JC Science - Electricity
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
1
New cards
What are everyday items made of?
Atoms
2
New cards
Proton
Location: nucleus
Charge: +1
Charge: +1
3
New cards
Neutron
Location: nucleus
Charge: 0
Charge: 0
4
New cards
Electron
Location: electron shells
Charge: -1
Charge: -1
5
New cards
Charged atom
An atom is charged if there is a difference in the number of protons + electrons
6
New cards
Positive charge
more protons than electrons
7
New cards
Negative charge
more electrons than protons
8
New cards
Static electricity
A buildup of charges on an object which then stays static (still). This creates an imbalance of charge on the surface
9
New cards
Electric discharge
The rapid transfer of electric charge from one object to another
10
New cards
When does electric discharge happen
When 2 objects with different amounts of charge are brought close to each other
11
New cards
Current electricity
The flow of electric charge through a circuit
12
New cards
Electric current (measurement + instrument + symbol)
Measurement: Ampere (A)
Instrument: Ammeter
Symbol: I
Instrument: Ammeter
Symbol: I
13
New cards
Potential difference (voltage)
The difference between the electric potential energy at two points in a circuit
14
New cards
Voltage (measurement + instrument + symbol)
Measurement: Volts (V)
Instrument: Voltemeter
Symbol: V
Instrument: Voltemeter
Symbol: V
15
New cards
Resistance
The opposition to the flow of electrons in a circuit. Resistance occurs if the flow of electrons is slowed down.
16
New cards
Resistance (measurement + instrument + symbol)
Measurement: Ohms (Ω)
Instrument: Ohmmeter
Symbol: R
Instrument: Ohmmeter
Symbol: R
17
New cards
Lamp
Lights up
18
New cards
Voltmeter
Measures voltage
19
New cards
Ammeter
Measures the current
20
New cards
Cell
Gives electrons energy. Energy source
21
New cards
Battery
Gives electrons energy. Energy source
22
New cards
Switch
Turns off or on the curreny
23
New cards
Resistor
Slows down the current
24
New cards
Variable resistor
Slows down the current (variable amount)
25
New cards
Motor
Makes something move
26
New cards
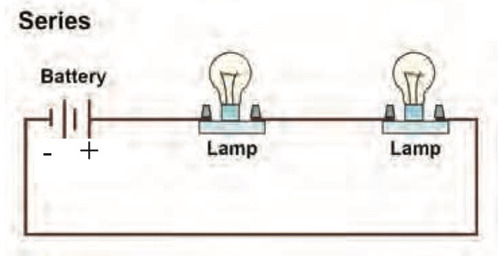
Series circuit
-A series circuit only has one path
-The electrons pass through all components
-Electrons share the energy between components
-The electrons pass through all components
-Electrons share the energy between components
27
New cards
Switches in series circuits
-The switch controls both bulbs
-If one bulb breaks the circuit doesn't work
-If one bulb breaks the circuit doesn't work
28
New cards
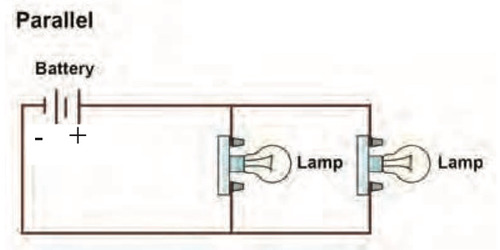
Parallel circuits
-Parallel circuits have multiple paths/loops
-The electrons splits along different paths
-The bulbs get the full amount of energy (it is NOT shared)
-The electrons splits along different paths
-The bulbs get the full amount of energy (it is NOT shared)
29
New cards
Ohm's Law
-The amount of current passing through a material is proportional to the voltage across the material
-As voltage increases, current increases
-As voltage increases, current increases
30
New cards
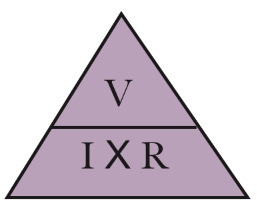
Ohm's law equation
R\= V/I
V\= IxR
I\= V/R
Triangle (V: top, R: right, I: left)
Very Important Rule
V\= IxR
I\= V/R
Triangle (V: top, R: right, I: left)
Very Important Rule
31
New cards
Fuses
A fuse is a safety device. A fuse is a thin piece of wire that melts if there is a fault in the appliance. If too much current flows through it then the wire melts + stops current flowing.
32
New cards
Voltmeter on a circuit
-A voltmeter is attached to the side
-It measures the difference in current before a resistor and after a resistor
-It measures the difference in current before a resistor and after a resistor
33
New cards
Ammeter in a circuit
-Connected in a series
-It records circuits current
-It records circuits current
34
New cards
Ohmmeter in a circuit
-Connected in a series
35
New cards
Electrical power
The rate at which electrical energy is produced or consumed
36
New cards
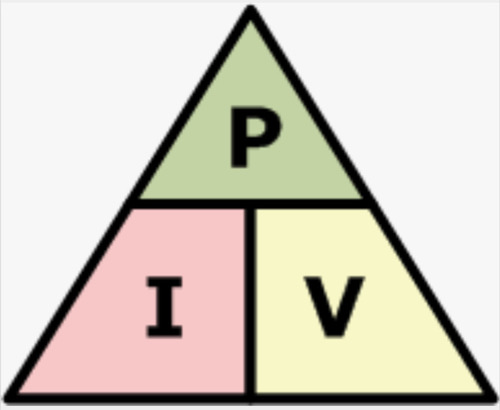
electrical power equation
P\=IxV
I\= P/V
V\=P/I
P: top I: left V: right
I\= P/V
V\=P/I
P: top I: left V: right
37
New cards
What is electrical power measured in
Watts (W)
38
New cards
Power rating
a measurement of how much electrical energy an electrical device consumes for every second it is in use
39
New cards
Bulb
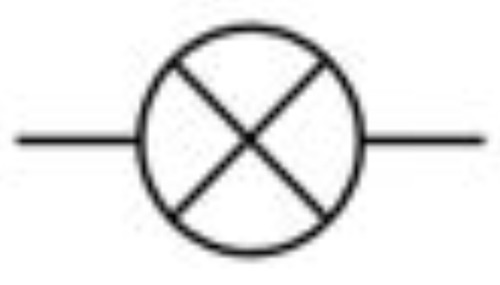
40
New cards
Voltmeter

41
New cards
Ammeter
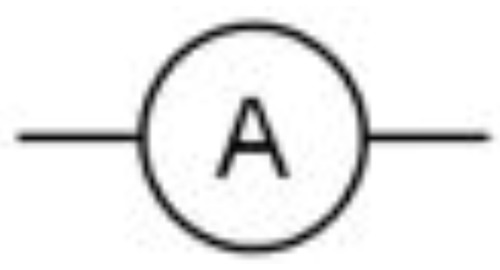
42
New cards
Battery

43
New cards
Resistor

44
New cards
Variable resistor
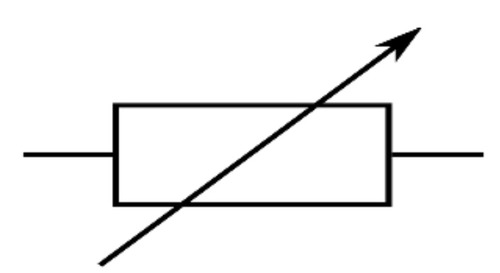
45
New cards
Motor
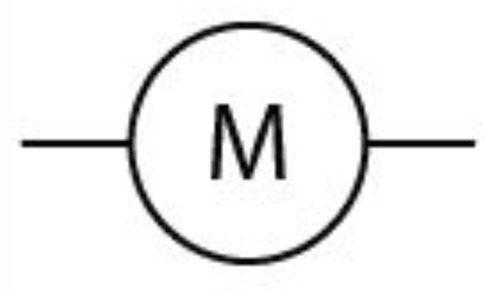
46
New cards
Lamp
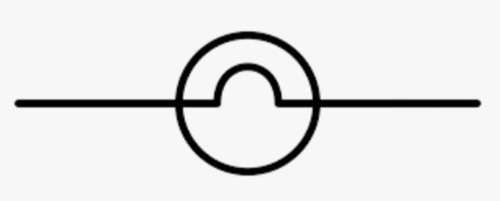
47
New cards
Cell
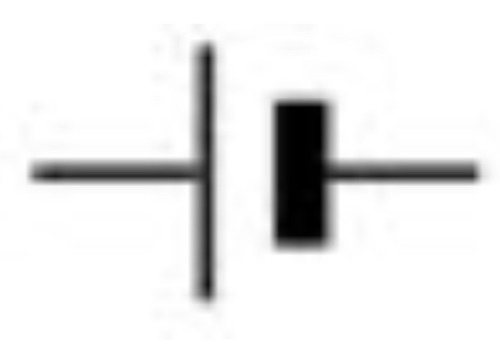
48
New cards
Switch
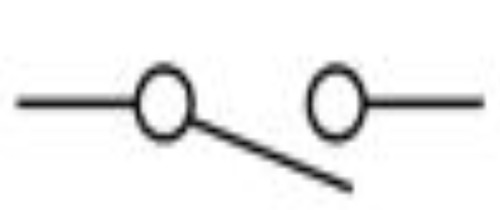
49
New cards
Ohmmeter
Measures resistance
50
New cards
In electronic circuits there is:
Input, Process, Output
(Input usually received through sensors)
(Input usually received through sensors)
51
New cards
Resistors
-Resistors are used to control the flow of current in a circuit
-Many different types of resistors
-Many different types of resistors

52
New cards
What do resistors protect
They protect the more complex electronic components from having too much electric flow in them + damaging them
53
New cards
Light Dependent Resistors (LDR)
-They vary the amount of current that can pass through them depending on the amount of light shining on them
-Little light: high resistance + low current
-Lots of light: low resistance + high current
-Used to detect the amount of fight
-Little light: high resistance + low current
-Lots of light: low resistance + high current
-Used to detect the amount of fight
54
New cards
LDR uses
Automatic night lights, automatic phone screen brightness
55
New cards
Input + output for LDR
Input: Light level
Output: Amount of current allowed to flow through
Output: Amount of current allowed to flow through
56
New cards
Symbol for LDR
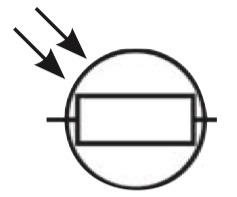
57
New cards
Thermistor
A type of resistor where the resistance depends on the temperature
58
New cards
Thermistor uses
Digital thermometers, turning off a boiling kettle, controlling temperature in a house
59
New cards
Thermistor input + output
Input: Temperature
Output: How much current to flow through
Output: How much current to flow through
60
New cards
Symbol for thermistor
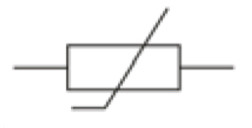
61
New cards
Diode
-Electronic components that only allow current to flow through them in one direction.
-They flow from positive to negative
-They flow from positive to negative
62
New cards
What are diodes used for
To make sure other electric components aren't damaged by the current flowing in the wrong direction
63
New cards
Forward bias
When diodes are connected in a way that allows current to flow
64
New cards
Reverse bias
When diodes are connected in a way that does not allow current to flow through
65
New cards
Symbol for diodes
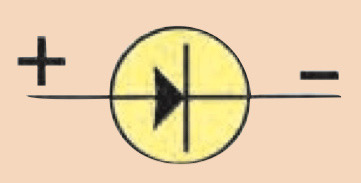
66
New cards
Light Emitting Diode LED
Diodes that light up when current is flowing through them
67
New cards
LEDs + current
-LEDs have to be connected in a forward face bias to work
-If too much current flows through then it could break
-LEDs usually have resistors in the circuit for this reason
-If too much current flows through then it could break
-LEDs usually have resistors in the circuit for this reason
68
New cards
LED legs
2 legs
Longer leg: connects to positive side of battery
Shorter leg: connects to negative side of battery
Longer leg: connects to positive side of battery
Shorter leg: connects to negative side of battery
69
New cards
Benefits of LEDs
-Use less energy than bulbs
-Last for longer
-Doesn't produce as much heat
-Last for longer
-Doesn't produce as much heat
70
New cards
Uses of LEDs
-Television screens
-Car indicators + headlights
-Decorative lights
-Car indicators + headlights
-Decorative lights
71
New cards
Symbol for LED
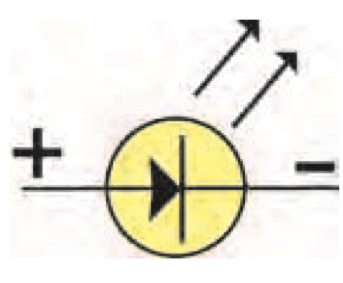
72
New cards
Why is it important to know if an electrical appliance is on or not
So you don't waste energy