Anorectal and Colorectal Cancer
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
TRIGGER WARNING BUTTHOLES - italicised is outside resources
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
prevent sphincter damage (when they get damaged through straining/engorgement → hemorrhoids)
What is the purpose of hemorrhoid cushions - normal anatomy
Internal (arise from superior hemorrhoidal cushion), External (arise from hemorrhoidal plexus - more common thrombosis)
Classifications of hemorrhoids
Internal
Which type of hemorrhoid is above/proximal to the dentate line, normally painless, and represents a majority of hemorrhoids and sources of rectal bleeding?
1
Which grade of internal hemorrhoids has painless bleeding and on exam you find prominent vascular engorgement bulging into the canal without prolapse?
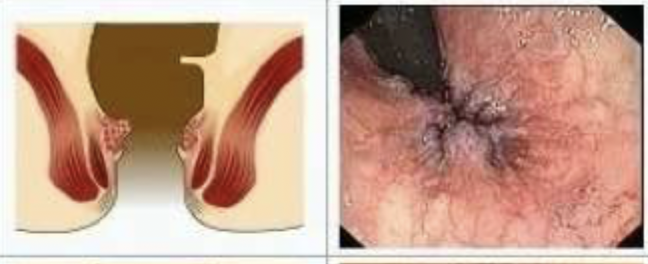
2
Which grade of internal hemorrhoids has painless bleeding and perianal itching and on exam you find that the hemorrhoid prolapses with straining but reduces spontaneously?
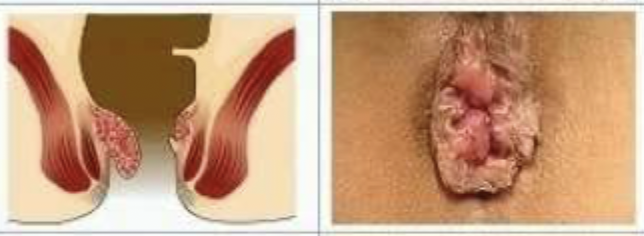
3
Which grade of internal hemorrhoids has painless bleeding, perianal itching, swelling, and staining/soilage with mucous or feces and on exam you find that the hemorrhoid prolapses beyond the dentate line and is only reducible with manual pressure?
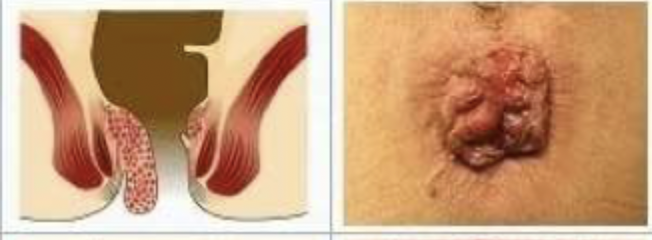
4
Which grade of internal hemorrhoids has pain, bleeding, swelling, and staining/soilage with mucous or feces and on exam you find grossly evident prolapse that is non-reduceable?
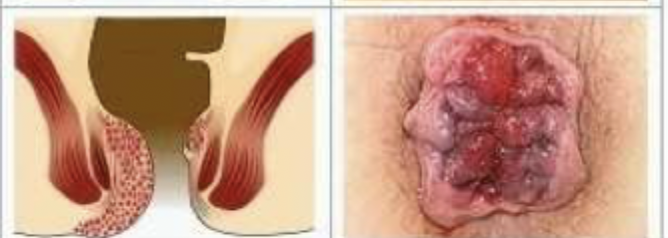
External
Which classification of hemorrhoids originate distal to the dentate line, painful when thrombosed, and is a common source of rectal pain, itching, and blood of toilet paper?
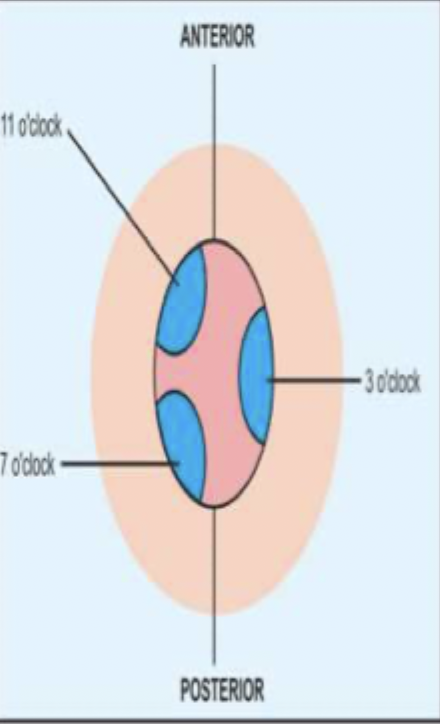
Right anterior (11 o’clock), Right posterior (7 o’clock), left lateral (3 o’clock)
Anatomical location of the hemorrhoids can be described as
Straining with BMs (due to constipation, lack of fiber, lack of hydration), prolonged sitting (think about occupation), Pregnancy, obesity, liver disease (collateral circulation)
Risk factors for hemorrhoids
external thrombosed, internal stage 4
Rectal pain with hemorrhoids is caused by
Warm sitz baths, analgesics, ointment (prep H, tucks, anusol) - most resolve in 2-3 days
57 y/o male presents to the clinic for rectal bleeding. He states that when he wipes, its bright red and he feels some “lumpy stuff” back there. On physical exam you note a bluish, perianal nodule. What is your conservative treatment plan?
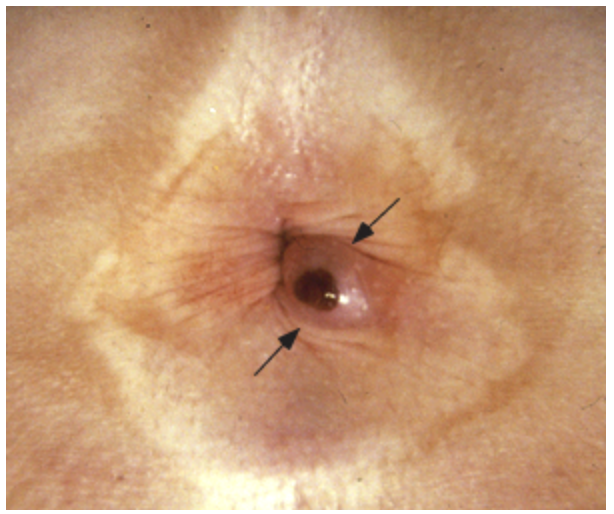
thrombectomy with elliptical incision and a clot removal within 24-48 hrs
57 y/o male presents to the clinic for rectal bleeding. He states that when he wipes, its bright red and he feels some “lumpy stuff” back there. On physical exam you note a erythematous, perianal nodule that is firm and tender to the touch. It’s acute thrombosed so what’s your treatment plan?
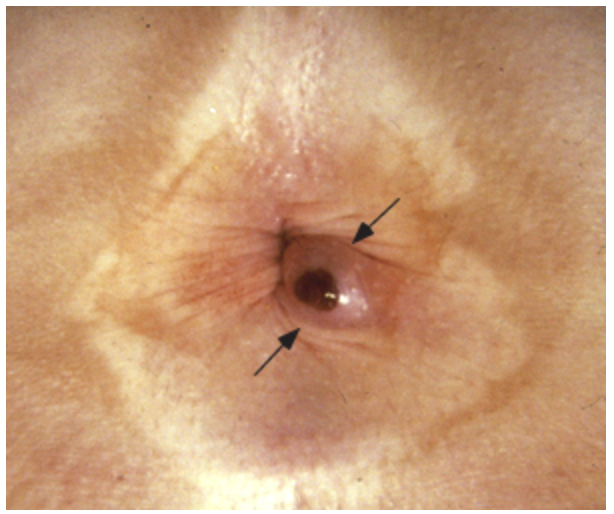
Rubber band ligation (preferred), Injection sclerotherapy, electrocautery
36 y/o pregnant female presents to the clinic for rectal bleeding that has been going on the last few months. She also reports that its been itchy. During the DRE, when the patient bears down you note a hemorrhoid that passes the dentate line and is only reducible with manual pressure. What is your treatment plan - its recurrent?
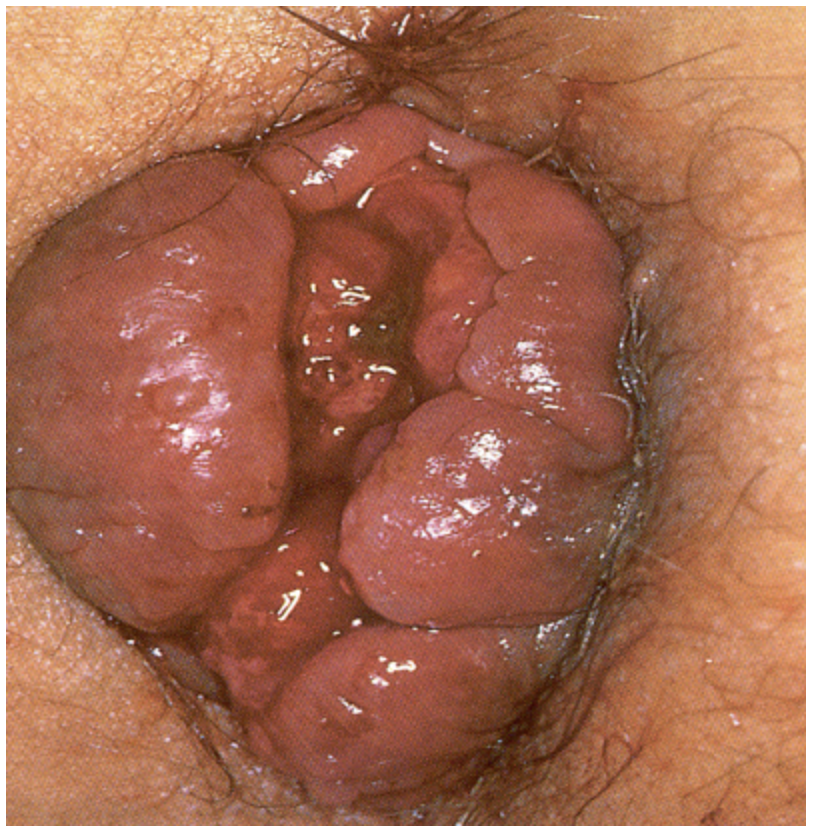
Increase fiber and fluid intake, limit straining or lingering on the toilet
36 y/o pregnant female presents to the clinic for painless rectal bleeding. She also reports that its been itchy. During the DRE, when the patient bears down you note a hemorrhoid prolapses but then goes back in. What is your conservative treatment plan?
Treat with Prep H, tucks, Anusol → ligate later
36 y/o pregnant female presents to the clinic for rectal pain She also reports fecal soilage. During the DRE, you note a non-reducable mass with mucosal atrophy. What is your conservative treatment plan?
Surgical hemorrhoidectomy (note: pain can continue for up to 2-4 weeks post op and has higher remission rates when compared to band ligation)
36 y/o pregnant female presents to the clinic for painful rectal bleeding for the last few months. She also reports fecal soilage. During the DRE, you note a bloody non-reducible mass with mucosal atrophy. What is your treatment plan?
LGIB from other sources, anal fissure, IBD (UC or CD), colitis, rectal ulcer/chancre, rectal abscess/fistula, cancer
DDX for hemorrhoids
Anal fissure
A linear/triangular tear or ulcer around 5 mm in length due to trauma at the anal canal
Constipation (Most common), diarrhea, vaginal delivery, anal sex
Risk factors for anal fissures
usually midline (12 or 6 o’clock) if not that’s a bad sign
Most common sites of anal fissures
Fiber supplements, sitz baths, topical anesthetics (Lidocaine jelly - do not use alone), Stool softeners
24 y/o male patient to the clinic for a severe, sharp pain in the rectal area that started about a week ago. He also reports blood streaking in the stool and that pain increases on defecation. On physical exam you note cracks in the epithelium of the sphincter. What is your conservative treatment?
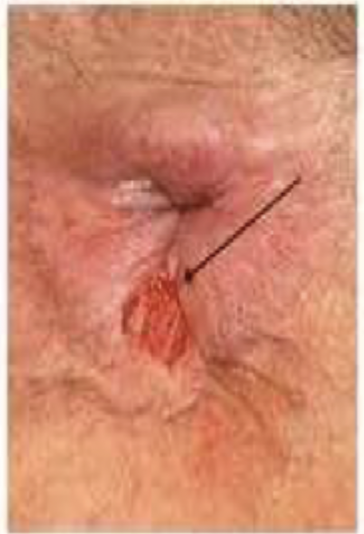
Topical Nitro 0.2-0.4% or diltiazem, Botox injection (if high surgery risk), Internal lateral sphincterotomy (Gold standard but last resort - heals 95% of patients in 3 weeks; only for peeps with low risk of incontinence)
24 y/o male patient to the clinic for a severe, sharp pain in the rectal area that started 10 weeks ago. He states that he’s tried stool softeners and sitz baths but nothing is working. He also reports blood in the stool and that pain increases on defecation. On physical exam you note cracks in the epithelium of the sphincter and external skin tags (sentinel piles). What is your treatment?

LGIB from other sources, hemorrhoid, IBD (UC/CD), colitis, infectious ulcer/chancre, rectal abscess/fistula, cancer
DDX for anal fissures
Anorectal abscess
An abcess that usually originates from an infected anal crypt gland (~50% will become chronic fistula)
Diarrhea/constipation, trauma, hard stool, superficial skin infection, CD, fissures, fistula, DM, poor hygiene
Risk factors for anorectal abscess
CBC (elevated WBCs), CT scan w/contrast (we don’t go in blind), Go ahead and call the surgeon in
35 y/o male presents to the ER for severe constant pain that leaves him unable to sit down. He also reports muscle aches. Vitals are stable with the exception of a temp 102. On a physical exam erythematous area induration around the anus with fluctuance on DRE. What do you want to do besides go home?
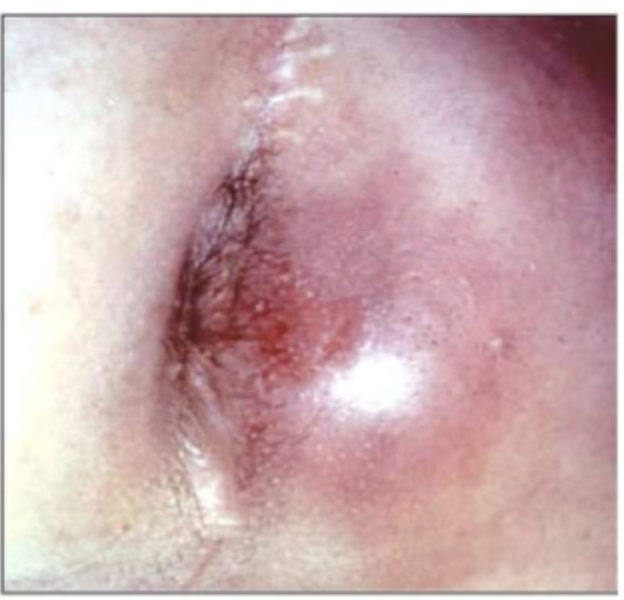
Spontaneously drain and heal, Spontaneously drain and form a permanent fistula, remain undrain and progress to sepsis
Possible outcomes of anorectal abscesses
sphincter injury, necrotizing injury, sepsis/death
Worsening progression of anorectal abscesses?
Surgical drainage with culture, Start antibiotics Augmentin/Cipro + Metro
35 y/o male presents to the ER for severe constant pain that leaves him unable to sit down. He also reports muscle aches. Vitals are stable with the exception of a temp 102. On a physical exam erythematous area induration around the anus with fluctuance on DRE. Labs reveal an elevated white count. OMG you’re the surgeon now, what’s your game plan?
regular diet, fiber supplements and stool softener, sitz bath, follow up in 2-4 weeks
35 y/o male presents to the ER for severe constant pain that leaves him unable to sit down. He also reports muscle aches. Vitals are stable with the exception of a temp 102. On a physical exam erythematous area induration around the anus with fluctuance on DRE. Labs reveal an elevated white count. OMG you’re the surgeon now, what’s your post-op game plan?
Reoccurrence of infection/abscess, incontinence (iatrogenic), fistula
Complications of anorectal abscess
Delay in diagnosis, virulence of pathogen, metastatic infection, previous abscess
Necrotizing anorectal infection risk factors
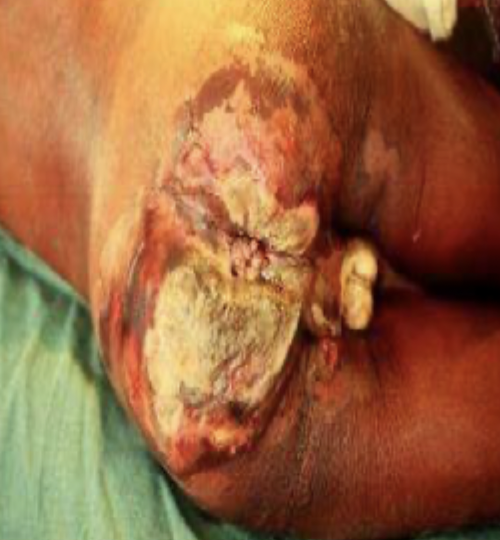
anal fissure, anal fistula, hemorrhoids, buttock skin abscess, pilonidal abscess
DDX for anorectal abscess
Anorectal fistula
A persistent epithelialized track that connects an abscess with the perirectal skin on the outside skin of the buttocks
Males, mean age is 40, anal abscess (most common), lymphogranuloma venereum, CD, proctitis, rectal tuberculosis, retained rectal foreign bodies, anorectal or colon cancers
Anorectal Fistula Risk Factors
Anoscopy or sigmoidoscopy (avoid creating a false track, may need anesthesia) Colonoscopy and barium enema (IBD or recurrent), CT/MRI w/ contrast (helpful with concurrent disease) MRI (if hx of CD),
45 y/o male presents to the ED for intermittent rectal pain that worsens on defecation and activity. On physical exam you note tenderness, erythema, and malodorous drainage. What diagnostics do you want?
eliminate fistula, prevents recurrence, preserve sphincter function
45 y/o male presents to the ED for intermittent rectal pain that worsens on defecation and activity. On physical exam you note tenderness, erythema, and malodorous drainage. Imaging studies reveal air in a fistula tract. What is the goal of surgery?
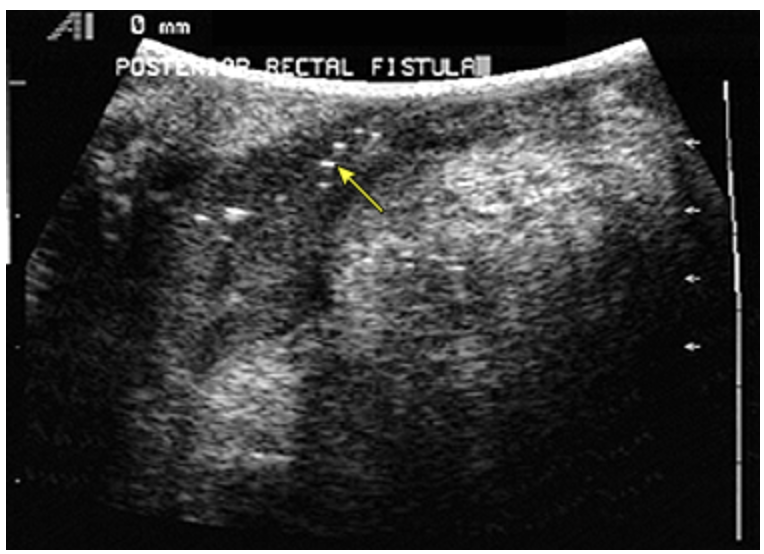
Rectal prolapse
A condition where the rectum protrudes through the anus due to loss of supportive structures (pelvic floor muscles and anal sphincters) - more common in elderly women
Chronic constipation/straining, pelvic floor dysfunction, neurological disorders (spinal cord injuries, dementia, stroke), connective tissue disorders, multiple vaginal deliveries, previous surgeries, cystic fibrosis
Risk factors for rectal prolapse
partial (muscosal), complete (full thickness), internal (intussusception)
Types of rectal prolapse
partial (mucosal)
Which type of rectal prolapse is when only the rectal mucosa protrudes
complete (full-thickness)
Which type of rectal prolapse is when the entire rectal wall protrudes
internal prolapse
Which type of rectal prolapse is when the rectum folds within itself without external protrusion - AKA occult
X-ray defecography, MRI defecography, colonoscopy (r/o malignancy)
76 y/o female presents to the clinic for fecal incontinence. She notes that she has some discomfort when sitting down due to a mass. On exam you note a visible mass protruding from the rectum and decreased anal sphincter tone on DRE. What diagnostics do you want?
High fiber (25-30g/day) stool softeners, pelvic floor exercises, biofeedback therapy, Increases fluids (1-2 L/day)
76 y/o female presents to the clinic for fecal incontinence. She notes that she has some discomfort when sitting down to a mass. On exam you note a visible mass protruding from the rectum and decreased anal sphincter tone on DRE. What is your conservative treatment plan to minimize symptoms before repair?
abdominal or perineal approaches, Laparoscopic and robotic-assisted techniques, Rectopexy, Delorme’s, Altemeier’s, Possible reduction (put patient in lateral recumbent and apply persistent and gentle pressure)
76 y/o female presents to the clinic for fecal incontinence. She notes that she has some discomfort when sitting down to a mass. On exam you note a visible mass protruding from the rectum and decreased anal sphincter tone on DRE. What is your treatment plan?
ulceration, strangulation, fecal incontinence
Complications of rectal prolapse - prognosis is good but recurrence is possible
hemorrhoids, rectal intussusception, solitary rectal ulcer syndrome, pelvic organ prolapse, cancer
DDX of rectal prolapse
Colorectal Cancer
The 3rd leading cause of cancer-related death in the US but is one of the most surgically curable diseases
adenocarcinoma (from an adenomatous or serrated polyp)
Colorectal cancer is usually a type of
Above 45, Fhx of colon cancer or adeonmatous polyps, Diet rich in red meat and fat, EtOH (beer),
Risk factors for colorectal cancer → 75% of patients have NO predisposing risk factors
ASA (does not affect prevention), NSAIDs (in high risk patients and those with hx of polyps), high fiber, fruits, and veggies
What things reduce the risk of colorectal cancer?
Chronic blood loss (hematochezia, anemia), fatigue, dyspnea on exertion, pallor
If colon cancer is on the right side → what is the presentation?
Bowel changes or obstruction, colicky pain, pencil stools
If colon cancer is on the left side → what is the presentation?
fecal urgency, tenesmus, hematochezia
Rectal cancers often presents with
CBC (anemia), CMP (LFTs if liver metastasis), CEA (not for screening, just prognosis), Colonoscopy (#1 draft pick), CT chest and abdomen for staging, MRI/Endorectal U/S (depth of penetration - guides approach)
65 y/o male presents to the clinic for fatigue and weight loss. He also reports that when he does yard work, he can’t do many things without getting out of breath. On physical exam you note hepatomegaly and melena on DRE. What diagnostics do you want?
Surgical resection (1st choice - must be able for regional dissection of 12 lymph nodes) + systemic chemo and radiation
65 y/o male presents to the clinic for fatigue and weight loss. He also reports that when he does yard work, he can’t do many things without getting out of breath. On physical exam you note hepatomegaly and melena on DRE. Let’s say the cancer is localized, what is your treatment plan?
Chemo with 5-fluorouracil (node positive, T3 or greater)
Gameplan for rectal carcinoma BEFORE surgery
Low anterior resection with a colorectal anastomosis; abdominoperineal section with a colostomy
What is the surgical gameplan for rectal carcinoma?
resection
Treatment plan for node-negative colorectal malignancy (70+% 5yr)
resection with chemo
Treatment plan for node-positive colorectal malignancy (67% 5 yr if less than 5 nodes, 33% if more)
surgical resection is possible, Ablative techniques or palliative care if not
Treatment plan for Metastatic disease (5-7% yr)
Labs q3-6 months for 2 years then q6 months for another 5; CT scans annually for 5 years, If colonoscopy before resection → repeat 1 year post; if no colonoscopy before resection → do one 3-6 month post surgery, then 3-5 years if neg; Proctoscopy surveillance annually, New symptoms or CEA increase → CT scan and colonoscopy (PET if nonconclusive)
Follow up plan for colorectal cancer
If average risk 50-75 (stool based test and colonoscopy)
General screening rules for colorectal cancer
annual FOBT, FIT; Q1-3 year FIT-DNA; q5 year flexible sigmoidoscopy w/ or w/o FIT, CT colonography; q10 year colonoscopy
Screening rules for colorectal cancer for people of average risk and over 45
Begin screening at 40; colonoscopy preferred
Screening rules for colorectal cancer for people who have a 1st degree relative with colon cancer diagnosed after 60
Begin screening at 40 or 10 years before family was diagnosed; colonoscopy preferred every 5
Screening rules for colorectal cancer for people who have a 1st degree relative with colon cancer or advanced adenoma diagnosed before 60 or 2 first degrees diagnosed after 60