Lecture 14 - Animals: Mollusks, Nematodes, and Arthropods
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
General characteristics of all Mollusks?
-Protostome
-Mostly dioecious (except some snails and slugs)
-Live in freshwater, oceans, and on land
-Coelomates
-Soft bodies, most have calcium carbonate (CaCO3) shell
-Complete alimentary canal (GI tract)
-Open circulatory system
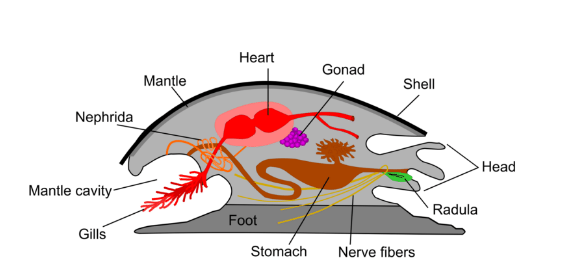
Three main parts of a mollusk anatomy and their uses
Foot: movement
Visceral mass: contains most internal organs
Mantle: tissue covering visceral mass, used for gas exchange and secrets CaCO3 shell in some
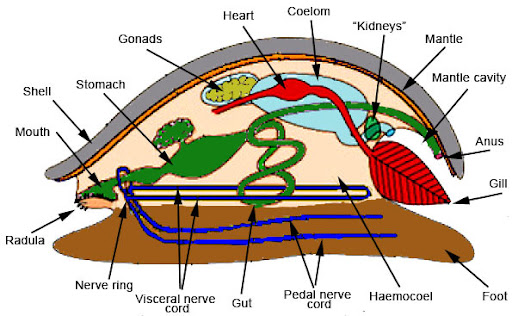
Where is the mantle cavity located and what is it used for?
Below mantle and intestine, its a water filled chamber containing gills, anus, and excretory pores, used to enclosed and protect internal organs
What are radula used for?
Scraping food like algae and bacteria off rocks
Monoecious
Both male and female reproductive organs
Dioecious
Separate sexes
What are the members of the class Polyplacophora known as?
Many plates bearer (chitons)
General features of Polyplacophora (marine mollusks)
-Outer shell made of 8 plates of CaCO3
-No cephalization
-No internal segmentation
-Live in marine and intertidal zones
-Foot to move slowly and attach tightly to rocks
-Radula scrape algae for food
Who are the members of the class Gastropoda
Slugs and snails
General features of Gastopoda (mollusks)
-Terrestrial, freshwater, and marine living
-Sea slugs: marine mollusks with no shell, shell shed during larval stage
-Snails: retain shell, undergo torsion
What does torsion do during snail larval development?
Rotating visceral mass 180 degrees and brings anus to anterior region above head
Protects heads w/ mantle cavity
Who are the members of Class Bivalvia?
Clams
Oysters
Muscles
Scallops
General features of Bivalvia (mollusks)
-Shell divided into 2 halves with hinge
-No head
-No radula
-Mostly sedentary
-Mostly suspension feeders: incurrent siphon captures food, gets caught on gills, wiped off by palps, which secretes mucus to capture food and direct it into mouth
-Respiration: water enters via incurrent siphon, passes over gills for gas exchange, exit via excurrent siphon
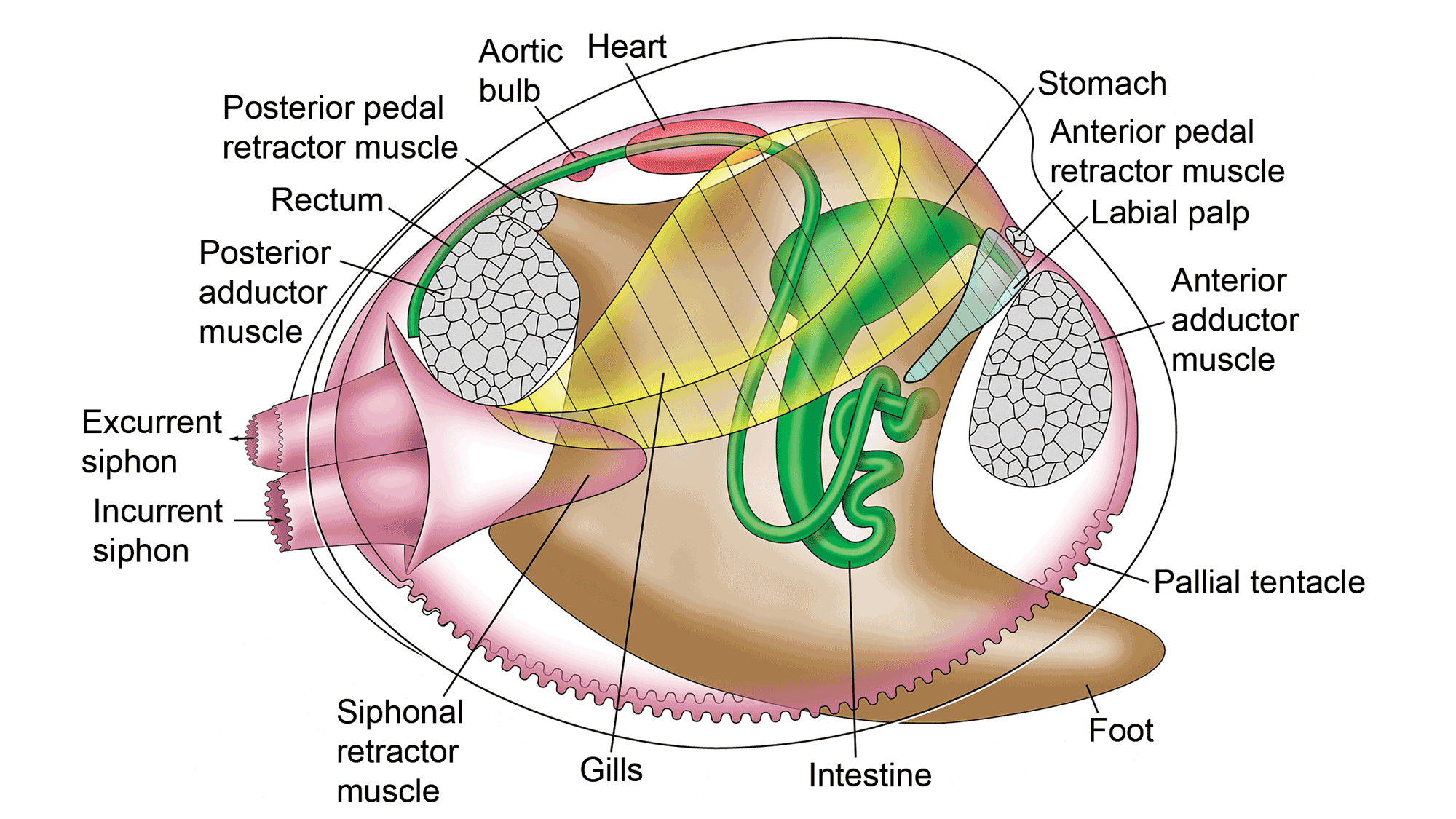
Suspension feeders
Capture and ingestion of food particles suspended in water
Who are the members of class Cephalopoda?
Squid
Cuttlefish
Octopus
Nautilus
General features of Cephalopoda (mollusks)
-Marine predators
-Most have no shell or very reduced and internal
-Closed circulatory system
-well-developed sense organs and has a brain
-parrot-like beak for slicing prey
-many use chromatophores (pigment containing and light reflecting cells) for camoflage
Defining features of Ecdysozoans?
-Bilateral symmetry
-Protostome
-Builds and sheds a cuticle (ecdysis)
Whats a cuticle
tough, flexible outer covering (animal sheds in order to grow)
General characteristics of Nematodes?
-Psudocoelomates
-Mostly dioecious
-Clade ecdysozoan
-Live in moist soils and aquatic environments
-Alimentary canal
-No circulatory system
-Some species are parasitic to plants and animals, while others are free-living
Nematode anatomy
-Unsegmented, cylindrical bodies with tapered ends
-Longitudinal muscles, move by thrashing
-No circulatory system, transport nutrients via fluid in psedocoelom
-Must shed cuticle to grow
Give examples of parasitic Nematodes
Trichinellosis: ingesting undercooked meat (e.g. pork) infected with encysted Trichinella larvae in muscles
Pinworms: spread through fecal-oral routes
Hookworms: not wearing shoes
General characteristics of Arthropods
-Highly reduced coelom
-Most are dioecious
-Found in nearly all habitats
Features of arthropods: Segmentation
Body plan made of repeating segments with specialized functions
3 regions: head, thorax, abdomen
Features of arthropods: Jointed appendages
-Appendages emerge from segments in pairs
-Specialized for walking (legs/wings), feeding (mouthparts), sensory perception (antennae), and defense (pinchers)
Features of arthropods: Chitinous exoskeleton
-Arthropod cuticle
-Exoskeleton: rigid, outer covering that protects and supports
-Layers of chitin and proteins
-Attachment for muscles to move appendages
-May be thick/hard or thin/flexible
-Prevents water loss on land
-Must be shed for organism to grow
Arthropod circulatory systems
Heart pumps hemolymph into sinuses (hemocoel)
-Hemolymph bathes organs directly
-Tubular heart (located dorsally) has pores with valves to uptake hemolymph
-Valves ensure one way flow of hemolymph
What are Malpighian tubes used for?
Collect nitrogenous wastes from hemolymph and released them into the gut
Respiratory system for Arthropods: Gills
-Mostly in aquatic arthropods
-Used for respiration, osmoregulation, and nitrogen removal
Respiratory system for Arthropods: Book lungs
-Spiders and scorpions
-Thin plates stacked like book pages in the abdomen to exchange gases with atmosphere
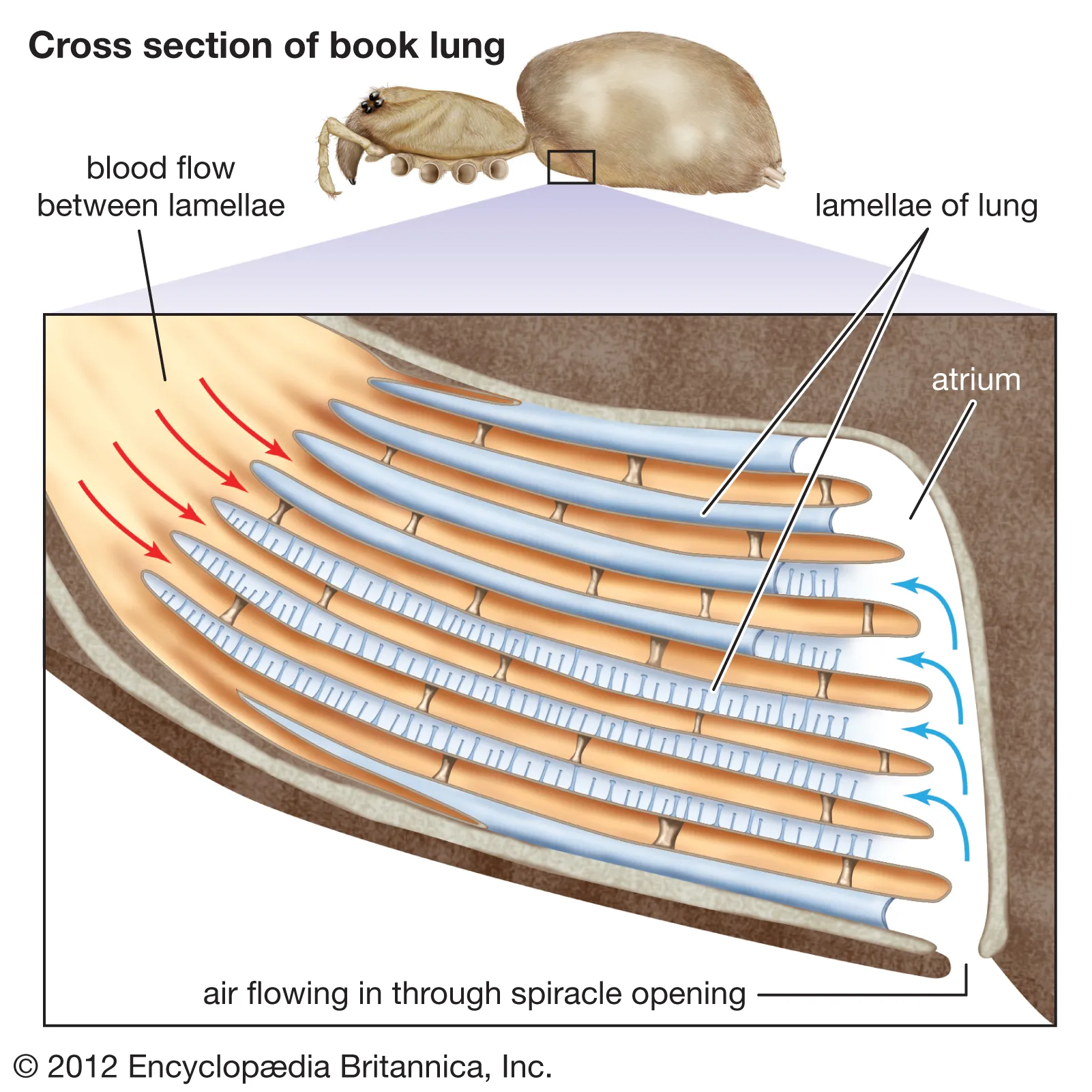
Respiratory system for Arthropods: Tracheal systems
-Insects
-Internal series of air-filled tubes (trachea) that open to the outside at closeable valves (spiracles)
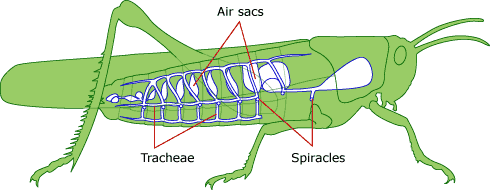
Who are the members of Chelicerates
Sea spiders
Horseshoe crabs
arachnids
General features of Chelicerates (arthropods)
-Chelicerae: claw-like feeding appendages (pincers or fangs)
-No antennae
-Simple eyes with single lens
-Mostly predators, parasites, and scavengers
Main features of Myriapods (arthropods)
-Terrestrial
-1 pair of antennae
-3 pairs of appendages modified as mouthparts including mandibles
Millipedes
-Myriapods
-Slow moving detritivore (feeds on dead materials)
-Trunk segments formed from 2 fused segments
-Trunk segments each have 2 pairs of legs
Centipedes
-Fast moving predators
-Flattened dorsoventrally
-1 pair of legs per trunk segments
-Poison claws to paralyze prey
Who are the Pancrustaceans
Crabs
Lobsters
Shrimps
Barnacles
Pill bugs
Lice
Etc
General features of Crustaceans (arthropoda)
-Marine, freshwater, and terrestrial
-Dioecious
-2 pairs of antennae
-3 or more pairs of appendages are modified as mouthparts
-Have appendages on their post-genital region (tail)
General features of insects
-Hexapod (six-footed)
-Almost all terrestrial habitats, some marine
-Dioecious
-Wings are extensions of the cuticle
-Flight key to dispersal and diversification
Complete metamorphosis
Insect goes through 4 distinct stages
egg→ larva (feeding)→ pupa (sessile and nonfeeding)→ adult
Incomplete metamorphosis
-Young (nymphs) look like adults
-Undergo series of molts to reach adult size
-Gradual changes from egg→ nymph→ adult
Difference between pupa, larva, and nymphs
Pupa: sessile and nonfeeding
Larva: feeding stage (diff from adult)
Nymph: lack wings and reproductive organs, eat the same food as parents