Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy, Placentation, Pregnancy, and partrition
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What is the signal of maternal recognition in pigs?
Estradiol
Cattle have what type of placental classification?
Cattle have a Cotyledonary-Epitheliochorial placenta
Pigs have what type of placental classification?
Pigs have a diffuse-Epitheliochorial type placental classification
What are the precursor cells that will develop into the chorion?
Mesoderm and trophectoderm
What are the precursor cells that will develop into the amnion?
Mesoderm
T/F: The process of placentation is more invasive in women than domestic species
True: placentation is more invasive in women than domestic species
T/F: The process of placentation is more invasive in rodents than domestic species
True: Placentation is more invasive in rodents than domestic species
What type of placenta do dogs have?
Dogs have Endotheliochorial-Zonary placenta type
Within the placenta of a mid-pregnant ewe you would observe cholesterol being converted into pregnenolone by?
Cytochrome P450 side chain cleavage (scc) will convert cholesterol to pregnenolone, and 3 Beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3B-HSD) will convert pregnenolone to progesterone
During parturition, what type of signal is sent to the posterior pituitary from the cervix?
The cervix sends oxytocin and pressure receptors
During parturition, describe 3 effects of estradiol on the reproductive tract of mom:
Enhances secretion to lubricate birth canal
Increase OT-R (oxytocin receptors)
Helps assist a signal to cause contractions in the myometrium
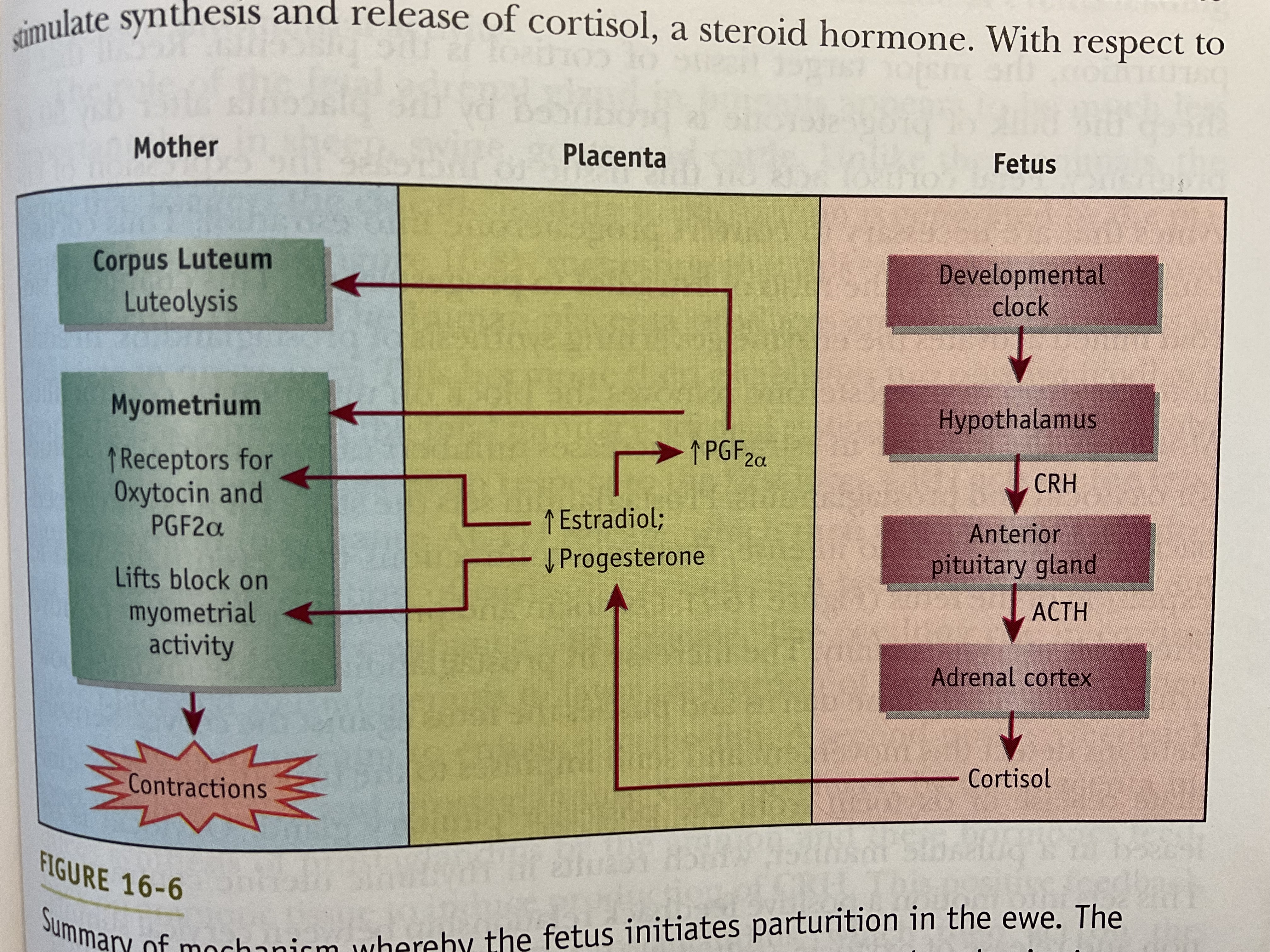
What is corticotropin releasing hormone, where is it produced, and what endocrine gland does it target?
Corticotropin releasing hormone: Stimulates synthesis and secretion of cortisol
Produced: Released form hypothalamus, stimulating anterior pituitary to release ACTH
Endocrine gland targeted: Adrenal Cortex
At the onset of parturition, identify one enzyme that you would expect to differ in the placenta during the shift in steroidgensis
Progesterone is the major steroid produced by the placenta. During parturition, progesterone will decrease. The enzyme 3B-HSD converts pregneolone to progesterone, so this enzyme may be impacted by parturition.
What occurs to the myometrium when progesterone decreases?
A decrease in P4 during pregnancy will lift the block on myometrial activity causing contractions
What are the five cellular mechanisms that mediate the transfer of materials from the blood or extracellular space across the trophoblast?
Simple Diffusion
Restricted diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Active transport
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Simple Diffusion
Lipophilic molecules across the trophoblast (oxygen)
Restricted diffusion
Restricted diffusion of hydrophilic molecules through aqueous channels (mannitol: Sugar molecule). Size of molecule can also be impacted by this.
Facilitated diffusion
Requires a transporter protein (D-glucose). Goes from high concentration to low
Active transport
Requires a transporter protein and goes from LOW to HIGH concentration.
Ex: Amino acids- important for muscle growth!
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Receptor-mediated endocytosis: A cellular process where cells import specific molecules by binding them to cell surface receptors, forming a vesicle to bring molecules inside
Immunoglobulins (antibodies): Proteins produced by the immune system to fight infections
What are some important substances transported between mother and fetus?
Glucose, lactose, amino acids, lipids, ions, calcium, phosphorous, magnesium, trace minerals, proteins, respiratory gases, various drugs
What are some functions of estradiol?
Support growth of follicles
Induce expression of heat behavior
Induce ovulation
Relax the cervix
Induce mucus production by the cervix
Contractions in uterus and oviduct to direct sperm to the oocyte
What are some functions of progesterone?
Prevents expression of heat behavior
Prevents ovulation
Closes the cervix
Prevents contractions of the uterus and oviduct
Supports pregnancy
The growing fetus will develop within two layers of fetal membranes. What are these fluid-filled membranes?
Amnion (adjacent to the membrane) and Chorioallantois (outside the amnion)
Where does placental attachment occur?
Along the outer surface of the chorioallantois
In pigs, what is the placental attachment the is attached along the entire fetal membrane?
In pigs, the attachment is called “diffuse”
In ruminants, attachment occurs at specific sites called _______, and have __________ placental attachment
In ruminants, attachment occurs at specific sites called cotyledons, and have Cotyledonary placental attachment
In ruminants, how do cotyledons of the chorioallantois attach to the uterus?
The cotyledons of the chorioallantois attach to caruncles along the inner surface of the uterus
When the fetus is large enough, pressure of the fetus on the cervix releases what hormone?
Oxytocin is released due to pressure against the cervix and will induce contractions, further pressing fetus again cervix=positive feedback cycle
The germ layer endoderm will give rise to what major types of tissues?
Digestive system
Respiratory system
Endocrine glands
The germ layer mesoderm will give rise to what major types of tissues?
Skeleton
Muscle
Heart and blood vessels
Reproductive organs
The germ layer ectoderm will give rise to what major types of tissues?
Nervous system
Skin
Hair
In order for pregnancy to advance beyond the blastocyst stage, the conceptus must provide a signal to maintain maternal production of ___________ and form a placenta with the maternal uterus
The conceptus must provide a signal to maintain maternal production of progesterone
What is the major pre-requisite for maternal recognition of pregnancy and implantation of the embryo into the uterus?
Development of the trophectoderm
How does the maternal recognition of pregnancy signals prevent/delay luteolysis?
The signal of maternal recognition of pregnancy stops luteolysis by interfering with prostaglandin-induced regression of the CL OR by boosting the luteotropic signal
What are the cells of the embryo that send signals to uterine epithelial cells to prevent luteolysis?
Trophoblast
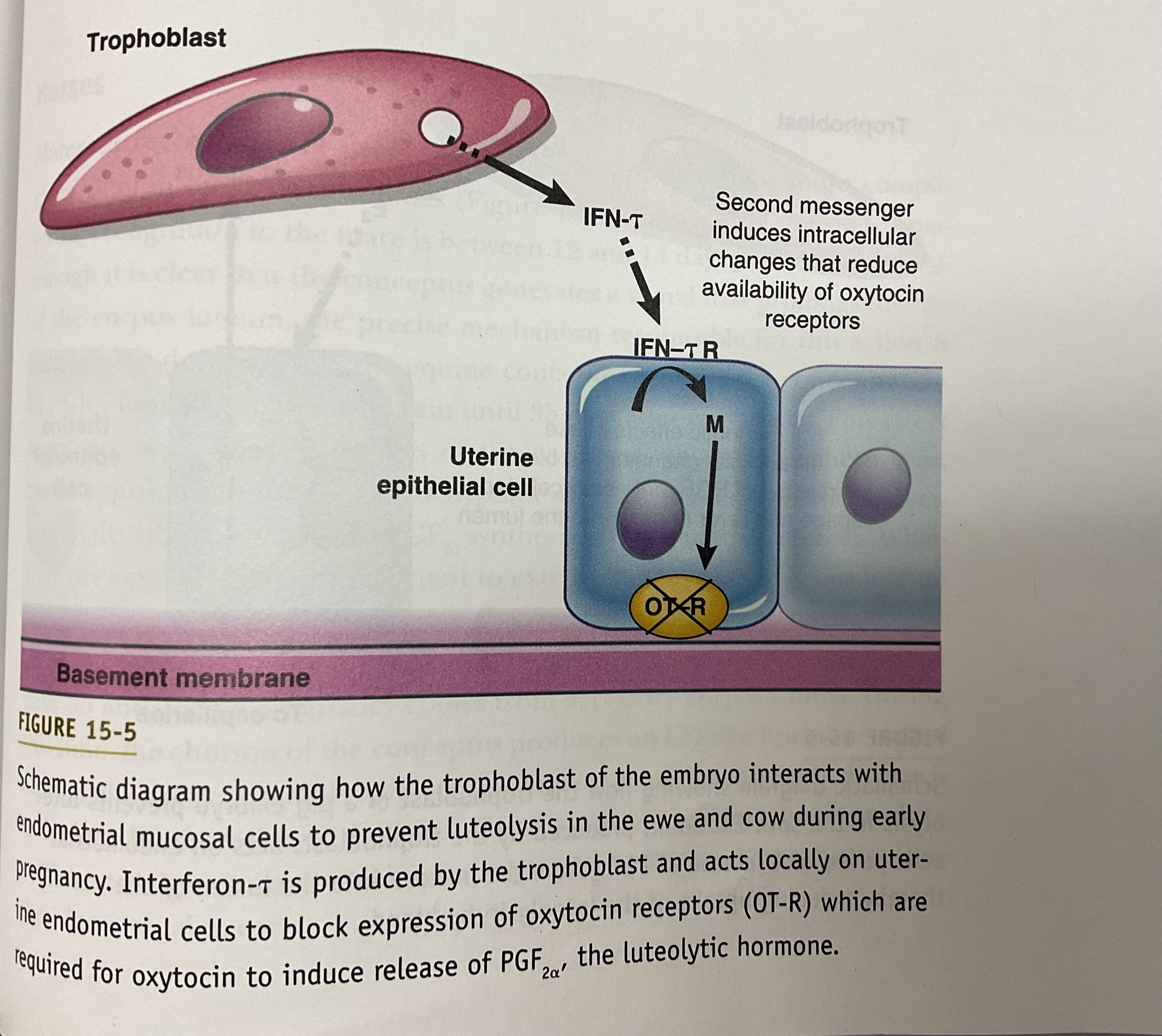
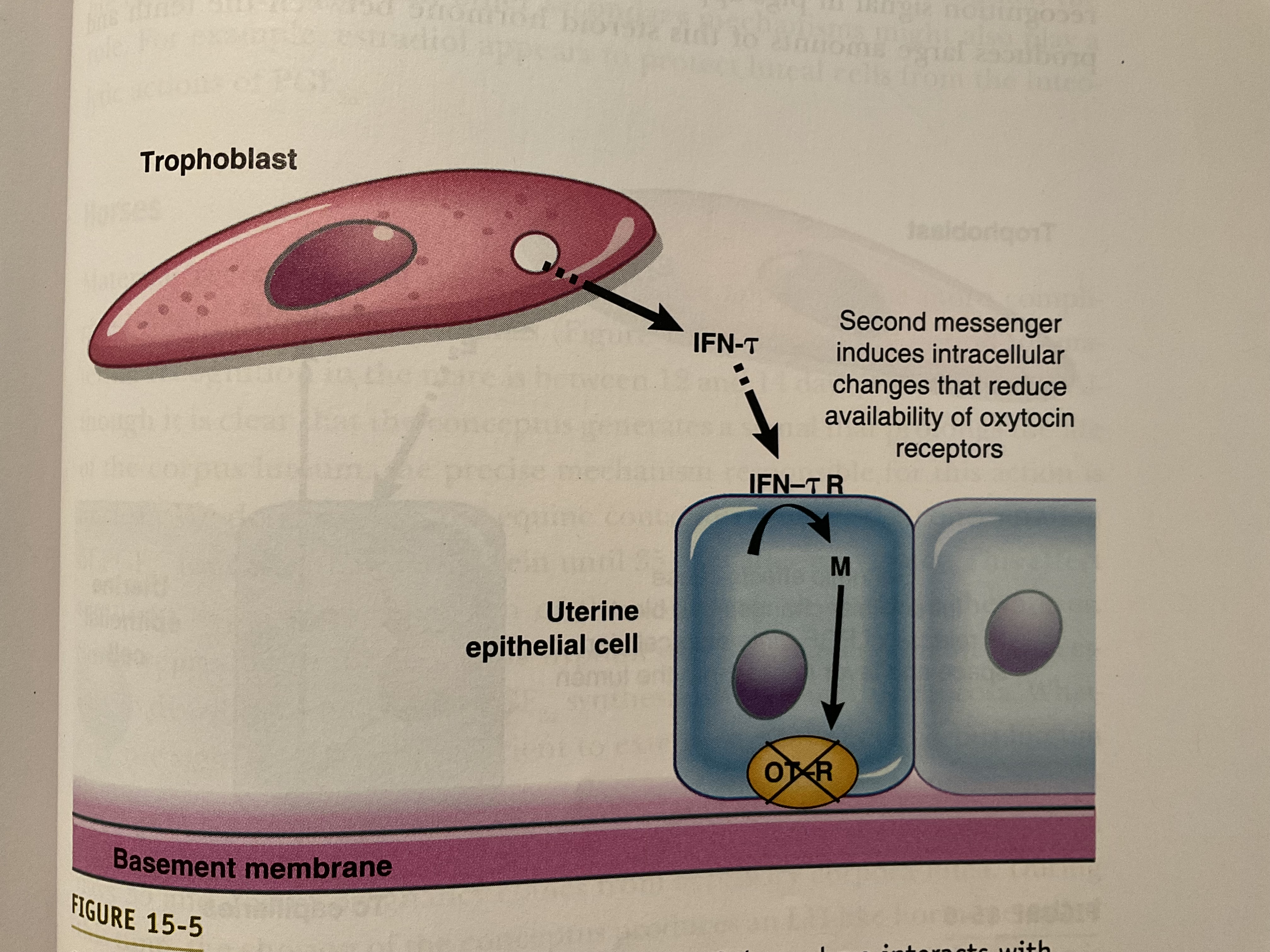
What is the peptide produced by trophoblasts that signal the uterus to prevent luteolysis in ewes?
The peptide signal ovine interferon (oIFn-t) produced by the trophoblast will be detected by the uterus to prevent luteolysis
What is the peptide produced by trophoblasts that signal the uterus to prevent luteolysis in cows?
The pregnancy-recognition signal in cows is bovine interferon (bIFN-t)
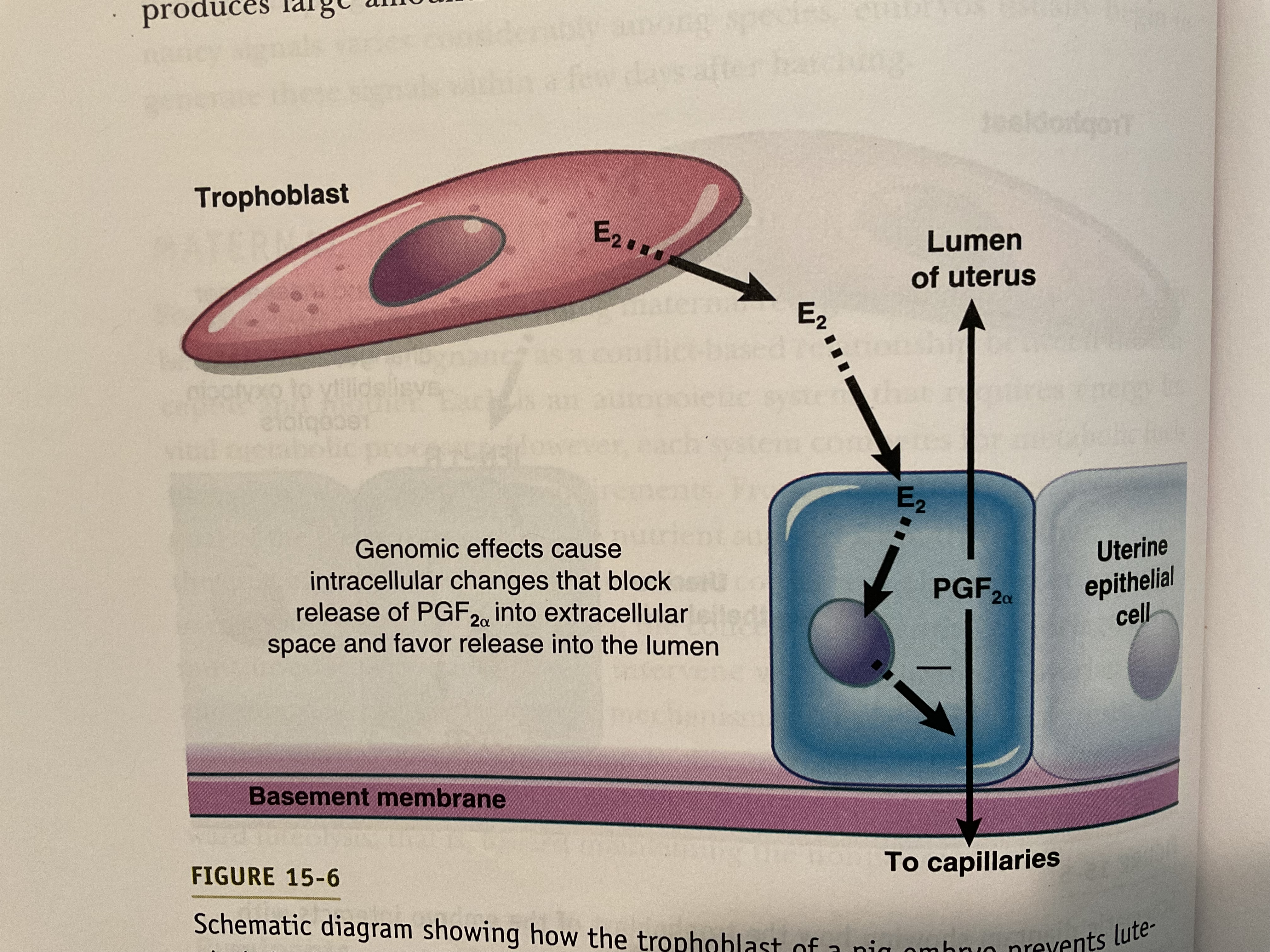
Explain how the estradiol signal in swine prevents luteolysis?
Estradiol produced by the trophoblast acts on endometrial cells to redirect release of prostaglandins from the mucosa into the lumen of the uterus , thereby reducing uptake of the luteolysin by blood
Describe how the signal interferon-t in ewes and cows prevent luteolysis
Trophoblast of the embryo produces interferon-t and acts on uterine endometrial cells to black expression of oxytocin receptors (OT-R) which are required for oxytocin to induce release of PGF2a, the luteolytic hormone
What is the equine blastocyst capsule that causes the signal of maternal recognition to be unknown?
Elastic glycocalyx
What is the secondary messenger in the uterine endometrial cell that will cause the blocking of estrogen stimulation of oxytocin receptors when in contact with IFN-t?
IFN-t inhibits ERa, thus blocking the estrogen stimulation of oxytocin receptors
What are the 3 ways interferon-tau exert its antiluteolytic effects:
Inhibiting effects of estrogen and/or progesterone necessary for synthesis of endometrial receptors for oxytocin
Inhibiting endometrial synthesis and/or recycling of OT receptors directly
Inducing the endometrium to synthesize an inhibitor of an enzyme(s) necessary for synthesis of PGF2alpha
What hormone and enzyme activates PGF2alpha?
Hormone: Oxytocin is released from the posterior pituitary activated by E2 to target OT-R on the endometrium (endometrial cells)
Enzyme: Cox-2 converts arachidonic acid to PGF2alpha
What uterine layer causes contractions?
Myometrium
Though the signal of maternal recognition is unknown in mares, what are the hypothesized signals?
The hypothesized signal in mares is E2 and coceptus secretory proteins (CSP’s)
Why is luteal regression the default mechanism when theire is no embryonic signal?
Lutealization is a default mechanism since it saves energy and reproductive efficiency
What part of the embryonic membrane is avascular?
The chorion is avascular
How is the allantochorion created?
The allantois expands and eventually fuses with the chorion to form the allantochorion
What are all 6 layers of the epitheliochorial placenta type based on maternal/fetal barrier?
Fetal endothelium
Fetal connective tissue (includes basement membrane of chorion)
Fetal chorionic epithelium
Maternal endometrial epithelium
Maternal connective tissue (Includes the basement membrane of endometrium)
Maternal endothelium
Name all 4 species that have an epitheliochorial maternal-fetal barrier type placenta:
Cow
Ewe (sheep)
Mare (horse)
Pig
Name the 2 species that have a endotheliochorial maternal-fetal barrier type placenta
dogs
cats
What are the 4 layers of the endotheliochorial placental classification of the maternal/fetal barrier?
Fetal endothelium
Fetal connective tissue
Fetal chorionic epithelium
Maternal endothelium
What the 3 layers of the hemochorial placenta classification of the maternal-fetal barrier?
Fetal endothelium
Fetal connective tissue including the basement membrane of the chorion
Fetal chorionic epithelium
During partition, the increase of PGF2alpha does what 2 things?
Luteal regression (decreases P4 further)
Relaxin (hormone) release from CL (relaxation of ligaments in pelvis, enlarging pelvic opening)
What are the impacts of the increase of E2 during parturition?
Enhances secretion to lubricate the birth canal (cervical and vaginal)
Increases OT and PGF2a (FP) receptors
In addition to PGF2a, what do prostaglandins do to assist in parturition?
The enzyme cox-2 converts arachidonic acid to prostaglandins to help assist in luteal regression and contractions. PGF2a binds to FP on the myometrium causing smooth muscle contractions