Brain mapping (Chapter 3)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Early mapping methods
appearance tissue and staining
Brain networks
collection of brain regions that are connected and work together to support brain function (cable wires example)
Brain connection project
Attempt to map all neural connections
Computer Topography scans (CT scans)
Combinations of x ray photos
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
maps with magnetic fields and radio waves
Diffusion Tension imaging (DTI)
MRI variation, helps researchers assess the size and direction of connections
Phrenology
1800s Pseudoscience that believed bumps on a skull correlated with abilities and personality traits (led to localization)
Localization
certain parts of the brain have certain functions
Neuropsychology
Looking at brain function through brain damage
Lesion
abnormal brain tissue caused by illness, trauma, or surgical intervention
Dissociation
A brain area is involved in a function but not in another function
double dissociation
Gold standard for lesion testing; Ex. you have eye damage, can’t see but can still hear
Broca’s area
area that produces language
Wenike’s area
responsible for comprehension
Single-cell recording
measuring the electrical activity from one neuron
Electroencephalography (EEG)
recording of electrical waves from thousands of neurons
magnetoencephalography (MEG)
Recording of magnetic fields made by brain (looks at when activity occurs)
Event related potential (ERP)
Synchronized electrical response to an event; averaged EEG data; visualizes cognitive process
Position emission potential
Glucose tracked to assess areas of activity
Functional Magnetic resonance imagine (FMRI)
Displays brain acitivty area
Deep brain stimulation (DBS)
Stimulating specific parts of the brain with an implemented electrode
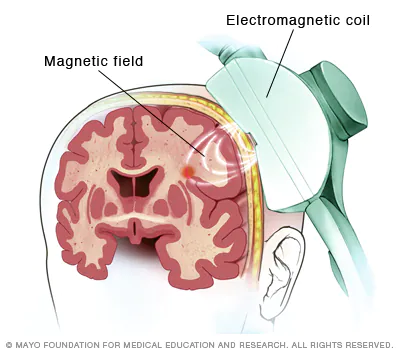
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
short, high powered electrical surge to coil
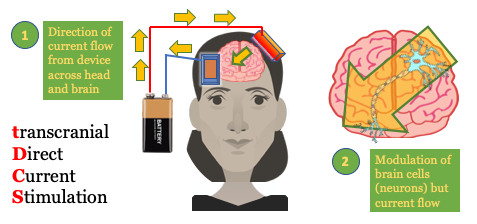
Transmittal Direct Current Stimulation
Low electrical current; several minutes