Psych-Exam 2 (Multiple choice)
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is based off of what the professor told us is on the exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Sensation (the same for everyone)
The detection of physical energy or objects that are sensed by a sense organ
The five senses and their scientific meaning
Sight (Vision), Hearing (Audition), Smell (Olfaction), Taste (Gustation), Touch (Tactation)
Perception (subjective)
How we interpret or make sense of the things we are sensing.
Weber’s Law
difference threshold is proportionate to the original intensity of the stimulus. (Can change over time)
Selective attention
This happens when one is overwhelmed by unwanted stimuli. The focusing of attention on selected aspects of the environment.
Inattentional blindness
failure to perceive something because you are not paying attention to it.
Synesthesia
Stimulation of one sense evokes a sensation in another (VERY rare)
Condition where someone can see sound, hear colors, or taste colors, etc.
Synesthesia. Can test for this. Nerves may be crossed or abnormally connected.
Absolute threshold
the smallest quantity of physical energy that can be reliably detected by an observer. Can change over time. (50%)
Difference threshold
change in a stimulus that can barely be detected by an organism.
What does the cornea do?
protects the eye and bends light to the lens
What does the lens do?
focuses incoming light
What does the iris do? (colored part of eye)
controls the amount of light going into your eye. expands and contracts the pupil which blocks light.
What is the retina?
Neural tissue that lines the back of the interior eye. This contains rods and cones
What are rods?
receptors that respond to light brightness. They work better in the dark
What are cones?
receptors that respond to color. work better in the light
Fovea
The center of the retina (back of eye). there are only cones here
Dark adaptation
when you gradually see more and more things in the dark when you are in the dark for a longer period of time.
Ganglion cells
types of neurons in the retina that gather info from the rods and cones. They form the optic nerve
Optic nerve
Carries information from the eye to the thalamus to be processed and sent to the brain.
Binocular cues
Cues that require both eyes
Convergence (Binocular cue)
turning your eyes inward (cross eye)
Depth perception (Binocular cues)
messages from our bodies and environments that convey information about depth and distance
Retinal disparity (Binocular Cues)
The slight difference in lateral separation between two objects seen by the left and right eye. (Close one eye and focus on and object and switch)
Monocular cues
Cues which use one eye
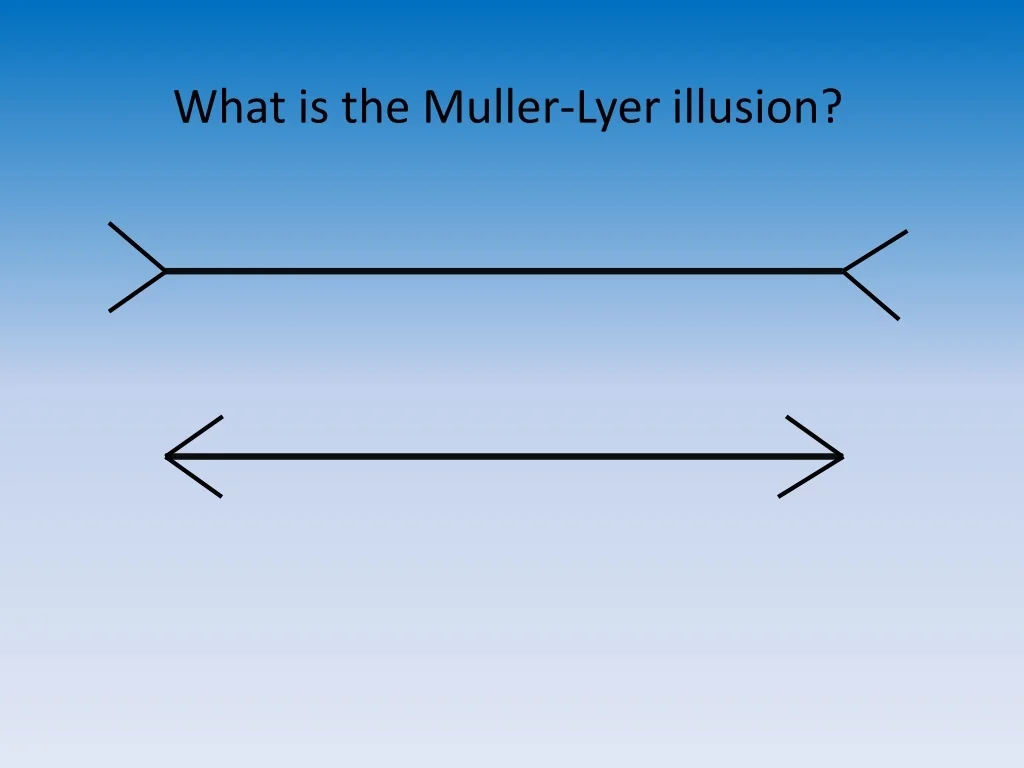
Mueller-Lyer
When two lines of the same length are given opposite arrow end tips, one line appears longer
hair cells in ear are where?
The organ of corti
Cochlea
snail shaped fluid filled organ in the inner ear contains the organ of Corti where the receptors for hearing are located.
What is MMPI
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory. A 500-question test, most reliable.
Jung
believed there is a collective unconscious, shared memory bank inherited from ancestors. It contains things called archetypes
he believed the main goal of personality development is self-realization or individuation
Archetypes
Universal symbols, themes, or images that appear across different cultures and myths.
Internal locus of control
Belief that one’s effort and decisions determine outcomes
External locus of control
Belief that luck, fate, and other people determine outcomes
Unconditional positive regard
Being genuine, open to experience, self-disclosing, and empathic. (Achieve our full potential)
Family studies
Starts with one person who has a trait of interest and examines the presence of the trait in first-degree, second-degree, and more distant relatives
Twin studies
Data from many pairs of twins are collected. Rates of similarity for identical and fraternal pairs are compared.
Adoption study
Compares biologically related people, including twins, who have been reared either separately or apart
The three divisions of twin studies
Heritability (Genetic Influence), Nonshared environment (Circumstances unique to the individual), Shared environment (parenting style).
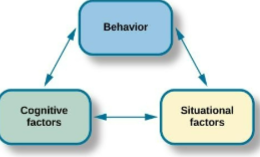
Reciprocal Determination
Sensory deprivation
When one sense is taken away
Spinal Reflexes
A protective reflex that does not need to travel to the brain in order to be used. An example is pulling your hand away from a hot surface to avoid being burned.
Neurogenesis and where does it take place?
Neurogenesis is the process by which new neurons (nerve cells) are formed in the brain. Neurogenesis occurs in only two areas of the CNS. The Olfactory Bulb and the Hippocampus.
Split brain
When the connection of the corpus callosum is damaged or severed it prevents the two halves of the brain from communicating.
Refractory period
After action potential the neuron enters a refractory period in which it cannot fire again.
Re-uptake
Neurotransmitters released into the synapse are reabsorbed back into the presynaptic neuron (neuron that fired it). This helps to clear out the synapse.
Efferent neuron
(E-Exit) Carries information from the brain to the muscles and glands.
Afferent neuron
(A- Arrive) Carries information from the sensory receptors TO the brain.
Excitatory charge
Increases the likelihood for the next neuron to have an action potential and fire neurotransmitter.
Inhibitory charge
Decreases the likelihood for the next neuron to have an action potential and fire neurotransmitter
Definition for thyroid gland
Affects metabolism
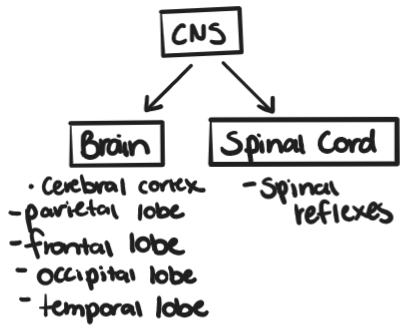
The Central Nervous System definition
CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord. It receives, processes, interprets, and stores sensory information such as:
-Hearing
-Seeing
-Touching
-Smelling
-Tasting
CNS sends messages to cells/organs/parts of the body.
CNS
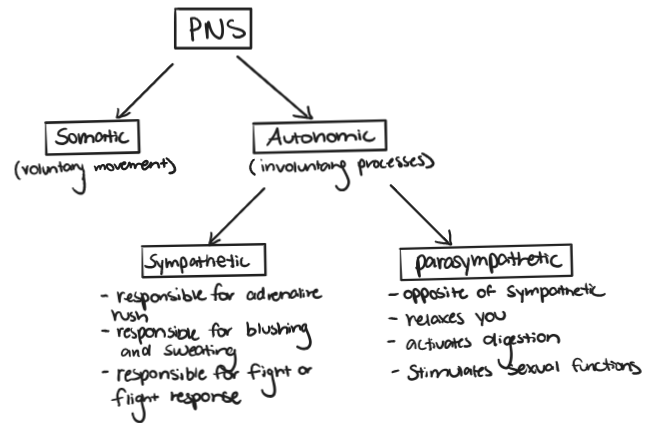
Peripheral Nervous System definition
All of the nervous system EXCEPT the brain and spinal cord. All sensory and motor nerves. Sends information to the spinal cord and then brings messages back to muscles and organs from the brain.
PNS
Rogers ideal self
The person you would like to be. It’s your goals, ambitions, and the standards you set for yourself.
Rogers actual self
Who you actually are in the present moment—your actual thoughts, behaviors, and experiences.