Other Liver Disease
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
A pt presents with complaints of abd pain, fever, and encephalopathy. Upon history taking you note the pt has had recent heavy periods of heavy drinking. The PE findings are hepatomegaly and jaundice. LFT elevation of AST> ALT 2:1. ---- what is the likely dx?
Alcoholic LD
What are the diagnostics for alcoholic LD?
LFT elevation- AST > ALT, 2:1*
liver biopsy
What is the tx for SEVERE alcohol hepatitis?
◦Methylprednisolone x 1 month
◦N-acetylcysteine
◦Pentoxifylline
What is the tx for alcoholic LD?
◦EtOH cessation
◦Hospitalized pt should be monitored (CIWA)
◦Nutritional support: Folic acid, thiamine, zinc
What are most indications of drugs that case toxin induced liver injury?
TYLENOL!!! APAP, NSAIDs (diclofenac and coxibs) and antibiotics
What is the MCC of acute fulminant liver failure?
Drug and Toxin Induced Liver Injury
What are the diagnostics for drug and toxin induced liver injury?
◦Thorough history, clinical suspicion
◦Liver biopsy: if cause unclear, guide treatment, extent of damage
◦LFTs: often > 25x ULN
What is the tx for drug and toxin induced liver injury?
◦Liver failure = admission
◦Refer to GI or hepatologist
What is the MCC of chronically elevated LFTs?
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
What are the diagnostic options for (Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease?
ALT: AST > 1, mild increases <4x
Imaging:
US, CT, MRI
Percutaneous liver biopsy = diagnostic and standard approach to assessing degree of inflammation and fibrosis
What are some comorbid conditions that can cause NAFLD?
Diabetes, obesity, hyperlipidemia, insulin resistance
What are some medications that can cause NAFLD?
Corticosteroids, antiretrovirals, tamoxifen
A pt presents with mild RUQ pain. She has a hx of diabetes. PE notes hepatomegaly. Diagnostics show ALT: AST >1. Biopsy reveals inflammation and fibrosis. --- what is the likely dx?
NAFLD
What is the MCC of chronically elevated LFTs?
NAFLD
What are the diagnostics for NAFLD?
◦ALT: AST > 1, mild increases <4x
◦US, CT, MRI
◦Percutaneous liver biopsy = diagnostic and standard approach to assessing degree of inflammation and fibrosis
What is the tx for NAFLD?
◦Exclude other causes of steatosis
◦Weight loss, dietary fat restriction, moderate exercise, EtOH cessation
◦Medications aimed at decreasing insulin resistance
What occurs as Irreversible liver fibrosis with nodular regeneration, secondary to chronic liver disease --> nodules lead to increased portal pressure?
cirrhosis
What are the MCC of cirrhosis in the US?
hep C and EtOH
A pt presents with complaints of fatigue, nausea, lack of appetite, and itching. Upon PE you see caput medusa and palmar erythema on the skin. --- What is the likely dx?
cirrhosis
What are some skin manifestations for cirrhosis?
spider angiomas, caput medusa, muscle wasting, bleeds, palmar erythema, jaundice, Dupuytren’s contractures
A pt presenting with confusion, and lethargy with PE findings of asterixis and fetor hepaticus-- what is the likely issue because of what dx?
hepatic encephalopathy-- cirrhosis
What can present with cirrhosis due to portal HTN?
esophageal varices
What are the diagnostics for cirrhosis?
◦Ultrasound: Ascites, hepatic nodules, HCC, vein patency, elastrography
◦MRI
◦Liver bx
◦Labs: CBC: macrocytic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. PT/INR: increase. CMP: AST/ALT, ALP (Normal or elevated), bilirubin increase, Albumin: low
◦FibroSure: serum marker of fibrosis
What are some complications of cirrhosis?
◦HCC
◦Liver failure
◦Hepatorenal syndrome
What is the tx for encephalopathy bc of cirrhosis?
Lactulose, neomycin, rifaximin
What are the recommended vaccines for cirrhosis?
HAV, HBV, pneumococcal, influenza
To treat pruritis secondary to liver cirrhosis, what can be used?
cholestyramine
For a pt presenting with ascites due to cirrhosis what is the tx?
salt restriction 2g/day, fluid restrictions, spironolactone, furosemide, paracentesis
What is the definitive management for cirrhosis?
liver transplant
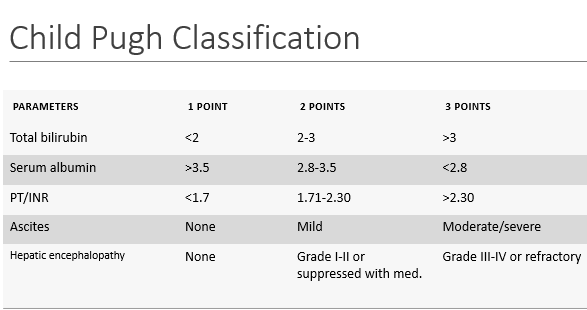
What measures child survival rate based on lab values?
child pugh classification
*don’t memorize*
What is characterized by rapid liver failure + hepatic encephalopathy (often w/ coagulopathy)?
Acute Hepatic Failure (Fulminant Hepatitis):
What is the MCC of acute hepatic failure (fulminant hepatitis)?
APAP (Tylenol)
A pt presents with encephalopathy and coagulopathy. Upon PE you note hepatomegaly and jaundice. The diagnostics show increase in ammonia and hypoglycemia---- what is the likely dx?
acute hepatic failure
What are the diagnostics and results of acute hepatic failure?
◦↑ ammonia
◦↑ PT/INR*
◦↑ LFTs (> 10x AST/ALT; TB, ALP)
◦↓ albumin
◦Hypoglycemia
What is the ONLY definitive treatment for acute hepatic failure?
liver transplant
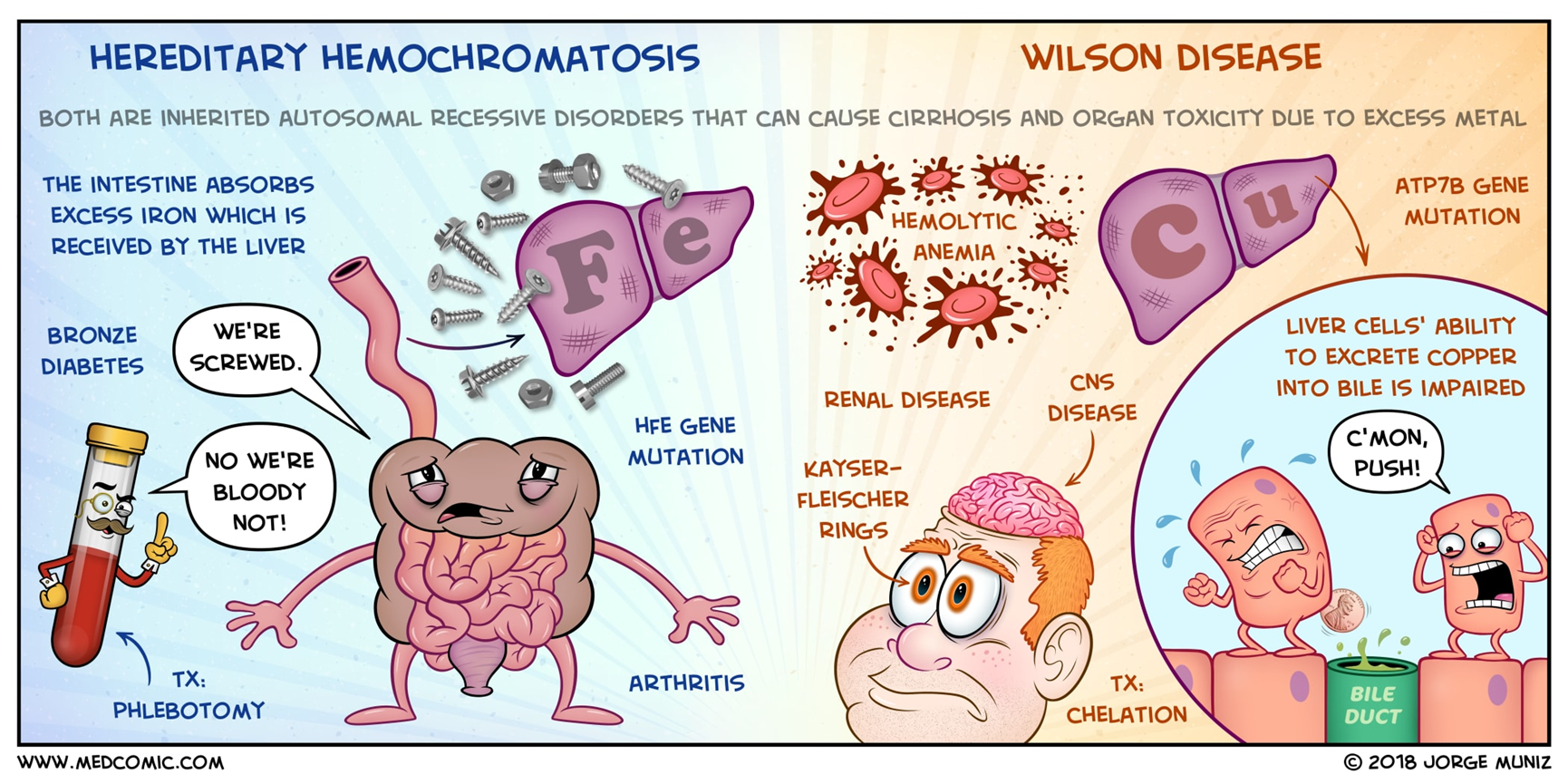
What is a rare autosomal recessive disease that occurs due to a mutation on chr 13 in the gene ATP7B that causes free copper accumulation in the liver, brain, kidney, and cornea?
wilsons disease
Is Wilsons disease autosomal recessive or dominant?
recessive
What should be suspected in any patient under age 40 with chronic hepatitis or acute liver failure?
wilsons disease
A young male adult comes into the office with the mother complaining of personality and behavior changes. Upon PE you note kayser fleisher rings (corneal copper deposits)--- what is the likely dx?
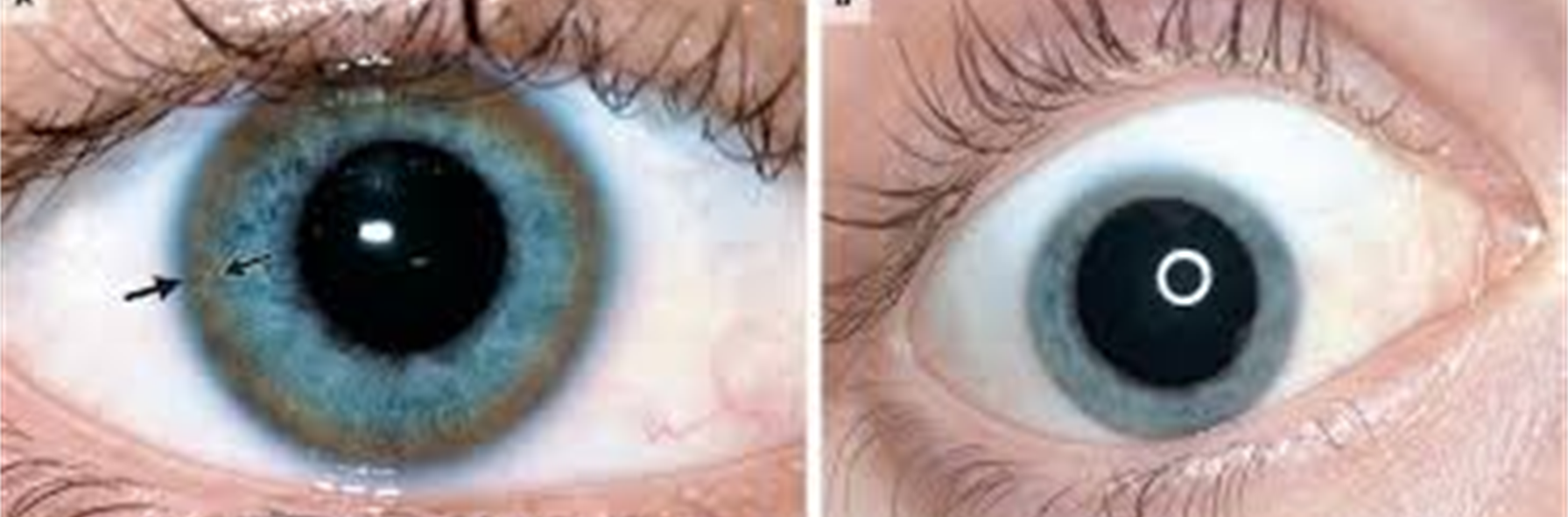
wilsons disease
What are the diagnostics for wilsons disease?
◦↑ urinary Cu excretion (40+ mcg/24h)
◦↓ ceruloplasmin (<14mg/dL)
◦Coombs-negative hemolytic anemia
◦Liver bx: increased Cu
◦Genetic testing: ATP7B mutation
What is the genetic testing for wilsons disease?
ATP7B mutation
What is the drug of choice for Wilson’s Disease?
Trientine 2nd line
For a liver biopsy with suspected wilsons disease-- what is the likely dx?
increased Cu
What is an autosomal recessive mutation that occurs on teh HFE gene on chromosome 6 that causes increased accumulation of iron in the liver, pancreas, heart, adrenals, testes, pituitary, and kidneys?
hemochromatosis
A pt presents with complaints of fatigue, arthralgias, and impotence. PE you note hepatomegaly, cardiomegaly, and skin pigmentation (“bronze diabetes”). This pt does have a hx of DM. ---- what is the likely dx?
hemochromatosis
The clinical presentation of "bronze diabetes" occurs in what diagnosis?
hemochromatosis
What is the diagnostic testing for hemochromatosis?
◦CMP: Mildly elevated LFTs
◦↑ plasma iron
◦>45% transferrin saturation
◦↑ ferritin
◦Gene testing: HFE mutation (Chromosome 6)
◦MRI or CT scan (MRI assess degree of fibrosis)
◦Liver biopsy to determine cirrhosis
What is the genetic testing for suspected hemochromatosis?
HFE mutation on chr 6
What is the tx for hemochromatosis?
◦Avoid foods rich in Fe
◦Weekly phlebotomy
◦Proton-pump inhibitors- Decrease intestinal Fe absorption
◦Chelating agents for those who cannot tolerate phlebotomies- Deferoxamine
What is a complication seen in hemochromatosis?
Cirrhosis- more likely if male, DM, with ETOH or steatosis; cardiac conductions issues
differentiate between herditary hemochromatosis and welson disease
What is a hepatic venous outflow obstruction that MC occurs due to hepatic vein thrombosis?
Budd chiari syndrome
What are the risk factors associated with budd chiari syndrome?
◦Idiopathic
◦Hypercoagulable state* 75% of patients
◦Genetic mutations: often JAK2
What is the pathophys of bud chiari syndrome?
hepatic vein thrombosis or occlusion
→ ↓ liver drainage, portal HTN, necrosis, fibrosis → cirrhosis
Budd Chiari syndrome is most commonly seen in what demographic?
Women aged 20-30s
What presents with the classic triad of ascites, hepatomegaly, and RUQ pain?
budd chiari syndrome
What presentation of budd chiari syndrome is most common?
Subacute
(others: acute with liver failure, acute w/o liver failure, chronic)
A 20yo F pt presents with abd pain. Upon PE you note the triad of ascites, hepatomegaly, and RUQ pain. While waiting for the diagnostic US--- what is the likely dx?
budd chiari syndome
What is the diagnostic for budd chiari syndome?
US
If non-invasive tests (US) fails for suspected budd chiari syndrome -- what is the 2nd GS?
venography
What is the tx for budd chiari syndome?
Shunts, angioplasty with stent, pharmacologic tx of coagulopathy
What is the management for ascites due to budd chiari syndrome?
diuretics, low Na diet, large volume paracentesis
What is a hepatic invasion of the bile duct that is MCC by acute cholangitis?
pyogenic hepatic abscess
What are the RFs for pyogenic hepatic abscess?
older age, male, comorbid conditions, PPI use
A pt presents with insidious onset of epigastric RUQ pain and fever. Upon PE you note RUQ tenderness and jaundice. A CBC shows a L shift and the LFTs are elevated ---- what is the likely dx?
pyogenic hepatic abscess
What is the tx for pyogenic hepatic abscess?
IV abx: Ceftriaxone (Rocephin) 2g Qdaily and metronidazole (Flagyl) 500mg QID x typically 2-3 weeks but up to 6 weeks
What is the term for Pathologic accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity?
ascities
A pt presents with a hx of increasing abd girth and pain. Upon PE you note signs of portal HTN, elevated JVD, and large tender liver. Diagnostics of abdominal paracentesis show milky/bloody fluid. --- what is the likely dx?
ascities
What are the diagnostics for acities?
Abdominal paracentesis- milky, bloody
imaging: US and CT
Laproscopy
For a pt with likely ascites there will be an ____ in glucose and a ____ in LDH to differentiate from bacterial peritonitis.
decrease, increase
What is the tx for ascities?
based on underlying cause
What is the 5 criteria of pyogenic hepatic abscess that should be drained?
◦If >5 cm
◦Not having a rapid response to abx
◦>55 years old
◦Symptoms >7 days
◦Involvement of 2 lobes of liver