DNA Structure and Function: Part 5
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are the 3 molecular parts of a nucleotide?
5-carbon sugar
5-carbon Phosphate Group
Nitrogen-containing base
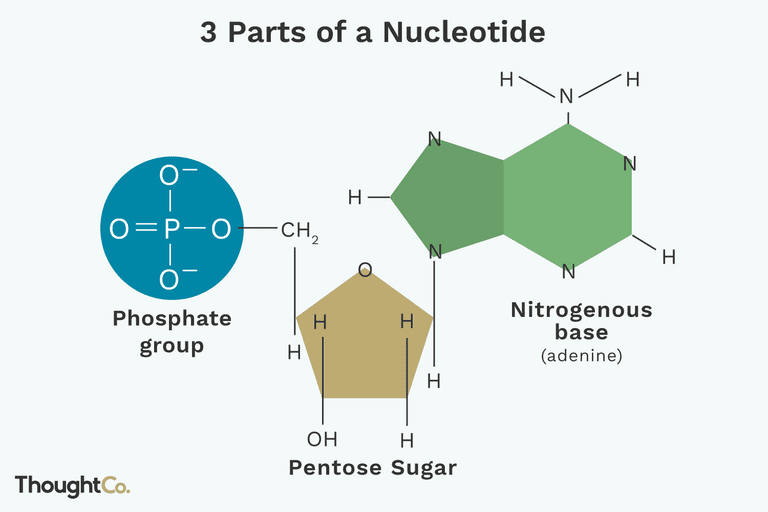
What is Sugar used for in a nucleotide?
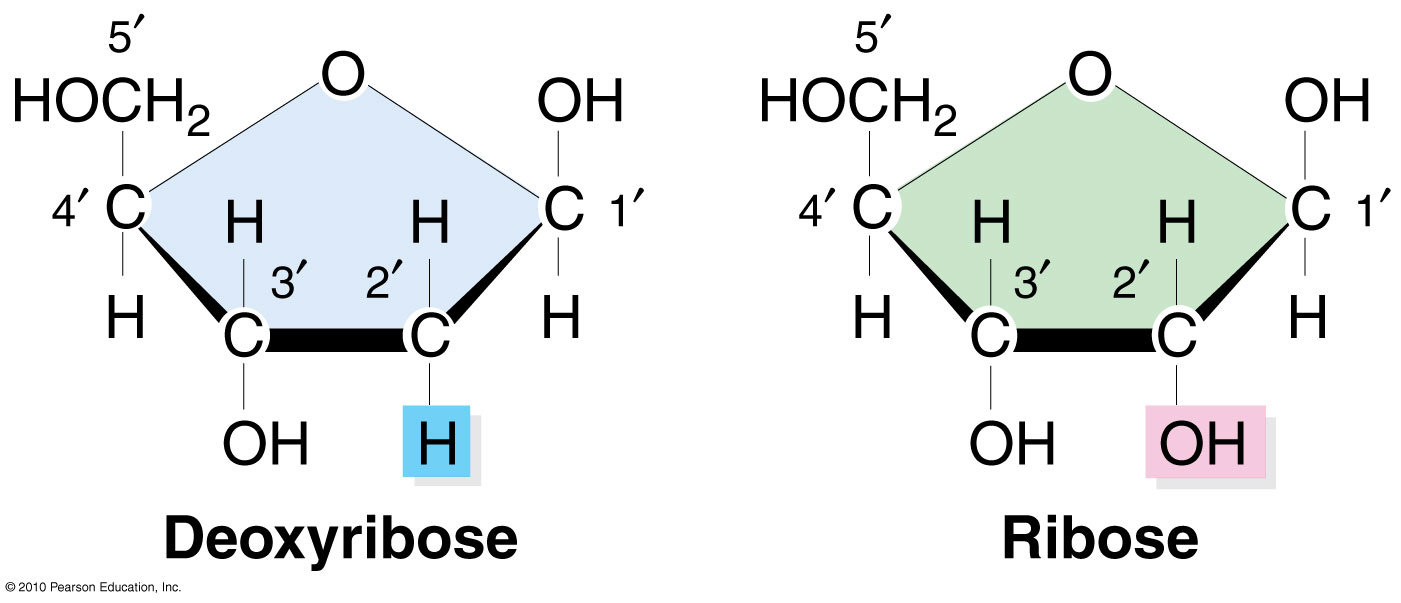
Sugar is either ribose or deoxyribose
Ribose → Has a hydroxyl group on its 2-prime carbon, used to make RNA nucleotides
Deoxyribose → missing the hydroxyl group on its 2-prime carbon, used to make DNA nucleotides
What is the phosphate group used for in a nucleotide?
It is used to link the nucleotides together, forming the backbone of DNA and RNA
What is the Nitrogenous (nitrogen-containing) base used for in a nucleotide?
The nucleotides are the backbone of DNA and RNA. Responsible for the base pairing that holds the double helix of both DNA and RNA together.
What is the definition of the term “strand”?
A single DNA strand
What is the definition of the term “directionality”?
When DNA polymers are made, new nucleotides can only be added
What is the definition of the term “backbone”?
A chain of sugars and phosphates in the strand ( a single DNA strand)
What is the definition of the term “complementarity”?
When the DNA base pairs A attach to T and G attaches to C
In RNA, A attaches to U and G attaches to C
What is the definition of the term “double helix”?
A pair of parallel helixes
What is the definition of the term “antiparallel”?
Parallel but moving or oriented in opposite directions
What is the definition of the term “major groove”?
The larger of the two sizes of gaps between two backbones
What is the definition of the term “minor groove”?
The smaller of the two sizes of gaps between two backbones
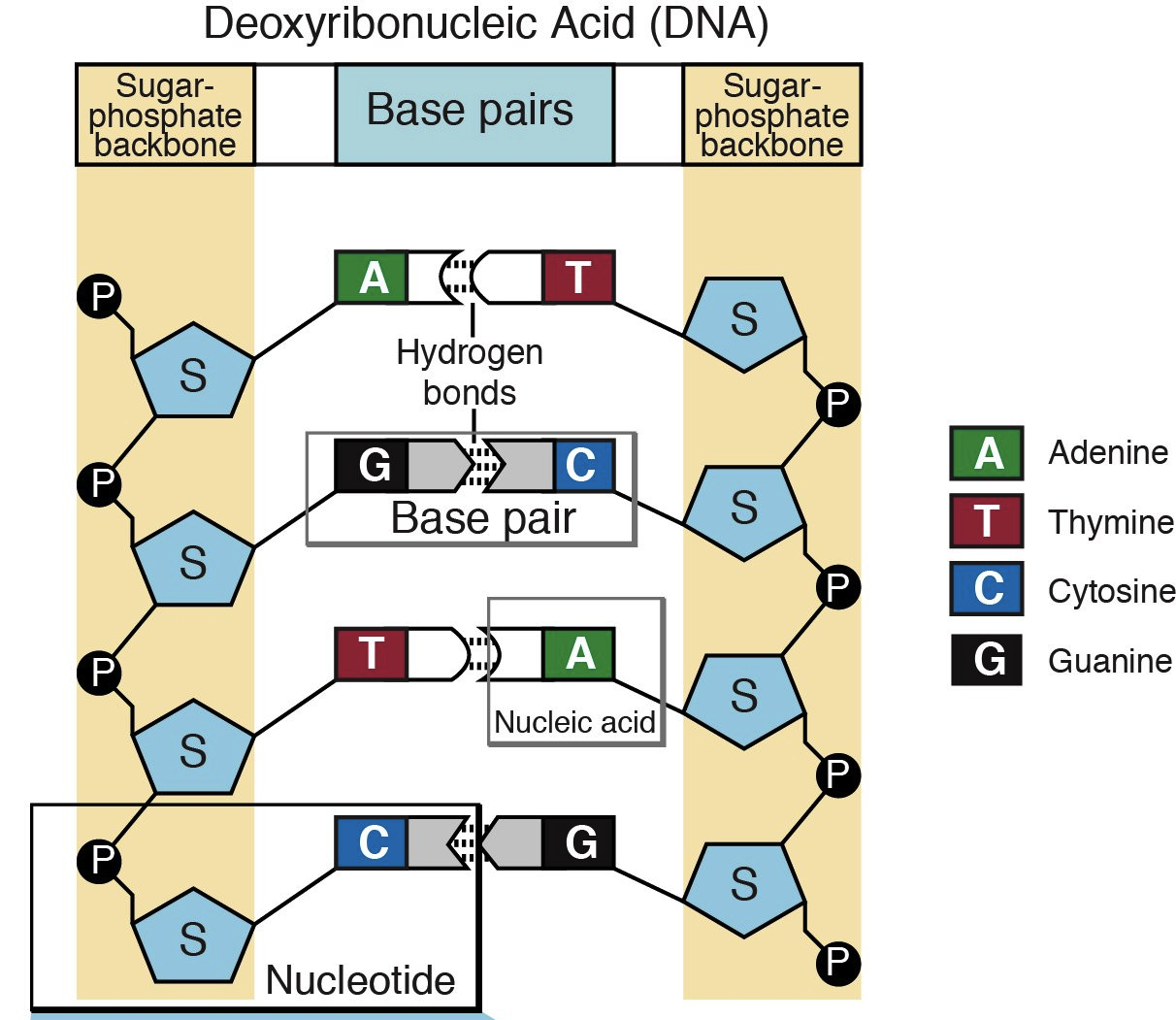
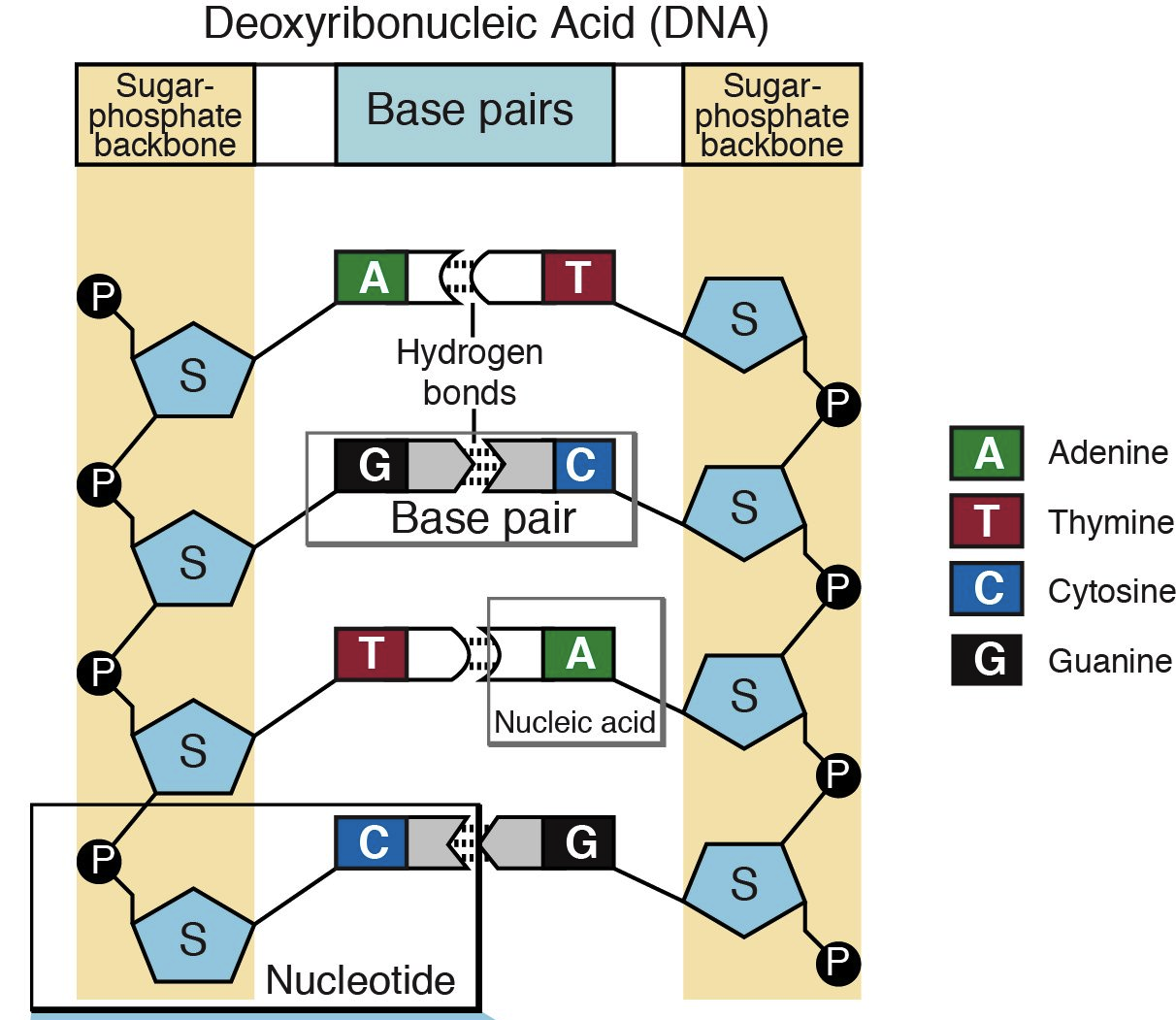
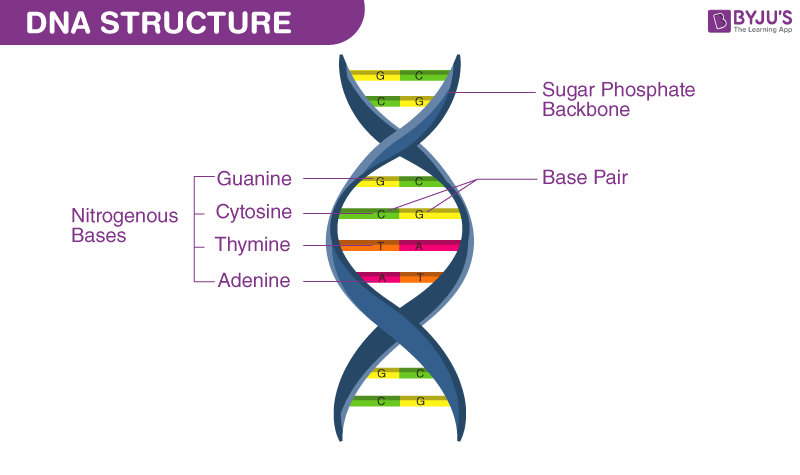
What is the complete structure of a DNA molecule?
Two strands are twisted around each other to form a double helix made up of nucleotides held together by phosphodiester bonds
The base pairs A, T, G, and C run from 5’ to 3’ parallel to each other, linking the double helix together
How are nucleotides used for energy storage?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the main nucleotide in the body that is used for energy storage
ATP has three phosphate bonds, and when one breaks, it releases some of the stored energy within the ATP molecule
ATP becomes ADP when breaking off a phosphate molecule
Which are the nucleotides that are used in DNA?
The nucleotides that are used in DNA are the ones that use deoxyribose instead of sugar.
What are the rules of base pairing?
A always pairs with T
G always pairs with C
In RNA ONLY, Uracil (U) will replace Thymine (T) when pairing with A. There is no thymine found in RNA
What is the major function of DNA?
To store information that is needed to make one or more proteins
What is the definition of “gene”?
Sequences of DNA that contain information to make protein or RNA
What is the definition of “genetic/DNA sequence”?
The order of bases in a DNA strand, read in a straight line from the 5-prime end to the 3-prime end
What is the definition of “gene expression”?
The process of using this genetic information to make RNA and protein
What is the definition of “coding DNA”?
DNA that contains the instructions for building proteins or amino acids
Makes up only 20% of chromosomal DNA
What is the definition of “non-coding DNA”?
DNA that does not code for proteins or amino acids
What is the principle of complementarity?
Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with Thymine
Guanine forms three hydrogen bonds with Cytosine
Why is the foundation of DNA replication the property of complementarity?
Because the base pairs forming bonds with each other is what gives DNA its stable and functional structure
What is the process of replication initiation? (what it is, where it starts, what happens during it)
Occurs simultaneously at multiple places on a chromosome
The sites where replication begins are called “replication origins”
What is a “replication bubble”?
The very first stage of replication
The DNA strands at the bubble are separated and under a microscope, looks like a bubble in the DNA
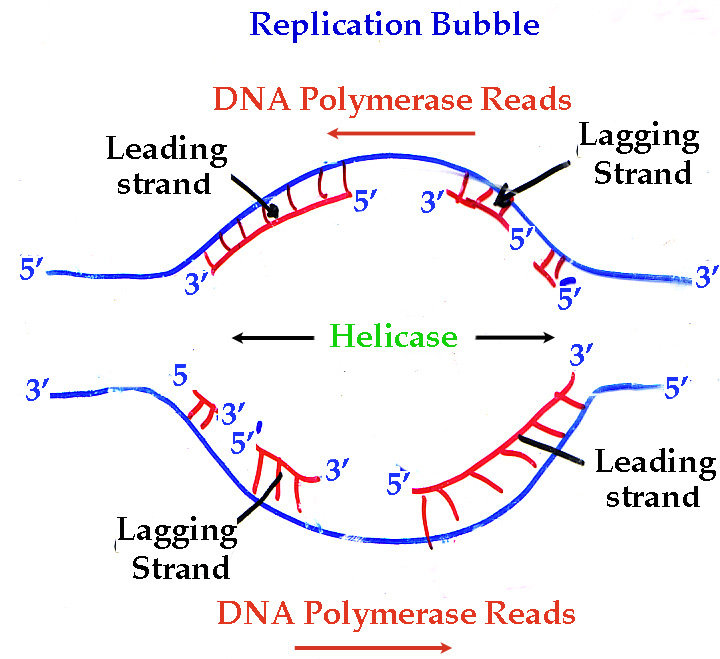
What is a “replication fork”?
The area where replication happens
Each replication bubble has two replication forks, one travelling in each direction
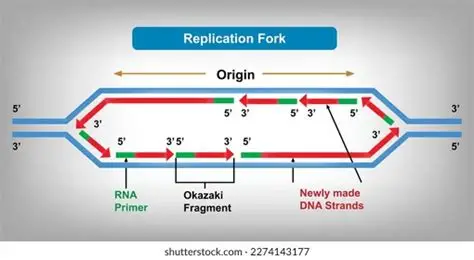
What is the definition of “bidirectional”?
When two things are travelling in opposite directions vs each other
How is DNA synthesized by DNA polymerase?
An enzyme called exonuclease is activated when base pairs are translated incorrectly
Exonuclease removes the wrong base by hydrolyzing (breaks down by chemical reaction with water) the hydrogen bond
Exonuclease will then go tell DNA Polymerase to replace the incorrect base pair
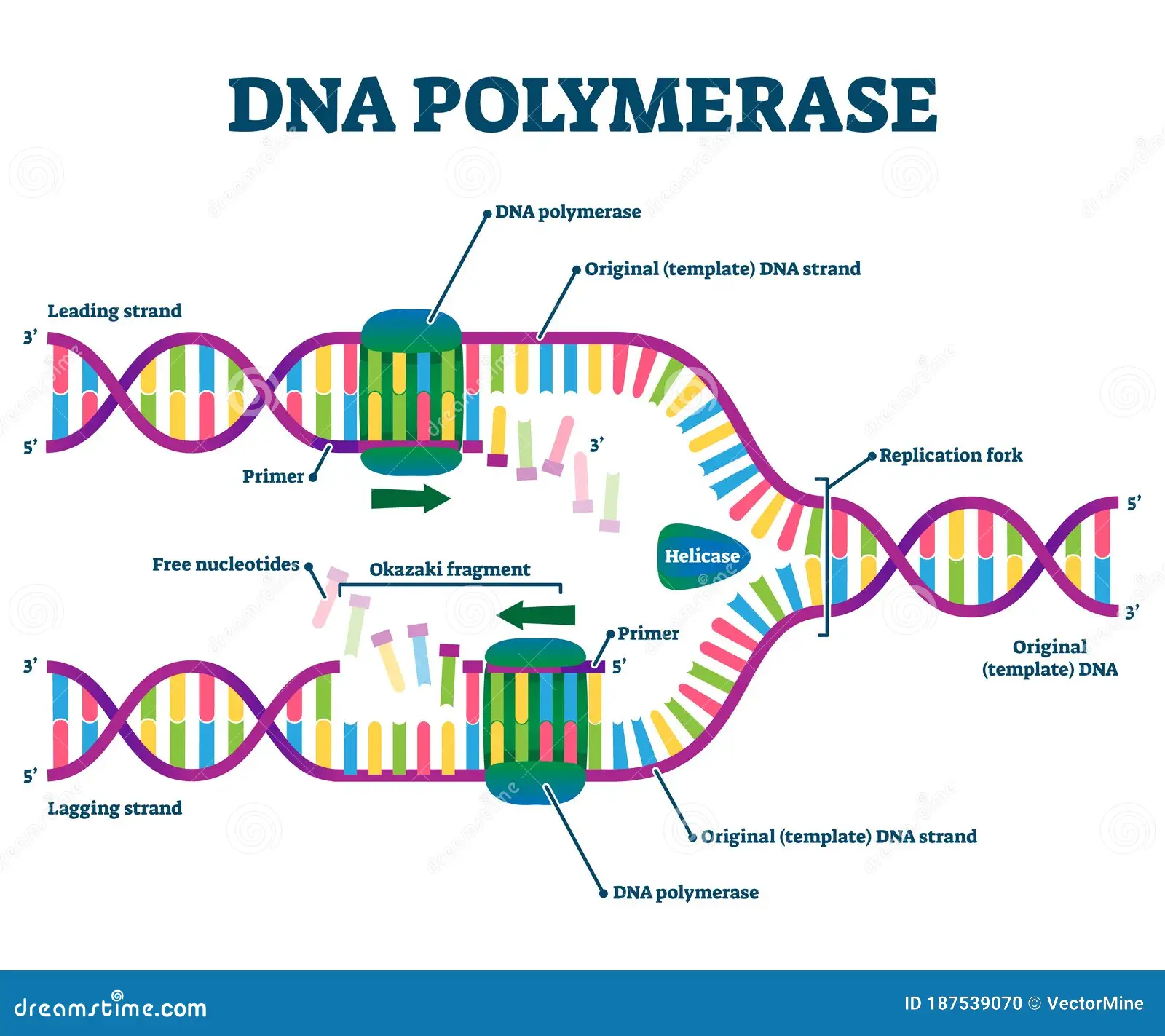
What is proofreading?
The polymerase goes over the replicated DNA to check for any imperfections
Why does DNA polymerase need to proofread?
DNA replication is not 100% accurate, and there may be mistakes that could be catastrophic to the DNA cell if not corrected