?
monomers that contain an amine and carboxylic acid group
what does a single monomer polyamide repeat unit contain?
1 N-H group, 1 carbonyl, everything between N-H and carbonyl
what are condensation polymerisation reactions?
any reactions where a monomer reacts to form a polymer and a small molecule (H20/HCl)
diol + diacyl chloride -> ? + ?
polyester + HCl
what does condensation of 1 monomer contaning an OH and COCl group produce?
polyester + HCl
diamine + diacyl chloride -> ? + ?
polyamide + HCl
what does condensation of 1 monomer contaning an NH2 and COCl group produce?
polyamide + HCl
2 types of condensation polymers?
polyesters and polyamides
3 condensation polymer examples?
terylene, nylon 6,6 and kevlar
properties of these condensation polymers?
strong!, high melting and boiling points
terylene: ship sails
nylon 6,6: parachutes
kevlar: bulletproof vests
terylene is an example of which condensation polymer?
polyester
nylon 6,6 is an example of which condensation polymer?
polyamide
kevlar is an example of which condensation polymer?
polyamide
how to distinguish between kevlar and nylon 6,6's repeat units?
kevlar has benzene rings
common name of a polyester?
terylene
why do polyesters have high melting points?
strong van der waals forces due to a lot of e-
polar C=O double bond = permanent dipole-dipole forces, increasing intermolecular forces
why do polyeamides have high melting points?
strong van der waals forces due to a lot of e-
polar C=O double bond = permanent dipole-dipole forces, increasing intermolecular forces
N-H bond = hydrogen bonding
why do addition polymers have lower m.p. than condensation polymers?
only have van der waals forces
why is kelvar stronger/has a higher m.p. than nylon 6,6 despite them both being polyamides?
nylon 6,6: arranged in long, flexible chains
kelvar: planar benzene rings = can stack closely = increases number of hydrogen bonds between chains = increases intermolecular forces strength
3 ways to dispose of plastics?
landfill
incineration
recycling
what is landfill?
solid waste is buried, vegetation can grow on top
what is incineration?
burning of solid waste (plastic) = energy production as it turns turbines
what is recycling?
Converting waste into reusable material:
sorted into polymers
some melted and remoulded
some separated into its monomers
advantages of recycling?
- reduces production of harmful chemicals, like dioxins
disadvantages of recycling?
cheaper to put in landfill or incinerate
takes longer
easy for plastic to get contaminated during recycling -> landfill
some plastics cant be recycled
you cant always make the plastic you started off with, so need to make it new if you want that
Define biodegradable
can be hydrolysed by living things into naturally occuring molecules within 6 months, such as CO2 and H2O
is PVC biodegradable?
no
is PLA biodegradable?
yes
what type of polymer is PVC?
addition polymer
what type of polymer is PLA?
condensation polymer
are condensation polymers biodegradable?
yes
are addition polymers biodegradable?
no x
why are condensation polymers biodegradable and addition polymers arent?
to hydrolyse, you'd need to break the chain:
addition polymers - C-C bond - strong + non polar
condensation: break amide or ester link (EASIER)
why are C-C bonds difficult to break?
strong and non polar -> unreactive and difficult to break
polyesters can be hydrolysed with water to form what?
carboxylic acid + alcohol
why can water react with polyesters and polyamides for hydrolysis?
ester/amide links contain C=O pola bonds, carbon has a slight positive charge, so nucleophiles (water) can attack it
why arent addition polymers biodegradable?
contain C-C non polar bonds, so cant be attacked by nucleophiles (water)