Unit 6: (6.10) Geothermal Energy
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
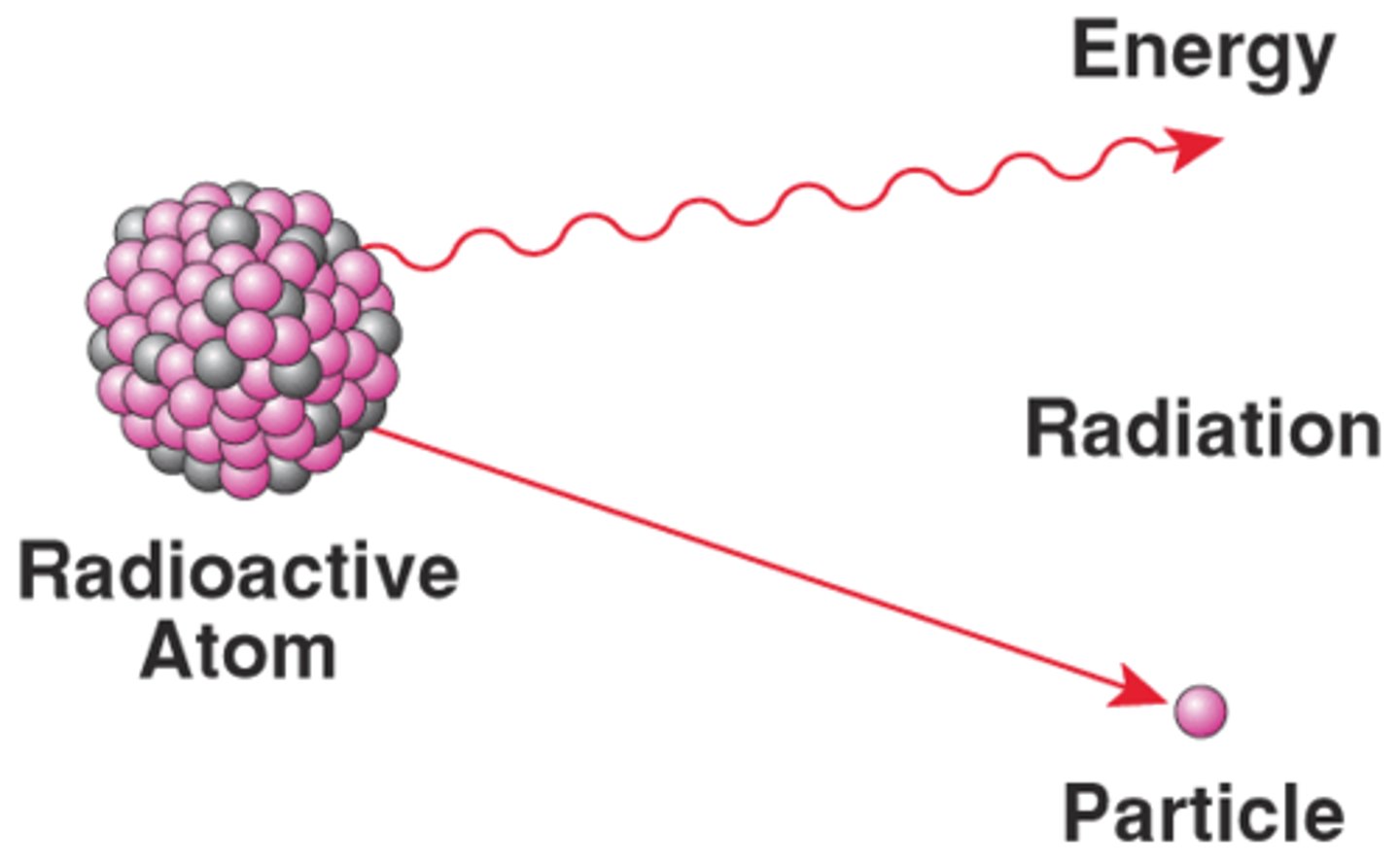
Radioactive decay
The breakdown of a radioactive element, releasing particles and energy (heat). Heat from radioactive decay in the earth's core heats groundwater that is utilized in geothermal energy systems.
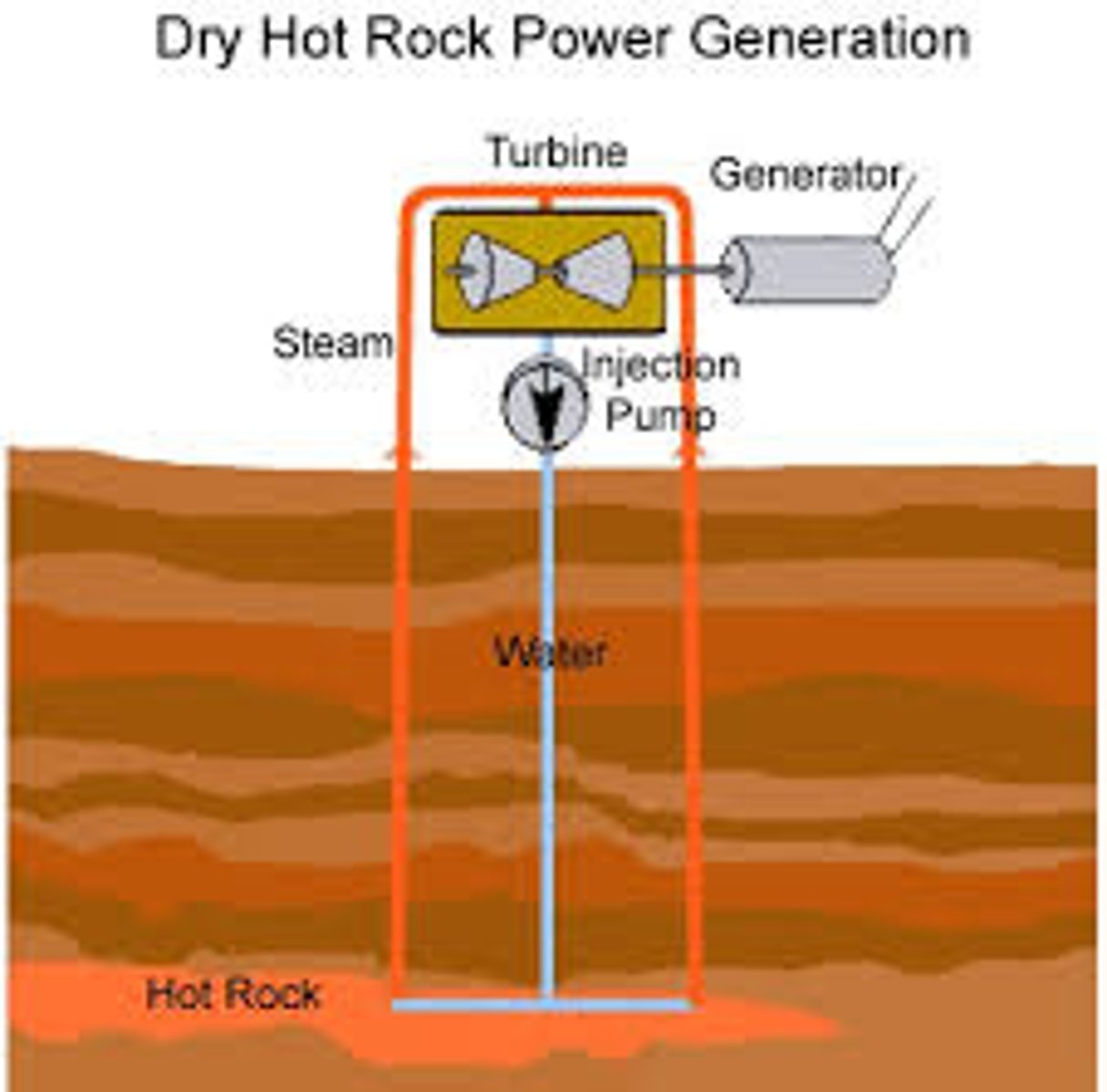
Geothermal Electricity
Steam generated from ground water sources heated by magma from earth's core is piped up to the surface at a geothermal power plant where it turns a turbine, which powers an electrical generator, after which the cooled water is returned to the ground water source
Geothermal home/building heating
Hot water or steam from hot water sources underground is piped into a home or building, where it warms the air in the building via a radiator. NOT TO BE CONFUSED WITH GROUND SOURCE HEAT PUMPS.
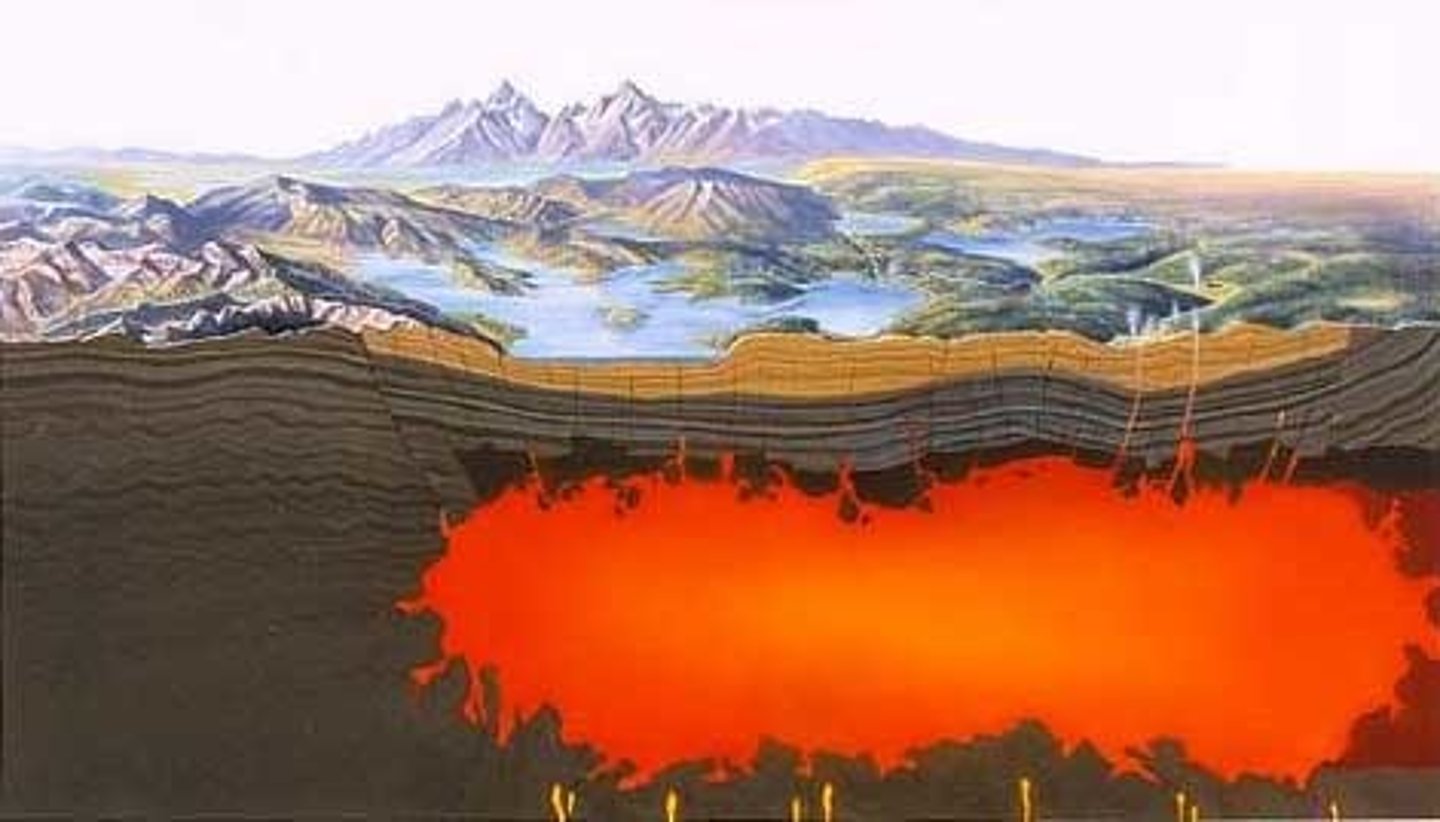
Magma
Molten rock beneath the earth's surface, particularly in the mantle

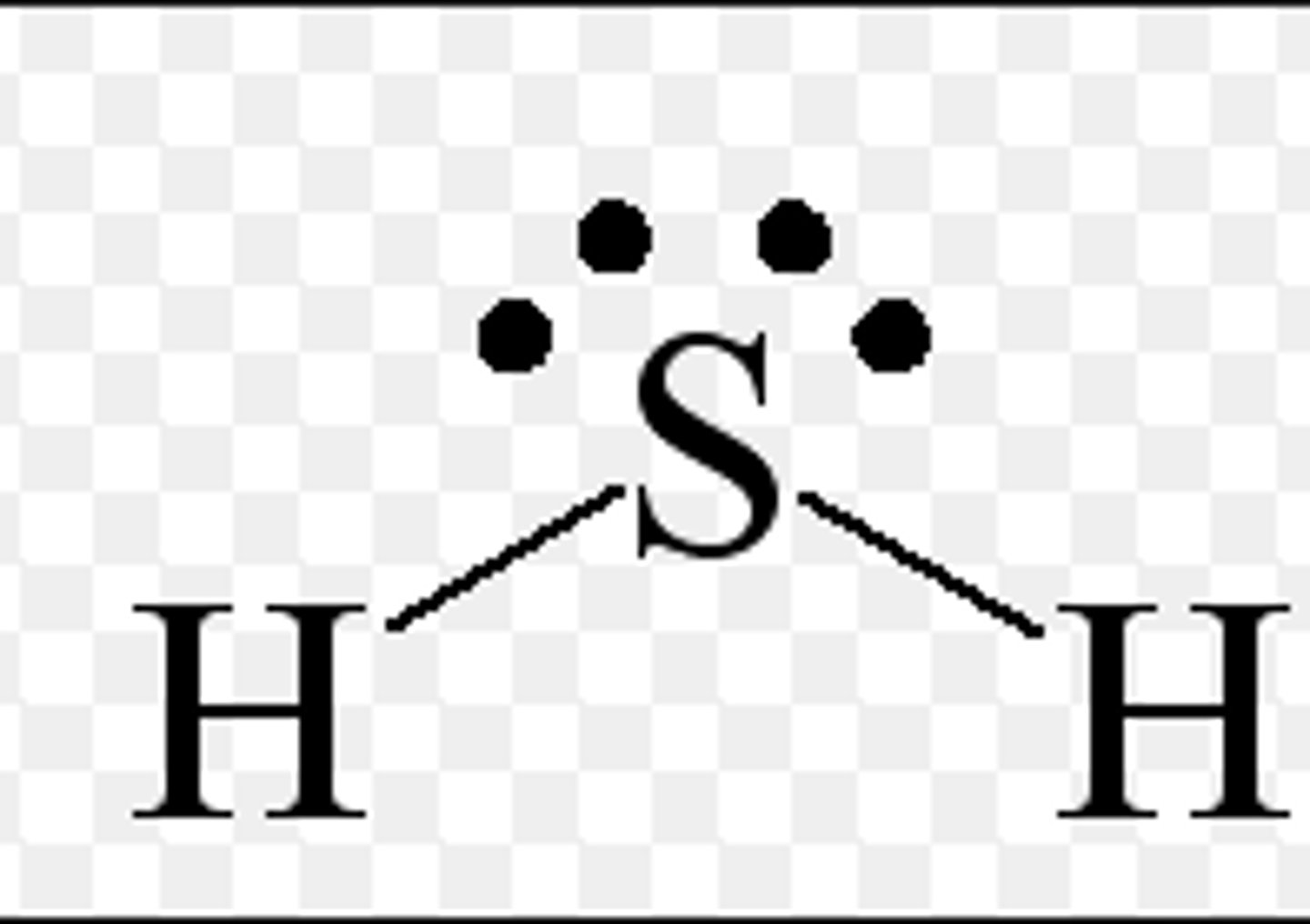
Hydrogen sulfide
A toxic gas that can be produced as a byproduct of the steam generation at geothermal power plants. Highly lethal to humans, even in small dosages.
ground source heat pump
Heating system for buildings that takes advantage of the constant, 50-60 degree temperature of the ground, about 10 feet below the surface. Heat source comes from the sun, not radioactive decay in earth's core. Heat-absorbing fluid is piped underground, where it is warmed by the ground, returned to the building, run through a compressor that converts it to hot gas, and then through a heat exchanger that warms the air in the house with the heat from the gas.
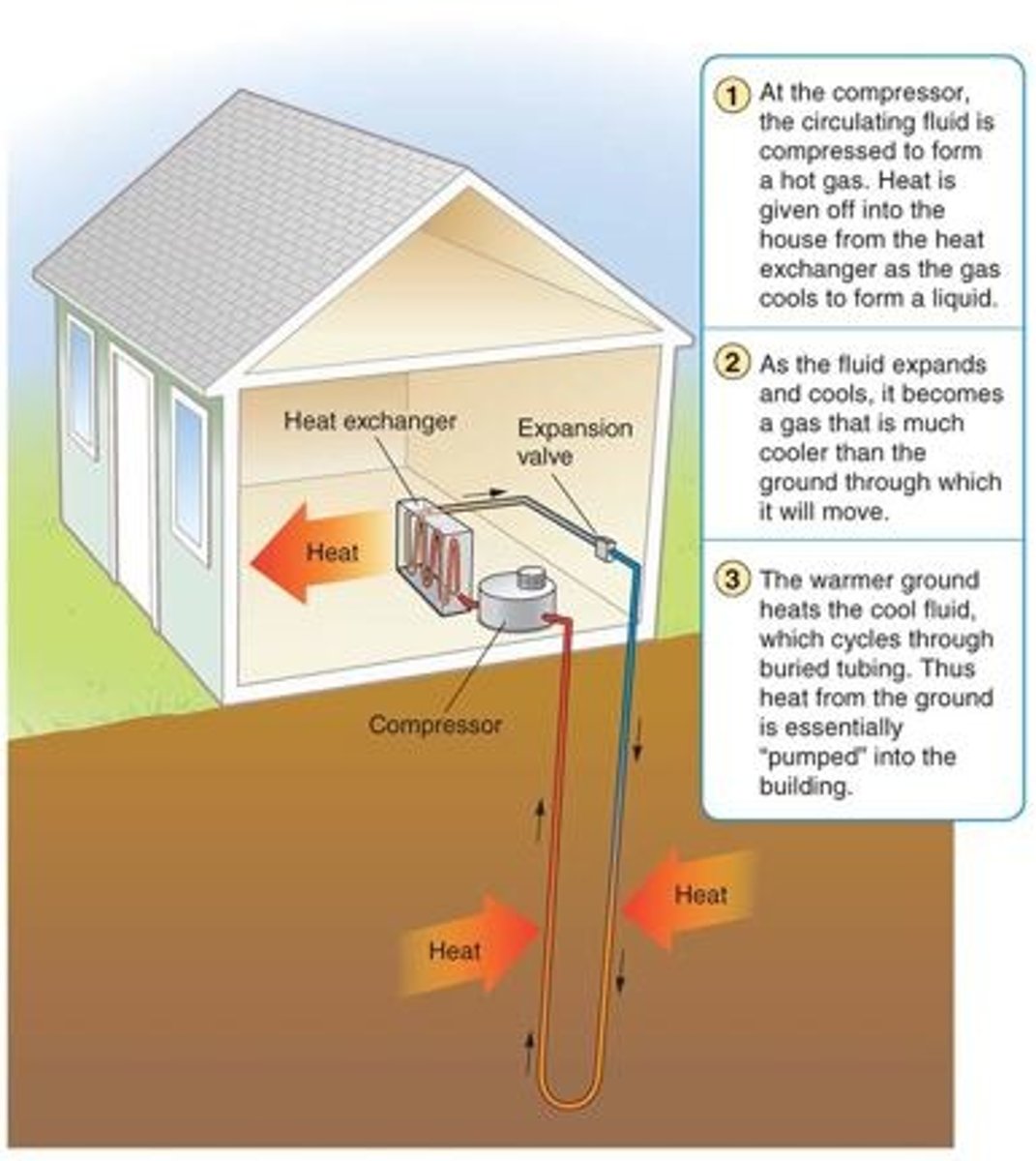
Compressor
A pump that compresses heating liquid into a hot gas receiver tank.
heat exchanger
Transfers heat from hot gas in a ground source heat pump system to the air in a building, providing heat to the building
advantages of geothermal energy
Ability to supply base-load electricity (constant supply)
Nondepletable heat source (radioactive decay of earth's core)
little to no CO2 emission and no NOx, SOx, PM, Ash, Lead, Mercury, CO
disadvantages of geothermal energy
High initial start up cost
Can emit lethal, Hydrogen Sulfide gas
Geographically limited (only available near high tectonic activity areas)
Can deplete groundwater sources if used water isn't returned to the ground water source