Topic 6 - Atmospheric Pressure and Wind
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is heat index?
a measure of how we feel in the heat on a hot summer day – similar to the wind chill factor
How is heat index calculated?
it is calculated using two factors: humidity and temperature
What is humidity?
The amount of water vapor in the air
What is a monsoon?
seasonal exceptionally heavy rainstorms during the spring and summer
Why do monsoons happen?
Seasonal reversal of wind that brings moist air inland – this causes heavy rain
What is air pressure?
The weight of the air molecules on top of earth
Who was Evangelista Torricelli? What did he do?
Student of Galileo, he discovered the relationship between weather and air pressure
High air pressure =
fine, nice weather
Low air pressure =
foul bad weather
How is air pressure measured?
Air pressure is measured with a barometer as Standard Air Pressure (SAP) at sea level
What is standard air pressure at sea level?
1013.2 millibars (mb)
Hurricanes have what type of air pressure?
Very low air pressure
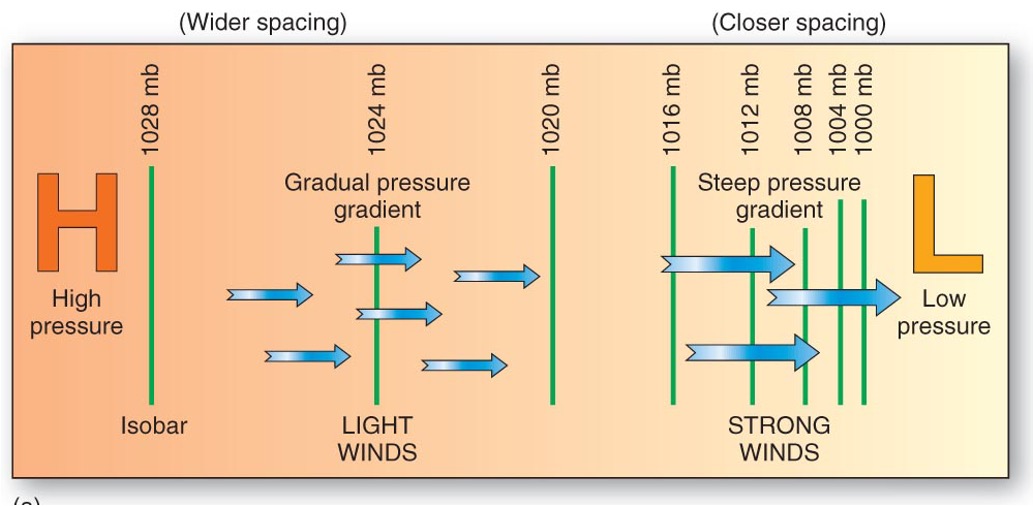
What is the relationship between the spacing of the lines and the wind speed?
if lines are close together that means there is strong wind and if lines are far apart that means that there is light winds
What is the Single-Cell Circulation Model?
The earliest study of global wind circulation was done by George Hadley in 1735
What was the idea of the Single-Cell Circulation Model?
there is one large convection cell in each hemisphere N and S
What is the Three-Cell Circulation Model?
it was developed during the 1920’s, instead of one big cell in each hemisphere there are three cells recognized in each hemisphere
Where are the Sub Polar Lows (polar front) located?
60 degrees N and S
where do the sub polar lows (polar front) form?
form where the westerlies and easterlies meet
what are the sub polar lows (polar front)?
its where cold air meets warm air = clouds and rain
where are the subtropical highs(STH) located?
20 and 30 degrees N and S
What forms at the Subtropical highs(STH)?
great world deserts
what happens at the subtropical highs (STH)?
dry air is sinking here, no cloud formation and windless area
What is the intertropical convergence zone(ITCZ)?
trade winds meet here - at the equator
what happens at the ITCZ?
warm/hot air rises, clouds form = a lot of rain, little to no horizontal wind
What is the term doldrums connected to ?
ITCZ
What happens at the polar highs?
there is cold air and dry air, super cold
What are the polar easterlies ?
meet the westerlies at 60 degrees - this forms the polar front
Where do the polar easterlies blow from?
blow from NE to SW
what is it like at the polar easterlies?
brutally cold and very dry
Where are the prevailing westerlies located?
from 30 to 60 degrees N and S
where do the prevailing westerlies blow from?
blow from SW to NE
what do the prevailing westerlies do?
bring our weather in North America - arrives mostly from the West
Where are the trade winds located?
from about 30 degrees to equator
What are trade winds?
start out dry and warm and arrive at the equator warmer and full of moisture
where do the trade winds blow from?
blow from NE to SW, meet at the equator
Why are the trade winds important?
very important for the trade routes and these winds take you back home